A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Tracking Microbial Contamination in Retail Environments Using Fluorescent Powder - A Retail Delicatessen Environment Example
In This Article
Summary
The overall goal of this study was to demonstrate the potential cross contamination mechanism of foodborne pathogen Listeria monocytogenes in a retail deli setting. This methodology may be applied to a variety of different environments to track pathogen contamination.
Abstract
Cross contamination of foodborne pathogens in the retail environment is a significant public health issue contributing to an increased risk for foodborne illness. Ready-to-eat (RTE) processed foods such as deli meats, cheese, and in some cases fresh produce, have been involved in foodborne disease outbreaks due to contamination with pathogens such as Listeria monocytogenes. With respect to L. monocytogenes, deli slicers are often the main source of cross contamination. The goal of this study was to use a fluorescent compound to simulate bacterial contamination and track this contamination in a retail setting. A mock deli kitchen was designed to simulate the retail environment. Deli meat was inoculated with the fluorescent compound and volunteers were recruited to complete a set of tasks similar to those expected of a food retail employee. The volunteers were instructed to slice, package, and store the meat in a deli refrigerator. The potential cross contamination was tracked in the mock retail environment by swabbing specific areas and measuring the optical density of the swabbed area with a spectrophotometer. The results indicated that the refrigerator (i.e. deli case) grip and various areas on the slicer had the highest risk for cross contamination. The results of this study may be used to develop more focused training material for retail employees. In addition, similar methodologies could also be used to track microbial contamination in food production environments (e.g. small farms), hospitals, nursing homes, cruise ships, and hotels.
Introduction
Cross contamination of foodborne pathogens in the food preparation environment, especially in the retail section, is a major concern due to an increased risk of foodborne illness from a variety of sources including the meats as well as the vegetables1-5. Most often, bacterial pathogens enter the retail environment through contaminated food products6. Ready-to-eat foods prepared at the retail level are of particular concern as there is usually no further intervention or treatment (i.e. cooking or heating) prior to consumption7. Moreover, pathogens present on contaminated RTE food can then be transferred to other food products or food contact surfaces in the retail environment.
While cross contamination can occur within virtually any type of retail food environment, delis are of particular interest specifically because of the association of RTE deli meats with the pathogen Listeria monocytogenes2. Based on a risk assessment analyses conducted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and U.S. Department of Agriculture Food Safety and Inspection Service (USDA-FSIS), contaminated deli meats are likely responsible for 90% of the cases of listeriosis - a rare yet severe human disease caused by L. monocytogenes - in the United States8. In general, deli meats sliced at retail and food service establishments have been associated with a higher risk of L. monocytogenes compared to presliced deli meats in a USDA inspected plant by the manufacturer9. This could be because of the increased likelihood of introduction of pathogens by food handlers, incoming raw ingredients, or processed foods that may become contaminated post-treatment7. Overall, listeriosis accounts for approximately 28% of the estimated deaths caused by foodborne illness per year in the U.S.
Because of the increased risk of L. monocytogenes contamination in deli meats sliced at the retail level, the deli slicer itself has been identified as an important factor for surface transfer of foodborne pathogens in the retail environment2,10. As indicated by Sheen1, slicing is the last processing step prior to consumption; therefore, the deli slicer should be considered a critical control point for both understanding and preventing cross contamination1.
The overall goal of this study was to develop a methodology to track contamination in the retail deli environment using a fluorescent powder such as Glo Germ. This is a fluorescent compound that has been used to simulate bacterial cross contamination and sanitary practices11,12. This study was designed to track pathogen transfer from contaminated meats to the slicer, the surrounding environment, and other deli meats. It is crucial to understand the pathways of contamination to develop both effective interventions and educational material for retail employees and managers. A similar approach may be employed to simulate pathogen transfer in other processing environments (e.g. poultry and beef), farms, and hospitals.
Protocol
1. Standard Curve
- Weigh 37.5 mg fluorescent powder and dissolve in 6 ml 200 proof ethanol. Make 2-fold serial dilutions of this solution in 200 proof ethanol.
- Vortex all the samples for 10 sec and measure the absorbance at 370 nm.
- Calculate the amount of fluorescent powder per 1 ml 200 proof ethanol.
- Prepare the standard curve (concentration in mg/ml on the y-axis and absorbance at 370 nm on the x-axis) to demonstrate the absorbance based on fluorescent powder concentration.
2. Inoculate Deli Meat (Bologna) with Fluorescent Powder
- Cut the deli meat into approximately 100 mm thick samples using a clean knife and cutting board. Prepare three samples labeled A, B, and C.
- Coat sample A evenly with fluorescent powder using a slightly damp, clean sponge. Spread the powder on the meat sample evenly. Do not inoculate samples B and C with the fluorescent powder.
- Wrap the samples with plastic wrap and label the fluorescent powder coated sample as ‘A’ and remaining two samples as B and C with tape.
- Place the samples in the deli case or refrigerator held at 4 °C in the mock kitchen where the experiment will be carried out.
3. Mock Deli Kitchen Preparation
- Provide clean gloves and 70% ethanol spray in the kitchen.
- Mount black compact fluorescent lights with 13 W bulbs around the slicer area.
- Prepare a 5 cm x 5 cm cutout of aluminum foil to serve as a template for swabbing.
- Prepare 15 ml tubes containing 6 ml 95% ethanol.
4. Video Setup
Mount three video cameras in strategic locations to observe all areas of the mock deli at the same time. Turn on the cameras before simulating the slicer procedure (as explained in Protocol 5) and analyze the results simultaneously (as explained in Protocol 7).
5. Simulating Deli Slicing Procedures to Track Cross Contamination
In order to improve sample size and incorporate variation, perform this study by recruiting participants after approval of protocol by the Institutional Review Board of the respective institution. The participant can be a college student who may or may not have experience working in retail deli environments. Ensure that each participant wears gloves once they enter the deli. Take a “before” picture under black fluorescent light followed by an “after” picture upon completion of study. Provide clear written and verbal instructions to each participant as follows:
- Go to refrigerator.
- Remove meat labeled "A".
- Unwrap meat and save plastic wrap.
- Place meat on carriage tray of slicer.
- Secure meat with meat grip.
- Turn power switch ON.
- Adjust slicer index knob to "2".
- Slice and dispense 5 pieces of meat onto deli paper.
- Turn power switch OFF and release meat grip.
- Place slices of meat in plastic bag labeled "A".
- Rewrap meat "A" and return to refrigerator.
- REPEAT Steps 2-11 with meats labeled "B" and "C".
6. Quantifying Fluorescent Powder
Quantify the fluorescent powder after completion of the mock slicing (Section 5.4) in the deli kitchen. For this do the following:
- Use the sterile 5 cm x 5 cm aluminum foil template and place it on the areas marked in Figure 1.
- Use a sterile calcium alginate cotton swab soaked in 95% ethanol, swab the area, and place in 6 ml 95% ethanol in a sterile polypropylene tube.
- Vortex the tube thoroughly and transfer to a glass cuvette to read the absorbance at 370 nm.
- Refer to the standard curve to determine the amount of fluorescent powder (y) using the following equation: y = mx + b where x is absorbency, m is the slope of the standard curve, and b is the intercept.
- For normalization of the data, calculate the percent of fluorescent powder per area sampled using the following formula:
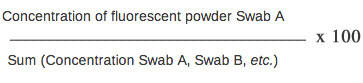
7. Video Analysis
Videotape the participants as they complete tasks 5.1-5.12. Sync and save the video recordings to DVD discs so that all angles can be viewed at the same time. Watch the videos to record the number of hand touches (the number of times volunteers touch areas in the mock deli) on various surfaces in the deli environment (4 different researchers will analyze the complete data set independently).
Results
Figure 1 represents the areas of the slicer that were swabbed after the volunteers completed the tasks assigned. The volunteers were videotaped to analyze the average frequency of hand contact on these various surfaces. The frequency of hand contact was analyzed by four different observers and averaged. These results are demonstrated in Figure 2. The data shows that the meat grip, deli meat wrapper, deli meat, and deli paper had the highest rates of hand contact (average of 8-14 contacts...
Discussion
The overall goal of this study was to demonstrate how bacterial cross contamination could occur in a retail deli environment in order to develop strategies to control and reduce the risk of foodborne illness. The retail deli environment has an especially high risk for L. monocytogenes contamination. The USDA-FSIS reported that deli meat sliced at the retail store has a seven times higher association with listeriosis that deli meat sliced and packaged at a federally inspected plant9.
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest declared.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all of the food safety lab students and volunteers who helped with this study. This research has been funded by a USDA National Integrated Food Safety Initiative (NIFSI) grant (Award #10507316).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Glo Germ Powder | Glo Germ Co | Purchased from vendor | |
| Ethanol | Sigma | E7023 | |
| Permanent markers | Sharpie | Purchased from stationary store | |
| Gloves | VWR | 82026-424 | |
| Deli Meat | NA | NA | Bologna Chub from regular grocery store |
| Cutting Board | NA | NA | A regukar kitchen cutting board |
| Knife | NA | NA | A regular kitchen knife |
| 5 cm x 5 cm sterile templates | NA | NA | Aluminum foil templates cut into 5 cm x 5 cm templates and sterilized |
| 15 ml Polypropylene centrifuge tubes | VWR | 89039-664 | |
| Cotton swabs | Puritan | 25-806 | |
| Glass cuvettes | VWR | 470019-186 | |
| Vortex | VWR | 58816-121 | |
| Flip camera | Flip Ultra HD | NA | Purchased online |
| Deli slicer | Bizerba | SE-12 | |
| Deli refrigerator | True Company | TDBD-722 | |
| Scale | NA | ||
| Spectrophotometer | Milton Roy Company | NA | Spectronic 20D |
References
- Sheen, S., Hwang, C. A. Mathematical modeling the cross-contamination of Escherichia coli O157: H7 on the surface of ready-to-eat meat product while slicing. Food Microbiol. 27, 37-43 (2010).
- Crandall, P., Neal, J., et al. Minimizing the risk of Listeria monocytogenes in retail delis by developing employee focused, cost effective training. Agric. Food Anal. Bacteriol. 1, 159-174 (2011).
- Koo, O. K., Sirsat, S. A., et al. Physical and chemical control of Salmonella in ready-to-eat products. Agric. Food Anal. Bacteriol. 2, 56-68 (2012).
- Hanning, I. B., Johnson, M. G., Ricke, S. C. Precut prepackaged lettuce: a risk for listeriosis?. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 5, 731-746 (2008).
- Hanning, I. B., Nutt, J. D., Ricke, S. C. Salmonellosis outbreaks in the United States due to fresh produce: sources and potential intervention measures. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 6, 635-648 (2008).
- Zhu, M., Du, M., et al. Control of Listeria monocytogenes contamination in ready‐to‐eat meat products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety. 4, 34-42 (2005).
- Lianou, A., Sofos, J. N. A review of the incidence and transmission of Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat products in retail and food service environments. J. Food Protect. 70, 2172-2198 (2007).
- . Quantitative risk assessment of relative risk to public health from foodborne Listeria monocytogenes among selected categories of ready-to-eat foods. , .
- Endrikat, S., Gallagher, D., et al. A comparative risk assessment for Listeria monocytogenes in prepackaged versus retail-sliced deli meat. J. Food Protect. 73, 612-619 (2010).
- Pradhan, A. K., Ivanek, R., et al. Comparison of public health impact of Listeria monocytogenes product-to-product and environment-to-product contamination of deli meats at retail. J. Food Protect. 74, 1860-1868 (2011).
- Jones, C. K. Handwashing Technique Analysis. Patent number 5900067. , (1999).
- Gibson, K. E., Koo, O. K., et al. Observation and relative quantification of cross-contamination within a mock retail delicatessen environment. Food Control. 31, 116-124 (2013).
- Xiao, M., Zheng, G., et al. Method and System for Fecal Detection. Patent number 5821546. , (1998).
- Waldroup, A., Kirby, J. Method and System for Fecal Detection. Patent number 5621215. , (1997).
- Ashby, K. D., Wen, J., et al. Fluorescence of dietary porphyrins as a basis for real-time detection of fecal contamination on meat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 51, 3502-3507 (2003).
- Cabrera-Diaz, E., Moseley, T. M., et al. Fluorescent protein marked Escherichia coli biotype I strains as surrogates for enteric pathogens in validation of beef carcass interventions. J. Food Protect. 72, 295-303 (2009).
- Byrd, J., Hargis, B., et al. Fluorescent marker for the detection of crop and upper gastrointestinal leakage in poultry processing plants. Poult. Sci. 81, 70-74 (2002).
- Vorst, K. L., Todd, E. C., et al. Transfer of Listeria monocytogenes during mechanical slicing of turkey breast bologna, and salami.. J. Food Protect. 69, 619-626 (2006).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved