A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Induction and Characterization of Pulmonary Hypertension in Mice using the Hypoxia/SU5416 Model
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes the induction of pulmonary hypertension (PH) in mice based on the exposure to hypoxia and the injection of a VEGF receptor antagonist. The animals develop PH and right ventricular (RV) hypertrophy 3 weeks after the initiation of the protocol. The functional and morphometrical characterization of the model is also presented.
Abstract
Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) is a pathophysiological condition, defined by a mean pulmonary arterial pressure exceeding 25 mm Hg at rest, as assessed by right heart catheterization. A broad spectrum of diseases can lead to PH, differing in their etiology, histopathology, clinical presentation, prognosis, and response to treatment. Despite significant progress in the last years, PH remains an uncured disease. Understanding the underlying mechanisms can pave the way for the development of new therapies. Animal models are important research tools to achieve this goal. Currently, there are several models available for recapitulating PH. This protocol describes a two-hit mouse PH model. The stimuli for PH development are hypoxia and the injection of SU5416, a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor antagonist. Three weeks after initiation of Hypoxia/SU5416, animals develop pulmonary vascular remodeling imitating the histopathological changes observed in human PH (predominantly Group 1). Vascular remodeling in the pulmonary circulation results in the remodeling of the right ventricle (RV). The procedures for measuring RV pressures (using the open chest method), the morphometrical analyses of the RV (by dissecting and weighing both cardiac ventricles) and the histological assessments of the remodeling (both pulmonary by assessing vascular remodeling and cardiac by assessing RV cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and fibrosis) are described in detail. The advantages of this protocol are the possibility of the application both in wild type and in genetically modified mice, the relatively easy and low-cost implementation, and the quick development of the disease of interest (3 weeks). Limitations of this method are that mice do not develop a severe phenotype and PH is reversible upon return to normoxia. Prevention, as well as therapy studies, can easily be implemented in this model, without the necessity of advanced skills (as opposed to surgical rodent models).
Introduction
Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) is a pathophysiological condition, defined by a mean pulmonary arterial (PA) pressure exceeding 25 mm Hg at rest, as assessed by right heart catheterization1,2. There is a variety of diseases that can lead to PH. In an attempt to organize the PH-associated conditions, several classification systems have been developed. The current clinical classification categorizes the multiple PH-associated diseases in 5 different groups1. This distinction is of importance since various groups of patients have diseases that differ in their clinical presentation, pathology, prognosis, and response to treatment2. Table 1 summarizes the current classification, complemented with the basic histopathological characteristics of each disease.
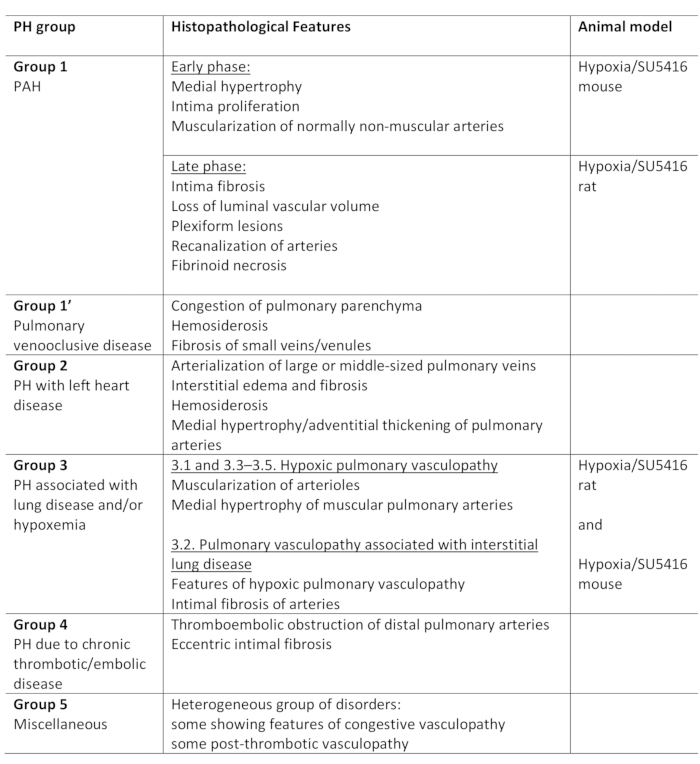
Table 1: Overview of the clinical classification of PH, along with the main histopathological features within the groups. Suitability of the Hypoxia/SU5416 protocol for modeling PH. This table has been modified from19. PH: Pulmonary Hypertension, PAH: Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Despite significant advances in the treatment of PH-associated diseases, PH still remains without a cure, with a 3-year mortality rate ranging between 20% and 80%3. This indicates the imperative need for understanding the underlying mechanisms of PH and, thereafter, the development of novel therapies to prevent, slow down the progression, and cure the disease. Animal models are of crucial importance to this scope. Currently, various models exist to study PH. The interested reader is referred to the excellent reviews on this topic2,3,4. Bearing in mind the variety of diseases leading to PH, it is obvious that the diverse conditions of human PH cannot be perfectly recapitulated in one animal model. The animal models available can be categorized in i) single-hit, ii) two-hit, iii) knockout, and iv) overexpression models3. In the single-hit models, PH is induced by a single pathological stimulus, whereas two-hit models combine two pathological stimuli with the goal of inducing more severe PH and thus more closely imitate the complex human disease. Besides the etiological differences, the several stimuli result in PH modeling differences that depend also on the species and the genetic background of the animals4.
One of the most commonly used classic PH rodent models is the chronic hypoxia model2. Hypoxia is known to induce PH in humans as well as in several animal species. Hypoxia has the advantage of being a physiologic stimulus for PH (Table 1). However, while the degree of hypoxia used for inducing PH in rodents is much more severe than in humans, the single insult (hypoxia) leads only to a mild form of vascular remodeling. This does not imitate the severity of the human disease. The addition of a second-hit, an extra stimulus for inducing PH, showed promising results: injection of the compound SU5416 to rodents combined with the hypoxic stimulus induces a more severe PH phenotype2,5,6. SU5416 is an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-2. It blocks the VEGF receptors and leads to endothelial cell apoptosis. Under hypoxic conditions, this stimulates the proliferation of a subset of apoptosis-resistant endothelial cells. Furthermore, SU5416 leads to smooth muscle cell proliferation. The combination of these effects results in pathologic vascular remodeling of the pulmonary circulation and leads to elevated PA pressure and right ventricular remodeling2,5,7. The model was first described in rats6 and later on applied to mice4,5,7. The mouse model exhibits less severe vascular remodeling compared to rats. Furthermore, when returned to normoxia, PH continues to progress in rats, while in mice it is partially reversible.
The following protocol describes all the steps for modeling PH in mice using the Hypoxia/SU5416 method (planning, timeline, execution). Additionally, the characterization of the model is described in this protocol: functionally (by invasively measuring the right ventricular (RV) pressure using the open chest technique), morphometrically (by dissecting and weighing both the right and left ventricles), as well as histologically (by evaluating pulmonary vascular remodeling, right ventricular cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and fibrosis).
All the steps and methods described in this protocol can be easily implemented by investigators at any experience level. While the functional measurements of the RV using the open chest technique (described here) is not the gold standard method in the field, it has the advantage that it can be quickly learned and accurately reproduced even by a less experienced experimenter.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
Prior to any animal experimentation obtain the local institutional animal care committee authorization. The current experiments were performed after approval by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
1. PH induction
- Preparation
- Before beginning the study, carefully plan the experimental design. Ensure that mice are subjected to hypoxia at the same time point as the first SU5416 injection. An example of the experimental design for inducing PH using the Hypoxia/SU5416 method is shown in Figure 1A. Control mice received only the vehicle. For this model, SU5416 will be injected to the mice once per week for 3 consecutive weeks.
- Use eight to twelve-week-old C57BL/6 mice for this study. House the animals at 18-20 °C in a 12-h light-dark cycle. Ensure that food and water are accessible ad libitum.
- Weigh the animals. Assign them randomly to each group: Normoxia and Hypoxia/SU5416.
- Prepare the hypoxic chamber as shown in Figure 1B. Secure nitrogen (N2) tanks near the chamber. Set the oxygen (O2) controller at a point of 10% O2. Let the system reach a steady state.
- Prepare SU5416 for injection (use a dose of 20 mg/kg body weight). SU5416 does not dissolve in aqueous solutions; therefore, dissolve the calculated amount in 100 μL DMSO8. For example, for a 25 g mouse, the amount of SU5416 to be injected is 0.5 mg dissolved in 100 μL solvent (DMSO). The final concentration of SU5416 for this mouse is, therefore, 5 mg/mL.
CAUTION: SU5416 is a hazardous material. Carefully read the Safety Data Sheet accompanied by the product and make sure to take the recommended precautions when handling this substance. Wear protective gloves and (as for any injection) use eye protection. The chemical structure of SU5416 is shown in Figure 1C.
NOTE: Calculate an appropriate excess of the solution to compensate for the volume that will be lost during injection (e.g. in the syringe, vial etc.). Depending on the syringe used, the dead volume is approximately 200 μL. For a group of 10 mice, calculate an excess of 2 mouse doses. - Prepare the syringes for injection. Use 1 mL syringes with a 25 G x 5/8” needles.
- SU5416 subcutaneous injection
- Restrain the animal. Place the mouse on the lid of the cage to assist restraint. Grasp the skin and form a tent parallel to the spine. Make sure to grasp to the back of the head tightly, to avoid the potential bite injury by the mouse.
NOTE: The presence of two investigators makes the procedure faster and more accurate as one can hold the animal while the other performs the injection. - Insert the needle subcutaneously over the flank at the loose fold of the skin. Make sure to insert the needle parallel to the skin. Avoid penetrating the abdominal wall.
- Inject the syringe’s content (100 μL of dissolved SU5416 or vehicle).
NOTE: In order to avoid leakage after complete delivery, hold the syringe for approximately 10 s and slightly rotate the needle under the skin. - Withdraw the needle and return the animal to its cage. After SU5416 injection, place the cages in the ventilated hypoxia chamber.
- Restrain the animal. Place the mouse on the lid of the cage to assist restraint. Grasp the skin and form a tent parallel to the spine. Make sure to grasp to the back of the head tightly, to avoid the potential bite injury by the mouse.
- Exposure to hypoxia
- Monitor the ventilation over time. Make sure to maintain 10% of the oxygen supply. Maintain normoxia animals in a semi-sealable chamber in at 21% O2.
- Ensure that the chambers are equipped with an oxygen sensor to measure the oxygen level. Avoid extensive opening of the chambers. For cleaning and adding food and water open the chambers for not more than 20 min every 3 days.
- Inspect animals daily. Consider stress signals such as piloerection or significant loss of weight.
NOTE: Animals under Hypoxia/SU5416 are expected to lose weight5. This is an indication of disease development. - Repeat SU5416 injection weekly for 3 consecutive weeks (see Figure 1A for the overview of the experimental design).
NOTE: Varying the site of injection can help reduce skin irritations.
2. Functional characterization by invasive RV pressure measurements
- Preparation
NOTE: Select an anesthetic regime. Injectable or inhalable anesthetics can be used. Since a slight overdose of injectable anesthetics (especially from ketamine/xylazine or pentobarbital) can significantly affect the heart function, the use of volatile anesthetics is recommended. It is of great importance to use the same anesthetic for all mice within a study.- Use a vaporizer to assure an accurate anesthetics dose per animal. The dose for isoflurane is as following: induction 3-4%, maintenance 1% mixed with 100% oxygen.
NOTE: Wear personal protective equipment and avoid breathing the vapor. - Prepare a heating pad and/or warming lamps for maintaining body temperature. Prepare a rectal temperature probe for monitoring body temperature.
- Ensure proper ventilation. Prepare the ventilator beforehand. Prepare the Y-tube connector and check the function of the ventilator using the manual mode. Ensure the inspiratory pressure is <1 cm H2O to avoid barotrauma. Set the respiratory rate at 110 breaths/min.
- Prepare an endotracheal tube by cutting a 20 G intravascular catheter.
- Prepare the instruments needed: small forceps, scissors, elastic hook retractors, vessel cauterizer, and cotton swabs. On a cotton swab adjust a small 25 G x 5/8” needle that will be used to make a small puncture in the right ventricle.
- Prepare the Pressure Catheter, the Pressure-volume Control Unit and initiate the data acquisition software. Place the PV Catheter in a 15 mL tube filled with PBS at 37 °C for 15 min and calibrate according to the manufacturer's protocol.
- For the perfusion and fixation of the organs, prepare PBS and a solution of 50% PBS / 50% OCT. Prepare 2 x 10 mL syringes (with a 25 G needle): one will be used for perfusing the heart and the lung with PBS in situ and the second one for injecting the OCT/ PBS (50/50) solution to the lung specimen that will be used for histologic examination.
- Use a vaporizer to assure an accurate anesthetics dose per animal. The dose for isoflurane is as following: induction 3-4%, maintenance 1% mixed with 100% oxygen.
- Intubation
- Weigh the mouse and record the health status before anesthesia.
- Induce anesthesia with 3-4% isoflurane. Check the anesthesia depth by testing the toe-pinch reflex: pinch the toe of one of the limbs firmly. If the animal withdraws the limb, it is a sign of insufficient anesthesia.
- After anesthesia induction, shave the neck and the chest areas.
- Place the mouse on the heating pad. Place a rectal temperature probe for monitoring body temperature.
NOTE: Maintenance of body temperature is of importance for the functional measurements. The body temperature should be approximately 36.5-37 °C. - Using curved forceps attach a suture thread to the upper incisors of the mouse, stretch and fix to the heating pad with surgical tape. Secure the limbs of the mouse using surgical tapes.
- For intubating the animal make a small incision of approximately 1 cm in the medial cervical skin using small scissors.
NOTE: Oral intubation is an alternative method that requires more experience. - With a cotton-tipped applicator separate bluntly the parotid and submandibular salivary glands at the midlevel. This will expose the muscles overlying the trachea.
- Carefully cut these muscles exposing the trachea.
- With small scissors make a small incision between the tracheal cartilages and insert the prepared endotracheal tube. Take out the metal guide of the intravascular catheter.
- Connect the catheter to the ventilator. Verify the tracheal tube position by manually gently inflating the lungs. Secure the position with tape.
- Maintain a 1% isoflurane anesthesia throughout the procedure.
- Regularly monitor the depth of anesthesia by testing the toe pinch reflex. Adjust the anesthesia accordingly.
NOTE: The recommended heart rate during the experiments, under 1% isoflurane anesthesia, is approximately 400 beats /min. Maintenance of body temperature and anesthesia are essential for controlling the heart rate. Excess of isoflurane can reduce the heart rate. However, recovery can be achieved by reducing the isoflurane rate.
- RV pressure measurements (open chest approach)
- With small scissors perform a skin incision of approximately 1 cm over the xiphoid process and the upper abdominal part. Separate the skin covering the chest and the abdominal wall of the upper abdominal quadrants: start at the middle line, distal to the xiphoid and carefully move laterally on both sides. Use thermocautery to control bleeding.
NOTE: The goal is to have access to the thoracic cavity through the abdominal wall. - Open the abdominal cavity and cut the diaphragm carefully, taking care not to injure the beating heart or the lungs.
NOTE: The goal is to expose the apex and the right ventricle of the heart. Good exposure and view of the heart are of crucial importance for the correct placement of the catheter. It is of great importance to avoid bleeding throughout the procedure. Even small changes in the intravasal volume can change the load of the right heart and affect the recorded parameters. - Gently remove the pericardium using a cotton-tipped applicator.
- Just before placing the pressure catheter in the heart, bring the catheter next to the mouse.
- Using the prepared cotton-tipped applicator with the needle makes a stab wound in the apical distal part of the right ventricle. Carefully remove the needle and insert the pressure catheter into this hole.
NOTE: This should work without applying force. In case this is not possible, try making a new hole near the first one in order to avoid extended injury of the heart. The needle should not be inserted more deeply than approximately 3 mm. - Insert the pressure catheter parallel to the direction of the right ventricle, with the tip facing the pulmonary artery.
- Watch the pressure wave tracing to ensure the correct positioning of the catheter. Representative tracings are demonstrated in Figure 2.
- Allow the pressure signal to stabilize. Pause respirations and obtain at least 3 measurements. In between the individual measurements allow the animal to be ventilated.
- Once all measurements are recorded remove the catheter and place it back in the PBS filled tube in the water bath.
NOTE: After completion of the experiment, clean the catheter according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- With small scissors perform a skin incision of approximately 1 cm over the xiphoid process and the upper abdominal part. Separate the skin covering the chest and the abdominal wall of the upper abdominal quadrants: start at the middle line, distal to the xiphoid and carefully move laterally on both sides. Use thermocautery to control bleeding.
- Euthanasia and lung perfusion
- Upon completion of the experiment euthanize the mouse by exsanguination.
- Open the chest widely. Using scissors, cut the entire sternum and pay attention not to injure the heart or the lungs.
- Using iris scissors makes a small incision in the left ventricle to allow blood to leave the chamber.
- Place the 25 G needle of a syringe containing 10 mL of PBS in the right ventricle and inject the PBS solution until the lungs are cleared of blood.
- Once this step is completed, confirm euthanasia by vital tissue harvest (heart and lungs): cut the cava and aortic attachments and remove the heart and lungs en block.
3. Morphometric characterization
- Immediately after removing the heart and lungs (Step 2.4.5), isolate the heart and remove both atria. With curved tenotomy scissors dissect carefully the right ventricle (RV) from the left ventricle (LV), leaving the septum (S) with the left ventricle. Weigh RV and LV+S and calculate the Fulton index= RV/LV+ S (Figure 3)5,9.
- Take a part of the right ventricle and place it in an OCT prefilled embedding mold. Use the other part of the right ventricle for RNA and/or protein analysis. Snap freeze in dry ice and store at -80 °C.
- Use iris scissors to isolate the lungs from the heart and any other remaining tissue.
NOTE: For the preparation of the lungs, the perfusion as described above (Steps 2.4.3-2.4.5) is of great importance. - Snap freeze part of the lungs and store it for RNA, protein extraction or other assays.
- Use the other part of the lungs for histological analysis. For this purpose, insert the syringe containing 50% PBS and 50% OCT in a bronchus of the used lobe10,11. The experimenter can easily see that the lung gets inflated when the syringe’s content is perfused in the tissue.
- Place these pieces of lung in embedding molds prefilled with OCT and snap freeze them in dry ice. Store the samples at -80 °C after they are frozen.
- Prepare 8 μm sections of RV and lung using a cryostat machine. Air dry the sections at room temperature for 30 min.
- Fix the slides at room temperature using 10% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 min.
NOTE: PFA is a known human carcinogen. Reduce the exposure risk by using a chemical fume hood, proper procedures and personal protective equipment. Refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for further information. - Vascular remodeling assessment by Hematoxylin/Eosin staining
Note: Perform Hematoxylin/Eosin staining in order to assess the structural changes of the heart and vascular remodeling in the lung (Figure 3).- Stain with Hematoxylin solution for 8 min.
- Rinse with running tap water for 5 min followed by a quick rinse in distilled water.
- Rinse in 95% EtOH for 1 min and counter-stain in the Eosin solution for 1 min.
- Dehydrate (80% Ethanol 10-30 s, 100 Ethanol for 1 min and 100% Toluol for 3 min).
- Mount and cover with a coverslip. Dry the slides overnight at room temperature.
NOTE: The solutions used for staining may be hazardous. Reduce the exposure risk by using a chemical fume hood, proper procedures and personal protective equipment. Refer to the MSDS for further information.
- Right ventricular fibrosis assessment by Picrosirius Red Staining
NOTE: In the Picrosirius Red Staining, Picrosirius Red, which is acid, binds to collagen12. Therefore, this staining can be used for a histological examination of the collagen content.- Incubate the slides in a preheated Bouin’s Solution at 58 °C for 1 h.
- Wash the slides in running tap water to remove yellow color from sections for 10-15 min.
- Stain in 0.1% Fast Green for 20 min at room temperature.
- Rinse in 1% Acetic Acid for 1 min.
- Rinse in tap water for 5 min.
- Stain in 0.1% Sirius red for 30 min at room temperature followed by dehydration in Toluol.
CAUTION: The solutions used for staining may be hazardous. Reduce the exposure risk by using a chemical fume hood, proper procedures and personal protective equipment. Refer to the MSDS for further information.
- RV cardiomyocyte hypertrophy assessment by WGA Staining
NOTE: Hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) at the cellular level can be assessed by performing a Wheat Germ Agglutinin (WGA) staining (Figure 4).- Fix the slides in cold Acetone solution for 15 min followed by 3 steps of washing in PBS (5 min each).
- Block with 10% goat serum in a Dako solution for 30 min at room temperature.
- Incubate the slides with WGA: Add WGA 1:200 and incubate for 1 ½ h at 37 °C in the dark.
- Wash the slides three times with PBS.
- Incubate the slides with a nucleic acid dye.
- Wash the slides three times with PBS.
- For mounting, remove the excess of liquid and apply mounting media and a coverslip. Dry the slides for 1 hour at room temperature in the dark and store at 4 °C.
NOTE: The solutions used for staining may be hazardous. Reduce the exposure risk by using a chemical fume hood, proper procedures and personal protective equipment. Refer to the MSDS for further information.
- Perform immunochemistry of the lung to further and specifically assess vascular remodeling. For example, smooth muscle cell staining can be used to assess the muscularization of the vessels, while von Willebrand Factor staining can be used to visualize endothelial changes. These methods are described elsewhere5.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
In this protocol, we describe in detail the creation of the Hypoxia/SU5416 model for inducing PH in mice. Furthermore, we detail all the needed steps for performing pulmonary vascular and cardiac evaluation at the end of the observation period.
An overview of the experimental design for this model is shown in Figure 1A13,14. Mice are subjected to normobaric hypoxia (10% O2
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
This protocol describes how to model PH in mice by combining two pathological stimuli: chronic hypoxia and SU5416 injection (Hypoxia/SU5416)18. In an attempt to correlate this mouse model with the human PH condition, one inevitably must look at the current PH classification, shown in Table 1. PH in almost all forms is characterized by pulmonary vasoconstriction and aberrant proliferation of endothelial and smooth muscle cells. This leads to elevated pressure in the pulmonary arter...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to declare.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the American Heart Association (AHA- 17SDG33370112 and 18IPA34170258) and from the National Institutes of Health NIH K01 HL135474 to Y.S. O.B was supported by the Deutsche Herzstiftung.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acetic acid glacial | Roth | 3738.1 | |
| Acetone, Histology Grade | The Lab Depot | VT110D | |
| ADVantage Pressure-Volume System | Transonic | ADV500 | |
| Bouin's solution | Sigma | Ht10132 | |
| Cautery System | Fine Science Tools | 18000-00 | |
| Connection tubing and valves | |||
| Cotton-Tipped Applicators | Covidien | 8884541300 | |
| Coverslips, 24 x50 mm | Roth | 1871 | |
| Data Acquisition and Analysis | Emka | iox2 | |
| Direct Red 80 | Sigma | 365548-5G | |
| DMSO (Dimethyl Sulfoxide) | Sigma Aldrich | 276855 | |
| Dry ice | |||
| Dumont # 5 forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11251-10 | |
| Dumont # 7 Fine Forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11274-20 | |
| Embedding molds | Sigma Aldrich | E-6032 | |
| Eosin Solution Aqueous | Sigma | HT110216 | |
| Ethanol, laboratory Grade | Carolina Biological Supply Company | 861285 | |
| Fast Green FCF | Sigma | F7252-5G | |
| Fine scissors | Fine Science Tools | 14090-09 | |
| Goat Serum | invitrogen | 16210-064 | |
| Heating pad | Gaymar | T/Pump | |
| Hematoxylin 2 | Thermo Scientific | 7231 | |
| Hypoxic chamber | Biospherix | A30274P | |
| Induction chamber | DRE Veterinary | 12570 | |
| Intubation catheter (i.v. catheter SurFlash (20 G x 1") ) | Terumo | SR*FF2025 | |
| Iris scissors | Fine Science Tools | 14084-08 | |
| Isoflurane | Baxter | NDC-10019-360-40 | |
| Isoflurane vaporizer | DRE Veterinary | 12432 | |
| Mice (C57BL/6) | Charles River | ||
| Needles 25 G x 5/8" | BD | 305122 | |
| OCT | Tissue Tek | 4583 | |
| PBS (Phosphate Buffered Saline) | Corning | 21-031-CV | |
| Piric Acid- Saturated Solution 1.3 % | Sigma | P6744-1GA | |
| Pressure volume catheter | Transonic | FTH-1212B-4018 | |
| Retractor | Kent Scientific | SURGI-5001 | |
| Static oxygen Controller ProOx 360 | Biospherix | P360 | |
| SU 5416 | Sigma Aldrich | S8442 | |
| Surgical Suture, black braided silk, 5.0 | Surgical Specialties Corp. | SP116 | |
| Surgical tape | 3M | 1527-1 | |
| Syringe 10 ml | BD | 303134 | |
| Syringes with needle 1 ml | BD | 309626 | |
| Sytox Green Nuclein Acid Stain | Thermo Scientific | S7020 | |
| Tenotomy scissors | Pricon | 60-521 | |
| Toluol | Roth | 9558.3 | |
| Ventilator | CWE | SAR-830/P | |
| WGA Alexa Fluor | Thermo Scientific | W11261 | |
| Xylene | Roth |
References
- Galie, N., et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). European Heart Journal. 37 (1), 67-119 (2016).
- Stenmark, K. R., Meyrick, B., Galie, N., Mooi, W. J., McMurtry, I. F. Animal models of pulmonary arterial hypertension: the hope for etiological discovery and pharmacological cure. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cell Molecular Physiology. 297 (6), 1013-1032 (2009).
- Maarman, G., Lecour, S., Butrous, G., Thienemann, F., Sliwa, K. A comprehensive review: the evolution of animal models in pulmonary hypertension research; are we there yet. Pulmonary Circulation. 3 (4), 739-756 (2013).
- Gomez-Arroyo, J., et al. A brief overview of mouse models of pulmonary arterial hypertension: problems and prospects. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cell Molecular Physiology. 302 (10), 977-991 (2012).
- Ciuclan, L., et al. A novel murine model of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 184 (10), 1171-1182 (2011).
- Taraseviciene-Stewart, L., et al. Inhibition of the VEGF receptor 2 combined with chronic hypoxia causes cell death-dependent pulmonary endothelial cell proliferation and severe pulmonary hypertension. FASEB Journal. 15 (2), 427-438 (2001).
- Vitali, S. H., et al. The Sugen 5416/hypoxia mouse model of pulmonary hypertension revisited: long-term follow-up. Pulmonary Circulation. 4 (4), 619-629 (2014).
- Breen, E. C., Scadeng, M., Lai, N. C., Murray, F., Bigby, T. D. Functional magnetic resonance imaging for in vivo quantification of pulmonary hypertension in the Sugen 5416/hypoxia mouse. Experimental Physiology. 102 (3), 347-353 (2017).
- Wang, Z., Schreier, D. A., Hacker, T. A., Chesler, N. C. Progressive right ventricular functional and structural changes in a mouse model of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Physiological Reports. 1 (7), 00184(2013).
- Momcilovic, M., et al. Utilizing 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging and Quantitative Histology to Measure Dynamic Changes in the Glucose Metabolism in Mouse Models of Lung Cancer. Journal of Visualized Experiment. (137), 57167(2018).
- Guma, S. R., et al. Natural killer cell therapy and aerosol interleukin-2 for the treatment of osteosarcoma lung metastasis. Pediatric Blood Cancer. 61 (4), 618-626 (2014).
- Lattouf, R., et al. Picrosirius red staining: a useful tool to appraise collagen networks in normal and pathological tissues. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 62 (10), 751-758 (2014).
- Penumatsa, K. C., et al. Transglutaminase 2 in pulmonary and cardiac tissue remodeling in experimental pulmonary hypertension. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cell Molecular Physiology. 313 (5), 752-762 (2017).
- Wang, Z., et al. Organ-level right ventricular dysfunction with preserved Frank-Starling mechanism in a mouse model of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Journal of Applied Physiology. 124 (5), 1244-1253 (2018).
- van de Veerdonk, M. C., Bogaard, H. J., Voelkel, N. F. The right ventricle and pulmonary hypertension. Heart Failure Reviews. 21 (3), 259-271 (2016).
- Emde, B., Heinen, A., Godecke, A., Bottermann, K. Wheat germ agglutinin staining as a suitable method for detection and quantification of fibrosis in cardiac tissue after myocardial infarction. European Journal of Histochemistry. 58 (4), 2448(2014).
- Pena, S. D., Gordon, B. B., Karpati, G., Carpenter, S. Lectin histochemistry of human skeletal muscle. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 29 (4), 542-546 (1981).
- Bueno-Beti, C., Hadri, L., Hajjar, R. J., Sassi, Y. The Sugen 5416/Hypoxia Mouse Model of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1816, 243-252 (2018).
- Colvin, K. L., Yeager, M. E. Animal Models of Pulmonary Hypertension: Matching Disease Mechanisms to Etiology of the Human Disease. Journal of Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine. 4 (4), (2014).
- Benza, R. L., et al. Predicting survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: insights from the Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-Term Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Disease Management (REVEAL). Circulation. 122 (2), 164-172 (2010).
- Jacob, S. W., Rosenbaum, E. E. The toxicology of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Headache. 6 (3), 127-136 (1966).
- Jacob, S. W., Wood, D. C. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Toxicology, pharmacology, and clinical experience. American Journal of Surgery. 114 (3), 414-426 (1967).
- Abraham, D., Mao, L. Cardiac Pressure-Volume Loop Analysis Using Conductance Catheters in Mice. Journal of Visualized Experiment. (103), 52942(2015).
- Ma, Z., Mao, L., Rajagopal, S. Hemodynamic Characterization of Rodent Models of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Journal of Visualized Experiment. (110), 53335(2016).
- Townsend, D. Measuring Pressure Volume Loops in the Mouse. Journal of Visualized Experiment. (111), 53810(2016).
- Penumatsa, K. C., Warburton, R. R., Hill, N. S., Fanburg, B. L. CrossTalk proposal: The mouse SuHx model is a good model of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Journal of Physiology. 597 (4), 975-977 (2019).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved