このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Method Article
CRITICとボックスベンケン応答曲面法の組み合わせに基づくザンバを用いた鉄板川の加工技術の最適化
要約
本プロトコルは、CRITICとBox-Behnken応答曲面法を組み合わせたザンバ炒め鉄板川の効率的かつ標準的な無害化処理方法を記載しています。
要約
中国語でTiebangchui(TBC)と呼ばれる トリカブト振り子 ブッシュの乾燥根は、最も有名なチベット薬の一つです。中国北西部で広く使用されているハーブです。しかし、TBCの強い毒性と、その治療用量と毒性用量が類似しているため、中毒の多くの症例が発生しています。したがって、その毒性を低減するための安全で効果的な方法を見つけることは緊急の課題です。チベット医学の古典を検索すると、ザンバで炒めたTBCの加工方法が「青海省のチベット医学の加工仕様書(2010)」に記録されていることがわかります。ただし、特定の処理パラメータはまだ明確ではありません。そこで本研究では、残葉炒めTBCの加工技術の最適化と標準化を目的とする。
まず、TBCのスライス厚、残波量、処理温度、時間の4因子について一因子実験を行った。残葉炒めTBC中のモノエステルおよびジエステルアルカロイド含量を指標として、CRITICとBox-Behnken応答曲面法を組み合わせて、残葉炒めTBCの加工技術を最適化しました。残葉炒めの加工条件は、TBCスライス厚2cm、残葉3倍、加工温度125°C、炒め物60分とした。本研究により,残葉炒めTBCの最適かつ標準的な加工条件が決定され,残葉炒めTBCの安全な臨床利用と工業生産の実験的基礎が得られた。
概要
トリカブト振り子ブッシュとA.フラバムハンドの乾燥した根は、最も有名なチベット薬の1つであり、中国語でTiebangchui(TBC)と呼ばれています1,2。TBCの乾燥した根は、寒さや風を払いのけ、痛みを軽減し、ショックを和らげるのに役立ちます。「中華人民共和国保健部の医薬品基準(チベット医学)」の第1巻に記録され、TBCの乾燥根は関節リウマチ、あざ、その他の風邪病の治療に一般的に使用されていると述べています3。しかし、TBCの臨床治療用量はその毒性用量と同様であり、不適切な使用による中毒または死亡の事件が頻繁に報告されています4。したがって、TBCの毒性を低減し、有効性を維持することは、長年にわたって研究のホットスポットとなっています。
チベット医学では、処理はTBCの毒性を軽減するための最も効果的な方法の1つです。「青海省のチベット医学の加工仕様(2010)」によると、元のハーブ(TBC)を鉄鍋に入れ、ザンバが黄色くなるまでザンバと一緒に炒めた後、ザンバを取り除き、ハーブを空気中で乾燥させます5,6。しかし、特定のプロセスパラメータは文書化されていないため、残葉炒めTBCの加工技術と品質を管理することは困難です。CRITIC法は、ファジー化や主観性を回避し、重み付け7の客観性を高めることができる客観的重み付け法です。Box-Behnken応答曲面法は、多項式フィッティング8を介して各因子間の相互作用を直接反映できます。Box−ベンケン応答曲面とCRITIC法との組み合わせは、最適化された処理プロトコル9、10を獲得するための処理技術を最適化するために一般的に使用される。本論文では、モノエステルジテルペノイドアルカロイド(MDA)(ベンゾイルアコニチン)と2つのジエステルジテルペノイドアルカロイド(DDA)(アコニチン、3-デオキシアコニチン)を評価指標として使用しました。CRITICとBox-Behnken応答曲面法を組み合わせることで、残葉炒めTBCの加工技術を最適化し、臨床的に安全に使用できる標準的な加工法を確立しました。
プロトコル
残葉炒めTBC処理法は、CRITICとボックスベンケン応答曲面法を組み合わせて最適化および標準化されました。ベンゾイルアコニチン、アコニチン、および3-デオキシアコニチンをこの手順中の評価指標として使用しました。
1. サンプル溶液の調製
- 標準物質原液を調製する。電子分析天びんで9.94 mgのベンゾイルアコニチン、8.49 mgのアコニチン、および6.25 mgの3-デオキシアコニチン(材料表)を正確に計量し、10 mLメスフラスコに入れます。次に、0.05%塩酸メタノール溶液を加えて固形分を溶解し、容量を10mLにします。最後に、混合物をよく振って、0.9940 mg / mLベンゾイルアコニチン、0.8490 mg / mLアコニチン、および0.6250 mg / mLの3-デオキシアコニチンの標準物質ストック溶液を取得します。
注意: 塩酸は腐食性の高い物質です11.手袋、白衣、ゴーグル、ヒュームフードなどの適切な保護具を使用してください。 - 試験サンプル溶液を調製する。
- 残葉炒めたTBC粉末2gを円錐フラスコに入れて炒めます。
- TBC30g(2cm)と残波90gの重さを量り、予熱した炒め機に入れて残波炒め物を作ります。炒め物の時間と温度をそれぞれ40分と140°Cに設定します。処理を完了するようにマシンを設定します。
- 高速粉砕機を使用して、残葉炒めたTBCを50メッシュ(0.355 mm)のふるいを通過できる粉末サンプルに別々に粉砕します。
- 以前の研究に基づいて、3 mLのアンモニア溶液と50 mLのイソプロピルアルコールと酢酸エチルの混合溶液(1:1 v / vの比率)を上記の円錐形フラスコに追加します12,13。
注意: アンモニア溶液を調製するには、40 mLの濃アンモニア溶液を100 mLメスフラスコに加え、精製水で測定ラインに充填します。濃アンモニア溶液は臭いが強いため、適切な保護対策を講じてください。 - 上記のサンプルと円錐フラスコの重量を量り、重量を記録します。 超音波処理 30 分 (電圧: 220 V, 周波数: 40 kHz).
注:アコニチンアルカロイドは熱によって容易に分解されます。したがって、超音波抽出の温度は25°C未満でなければなりません。 - 超音波抽出後にサンプルと円錐フラスコを計量します。
- イソプロピルアルコールと酢酸エチルの混合物(1:1 v / vの比率)を追加することで、失われた体重を補います。
- サンプル溶液をろ過します。ろ液25 mLをロータリーエバポレーターを用いて40°Cで蒸発乾固します。
- 残渣に0.05%塩酸メタノール溶液5 mLを加えて溶解し、0.2 μmシリンジフィルターでろ過し、高速液体クロマトグラフィー(HPLC)で分析します。
- 残葉炒めたTBC粉末2gを円錐フラスコに入れて炒めます。
- 0.1988 mg/mL ベンゾイルアコニチン、0.0509 mg/mL アコニチン、および 0.0938 mg/mL 3-デオキシアコニチンを含む混合参照溶液を調製します。
注:各標準物質(ベンゾイルアコニチン0.9940 mg、アコニチン0.2545 mg、および3-デオキシアコニチン0.4690 mg)を、溶解媒体として0.05%塩酸メタノール中の5 mLメスフラスコに溶解します。 - 6.16 gの酢酸アンモニウム(材料表)を2 Lの超純水(移動相A)に溶解して、0.04 M酢酸アンモニウム緩衝液を調製します。アンモニアを使用してpHを8.50に調整します。
注意: アンモニアは危険物です。手袋、白衣、ゴーグル、ヒュームフードなどの適切な保護具を使用してください。 - 2 Lの超高純度100%アセトニトリル(移動相B)をろ過し、脱気します。
注意: アセトニトリルは危険物です13.手袋、白衣、ゴーグル、ヒュームフードなどの適切な保護具を使用してください。
2. クロマトグラフィー条件
- 前処理したサンプル溶液10 μLをバイナリーポンプを備えたHPLCシステムに注入します。MDA および DDA 分離には、移動相 A および B を備えた ODS-3 カラム (5 μm x 4.6 mm x 250 mm、30 °Cで動作) を使用する HPLC システムを使用します。技術的な複製のために各サンプルを3回注入します。
- ODS-3カラムの 表1 に示すようにメソッドをプログラムします。 流速 を 1.0mL/min 、 検出波長 を 235nmとしてください。
- すべてのターゲット化合物のピーク面積を記録します。
注:機器の詳細は、 材料表に記載されています。
3.システム適応性テスト
注意: ステップ2〜3.1を実行するためのクロマトグラフィー条件については、セクション3.5を参照してください。
- 濃度とピーク面積の線形関係を調べます。
- ベンゾイルアコニチン溶液のさまざまな濃度(19.88、39.76、59.64、159.04、198.80、および497.00 μg / mL)を準備します。
- アコニチン溶液のさまざまな濃度(8.49、16.98、25.47、33.96、50.94、および169.80 μg / mL)を準備します。
- 3-デオキシアコニチン溶液のさまざまな濃度(1.875、12.50、37.50、62.50、93.75、および125.00 μg/mL)を調製します。
- 上記の基準溶液を低質量濃度から高質量濃度まで注入し、ピーク面積を記録します。
- ピーク面積に対する基準溶液濃度(μg/L)のプロットから3つの線形回帰式を求めます。
注意: ベンゾイルアコニチン、アコニチン、および3-デオキシアコニチンの濃度がこの標準曲線の線形範囲内にあることを確認してください。
- 10 μLのサンプル溶液をHPLCシステムに6回繰り返し注入して精密試験を行い、セクション2で説明したのと同じHPLC条件下でサンプルを実行します。ベンゾイルアコニチン、アコニチン、および3-デオキシアコニチンのピーク領域を記録します。
- 調製した試料溶液を10 μL注入して安定性試験実験を行い、0時間、2時間、4時間、8時間、12時間、24時間後のピーク面積を決定します。
注:ピーク面積は、参照されたHPLCシステムによって自動的に記録されます。これらの時点は、関連文献15、16、17に基づいていた。 - 残葉炒めTBCの同じバッチを取り、ステップ1.2の方法に従って6つの試験サンプル溶液を並行して調製することにより、再現性試験を実行します。各サンプル10 μLをHPLCシステムに注入し、セクション2の説明に従ってサンプルを実行します。
注:再現性は、6つのサンプル間の濃度差を比較することによって評価されました。 - 試験液用に残葉炒めTBCの同一バッチを6回に分けて回収実験を行う。次に、各指標成分の基準物質を試験液の6つの部分に~100%添加し、回収率を算出した。これらのサンプル(10 μL)をセクション2で説明したのと同じ条件でHPLCシステムに注入し、式(1)を使用して回収率を計算します。
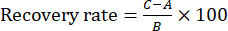 (1)
(1)
注:式(1)において、Aは試験液中の測定対象成分の量、Bは基準物質の添加量、Cは基準物質と残葉炒めTBC試料を含む溶液の測定値である。
4.単一因子実験
- スライスの厚さの比較
- TBCの厚さがそれぞれ0.5、1、2、3、および4 cmである30 gのTBCを含む5つのグループをテスト用に準備します。残膳はTBC(90g)の3倍の量です。
注:TBCは有毒です。手袋、白衣、ゴーグル、ヒュームフードなどの適切な保護具を使用し、切断プロセス中は注意してください。事前実験を通じて、TBCとザンバが完全に接触するためには、3倍の量のザンバが必要であることがわかりました。したがって、正式な実験計画では、スライスの厚さを調べるときに3倍のザンバ量を選択しました。 - 自動炒め機の温度と時間をそれぞれ 140°C と 40分に設定します。
- 自動炒め機が設定温度まで加熱された後、TBC~30gと残波90gを機械に加えます。
- 手順 1.2 に従ってサンプル 溶液を準備します。標準曲線に従って、異なる加工製品におけるMDAとDDAの含有量を計算します(表2)。セクション6のCRITIC法による結果に基づいて包括的なスコアを計算します。
- このようにして、残場の量、および条件を最適化するための処理温度と時間を比較します。
- TBCの厚さがそれぞれ0.5、1、2、3、および4 cmである30 gのTBCを含む5つのグループをテスト用に準備します。残膳はTBC(90g)の3倍の量です。
- 残膳の量の比較
- ザンバの量がそれぞれTBCの1倍、2倍、3倍、4倍、5倍のTBC(2 cm)で、それぞれ30 gのTBC(2 cm)を含む5つのグループのテストを実行します。
- 炒め機の電源を入れて処理します。炒め物の時間と温度を 40分 、 140°Cに設定します。
- 手順 1.2 に従ってサンプル 溶液を準備します。標準曲線に従って、異なる加工製品中のMDAとDDAの含有量を計算します(表2)。セクション6のCRITIC法 による 結果に基づいて包括的なスコアを計算します。
- 処理温度の比較
- それぞれ30 gのTBC(2 cm)と90 gのザンバを使用して、5つのグループのテストを実行します。
- 炒め機の電源を入れて処理します。処理温度を100°C、120°C、140°C、160°C、180°Cに設定します。 処理時間を 40 分に設定します。
注:事前実験により、処理温度が100°C未満の場合、ザンバの黄変の速度は非常に遅く、温度が高すぎる(180°Cを超える)とザンバは燃えやすく、黒くなることがわかりました。そこで、100°Cと180°Cをそれぞれ加工時の温度の最小値と最大値とした。 - 手順 1.2 に従ってサンプル 溶液を準備します。MDA と DDA のピーク領域を記録します。標準曲線に従って、異なる加工製品中のMDAとDDAの含有量を計算します(表2)。セクション6のCRITIC法 による 結果に基づいて包括的なスコアを計算します。
注:実験には160°Cと180°Cの高温が含まれます。 実験室の安全コードに従って、実験中の安全性に注意してください。
- 処理時間の比較
- それぞれ30 gのTBC(2 cm)と90 gのザンバを使用して、5つのグループのテストを実行します。
- 炒め機の電源を入れて処理します。処理時間を 20、40、60、80、および 100 分に設定します。温度を140°Cに設定します。
- 手順 1.2 の説明に従ってサンプル ソリューションを準備します。MDA と DDA のピーク領域を記録します。標準曲線に従って、異なる加工製品のMDAとDDAの品質を計算します(表2)。セクション6のCRITIC法 による 結果に基づいて包括的なスコアを計算します。
5. 応答曲面法(RSM)を用いた残葉炒めTBCの加工技術最適化
- ボックス・ベンケン応答曲面設計
- スライスの厚さ(A、1〜3 cm)、ザンバの量(B、2〜4倍)、処理温度(C、100〜140°C)、および処理時間(D、40〜80分)の範囲を、一因子検定を使用した予備実験(ステップ4.1〜4.4)によって決定します。
注: 4 つの変数のコード値とその水準を 表 3 に示します。各変数の3つの水準は、-1、0、および1としてコード化されました。
- スライスの厚さ(A、1〜3 cm)、ザンバの量(B、2〜4倍)、処理温度(C、100〜140°C)、および処理時間(D、40〜80分)の範囲を、一因子検定を使用した予備実験(ステップ4.1〜4.4)によって決定します。
- ソフトウェアを使用して行列を生成し、応答曲面モデルを解析します。
メモ: ソフトウェアの使用方法のスクリーンショットは、 補足ファイル 1 に示されています。- 24回の実験で構成される3水準4因子のBox-Behnken計画(この研究で行われた)を使用し、5回の反復(実行順序1、9、14、16、および25)を測定して、純粋な誤差平方和を計算します(表4)。総合スコア(Y)を応答として設定します(手順1〜4、 補足ファイル1)。
- ホームページで新規計画(ステップ1、補足ファイル1)をクリックし、計画ページの左パネルで応答曲面 |Box-Behnken および表の 4 つの因子のパラメータを設定します (ステップ 2、補足ファイル 1)。
- [次へ]をクリックし(ステップ2、補足ファイル1)、応答名を設定して、[完了]をクリックします(ステップ3、補足ファイル1)。
- 上記の操作で応答曲面計画を生成します(ステップ4、 補足ファイル1)。
- 24回の実験で構成される3水準4因子のBox-Behnken計画(この研究で行われた)を使用し、5回の反復(実行順序1、9、14、16、および25)を測定して、純粋な誤差平方和を計算します(表4)。総合スコア(Y)を応答として設定します(手順1〜4、 補足ファイル1)。
- 応答曲面用に設計された29のシナリオに基づいて実験を完了します。
- 手順 1.2 に従ってサンプル 溶液を準備します。
- MDA と DDA のピーク領域を記録します。
注:ピーク面積は、参照されたHPLCシステムによって自動的に記録されます。 - さまざまな加工製品のMDAとDDAの品質を計算します。
- ステップ6のCRITICメソッド を使用した 結果に基づいて包括的なスコアを計算します。
メモ: 具体的な方法は、手順 6 で説明します。 - 得られた29回の試行の総合スコアをコンピュータに入力し、参照したソフトウェアを用いて解析する(ステップ5、 補足ファイル1)。
- ソフトウェアを使用して、3Dモデルグラフにプロットされた多項式方程式と応答曲面分析の統計的検証を実行します(手順6〜8、 補足ファイル1)。
- 左側のナビゲーション ウィンドウの [分析] (+) で [Y] をクリックし、[構成] ウィンドウで [分析の開始] をクリックします (手順 6、補足ファイル 1)。
- トップメニューの ANOVA をクリックし、分散分析を表示する結果の表を確認します(ステップ7、 補足ファイル1)。
- トップメニューで、 モデルグラフ をクリックしてから 3D曲面 をクリックして、合成スコアに対する処理パラメータの影響を反映した応答曲面プロットを取得します(ステップ8、 補足ファイル1)。
- 予測最適条件(ステップ9、 補足ファイル1)で応答曲面モデルの検証を行い、処理技術の安定性を検証します。左側の ナビゲーション ペインの [最適化]で、[ 数値 ]をクリックし、トップメニューで[ ソリューション]をクリックします。予測された最適条件を観察します。
6. モデル評価
注: このステップは、各単一因子実験または応答曲面実験が完了した後に実行されます。各実験(スライス厚さの比較など)が完了した後、ステップ1.2およびセクション2に従って、異なるサンプル中のMDAおよびDDAの含有量を測定し、5つのデータセットを取得します。データを 補足表S1に示す。
- インデックスの無次元処理
注: この手順では、測定値 (Xij) を無次元相対値に変換して、各インデックスの値が同じ数量レベルになるようにします。この操作により、異なる単位または桁違い18の指標の包括的な分析と比較が容易になります。例示の目的で、スライス厚さの値は、以下に示す計算に用いた(補足表S1)。- MDAの内容を標準化する(MDAを取得する。MDAはベンゾイルアコニチンを指す)を用いて式(2)とする。
注:インデックス「i」は4つの因子のうちの1つを表し、スライスの厚さは最初に調査される因子です。したがって、i の値は 1 に等しくなります。インデックス「j」は、因子の各水準を表します。したがって、スライスの厚さが第1レベル(0.5cm)の場合、Jは1に等しくなります。スライスの厚さが第5レベル(4cm)の場合、jは5に等しい。厚さ0.5,1,2,3,4 cmのTBC処理中のMDA(Xij)の含有量はそれぞれ0.9693,1.0876,1.3940,1.4185,1.3614 mg/gであった。したがって、x j、maxは 1.4185、xj、min は0.9693です。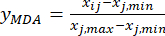 (2)
(2)
こうして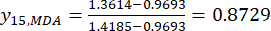
ここで、Xij は、i番目の因子およびj番目のレベルでの実験のMDAの測定された含有量であり、xj、minは、 このグループの実験におけるMDAの最小含有量です。xj、max はこの実験群におけるMDAの最大含有量である。したがって、 i = 1, 2, ..., m、および j = 1, 2, ..., n となります。
注:したがって、MDAの標準化値は、式(2)を使用して0.0000、0.2634、0.9455、1.0000、および0.8729です。 - DDAの総内容を標準化する(yDDAを取得する。DDAは、式(3)の式を用いて、アコニチンおよび3-デオキシアコニチンを指す。
注: i は4つの因子の1つであり、 jは 因子の各水準です。Xij は、i番目の因子およびj番目のレベルでの実験のDDAの測定された含有量です。xj、minは、 このデータのグループ実験におけるDDAの最小含有量です。xj、maxは、 このデータのグループ実験におけるDDAの最大含有量です。このようにして、 i = 1, 2, ..., m、および j = 1, 2, ..., n となります。厚さ0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4 cmのTBC処理中のDDAの含有量(Xij)はそれぞれ0.3492, 0.2692, 0.2962, 0.5354, 0.5124 mg/gであった。したがって、x j、max は0.5354、xj、min は0.2692です。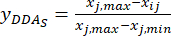 (3)
(3)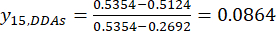
注:標準化された値は、式(3)を使用して0.6995、1.0000、0.8986、0.0000、および0.0864です。
- MDAの内容を標準化する(MDAを取得する。MDAはベンゾイルアコニチンを指す)を用いて式(2)とする。
- 式に従って、対応するコントラスト強度(Si)、競合(δi)、情報(Ci)、およびインデックス重み(Wi)を計算します。(4)〜(7)、それぞれ19、20。
注:i = 1、2、...、m. yijは、i番目の因子およびj番目のレベルでの実験のMDAまたはDDAの内容の標準化データです。- コントラスト強度を推定するには、まず平均MDA値を計算します。
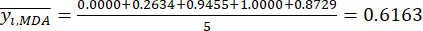
ここで 、はMDAの平均値です。
、はMDAの平均値です。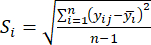 (4)
(4)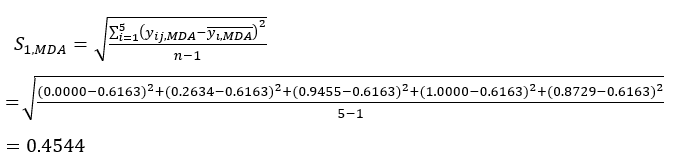
- 競合値を計算するには、まず Excel21 の CORREL 関数を使用してij γ相関係数を推定します。
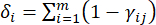 (5)
(5)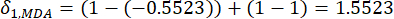
- 情報値は次のように計算します。
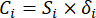 (6)
(6)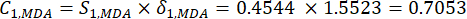
注: 同様に、C1、DDAS = 0.7210 - インデックスの重みは次のように計算します。
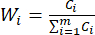 (7)
(7)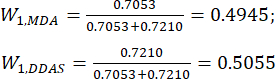
注:したがって、スライスの厚さと比較したMDAとDDAの重み係数は、それぞれ0.4945と0.5055として確立されました。
- コントラスト強度を推定するには、まず平均MDA値を計算します。
- スライスの厚さの包括的なスコアを計算します。
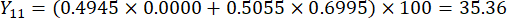
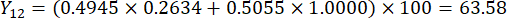
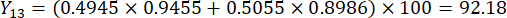
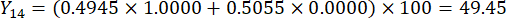
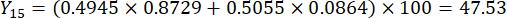
注:Y13 は最大値です。したがって、スライスの厚さの最良のパラメータは3番目のレベル - 2 cmです。
結果
この研究では、使用した溶出勾配は、デバッグを繰り返した後に決定された、残葉炒めTBCの3つのインデックス成分に対して良好な分解能(図1)を示しました。残葉炒めTBCの3つの指標成分は、特定の濃度範囲内で良好な線形関係を示した(表2)。残葉炒めTBCの精度(表5)、安定性(表6)、再現性(表7)、サンプル回収率(表8)は、い...
ディスカッション
TBCは、風邪をほぐし、痛みを和らげる効果がある重要なチベット薬です。それは何千年もの間中国で外傷性損傷とリウマチ性関節痛を治療するために主に使用されてきました24,25,26。ジテルペノイドアルカロイドは、TBC27,28,29の有効成分と毒性成分の両?...
開示事項
著者は、開示すべき利益相反はありません。
謝辞
この研究は、中国国家自然科学基金会(第82130113号)、中国ポスドク科学基金会(第2021MD703800号)、四川省科学技術部青年科学財団(第2022NSFSC1449号)、成都中医薬大学の「興林奨学生」研究促進プログラム(第2022NSFSC1449号)の財政的支援を受けました。BSH2021009)。
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 3-Deoxyaconitine | Chengdu Desite Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | DST221109-033 | |
| Aconitine | Chengdu Desite Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | DSTDW000602 | |
| Ammonium acetate | Tianjin Kermel Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd | Chromatographic grade | |
| Benzoylaconitine | Chengdu Desite Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | DSTDB005502 | |
| Design-Expert software | Stat-Ease, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA | version 13.0 | |
| Electronic analytical balance | Shanghai Liangping Instruments Co., Ltd. | FA1004 | |
| High performance liquid chromatography | SHIMADZU Co., Ltd. | LC-20A | |
| High-speed smashing machine | Beijing Zhongxing Weiye Instrument Co., Ltd. | FW-100 | |
| Millipore filter | Tianjin Jinteng Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd | φ13 0.22 Nylon66 | |
| stir-Fry machine | Changzhou Maisi Machinery Co., Ltd | Type 5 | |
| Tiebangchui | Gannan Baicao Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd | 20211012 | |
| Ultra pure water systemic | RephiLe Bioscience, Ltd. | Genie G | |
| Ultrasonic cleansing machine | Ningbo Xinyi Ultrasonic Equipment Co., Ltd | SB2200 | |
| Zanba | 27 Chuanzang Road, Ganzi County | - |
参考文献
- Li, C. Y., et al. Aconitum pendulum and Aconitum flavum: A narrative review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, bioactivities and processing methods. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 292, 115216 (2022).
- Wang, J., Meng, X. H., Chai, T., Yang, J. L., Shi, Y. P. Diterpenoid alkaloids and one lignan from the roots of Aconitum pendulum Busch. Natural Products and Bioprospecting. 9 (6), 419-423 (2019).
- Yu, L., et al. Traditional Tibetan medicine: therapeutic potential in rheumatoid arthritis. Frontiers In Pharmacology. 13, 938915 (2022).
- Zhao, R., et al. One case of ventricular arrhythmia caused by poisoning of traditional Chinese medicine Aconitum pendulum Busch. Journal of People's Military Medical. 61 (4), 346-348 (2018).
- Qinghai Medical Products Administration. Processing specification of Tibetan medicine of Qinghai province. Qinghai Nationalities Publishing House. , 96-97 (2010).
- Li, J., et al. Comparison of three objective weighting methods to optimize the extraction process of Jianwei Chupi granules. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University. 38 (6), 91-97 (2022).
- Feng, Z. G., et al. Processing methods and the underlying detoxification mechanisms for toxic medicinal materials used by ethnic minorities in China: A review. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 305, 116126 (2023).
- Hsu, Y. T., Su, C. S. Application of Box-Behnken design to investigate the effect of process parameters on the microparticle production of ethenzamide through the rapid expansion of the supercritical solutions process. Pharmaceutics. 12 (1), 42 (2020).
- Cheng, F., et al. Optimization of the baked drying technology of Cinnamomi Ramulus based on CRITIC combined with box-behnken response surface method. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials. 2022 (8), 1838-1842 (2022).
- Huang, X., et al. Optimization of microwave processing technology for carbonized Gardenia jasminoides by Box-Behnken response surface methodology based on CRITIC weighted evaluation. Chinese Herbal Medicines. 48 (6), 1133-1138 (2017).
- Elling, U., et al. Derivation and maintenance of mouse haploid embryonic stem cells. Nature Protocols. 14 (7), 1991-2014 (2019).
- Gu, J., Wang, Y. P., Ma, X. Simultaneous determinnation of three diester diterpenoid alkaloids in the toots of Aconiti flavi et penduli by HPLC method. Chinese Pharmaceutical Affairs. 28 (6), 618-621 (2014).
- Zhang, Y., Fu, X. UPLC simultaneous determination of six esteric alkaloids components in Aconitum Flaram Hand.Mazz. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine. 16 (5), 62-65 (2020).
- Rumachik, N. G., Malaker, S. A., Paulk, N. K. VectorMOD: Method for bottom-up proteomic characterization of rAAV capsid post-translational modifications and vector impurities. Frontiers In Immunology. 12, 657795 (2021).
- Wang, Y. J., Tao, P., Wang, Y. Attenuated structural transformation of aconitine during sand frying process and antiarrhythmic effect of its converted products. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2021, 7243052 (2021).
- Wang, H. P., Zhang, Y. B., Yang, X. W., Zhao, D. Q., Wang, Y. P. Rapid characterization of ginsenosides in the roots and rhizomes of Panax ginseng by UPLC-DAD-QTOF-MS/MS and simultaneous determination of 19 ginsenosides by HPLC-ESI-MS. Journal of Ginseng Research. 40 (4), 382-394 (2016).
- vander Leeuw, G., et al. Pain and cognitive function among older adults living in the community. Journals of Gerontology Series A. Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 71 (3), 398-405 (2016).
- Lao, D., Liu, R., Liang, J. Study on plasma metabolomics for HIV/AIDS patients treated by HAART based on LC/MS-MS. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 13, 885386 (2022).
- Li, Y., et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness of VOC-contaminated soil preparation based on AHP-CRITIC-TOPSIS model. Chemosphere. 271, 129571 (2021).
- Zhong, S., Chen, Y., Miao, Y. Using improved CRITIC method to evaluate thermal coal suppliers. Scientific Reports. 13 (1), 195 (2023).
- Lewis, N. S., et al. Magnetically levitated mesenchymal stem cell spheroids cultured with a collagen gel maintain phenotype and quiescence. Journal of Tissue Engineering. 8, (2017).
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee. . Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. 4, (2020).
- Li, G., et al. Effect of response surface methodology-optimized ultrasound-assisted pretreatment extraction on the composition of essential oil released from tribute citrus peels. Frontiers in Nutrition. 9, 840780 (2022).
- Liu, X. F., et al. Hezi inhibits Tiebangchui-induced cardiotoxicity and preserves its anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects by regulating the pharmacokinetics of aconitine and deoxyaconitine. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 302, 115915 (2023).
- Smolen, J. S., et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews.Disease Primers. 4, 18001 (2018).
- Wang, F., et al. C19-norditerpenoid alkaloids from Aconitum szechenyianum and their effects on LPS-activated NO production. Molecules. 21 (9), 1175 (2016).
- Wang, B., et al. Study on the alkaloids in Tibetan medicine Aconitum pendulum Busch by HPLC-MSn combined with column chromatography. Journal of Chromatographic Science. 54 (5), 752-758 (2016).
- Liu, S., et al. A review of traditional and current methods used to potentially reduce toxicity of Aconitum roots in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 207, 237-250 (2017).
- Qiu, Z. D., et al. Online discovery of the molecular mechanism for directionally detoxification of Fuzi using real-time extractive electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 277, 114216 (2021).
- El-Shazly, M., et al. Use, history, and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry chemical analysis of Aconitum. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis. 24 (1), 29-45 (2016).
- Chan, T. Y. K. Aconitum alkaloid poisoning because of contamination of herbs by aconite roots. Phytotherapy Research. 30 (1), 3-8 (2016).
- Guo, L., et al. Exploring microbial dynamics associated with flavours production during highland barley wine fermentation. Food Research International. 130, 108971 (2020).
- Guo, T. L., Horvath, C., Chen, L., Chen, J., Zheng, B. Understanding the nutrient composition and nutritional functions of highland barley (Qingke): A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 103, 109-117 (2020).
- Wu, H., et al. Anti-myocardial infarction effects of Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata extracts and their influence on small molecules in the heart using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry imaging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 20 (19), 4837 (2019).
- Huang, G., et al. Study on cardiotoxicity and mechanism of "Fuzi" extracts based on metabonomics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 19 (11), 3506 (2018).
- Li, S. L., et al. An insight into current advances on pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity and detoxification of aconitine. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 151, 113115 (2022).
- Xie, Y., et al. Optimization of processing technology of braised Rehmanniae Raidx based on multiple indexes and response surface technology and correlation between components and color. Journal of Chinese Traditional Medicine. 47 (18), 4927-4937 (2022).
- Yang, X. Q., Xu, W., Xiao, C. P., Sun, J., Feng, Y. Z. Study on processing technology of Atractylodes chinensis with rice water and its pharmacodynamics of anti-diarrhea. Chinese Herbal Medicines. 53 (1), 78-86 (2022).
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請さらに記事を探す
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved