The ELISA, or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, is a widely used method for determining the presence or absence of a specific target protein.
Via a series of washing and binding steps, an antibody conjugated, or linked, to an enzyme will recognize a target protein at the bottom of a 96-well plate. When substrate is added to the sample, an enzymatic reaction will occur, causing a color change that allows the identification and quantification of the target protein.
Before we discuss how to perform an ELISA, let’s get familiar with the equipment and reagents that you will need.
The setting for an ELISA reaction is typically a 96-well flat bottom plate. The flat bottoms of the wells will help facilitate an even distribution of your experimental sample, as well as your capture and detection antibodies.
ELISAs detect the presence of specific target proteins in experimental aqueous solutions. Urine, cell culture media, and serum are common experimental samples.
In an ELISA, the antibody that directly binds to the target protein is the primary antibody. It has high affinity, that is, a high ability to bind tightly, for an epitope - a specific region - of the target protein. The primary antibody is usually unlabeled, or un-conjugated.
As mentioned, antibodies mostly bind to their target proteins through high affinity binding to a specific epitope. However, the experimental sample may contain pieces of cells that express nonspecific binding sites, sites that can bind the constant, or non-epitope specific, region of your detector antibodies.
Therefore, addition of a blocking buffer is essential in an ELISA to cover any nonspecific binding sites in your experimental samples. Otherwise you may have enzymatic reactions occurring in wells that do not contain target protein, giving you false positive data!
The secondary antibody in an ELISA is the antibody used to recognize the primary antibody. This antibody is usually conjugated to an enzyme. Sometimes the secondary antibody has a funky name. For example, if the secondary antibody made, or raised, in a donkey to recognize a primary antibody raised in a goat, the secondary antibody would be called a donkey anti-goat antibody. When it comes to naming secondary antibodies, the first name indicates the organism that produced the secondary antibody, and the second name represents the organism that produces the primary antibody.
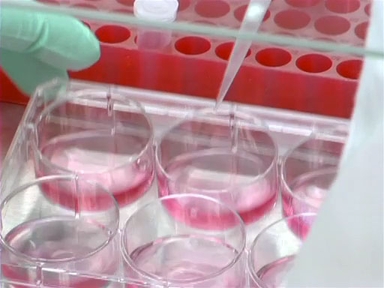
A substrate, which binds to the active site of the enzyme linked to the secondary antibody, will also be needed. The chemical reaction that occurs during this reaction causes a color change in the otherwise-colorless substrate. This so-called colorimetric assay allows the identification and quantification of the presence of the target protein.
The enzymatic reaction will continue as long as there is available substrate. Therefore, after a brief incubation period, a stop solution, which causes yet another color change to indicate the reaction has in fact been halted, is added to the wells.
A microplate reader will be used to quantify the concentration of the protein of interest in each well by reading the absorbance, that is, the amount of colored product, in each well. The absorbance is proportional to the amount of target protein present.
Now that you have all your equipment ready, let’s run an ELISA!
To perform a standard, or direct, ELISA, first coat the wells of the 96-well plate with your target protein of interest diluted in coating buffer. Plate your positive and negative controls at this time as well.
After incubating the coated plate long enough to give the protein time to completely adsorb, or attach, to the bottom of the plate, dump off the excess coating solution with a quick flick of your wrist.
Then block any possible non-specific binding or background signal by incubating each well in blocking buffer.
Now dump off the blocking buffer and wash the wells with a brief room temperature incubation in phosphate buffered saline, or PBS, and 1% BSA.
While the wells are being rinsed with PBS, prepare dilutions of a known concentration of the target protein to create a standard curve. The absorbance of the standard curve wells, which contain known concentrations of the target protein, will be used to calculate the concentration of target protein in your experimental sample wells based on a comparison of the absorbance of the sample wells to the absorbance of the standard curve wells.
Now it’s time to add the detection or primary antibody!
The plate is then incubated, usually at room temperature, to allow a sufficient amount of antibody to bind to the target protein for later detection and quantification of the protein.
After this incubation, excess antibody is removed and the wells are briefly washed with PBS.
Secondary antibody is then added to the plate, and the plate is once again incubated – typically on a rotating platform – to allow secondary antibody to bind. Washing steps are repeated as before.
Next, add the substrate to the plate to see which wells contain your target protein. Cover the plate to protect the reaction from light, and then after a brief incubation, halt the reaction with stop solution.
Finally, place your plate in the microplate reader to measure the absorbance or amount of colored solution, in each well. You will need to select which wells you want the reader to analyze. When the instrument is finished reading the plate, a readout of the absorbance for each well will be displayed.
It is important to note that each ELISA kit has a detection limit. That is, only protein concentrations above and below specific limits can be accurately determined. Very small concentrations of protein are usually too close to the background levels of non-specific staining, while very high concentrations may indicate that excess protein or antibody was not properly washed away in that sample well.
So why might you perform an ELISA? Let’s take a look at a few common applications.
Probably the most common type of ELISA performed is the sandwich ELISA.
In a sandwich ELISA, a 96-well plate is coated first with a primary antibody that recognizes the target protein of interest.
In this experiment, cell culture media harvested from human antibody-producing cell lines, were plated by an automated system onto 96-well plates pre-coated with a primary antibody that recognizes human antibodies.
After washing away the excess sample with PBS, an enzyme-linked secondary antibody is added, followed by a colorimetric substrate.
The absorbance is then measured in the same way as for a typical ELISA. For example, in this experiment, this ELISA data will be used to determine which cell lines produce the human antibody with the highest affinity for – that is best ability to bind accurately to – its target antigen.
The over-the-counter pregnancy test is one type of sandwich ELISA.
When the potentially pregnant woman’s urine is added to the test, enzyme-linked primary antibodies attached to the test will bind the pregnancy hormone hCG if it is present. If the woman is pregnant, a substrate-enyzme reaction will occur when the primary antibodies are recognized by substrate-bound secondary antibodies at the test site, and a colored line will appear.
Another type of ELISA is the competitive ELISA, which can be used to detect the presence of antibodies.
If the antibodies of interest are present in the sample, they will bind to the target protein attached to the bottom of the plate. Later, when enzyme-linked detection antibodies are added to the plate, the enzyme-linked antibodies will find few to no proteins to bind; they will have been “out-competed” by the antibodies of interest in the experimental sample.
In a competitive ELISA, then, the colored wells indicate the samples that actually do not contain the antibody of interest! Patient plasma samples are typically run in a competitive ELISA in order to determine if antibodies for certain pathogens, like the HIV virus, are present in the sample.
You’ve just watched JoVE introduction to performing an ELISA. In this video we reviewed: what an ELISA is and how it works; what equipment and reagents you will need to perform and ELISA; and some different applications of the assay. Thanks for watching, and remember not to let your substrate overdevelop!