A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Studying Large Amplitude Oscillatory Shear Response of Soft Materials
In This Article
Summary
We present a detailed protocol outlining how to perform nonlinear oscillatory shear rheology on soft materials, and how to run the SPP-LAOS analysis to understand the responses as a sequence of physical processes.
Abstract
We investigate the sequence of physical processes exhibited during large amplitude oscillatory shearing (LAOS) of polyethylene oxide (PEO) in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and xanthan gum in water — two concentrated polymer solutions used as viscosifiers in foods, enhanced oil recovery, and soil remediation. Understanding the nonlinear rheological behavior of soft materials is important in the design and controlled manufacturing of many consumer products. It is shown how the response to LAOS of these polymer solutions can be interpreted in terms of a clear transition from linear viscoelasticity to viscoplastic deformation and back again during a period. The LAOS results are analyzed via the fully quantitative Sequence of Physical Processes (SPP) technique, using free MATLAB-based software. A detailed protocol of performing a LAOS measurement with a commercial rheometer, analyzing nonlinear stress responses with the freeware, and interpreting physical processes under LAOS is presented. It is further shown that, within the SPP framework, a LAOS response contains information regarding the linear viscoelasticity, the transient flow curves, and the critical strain responsible for the onset of nonlinearity.
Introduction
Concentrated polymeric solutions are used in a variety of industrial applications primarily to increase viscosity, including in foods1 and other consumer products2, enhanced oil recovery3, and soil remediation4. During their processing and use, they are necessarily subjected to large deformations over a range of timescales. Under such processes, they demonstrate rich and complex nonlinear rheological behaviors that depend on the flow or deformation conditions1. Understanding these complex nonlinear rheological behaviors is essential for successfully controlling processes, designing superior products, and maximizing energy efficiency. Aside from the industrial importance, there is a great deal of academic interest in understanding the rheological behaviors of polymeric materials far from equilibrium.
Oscillatory shear tests are a staple component of every thorough rheological characterization because of the orthogonal application of strain and strain rate5, and the ability to independently control the length and time scales probed by tuning the amplitude and frequency. The stress response to small amplitude oscillatory shear strains, which are small enough not to disturb a material's internal structure, can be decomposed into components in phase with the strain and in phase with strain rate. The coefficients of the components in phase with the strain and the strain rate are collectively referred to as the dynamic moduli6,7, and individually as the storage modulus,  , and loss modulus,
, and loss modulus, 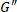 . The dynamic moduli lead to clear elastic and viscous interpretations. However, interpretations based on these dynamic moduli are valid only for small strain amplitudes, where the stress responses to sinusoidal excitations are also sinusoidal. This regime is generally referred to as the small amplitude oscillatory shear (SAOS), or the linear viscoelastic regime. As the imposed deformation becomes larger, changes are induced in the material microstructure, which are reflected in the complexity of the non-sinusoidal transient stress responses8. In this rheologically nonlinear regime, which more closely mimics industrial processing and consumer usage conditions, the dynamic moduli act as poor descriptions of the response. Another way to understand how concentrated soft materials behave out of equilibrium is therefore required.
. The dynamic moduli lead to clear elastic and viscous interpretations. However, interpretations based on these dynamic moduli are valid only for small strain amplitudes, where the stress responses to sinusoidal excitations are also sinusoidal. This regime is generally referred to as the small amplitude oscillatory shear (SAOS), or the linear viscoelastic regime. As the imposed deformation becomes larger, changes are induced in the material microstructure, which are reflected in the complexity of the non-sinusoidal transient stress responses8. In this rheologically nonlinear regime, which more closely mimics industrial processing and consumer usage conditions, the dynamic moduli act as poor descriptions of the response. Another way to understand how concentrated soft materials behave out of equilibrium is therefore required.
A number of recent studies9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16 have shown that materials pass through diverse intra-cycle structural and dynamical changes elicited by larger deformations in the medium amplitude oscillatory shear (MAOS)15,17 and large amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS) regimes. The intra-cycle structural and dynamical changes have different manifestations, such as breakage of microstructure, structural anisotropy, local rearrangements, reformation, and changes in diffusivity. These intra-cycle physical changes in the nonlinear regime lead to the complex nonlinear stress responses that cannot be simply interpreted with the dynamic moduli. As an alternative, several approaches have been suggested for the interpretation of the nonlinear stress responses. Common examples of this are Fourier transform rheology (FT rheology)18, power series expansions11, the Chebyshev description19, and the sequence of physical processes (SPP)5,8,13,14,20 analysis. Although all of these techniques have been shown to be mathematically robust, it is still an unanswered question as to whether any of these techniques can provide clear and reasonable physical explanations of nonlinear oscillatory stress responses. It remains an outstanding challenge to provide concise interpretations of rheological data that correlate to structural and dynamical measures.
In a recent study, the nonlinear stress response of the Soft Glassy Rheology (SGR) model8 and a soft glass made of colloidal star polymers7under oscillatory shear was analyzed through the SPP scheme. Temporal changes in the elastic and viscous properties inherent in nonlinear stress responses were separately quantified by the SPP moduli, 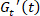 and
and 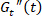 . Furthermore, the rheological transition represented by the transient moduli was accurately correlated to microstructural changes represented by the distribution of mesoscopic elements. In the study of the SGR model8, it was clearly shown that rheological interpretation via the SPP scheme accurately reflects the physical changes under all oscillatory shear conditions in the linear and nonlinear regimes for soft glasses. This unique capability to provide accurate physical interpretation of nonlinear responses of soft glasses makes the SPP method an attractive approach for researchers studying out-of-equilibrium dynamics of polymer solutions and other soft materials.
. Furthermore, the rheological transition represented by the transient moduli was accurately correlated to microstructural changes represented by the distribution of mesoscopic elements. In the study of the SGR model8, it was clearly shown that rheological interpretation via the SPP scheme accurately reflects the physical changes under all oscillatory shear conditions in the linear and nonlinear regimes for soft glasses. This unique capability to provide accurate physical interpretation of nonlinear responses of soft glasses makes the SPP method an attractive approach for researchers studying out-of-equilibrium dynamics of polymer solutions and other soft materials.
The SPP scheme is built around viewing rheological behaviors as occurring in a three-dimensional space (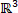 ) that consists of the strain (
) that consists of the strain (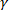 ), strain rate (
), strain rate (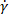 ), and stress (
), and stress ( )5. In a mathematical sense, the stress responses are treated as multivariable functions of the strain and strain rate (
)5. In a mathematical sense, the stress responses are treated as multivariable functions of the strain and strain rate (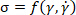 ). As the rheological behavior is regarded as a trajectory in
). As the rheological behavior is regarded as a trajectory in 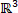 (or a multivariable function), a tool for discussing the properties of a trajectory is required. In the SPP approach, the transient moduli
(or a multivariable function), a tool for discussing the properties of a trajectory is required. In the SPP approach, the transient moduli 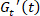 and
and 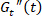 play such a role. The transient elastic modulus
play such a role. The transient elastic modulus 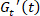 and viscous modulus
and viscous modulus 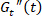 are defined as partial derivatives of the stress with respect to the strain (
are defined as partial derivatives of the stress with respect to the strain (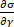 ) and the strain rate (
) and the strain rate (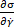 ). Following the physical definition of differential elastic and viscous moduli, the transient moduli quantify the instantaneous influence of strain and strain rate on the stress response respectively, whereas other analysis methods cannot provide any information on elastic and viscous properties separately.
). Following the physical definition of differential elastic and viscous moduli, the transient moduli quantify the instantaneous influence of strain and strain rate on the stress response respectively, whereas other analysis methods cannot provide any information on elastic and viscous properties separately.
The SPP approach enriches the interpretation of the oscillatory shear tests. With the SPP analysis, the complex nonlinear rheological behaviors of concentrated polymeric solutions in LAOS can be directly related to the linear rheological behaviors in SAOS. We show in this work how the maximum transient elastic modulus (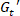 max) near the strain extrema corresponds to the storage modulus in the linear regime (SAOS). Furthermore, we show how the transient viscous modulus (
max) near the strain extrema corresponds to the storage modulus in the linear regime (SAOS). Furthermore, we show how the transient viscous modulus (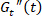 ) during a LAOS cycle traces the steady state flow curve. In addition to providing details of the complex sequence of processes that concentrated polymer solutions go through under LAOS, the SPP scheme also provides information regarding the recoverable strain in the material. This information, which is not obtainable through other approaches, is a useful measure of how much a material will recoil once stress is removed. Such behavior has impact on the printability of concentrated solutions for 3D printing applications, as well as screen printing, fiber formation, and flow cessation. A number of recent studies5,8,13 clearly indicate that the recoverable strain is not necessarily the same as the strain imposed during LAOS experiments. For instance, a study of soft colloidal glasses under LAOS13 found that the recoverable strain is only 5% when significantly larger total strain (420%) is imposed. Other studies16,21,22,23,24 using the cage modulus21 also conclude that linear elasticity can be observed under LAOS at the point close to the strain maxima, implying that the materials experienced relatively small deformation at those instants. The SPP scheme is the only framework for understanding LAOS that accounts for a shift in the strain equilibrium that leads to a difference between the recoverable and the total strains.
) during a LAOS cycle traces the steady state flow curve. In addition to providing details of the complex sequence of processes that concentrated polymer solutions go through under LAOS, the SPP scheme also provides information regarding the recoverable strain in the material. This information, which is not obtainable through other approaches, is a useful measure of how much a material will recoil once stress is removed. Such behavior has impact on the printability of concentrated solutions for 3D printing applications, as well as screen printing, fiber formation, and flow cessation. A number of recent studies5,8,13 clearly indicate that the recoverable strain is not necessarily the same as the strain imposed during LAOS experiments. For instance, a study of soft colloidal glasses under LAOS13 found that the recoverable strain is only 5% when significantly larger total strain (420%) is imposed. Other studies16,21,22,23,24 using the cage modulus21 also conclude that linear elasticity can be observed under LAOS at the point close to the strain maxima, implying that the materials experienced relatively small deformation at those instants. The SPP scheme is the only framework for understanding LAOS that accounts for a shift in the strain equilibrium that leads to a difference between the recoverable and the total strains.
This article aims to facilitate understandings and ease of use of the SPP analysis method by providing a detailed protocol for a LAOS analysis freeware, using two concentrated polymer solutions, a 4 wt% xanthan gum (XG) aqueous solution and a 5 wt% PEO in DMSO solution. These systems are chosen because of their broad range of application and rheologically interesting properties. Xanthan gum, a natural high-molecular-weight polysaccharide, is an exceptionally effective stabilizer for aqueous systems and commonly applied as a food additive to provide desired viscosification or in oil drilling to increase viscosity and yield points of drilling muds. PEO has a unique hydrophilic property and is often used in pharmaceutical products and controlled release systems as well as soil remediation activities. These polymeric systems are tested under various oscillatory shear conditions that are intended to approximate processing, transport, and end-use conditions. Although these practical conditions may not necessarily involve flow reversal as in oscillatory shear, the flow field can be easily approximated and tuned with the independent control of applied amplitude and imposed frequency in an oscillatory test. Furthermore, the SPP scheme can be used as described here to understand a broad range of flow types, including those that do not include flow reversals such as the recently-proposed UD-LAOS25, in which large amplitude oscillations are applied in one direction only (leading to the moniker "uni-directional LAOS"). For simplicity, and for illustrative purposes, we restrict the current study to traditional LAOS, which does include periodic flow reversal. The measured rheological responses are analyzed with the SPP approach. We demonstrate how to use the SPP software with simple explanations on salient calculation steps to improve readers' understanding and usage. A legend for interpreting the SPP analysis results is introduced, according to which the type of rheological transition is identified. Representative SPP analysis results of the two polymers under various oscillatory shear conditions are displayed, in which we clearly identify a sequence of physical processes that contains information on the material's linear viscoelastic response as well as the steady-state flow properties of the material.
This protocol provides salient details of how to accurately perform nonlinear rheological experiments, as well as a step-by-step guide to analyzing and understanding rheological responses with the SPP framework, as shown in Figure 1. We begin by providing an introduction to the instrument setup and calibrations, followed by specific commands for making a commercially-available rheometer collect high-quality transient data. Once the rheological data have been obtained, we introduce the SPP analysis freeware, with a detailed manual. Further, we discuss how to understand the time-dependent response of the two concentrated polymer solutions within the SPP scheme, by comparing the results obtained from LAOS with the linear-regime frequency sweep and the steady-state flow curve. These results clearly identify that the polymer solutions transition between distinct rheological states within an oscillation, allowing for a more detailed picture of their nonlinear transient rheology to emerge. These data can be used to optimize processing conditions for product formation, transport, and use. These time-dependent responses further provide potential pathways to clearly form structure-property-processing relationships by coupling the rheology with microstructural information obtained from small-angle scattering of neutrons, X-rays, or light (SANS, SAXS, and SALS, respectively), microscopy, or detailed simulations.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. Rheometer Setup
- With the rheometer configured in the SMT mode (see note), attach the upper and lower drive geometries. To maintain as close to a homogeneous shear field as possible, use a 50 mm plate (PP50) as the lower fixture, and a 2-degree cone (CP50-2) for the upper fixture.
Note: The rheometer we use (see the Table of Materials) can be configured in either a combined motor-transducer (CMT) or separate motor transducer (SMT) mode. With only a single motor integrated in the rheometer head, it acts as a traditional CMT stress-controlled rheometer and the data obtained require inertia corrections. With two motors incorporated in a SMT mode, the upper motor operates solely as a torque transducer and the bottom motor acts as a drive unit thus converting the rheometer into a typical strain-controlled rheometer.- Attach the bottom and top geometries.
- Click the zero-gap button in the control panel.
- Navigate to start service function under the Measuring set tab on top. Run the inertia calibrations for the upper and lower measuring systems, found in the dropdown menu.
- Run adjustments for the upper and lower motors.
- Specify the desired temperature in the control panel.
Note: The measurements at which experiments on XG and PEO solutions are performed are 25 ± 0.1 °C and 35 ± 0.1 °C, respectively.
- Load the material of interest on top of the bottom geometry with a spatula or pipette, ensuring no air bubbles are entrained in the sample.
Note: Approximate volumes of material required to completely fill a geometry are provided in the rheometry software under Setup | Measuring Systems.- Load 1.14 mL to fill the cone-and-plate geometry. Load higher viscosity samples with a spatula, and less viscous materials with a pipette.
Note: A spatula is used to load the polymer solutions. - Command the measuring system to trim gap and gently trim the excess material at the edge of geometry with a square-ended spatula, ensuring the spatula remains perpendicular to the axis of the rheometer.
Note: The quality of material loading will affect the rheological results significantly and any apparent under- or over-filling should be avoided. - Press the continue button in the rheometry software to move to the measurement gap.
Note: A complete loading process is illustrated in Figure 2.
- Load 1.14 mL to fill the cone-and-plate geometry. Load higher viscosity samples with a spatula, and less viscous materials with a pipette.
2. Running Oscillatory Shear Tests
Note: Two ways of running oscillatory shear tests are introduced. The first approach is designed for sinusoidal stresses and strains only and was used to collect the data we report here. The second method allows for arbitrary stress or strain schedules to be set.
- Sinusoidal oscillatory shear
- Navigate to Large amplitude oscillatory shear-LAOS under My apps in the software. Go to the Measurement box and click strain variable.
- Specify the initial (1%) and final values (4,000%) of a strain amplitude sweep. Specify the imposed frequency of 0.316 rad/s. Define the desired total number of strain amplitudes as 16 in the specified amplitude range, which results in the point density of 5 points per decade.
- Check the Get waveform box at the top to collect transient responses.
- Click the start button at the top to start the experiments and the raw data will be displayed in the rheometry software automatically.
- Arbitrary Stress or Strain Schedules
- To impose arbitrary-defined deformation, click Waveform sine generator under My apps in the software.
- Define a list of strain values that correspond to the function that is to be applied (not restricted to sinusoidal waveform). Generate the value list in an external program.
- Click edit under the strain value in the measurement box. Copy and paste these numbers into the value list.
- Specify the number of data points, point duration, and interval time to adjust the imposed frequency. For instance, specify the number of data points and the interval time as 512 points and 6.2832 s, respectively, if a cycle of sinusoidal strain is pasted into strain value list with 512 points and the frequency of 1 rad/s is desired.
Note: This approach is not recommended for running sinusoidal oscillatory shear due to the limited number of oscillatory cycles, and also due to the fact that automatic corrections which are enabled in an oscillatory test mode on the rheometer are disabled in this mode. Nonetheless, because there are no assumptions of sinusoidal strain built into the SPP framework, one can arbitrarily define imposed strain functions according to the processing conditions or end use the materials may experience, and the SPP framework remains applicable to analyze the rheological response. - Check the Get waveform box at the top. Then click the start button at the top to start the experiments.
3. Performing SPP analysis (SPP-LAOS software)
Note: The SPP analysis software is a MATLAB-based freeware package for analyzing rheological data with the SPP framework and is attached as Supplementary Files 1‒621.
- Format the data files to be tab-delimited text (.txt) consisting of four columns in the order of {Time (s), Strain (-), Rate (1/s), Stress (Pa)}.
Note: Users may need to modify the number of header lines in the function files to be able to process their data. See sample data files (Supplementary Files 7‒9). - To run SPP-LAOS software, open the m-file named RunSPPplus_v1.m in MATLAB.
Note: While RunSPPplus_v1.m is the main script to run the analysis, the package contains other function files that will be called from the main script, including SPPplus_read_v1.m, SPPplus_fourier_v1.m, SPPplus_numerical_v1.m, SPPplus_print_v1.m and SPPplus_figure_v1.m. - Navigate to the section labeled User-defined variables, and specify the following variables.
- Filename: Specify the name of .txt file that will be used for the SPP analysis.
Note: The file must match the above format requirement. - Run state: Place the vector as [1, 0] to run Fourier analysis mode for regular oscillatory shear response.
Note: The software employs two different methods of calculating the instantaneous SPP moduli,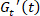 and
and 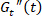 , based on Fourier transformation and numerical differentiation. The Fourier transform approach is designed for periodic input, such as oscillatory shear tests. Arbitrary time-dependent tests, which include, but are not limited to sinusoidal protocols, can be analyzed with the numerical differentiation approach.
, based on Fourier transformation and numerical differentiation. The Fourier transform approach is designed for periodic input, such as oscillatory shear tests. Arbitrary time-dependent tests, which include, but are not limited to sinusoidal protocols, can be analyzed with the numerical differentiation approach. - Run state: Input the vector as [0, 1] to run numerical-differentiation analysis mode for arbitrary time-dependent tests.
- Omega (Fourier analysis): Specify the angular frequency of oscillation, with units of rad/s.
- M (Fourier analysis): Define number of higher harmonics to be included in the SPP analysis. Adjust this number to include all the higher harmonics above the noise floor.
Note: This number must be a positive odd number and varies with amplitude and material. We include up to the 3rd harmonic in the MAOS regime, and up to the 55th harmonic at the largest amplitude investigated. - p (Fourier analysis): Specify the total number of periods of measuring time in the input data, which has to be a positive integer.
Note: The more periods of data that are collected, the higher the time resolution of the SPP parameters. - k (numerical differentiation): Define the step size for the numerical differentiation, which has to be a positive integer.
- num_mode (numerical differentiation): Specify num_mode to be either “0” (standard differentiation) or “1” (looped differentiation).
Note: There are two procedures implemented in the numerical differentiation scheme. The “standard differentiation” makes no assumptions about the form of the data. It utilizes a forward difference to calculate the derivative for the first 2,000 points of the data, a backward difference for the final 2,000 points, and a centered difference elsewhere. The “looped differentiation” assumes that the data is taken under steady-state periodic conditions, and includes an integer number of periods. These assumptions allow a centered difference to be calculated everywhere by looping over the ends of the data. - Select the run button at the top once all the variables are specified.
Note: The software will compute all SPP metrics associated with the data, and then display figures associated with the current analysis run and output a text file containing all the calculated SPP metrics for further analysis. - Iteratively adjust the number of harmonics to be included in the analysis from the output Fourier spectrum. Include all higher odd harmonics above the noise floor.
- Filename: Specify the name of .txt file that will be used for the SPP analysis.
4. Interpreting a LAOS Response
- Navigate to the Cole-Cole plot of the instantaneous SPP moduli
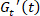 and
and 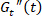 that is automatically generated by the SPP software.
that is automatically generated by the SPP software.
Note: A curve in the Cole-Cole plot is considered as the trajectory of the viscoelastic material state, and interpretations can be formed within an oscillation, in intra-cycle processes, or between successive periods, in inter-cycle processes. - Interpret stiffness by the instantaneous elastic modulus,
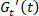 , and an increase/decrease of
, and an increase/decrease of 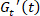 that indicates stiffening/softening. See Figure 3.
that indicates stiffening/softening. See Figure 3. - Interpret a material's viscosity based on the instantaneous viscous modulus,
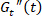 . An increase/decrease in this parameter represents thickening/thinning.
. An increase/decrease in this parameter represents thickening/thinning. - Transfer the focus to another Cole-Cole plot of the time derivatives of transient moduli
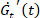 and
and 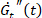 , which provide quantitative information about how much a response is stiffening (
, which provide quantitative information about how much a response is stiffening (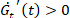 ), softening (
), softening ( ), thickening (
), thickening ( ), thinning ((
), thinning ((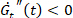 )). See Figure 3.
)). See Figure 3.
Note: With the values of the derivatives, the rate at which materials undergo stiffening/softening or thickening/thinning can be quantitatively determined. - Read the center of a trajectory (in a time-weighted average sense) in the Cole-Cole plot of
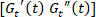 as the dynamic moduli, [
as the dynamic moduli, [
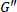 ].
].
Note: The dynamic moduli are averaged parameters over a cycle of deformation, and are insufficient to provide local information under LAOS. - Track the relative motion of the trajectory across amplitudes to understand the inter-cycle physics.
Note: Focusing on the relative motion of time-weighted average center is equivalent to a traditional strain amplitude sweep of the dynamic moduli. Nonetheless, one can easily analyze the across-amplitude motion of other specific points, for instance, the strain extrema. - Determine the transient differential viscosity
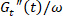 and overlay it on top of a steady-shear flow curve. Compare the transient LAOS response with steady-shear conditions.
and overlay it on top of a steady-shear flow curve. Compare the transient LAOS response with steady-shear conditions. - Determine the points of maximum
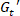 at the large amplitudes in the Cole-Cole plot of
at the large amplitudes in the Cole-Cole plot of 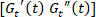 . See the star labeled in Figure 4c.
. See the star labeled in Figure 4c.
- Record the values of
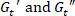 at those instants.
at those instants. - Plot them on top of the amplitude sweep of the dynamic moduli. See Figure 4d.
Note: Pay attention to any correspondence between the maximum transient elastic modulus and the linear viscoelastic .
.
- Record the values of
- Locate the instants of maximum
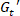 in the elastic Lissajous figure and record the corresponding strain values. See the star labeled in Figure 4a.
in the elastic Lissajous figure and record the corresponding strain values. See the star labeled in Figure 4a. - If
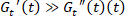 , then determine the equilibrium strain
, then determine the equilibrium strain 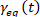 and the elastic strain
and the elastic strain 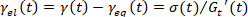 .
.
Note. With the displacement stress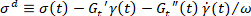 , when
, when 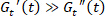 the equilibrium strain can be determined as
the equilibrium strain can be determined as 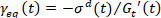 and the elastic strain can therefore be determined as the difference between strain and equilibrium strain5,13. The requirement of
and the elastic strain can therefore be determined as the difference between strain and equilibrium strain5,13. The requirement of 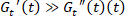 is derived and discussed elsewhere15.
is derived and discussed elsewhere15. - Plot the elastic strain as a function of the imposed strain amplitude. See Figure 4e. If the elastic strain is independent of the strain amplitude, then indicate this critical strain on the amplitude sweep as in Figure 4d.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Representative results of the SPP analysis from XG and PEO/DMSO solutions under oscillatory shear tests are presented in Figures 4 and 5. We first present the raw data as elastic (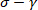 ) and viscous (
) and viscous (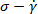 ) Lissajous-Bowditch curves in Figures 4a, 4b, 5a and 5b. ...
) Lissajous-Bowditch curves in Figures 4a, 4b, 5a and 5b. ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
We have demonstrated how to correctly perform large amplitude oscillatory shear rheometry tests using a commercial rheometer, and to run the SPP analysis freeware to interpret and understand the nonlinear stress responses of two distinct polymer solutions. The SPP framework, which has previously been shown to correlate with structural changes and facilitate understandings of numerous colloidal systems, can be equally applied to polymer systems. The responses of two concentrated polymeric solutions to LAOS have been inves...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Anton Paar for use of the MCR 702 rheometer through their VIP academic research program. We also thank Dr. Abhishek Shetty for the comments in the instrument setup.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| SPP analysis software | Simon Rogers Group (UIUC) | SPPplus_v1p1 | Attached as supplementary files |
| MATLAB | Mathwork | ||
| Rheometer | Anton Paar | MCR 702 TwinDrive | |
| 50mm 2-degree cone | Anton Paar | CP50-2 | Upper measuring system |
| 50mm plate | Anton Paar | PP50 | Lower measuring system |
| Xanthan gum (XG) | Sigma-Aldrich | 11138-66-2 | |
| Polyethylene oxide (PEO) | Sigma-Aldrich | 25322-68-3 | Mv=1,000,000 |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | Sigma-Aldrich | 67-68-5 |
References
- Dolz, M., Hernández, M. J., Delegido, J., Alfaro, M. C., Muñoz, J. Influence of xanthan gum and locust bean gum upon flow and thixotropic behaviour of food emulsions containing modified starch. Journal of Food Engineering. 81 (1), 179-186 (2007).
- Gupta, N., Zeltmann, S. E., Shunmugasamy, V. C., Pinisetty, D. Applications of Polymer Matrix Syntactic Foams. JOM. 66 (2), 245-254 (2013).
- Garcıa-Ochoa, F., Santos, V. E., Casas, J. A., Gómez, E. Xanthan gum: production, recovery, and properties. Biotechnology Advances. 18 (7), 549-579 (2000).
- Chang, I., Im, J., Prasidhi, A. K., Cho, G. -C. Effects of Xanthan gum biopolymer on soil strengthening. Construction and Building Materials. 74, 65-72 (2015).
- Rogers, S. A. In search of physical meaning: defining transient parameters for nonlinear viscoelasticity. Rheologica Acta. 56 (5), 501-525 (2017).
- Ferry, J. D. Viscoelastic properties of polymers. , John Wiley & Sons. (1980).
- Bird, R. B., Armstrong, R. C., Hassager, O. Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids. Volume 1: Fluid Mechanics. , John Wiley & Sons. New York. (1987).
- Park, J. D., Rogers, S. A. The transient behavior of soft glassy materials far from equilibrium. Journal of Rheology. 62 (4), 869-888 (2018).
- Rogers, S., Kohlbrecher, J., Lettinga, M. P. The molecular origin of stress generation in worm-like micelles, using a rheo-SANS LAOS approach. Soft Matter. 8 (30), 7831-7839 (2012).
- Lettinga, M. P., Holmqvist, P., Ballesta, P., Rogers, S., Kleshchanok, D., Struth, B. Nonlinear Behavior of Nematic Platelet Dispersions in Shear Flow. Phys Rev Lett. 109 (24), 246001(2012).
- Hyun, K., Wilhelm, M., et al. A review of nonlinear oscillatory shear tests: Analysis and application of large amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS). Progress in Polymer Science. 36 (12), 1697-1753 (2011).
- Park, J. D., Ahn, K. H., Lee, S. J. Structural change and dynamics of colloidal gels under oscillatory shear flow. Soft Matter. 11 (48), 9262-9272 (2015).
- Lee, C. -W., Rogers, S. A. A sequence of physical processes quantified in LAOS by continuous local measures. Korea-Australia Rheology Journal. 29 (4), 269-279 (2017).
- Rogers, S. A., Erwin, B. M., Vlassopoulos, D., Cloitre, M. A sequence of physical processes determined and quantified in LAOS: Application to a yield stress fluid. Journal of Rheology. 55 (2), 435-458 (2011).
- Wagner, M. H., Rolon-Garrido, V. H., Hyun, K., Wilhelm, M. Analysis of medium amplitude oscillatory shear data of entangled linear and model comb polymers. Journal of Rheology. 55 (3), 495-516 (2011).
- Radhakrishnan, R., Fielding, S. Shear banding in large amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOStrain and LAOStress) of soft glassy materials. Journal of Rheology. 62 (2), 559-576 (2018).
- Bharadwaj, N. A., Ewoldt, R. H. Constitutive model fingerprints in medium-amplitude oscillatory shear. Journal of Rheology. 59 (2), 557-592 (2015).
- Wilhelm, M. Fourier‐Transform Rheology. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering. 287 (2), 83-105 (2002).
- Ewoldt, R. H., Hosoi, A. E., McKinley, G. H. New measures for characterizing nonlinear viscoelasticity in large amplitude oscillatory shear. Journal of Rheology. 52 (6), 1427-1458 (2008).
- Rogers, S. A., Lettinga, M. P. A sequence of physical processes determined and quantified in large-amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS): Application to theoretical nonlinear models. Journal of Rheology. 56 (1), 1-25 (2011).
- Rogers, S. A. A sequence of physical processes determined and quantified in LAOS: An instantaneous local 2D/3D approach. Journal of Rheology. 56 (5), 1129-1151 (2012).
- Kim, J., Merger, D., Wilhelm, M., Helgeson, M. E. Microstructure and nonlinear signatures of yielding in a heterogeneous colloidal gel under large amplitude oscillatory shear. Journal of Rheology. 58 (5), 1359-1390 (2014).
- van der Vaart, K., Rahmani, Y., Zargar, R., Hu, Z., Bonn, D., Schall, P. Rheology of concentrated soft and hard-sphere suspensions. Journal of Rheology. 57 (4), 1195-1209 (2013).
- Poulos, A. S., Stellbrink, J., Petekidis, G. Flow of concentrated solutions of starlike micelles under large-amplitude oscillatory shear. Rheologica Acta. 52 (8-9), 785-800 (2013).
- Armstrong, M. J., Beris, A. N., Rogers, S. A., Wagner, N. J. Dynamic shear rheology of a thixotropic suspension: Comparison of an improved structure-based model with large amplitude oscillatory shear experiments. Journal of Rheology. 60 (3), 433-450 (2016).
- Calabrese, M. A., Wagner, N. J., Rogers, S. A. An optimized protocol for the analysis of time-resolved elastic scattering experiments. Soft Matter. 12 (8), 2301-2308 (2016).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved