A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
In vitro Reconstitution of the Active T. castaneum Telomerase
In This Article
Summary
Efforts to isolate the catalytic subunit of telomerase, TERT, in sufficient quantities for structural studies, have been met with limited success for more than a decade. Here, we present methods for the isolation of the recombinant Tribolium castaneum TERT (TcTERT) and the reconstitution of the active T. castaneum telomerase ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex in vitro.
Abstract
Efforts to isolate the catalytic subunit of telomerase, TERT, in sufficient quantities for structural studies, have been met with limited success for more than a decade. Here, we present methods for the isolation of the recombinant Tribolium castaneum TERT (TcTERT) and the reconstitution of the active T. castaneum telomerase ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex in vitro.
Telomerase is a specialized reverse transcriptase1 that adds short DNA repeats, called telomeres, to the 3' end of linear chromosomes2 that serve to protect them from end-to-end fusion and degradation. Following DNA replication, a short segment is lost at the end of the chromosome3 and without telomerase, cells continue dividing until eventually reaching their Hayflick Limit4. Additionally, telomerase is dormant in most somatic cells5 in adults, but is active in cancer cells6 where it promotes cell immortality7.
The minimal telomerase enzyme consists of two core components: the protein subunit (TERT), which comprises the catalytic subunit of the enzyme and an integral RNA component (TER), which contains the template TERT uses to synthesize telomeres8,9. Prior to 2008, only structures for individual telomerase domains had been solved10,11. A major breakthrough in this field came from the determination of the crystal structure of the active12, catalytic subunit of T. castaneum telomerase, TcTERT1.
Here, we present methods for producing large quantities of the active, soluble TcTERT for structural and biochemical studies, and the reconstitution of the telomerase RNP complex in vitro for telomerase activity assays. An overview of the experimental methods used is shown in Figure 1.
Protocol
1. Expression of recombinant TcTERT
- Inoculate 6 L of 2YT media (6 x 2 L Baffled Erlenmeyer Flasks containing 1 L of 2YT broth in each) from six fresh plates of transformed Rosetta(DE3)pLysS cells containing the synthetic TcTERT plasmid with a TEV cleavable N-terminal hexahistidine-tag.
- Grow cells at 37°C while shaking at 220 rpm to an OD600 of 0.5-0.6.
- Induce protein expression by adding 1 mM IPTG.
- Reduce temperature to 30°C, slow shaking to 150 rpm, and allow cells to express protein for 4-5 h.
- Harvest cells by centrifugation at 4°C and 3500 rpm for 30 min.
- Resuspend each 1 L cell pellet in 20 ml of buffer containing 25 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 0.5 M KCl, 15 mM Imidazole, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and 0.1 mM phenylmethyl sulphonyl fluoride (PMSF) and benzamidine.
- Flash freeze resuspended cell mixture by slowly dripping the cells into a 50 ml plastic conical tube filled with liquid nitrogen so that each drop freezes on impact in the liquid N2. Store frozen cells at -80°C until ready for protein purification.
2. Purification of TcTERT
- Thaw cells at room temperature until a liquid consistency is reached and then move to metal beakers on ice for sonication.
- Sonicate cells on ice for 2 min in 30 second intervals with 30 second pauses, at approximately 51 W of power.
- Spin down lysed cells at 18,000 rpm for 20 min to separate the soluble and insoluble protein fractions and carefully remove the supernatant for Nickel affinity chromatography.
- Equilibrate the Ni-NTA (nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid) column with buffer containing 25 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 0.5 M KCl, 15 mM imidazole, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and 0.1 mM PMSF and benzamidine.
- Load supernatant over the resin and collect the flow through.
- Wash the column with buffer containing 25 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 500 mM KCl, 15 mM imidazole, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and 0.1 mM PMSF to remove all residual and non-specifically bound proteins.
- Elute TcTERT of the Ni-NTA resin using an imidazole gradient of 15 - 300 mM and collect 3 ml fractions for SDS PAGE analysis.
- Use PAGE analysis to determine which fractions contain TcTERT protein and concentrate these fractions in an Amicon 30 kDa (Millipore) filter.
- Concentrate TcTERT fractions to a volume less than 10 ml for further purification.
- The TcTERT is further purified over the cation-exchange column (HS poros, Applied Biosystems) pre-equilibrated with buffer containing 25 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 500 mM KCl, and 1 mM DTT.
- Load the protein mix on the HS poros column and wash it to remove all protein and nucleic acid contaminants.
- Wash the column with buffer containing 500 mM KCl followed by 700 mM KCl to remove any remaining contaminants.
- Elute the TcTERT protein off the HS poros column with 1 M KCl buffer. At this point the protein should be more than 99% pure.
- Remove any protein aggregates by passing the protein over a Superdex-200 sizing column (size exclusion chromatography - GE Healthcare), pre-equilibrated with buffer containing 25 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 500 mM KCl, and 1 mM TCEP.
3. Tribolium castaneum beetle culture
- The T. castaneum beetles where initially provided as a gift by Dr. S. Brown, Division of Biology, Kansas State University.
- Start T. castaneum culture by adding one hundred adult beetles to a container with 28.5 g of flour and 1.5 g of dried baker's yeast.
- Store beetle cultures at room temperature and in a dark, humid environment for three to four weeks to allow for reproduction and growth. Place a beaker containing water in the beetle storage area to ensure a humid environment.
- Harvest the beetle larvae as needed for RNA isolation. Allow the remaining larvae to mature to adults, keeping them in the same culture.
- Every month, transfer the most active beetles (no more than a hundred) into a new flask containing fresh flour and yeast to replenish their food supply.
4. T. castaneum Total RNA isolation
- Harvest 20 beetle larvae from the culture (each culture should contain between 500-1000 larvae) by separating them from adult beetles and the flour/yeast culture. Eliminate flour or yeast particles attached to the beetles before grinding them.
- Sterilize the bench area, the mortar, and the pestle (consider treating the gloves as well) used for this procedure with RNaseZap (Ambion, Inc.) to remove all traces of ribonucleases before grinding the beetles.
- Grind larvae in liquid N2 into a fine powder using a mortar and pestle and transfer the powder to a 50 ml centrifuge tube while maintaining the liquid N2 to ensure that the powder stays frozen until the extraction buffer is added.
- Allow excess liquid N2 to evaporate from the powder. After the liquid N2 has evaporated, homogenize the beetle powder in 200 μl of extraction buffer (per 20 beetle larvae) containing 25 mM Tris-HCl, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 1 mM EGTA, 0.1 mM benzamidine, 200 mM KCl, 10% glycerol, 10 mM imidazole and 20U of RNasin, pH 7.5 and incubate on ice for 30 minutes.
- Centrifuge the homogenate at 15,000 rpm for 20 minutes at 4°C, collect the supernatant and flash freeze the sample in liquid N2. If necessary, samples can be stored at -80°C overnight.
- Extract the total RNA using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen).
5. In vitro reconstitution of Tribolium castaneum telomerase
- Mix 20 μg of recombinant His-tagged TcTERT with 50 μl of T. castaneum total RNA in the binding buffer containing 25 mM Tris-HCl, 200 mM KCl, 10% glycerol, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and 10 mM imidazole, pH 7.5.
- Incubate the TcTERT – total RNA mixture for two hours at 22°C in T. castaneum lysate in the presence of RNasin inhibitor to prevent RNA degradation.
- Purify the complex over a Ni-NTA column to remove lysate impurities and excess RNA.
6. Telomerase repeat amplification protocol (TRAP) assays
- Mix 4 μg of Ni-NTA purified T. castaneum telomerase in 50 μl elongation buffer containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH - 8.3), 7.5 mM MgCl2, 63 mM KCl, 0.05% Tween 20, 1 mM EGTA, 0.01% BSA, 0.5 mM dNTPs, 1 μM Tcas-TS DNA primer (5'-AAGCCGTCGAGCAGAGTC-3'), and incubate the mixture at 30°C for 60 minutes to allow elongation of the Tcas-TS DNA primer by the reconstituted T. castaneum telomerase.
- Extract the elongated single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) by adding an equal volume of phenol chloroform to the reaction mixture. Shake the mixture gently until the emulsion is homogeneous.
- Centrifuge the sample at 12,000 rpm for five minutes at 4°C to separate the ssDNA from contaminants.
- Transfer the top aqueous layer of the sample to a 1.5 ml eppendorf tube; add a final concentration of 10 mM NaOAc (pH 5.0), 1 mM of MgCl2, and 66.4% EtOH and then allow the sample to precipitate overnight at -20°C.
- Spin the sample at 15,000 rpm for thirty minutes at 4°C to pellet the precipitated ssDNA. Decant the solution using a pipettor and then add 200 μl of 70% EtOH to the sample to wash remaining NaOAc and MgCl2 from the sample. Centrifuge the sample for five minutes at the same speed and temperature to re-pellet the sample.
- Decant the EtOH solution using a pipettor and remove remaining traces of ethanol by allowing the eppendorf tube to incubate open at room temperature for three minutes. Having ethanol present in the sample will interfere with the PCR amplification step.
- Resuspend the ssDNA pellet (containing the telomerase elongated product and the Tcas-TS primer) in 50 μl of PCR reaction buffer containing 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8), 50 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 100 μM dNTPs (dATP, dGTP and dTTP), 10 μM [32P] dCTP, 1 μM Tcas-CX primer (5'-GTGTGACCTGACCTGACC-3') and 1.25 U Taq DNA polymerase.
- PCR amplify the telomerase elongation products (29 cycles of 94°C for 30 seconds, 50°C for 30 seconds, and 72°C for 1 minute), so that they are visible on a 12% polyacrylamide gel.
- Pre-run the 12% gel with Tris-Borate-EDTA (TBE) running buffer containing 44.5 mM Tris, 44.5 mM Boric Acid, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8 for thirty minutes prior to running the PCR samples. After pre-running and loading the gel with the PCR reactions, run the gel at 185 Volts for 1.5-2 hours at 4°Celsius or on ice.
- Dry the gel and use the phosphor imaging plate to visualize activity.
7. Representative Results:
An example of the purified TcTERT after size exclusion chromatography is shown in Figure 2. The protein concentrated after purification is run on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and is shown to be more than 99% pure (Figure 2A). The size exclusion (S200) chromatogram is also provided (Figure 2B) to demonstrate the purity and lack of aggregates from the purified protein sample. A yield of 5 mg protein after all purification steps have been completed is usually obtained although the final yield can vary.
A representative TRAP assay for the reconstituted T. castaneum telomerase is shown in Figure 3 as previously reported by Mitchell et al.12. The step-wise ladder of telomerase products can be seen in lane 1, however they are absent in both the RNase treated telomerase and the TERT active site mutant (D251A) samples in lanes 2 and 3 respectively.
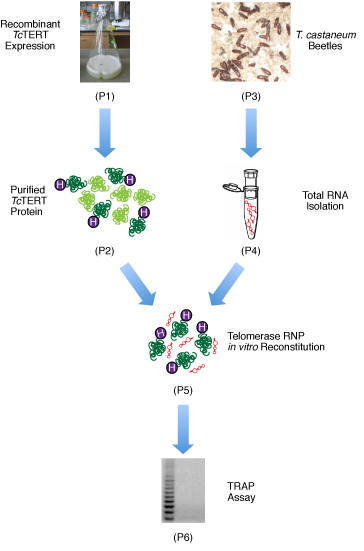
Figure 1. Flow chart of the steps involved in the reconstitution of the recombinant TcTERT. First, the recombinant TcTERT is over-expressed in E. coli. The protein is then purified by nickel, cation exchange, and size exclusion chromatography. The T. castaneum beetles are cultured in house and their larvae are used to isolate the total RNA. The purified TcTERT and the total RNA are then mixed to reconstitute the telomerase RNP complex, and a subsequent TRAP assay is used to confirm the RNP complex is an active telomerase.
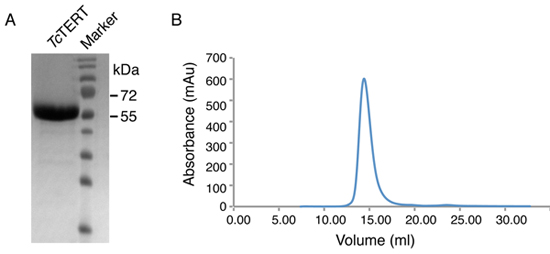
Figure 2. Size exclusion chromatogram and SDS PAGE analysis of TcTERT protein. (A) 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel of the TcTERT protein after size exclusion chromatography. The TcTERT protein (70 kDa) migrates faster on the SDS PAGE gel because it has a high isoelectric point (pI - 9.8). (B) Size exclusion chromatogram (Superdex S200) of the TcTERT protein.

Figure 3. TRAP assays of the in vitro reconstituted Tribolium castaneum telomerase adapted from Mitchell et al.12. Lane 1: wild type TcTERT and total RNA isolated from beetle larvae. Lane 2: wild type TcTERT and RNase treated larvae total RNA and cell extracts. Lane 3: active site mutant TcTERT (D251A) and beetle larvae total larvae RNA.
Discussion
The method presented here allows for the production of large amounts of the catalytic subunit of T. castaneum telomerase TERT in soluble, active form for structural and biochemical studies. The method of TcTERT over-expression is sensitive to subtle changes in temperature or cell density from those stated above and can dramatically affect the levels of protein expression. Specifically, we have found that inducing the cells for protein expression before the optical density reaches 0.5 at 600 nm, or lowe...
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest declared.
Acknowledgements
The research presented here was supported by the Pennsylvania Department of Health, The Ellison Medical, The V and The Emerald Foundations.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Rosetta(DE3)plysS Cells | Novagen, EMD Millipore | 70956 | |
| 2YT Broth | TEKnova, Inc. | Y0215 | |
| IPTG | Gold Biotechnology | I2481C | |
| MISONIX Sonicator 3000 | Qsonica, LLC. | ||
| ÄKTA Purifier FPLC | GE Healthcare | ||
| Ni-NTA Superflow Resin | Qiagen | 30410 | |
| Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter Device | EMD Millipore | UFC903008 | |
| POROS 50 HS Strong Cation Exchange Packing | Applied Biosystems | 1-3359-06 | |
| POROS 50 HQ Strong Cation Exchange Packing | Applied Biosystems | 1-2559-06 | |
| Superdex 200 10/300 Size-Exclusion Column | GE Healthcare | 17-5175-01 | |
| Phenol: Chloroform: Isoamyl 25:24:1 with 10mM Tris, pH 8, 1mM EDTA | Sigma-Aldrich | P3803-100mL | |
| RNaseZap | Ambion | AM9780 | |
| Recombinant Rnasin Ribonuclease Inhibitor | Promega Corp. | N251B | |
| RNeasy Mini Kit | Qiagen | 74104 | |
| DNA oligonucleotides | Integrated DNA Technologies |
References
- Gillis, A. J., Schuller, A. P., Skordalakes, E. Structure of the Tribolium castaneum telomerase catalytic subunit TERT. Nature. 455, 633-637 (2008).
- Greider, C. W., Blackburn, E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 43, 405-413 (1985).
- Harley, C. B., Futcher, A. B., Greider, C. W. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 345, 458-460 (1990).
- Hayflick, L. The Limited in vitro Lifetime of Human Diploid Cell Strains. Exp Cell Res. 37, 614-636 (1965).
- Blackburn, E. H. Telomeres: no end in sight. Cell. 77, 621-623 (1994).
- Kim, N. W. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science. 266, 2011-2015 (1994).
- Bodnar, A. G. Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science. 279, 349-352 (1998).
- Greider, C. W., Blackburn, E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 51, 887-898 (1987).
- Greider, C. W., Blackburn, E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 337, 331-337 (1989).
- Jacobs, S. A., Podell, E. R., Cech, T. R. Crystal structure of the essential N-terminal domain of telomerase reverse transcriptase. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 13, 218-225 (2006).
- Rouda, S., Skordalakes, E. Structure of the RNA-binding domain of telomerase: implications for RNA recognition and binding. Structure. 15, 1403-1412 (2007).
- Mitchell, M., Gillis, A., Futahashi, M., Fujiwara, H., Skordalakes, E. Structural basis for telomerase catalytic subunit TERT binding to RNA template and telomeric DNA. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 17, 513-518 (2010).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved