A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Design and Synthesis of a Reconfigurable DNA Accordion Rack
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
We describe the detailed protocol for design, simulation, wet-lab experiments, and analysis for a reconfigurable DNA accordion rack of 6 by 6 meshes.
Abstract
DNA nanostructure-based mechanical systems or DNA nanomachines, which produce complex nanoscale motion in 2D and 3D in the nanometer to ångström resolution, show great potential in various fields of nanotechnology such as the molecular reactors, drug delivery, and nanoplasmonic systems. The reconfigurable DNA accordion rack, which can collectively manipulate a 2D or 3D nanoscale network of elements, in multiple stages in response to the DNA inputs, is described. The platform has potential to increase the number of elements that DNA nanomachines can control from a few elements to a network scale with multiple stages of reconfiguration.
In this protocol, we describe the entire experimental process of the reconfigurable DNA accordion rack of 6 by 6 meshes. The protocol includes a design rule and simulation procedure of the structures and a wet-lab experiment for synthesis and reconfiguration. In addition, analysis of the structure using TEM (transmission electron microscopy) and FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer) is included in the protocol. The novel design and simulation methods covered in this protocol will assist researchers to use the DNA accordion rack for further applications.
Introduction
Mechanical systems based on DNA nanostructures or DNA nanomachines1,2,3,4,5 are unique because they produce complex nanoscale motion in 2D and 3D in the nanometer to ångström resolution, according to various biomolecular stimuli2,3,6. By attaching functional materials on these structures and controlling their positions, these structures can be applied to various areas. For example, DNA nanomachines have been proposed for a molecular reactor7, drug delivery8, and nanoplasmonic systems9,10.
Previously, we introduced the reconfigurable DNA accordion rack, which can manipulate a 2D or 3D nanoscale network of elements11 (Figure 1A). Unlike other DNA nanomachines that only control a few elements, the platform can collectively manipulate periodically arrayed 2D or 3D elements into various stages. We anticipate that a programmable chemical and biological reaction network or a molecular computing system can be built from our system, by increasing the number of controllable elements. The DNA accordion rack is a structure, in which the network of multiple DNA beams is connected to joints composed of single-stranded DNA (Figure 1B). The accordion rack generated by the DNA beams is reconfigured by the DNA locks, which hybridize to the sticky part of beams and change the angle between the beams according to the length of the bridging part of the locks (locked state). In addition, multi-step reconfiguration is demonstrated by adding new locks after formation of the free state by detaching DNA locks through toehold-based strand displacement12,13.
In this protocol, we describe the entire design and synthesis process of the reconfigurable DNA accordion rack. The protocol includes design, simulation, wet-lab experiments, and analysis for the synthesis of the DNA accordion rack of 6 by 6 meshes and a reconfiguration of these. The structure covered in the protocol is the basic model of the previous research11 and is 65 nm by 65 nm in size, consisting of 14 beams. In terms of the design and simulation, the structural design of the accordion rack is different from conventional DNA origami14,15 (i.e., tightly packed). Therefore, the design rule and molecular simulation have been modified from traditional methods. To demonstrate, we show the design technique using the modified approach of caDNAno14 and the simulation of the accordion rack using oxDNA16,17 with additional scripts. Finally, both protocols of TEM and FRET for analysis of configured accordion rack structures are described.
Protocol
1. Design of the 6 by 6 DNA Accordion Rack with caDNAno14
- Download and install caDNAno 2.0 software14 to design a DNA accordion rack (caDNAno 2.5 is also available on https://github.com/cadnano/cadnano2.5). Open caDNAno14 and click the Square Tool to add a new part with a square lattice.
- Number each beam of the accordion rack and draw on the left lattice panel of the caDNAno14 (Figure 2).
- Click the pencil tool and draw each beam on the right edit panel on the caDNAno14. Break beams every 32 bp, which is for joints between adjacent beams. Place staple crossovers in the same position as the joints. Use the Insert Tool and the Pencil Tool in caDNAno14 to let the joints have additional single-stranded crossovers.
- Click the Pencil Tool and connect the joints. Each beam has seven joints.
- Generate scaffold crossovers to merge the scaffolds into the single loop by using the previously reported scaffold routing algorithm11. Do not let the minimum binding domain between scaffold and staple strands be less than 8 bp (Figure 3).
- Place the scaffolds that are not used in the assembly at the vertices located on opposite sides of the accordion rack, as shown in Figure 3.
- Click the Break Tool. Break the strands where staple strands are circular or longer than 60 bp.
- Design the DNA lock strands.
- Click the Break Tool. Break 8 bp of a staple DNA region to make a sticky part and delete 8 bp of a staple DNA region. There are 18 sticky parts (Figure 1) in the 6 by 6 accordion rack.
- Place sequences that are reverse complementary to the sticky parts at both ends of lock strands and connect them by a bridging region, which consists of poly T strands of the desired length (Figure 1B).
- For the reconfiguration, add 8 bp of toehold sequences at the end of DNA locks for strand displacement. The toehold sequence used is in Table 2.
- Prepare poly A strands which are reverse complementary to the bridging region.
- Design strands that are reverse complementary to the DNA locks for the reconfiguration experiment.
- Click the Sequence Tool and click scaffold DNA. Choose the scaffold as standard M13mp18. Click the Export Tool and save sequence in csv format (Table 1).
2. Simulate the Structure with the oxDNA
- Download and install the oxDNA16,17. The latest source code is available on https://sourceforge.net/projects/oxdna/files/.
- Make starting configuration files from the caDNAno14 file using python script 'cadnano_interface.py', which is provided in the oxDNA16,17 package. The usage is as follows: ‘python cadnano_interface.py cadnano_file.json sq’. The topology file and configuration file are now generated.
Note: The topology file includes how many strands and nucleotides are in the structure and information regarding backbone-backbone bonds between nucleotides. The configuration file includes general information such as timestep, energy, and box size. Orientation information such as position vector, backbone-base vector, normal vector, velocity, and angular velocity of nucleotides is also included (Figure 4). - Change the information in the topology and configuration file from caDNAno14 to make them reflect the real structural information of the accordion rack. All beams are arranged in parallel when the topology and configuration files from caDNAno14 are visualized. However, the accordion rack is a lattice structure so the distance between bonded nucleotides are far for simulation (Figure 5).
- Rotate and move each beam to the desired lattice structure. The nine columns on the left in the configuration file are the position vector, backbone-base vector, and normal vector (Figure 4). To rotate a beam, rotate all of position, backbone-base, and normal vectors using rotational transformation. Then move a beam by changing the position vector to locate it as shown in Figure 5.
- Relax the structure using the script provided in the oxDNA package (see example in $oxDNA/EXAMPLES/RELAX_INITIAL_CONFIGURATION for further information).
- Run molecular dynamics simulation for ten million steps using the relaxed configuration file. The usage is as follows: ‘./oxDNA <input>’ Save data every 5000 or 10000 steps.
- Visualization
Note: The structures were visualized using cogli.- Download and install the latest version of the cogli (https://sourceforge.net/projects/cogli1/).
- Run the cogli with the topology and configuration files from the oxDNA simulation. The usage is as follows: ‘./cogli1 -t <topology file> <configuration file>’ .
- Hide the box by pressing b.
3. Synthesis of the Structure
Note: The synthesis method is adapted from the previous protocol15,18.
- Purchase the designed DNA staples from an oligonucleotide provider.
- Adjust the concentration of these DNA staples to 100 μM using nuclease-free water.
- Pool each DNA strand that constitutes a ‘free state’ structure into one tube and adjust the concentration to 2 μM for each strand.
- Pool DNA lock strands by length and number of lock sites into tubes and adjust the concentration to 2 μM for each strand. 18, 9, and 4 lock sites are used. Add poly A strands which are complementary to the bridging region at the same concentration.
- Pool strands that are reverse complementary to the DNA lock strands by length into tubes and adjust the concentration to 2 μM for each strand.
- Prepare MgCl2 solution of 300 nM by mixing 70 μL of nuclease-free water and 30 μL of the 1 μM MgCl2 solution. Prepare a 5x Tris EDTA solution by mixing 95 μL of nuclease-free water and 5 μL of the 100x Tris EDTA solution.
- Add 2 μL of staple DNA, 1.1 μL of MgCl2 solution, 2 μL of Tris EDTA solution, 7.6 μL of nuclease-free water and 7.3 μL of scaffold DNA of which the concentration is 110 nM to make 20 μL of mixed stock. Set the final concentration of the scaffold DNA to 40 nM, staple DNA to 200 nM, MgCl2 to 16 mM and Tris EDTA solution to 0.5x.
- Rapidly heat the mixed stock solution in a thermal cycler to 80 °C and cool to 60 °C at a rate of 4 min per °C and cool from 60 °C to 4 °C at a rate of 40 min per °C.
4. Purification of the Structure
Note: Samples of all structures were purified before analysis. In this section, we describe the protocol of PEG purification, which is adapted from previous literature19. The sample can also be purified by gel electrophoresis as described in previous literature15,18.
- Prepare 5 M of NaCl and 100x Tris-EDTA.
- Prepare precipitation-buffer by mixing 150 μL of PEG 8000, 500 μL of 100x Tris EDTA and 101 μL of 5 M NaCl and 249 μL of nuclease-free water.
- Prepare target-buffer by mixing 5.5 μL of 300 nM MgCl2 solution from Section 3.3, 10 μL of 5x Tris EDTA solution from Section 3.3 and 84.5 μL of nuclease-free water.
- Mix 20 μL of the synthesized structure from Section 3 and 20 μL of precipitation-buffer from Section 4.2. Then spin the mixed stock at 16000 x g at 4 °C. Remove the supernatant and dissolve pellet in the target-buffer from Section 4.3.
5. Reconfiguration of the Accordion Rack from a ‘Free State’ to a ‘Locked State’
- Synthesize the structure without DNA locks for the configuration experiment.
- Prepare DNA lock strands from Section 3.
- Add 2 μL of DNA lock strands of the desired length into 20 μL of the synthesized structure. The DNA lock strands’ concentration is five times higher than the structure.
- Incubate the sample for 0, 10, 25, 50, or 100 minutes to see how fast reconfiguration occurs.
- For the 100 minute incubation, incubate the sample at 50 °C for 30 minutes and slowly cool down to 25 °C at a rate of 0.33 °C/minute.
- For the 50 minute incubation, incubate the sample at 50 °C for 15 minutes and slowly cool down to 25 °C at a rate of 0.66 °C/minute.
- For the 25 minute incubation, incubate the sample at 50 °C for 7.5 minutes and slowly cool down to 25 °C at a rate of 1.32 °C/minute.
- For the 10 minute incubation, incubate the sample at 50 °C for 3 minutes and slowly cool down to 25 °C at a rate of 3.3 °C/minute.
- For the 0-minute incubation, store sample at 4 °C right after DNA locks strands are added.
- Right after the attaching step, rapidly cool down the sample to 4 °C to prevent unwanted denaturation.
6. Reconfiguration of the Accordion Rack from a ‘Locked State’ to a ‘Free State’
- Synthesize the structure with DNA locks of the desired length for the configuration experiment.
- Prepare reverse complementary strands from Section 3.
- Add 2 μL of strands that are reverse complementary to the lock strands of the desired length into 20 μL of the synthesized structure. The DNA lock strands’ concentration is five times higher than the structure.
- Incubate the sample for 0, 12, 60, 120, 240 minutes to see how fast reconfiguration occurs.
- For the 12, 60, 120, 240 minute incubation, rapidly heat the sample to 40 °C and slowly cool down to 20 °C for the time corresponding to each. Right after the detaching step, rapidly cool down the sample to 4 °C to prevent unwanted denaturation.
- For the 0-minute incubation, store sample at 4 °C right after reverse complementary strands are added.
7. TEM Imaging
Note: TEM imaging protocol was adapted from previous literature18,20.
- Prepare 1.25 M NaOH solution by mixing 87.5 μL of nuclease-free water and 12.5 μL of 10 M NaOH solution.
- Add 1 μL of 1.25 M NaOH solution to 50 μL of the 2% uranyl formate solution.
- Vortex the solution for 3 minutes and centrifuge at max speed for 3 minutes. Deposit 3 μL of the purified sample on the glow-discharged TEM grid for 3 minutes and rapidly wash out with filter paper.
- Deposit 7 μL of prepared uranyl formate solution for 30 seconds and rapidly wash out with filter paper.
- Measure the length and angle of the accordion structure imaged by TEM.
8. FRET Analysis
- Use Atto 550 and Atto 647N dye, for which the Förster distance is 6.5 nm. Replace Staple 58 and Staple 117 in Table 1 with fluorescently labelled strands. Then synthesize the structure with fluorescently labelled strands by the method described in Section 3.
- Measure the concentration of the purified sample.
- Normalize the sample to 10 nM and load 50 μL to the 384 microplates well.
- Excite the sample with donor and acceptor dyes at 550 nm and measure the fluorescence spectrum from 570 nm to 800 nm with a fluorometer.
- Measure the fluorescence spectrum of the donor-only sample in the same way.
- Excite the dyes of the sample at 650 nm and the fluorescence spectrum and measure from 670 nm to 800 nm. This is to measure the concentration of the acceptor.
- Obtain the standard deviations by repeating the same experiment with three samples, which are synthesized and purified separately.
- Calculate the FRET efficiency with the ratio A method as described by the equation below21.
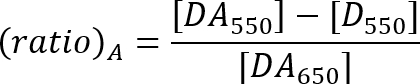
DA550: Acceptor peak fluorescence intensity of the sample with donor and acceptor at 550 nm excitation.
D550: Fluorescence intensity at the acceptor emission range of the donor-only sample at 550 nm excitation.
DA650: Acceptor peak fluorescence intensity of the sample with donor and acceptor at 650 nm excitation.
Results
The designed 6 by 6 DNA accordion rack is simulated from the oxDNA16,17 and the results are shown in Figure 6. From the simulation result, it was confirmed that the intended structure is formed without distortion of the structure.
The TEM images in Figure 7 are images of configured structures with a lock length ...
Discussion
This protocol introduces the entire process from design, simulation, synthesis, and analysis of the basic 2D DNA accordion rack. The modified design and simulation rules have been described because the design rule differs from that of standard DNA origami, in that the DNA accordion rack has additional nucleotides at the crossovers for flexibility14,15. From this, we expect that the protocol can accelerate various researches using DNA accordion racks. In addition,...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by the Global Research Development Center Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (2015K1A4A3047345) and Nano·Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (2012M3A7A9671610). The Institute of Engineering Research at Seoul National University provided research facilities for this work. Authors acknowledge gratitude towards Tae-Young Yoon (Biological Sciences, Seoul National University) regarding the fluorescence spectroscopy for the FRET analysis.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| M13mp18 Single-stranded DNA | NEB | N4040s | |
| 1M MgCl2 Solution | Biosesang | M2001 | |
| Tris-EDTA buffer | Biosesang | T2142 | |
| Nuclease-Free Water | Qiagen | 129114 | |
| 5M Sodium Chloride solution | Biosesang | s2007 | |
| PEG 8000 | Sigma Aldrich | 1546605 | |
| 10N NaOH | Biosesang | S2038 | |
| Uranyl formate | Thomas Science | C993L42 | |
| Thermal cycler C1000 | Biorad | ||
| Nanodropic 2000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | ||
| TEM (LIBRA 120) | Carl Zeiss | ||
| Fluorometer Enspire 2300 | Perkin-Elmer | ||
| Centrifuge | Labogene | LZ-1580 |
References
- Andersen, E. S., et al. Self-assembly of a nanoscale DNA box with a controllable lid. Nature. 459 (7243), 73-76 (2009).
- Cha, T. -. G., et al. Design principles of DNA enzyme based walkers: Translocation kinetics and photo-regulation. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 137 (29), 9429-9437 (2015).
- Gerling, T., Wagenbauer, K. F., Neuner, A. M., Dietz, H. Dynamic DNA devices and assemblies formed by shape-complementary, non-base pairing 3D components. Science. 347 (6229), 1446-1452 (2015).
- Pinheiro, A. V., Han, D., Shih, W. M., Yan, H. Challenges and opportunities for structural DNA nanotechnology. Nature nanotechnology. 6 (12), 763-772 (2011).
- Li, J., et al. Exploring the speed limit of toehold exchange with a cartwheeling DNA acrobat. Nature Nanotechnology. 1, (2018).
- Krishnan, Y., Simmel, F. C. Nucleic acid based molecular devices. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 50 (14), 3124-3156 (2011).
- Liu, M., et al. A DNA tweezer-actuated enzyme nanoreactor. Nature communications. 4, 2127 (2013).
- Douglas, S. M., Bachelet, I., Church, G. M. A logic-gated nanorobot for targeted transport of molecular payloads. Science. 335 (6070), 831-834 (2012).
- Kuzyk, A., et al. Reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules. Nature Materials. 13 (9), 862-866 (2014).
- Zhou, C., Duan, X., Liu, N. A plasmonic nanorod that walks on DNA origami. Nature communications. 6, 8102 (2015).
- Choi, Y., Choi, H., Lee, A. C., Lee, H., Kwon, S. A Reconfigurable DNA Accordion Rack. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 57 (11), 2811-2815 (2018).
- Chen, H., et al. Understanding the Mechanical Properties of DNA Origami Tiles and Controlling the Kinetics of their Folding and Unfolding Reconfiguration. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 136 (19), 6995-7005 (2014).
- Han, D., Pal, S., Liu, Y., Yan, H. Folding and cutting DNA into reconfigurable topological nanostructures. Nature Nanotechnology. 5 (10), 712-717 (2010).
- Douglas, S. M., et al. Rapid prototyping of 3D DNA-origami shapes with caDNAno. Nucleic Acids Research. 37 (15), 5001-5006 (2009).
- Castro, C. E., et al. A primer to scaffolded DNA origami. Nature methods. 8 (3), 221-229 (2011).
- Ouldridge, T. E., Louis, A. A., Doye, J. P. K. DNA Nanotweezers Studied with a Coarse-Grained Model of DNA. Physical Review Letters. 104 (17), 178101 (2010).
- Snodin, B. E. K., et al. Direct Simulation of the Self-Assembly of a Small DNA Origami. ACS Nano. 10 (2), 1724-1737 (2016).
- Amir, Y., Abu-Horowitz, A., Bachelet, I. Folding and Characterization of a Bio-responsive Robot from DNA Origami. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (106), e51272 (2015).
- Stahl, E., Martin, T. G., Praetorius, F., Dietz, H. Facile and Scalable Preparation of Pure and Dense DNA Origami Solutions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 53 (47), 12735-12740 (2014).
- Wei, B., Vhudzijena, M. K., Robaszewski, J., Yin, P. Self-assembly of Complex Two-dimensional Shapes from Single-stranded DNA Tiles. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (99), e52486 (2015).
- Clegg, R. M. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer and nucleic acids. Methods in enzymology. 211, 353-388 (1992).
- Kopperger, E., et al. A self-assembled nanoscale robotic arm controlled by electric fields. Science. 359 (6373), 296-301 (2018).
- Lauback, S., et al. Real-time magnetic actuation of DNA nanodevices via modular integration with stiff micro-levers. Nature Communications. 9 (1), 1446 (2018).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved