Method Article
Activación y conjugación de polisacáridos solubles utilizando 1-ciano-4-dimetilaminopiridina tetrafluoroborato (CDAP)
En este artículo
Erratum Notice
Resumen
Las proteínas y los ligandos que contienen aminas pueden unrse covalentemente a polisacáridos activados por el reactivo de cianilación, 1-ciano-4-dimetilaminopiridina tetrafluoroborato (CDAP), para formar conjugados de proteína covalente (ligando)-polisacárido. Este artículo describe un protocolo mejorado para llevar a cabo la activación controlada de CDAP a 0 °C y variando el pH y realizar la posterior conjugación de los polisacáridos activados.
Resumen
Las vacunas conjugadas son avances notables en vacunología. Para la preparación de vacunas conjugadas de polisacáridos, los polisacáridos se pueden funcionalizar convenientemente y vincularse a proteínas portadoras de vacunas utilizando tetrafluoroborato de 1-ciano-4-dimetilaminopiridina (CDAP), un reactivo cianilante fácil de manejar. CDAP activa los polisacáridos reaccionando con los grupos hidroxilo de carbohidratos a pH 7-9. La estabilidad y la reactividad de CDAP son altamente dependientes del pH. El pH de la reacción también disminuye durante la activación debido a la hidrólisis de CDAP, lo que hace que un buen control del pH sea la clave para la activación reproducible. El protocolo de activación original de CDAP se realizó a temperatura ambiente en soluciones de pH 9 sin búfer.
Debido a la rápida reacción bajo esta condición (<3 min) y la rápida caída de pH que la acompaña de la hidrólisis rápida de CDAP, fue difícil ajustar y mantener rápidamente el pH de reacción objetivo en el corto período de tiempo. El protocolo mejorado descrito aquí se realiza a 0 °C, lo que ralentiza la hidrólisis de CDAP y extiende el tiempo de activación de 3 min a ~15 min. La dimetilaminopiridina (DMAP) también se utilizó como tampón para preajustar la solución de polisacáridos al pH de activación objetivo antes de agregar el reactivo CDAP. El mayor tiempo de reacción, junto con la hidrólisis CDAP más lenta y el uso de tampón DMAP, facilita el mantenimiento del pH de activación durante todo el proceso de activación. El protocolo mejorado hace que el proceso de activación sea menos frenético, más reproducible y más susceptible de ampliación.
Introducción
Las vacunas conjugadas, como las que consisten en polisacáridos unidos covalentemente a una proteína portadora, se encuentran entre los notables avances en vacunología1,2. Los polisacáridos, como antígenos independientes de las células T, son poco inmunogénicos en los lactantes y no inducen memoria, cambio de clase o maduración de afinidad de anticuerpos3. Estas deficiencias se superan en las vacunas conjugadas con polisacáridos4. Como la mayoría de los polisacáridos no tienen un mango químico conveniente para la conjugación, primero deben hacerse reactivos o "activados". El polisacárido activado se une directamente con la proteína (o proteína modificada) o se funcionaliza para una derivatización adicional antes de la conjugación4. La mayoría de las vacunas conjugadas con polisacáridos autorizadas utilizan aminación reductora o cianilación para activar los hidroxilos polisacáridos. El bromuro de cianógeno (CNBr), un reactivo que se había utilizado previamente para activar resinas de cromatografía, se utilizó inicialmente para la derivatización de polisacáridos. Sin embargo, CNBr requiere un pH alto, típicamente ~ pH 10.5 o mayor, para desprotonar parcialmente los hidroxilos polisacáridos para que sean lo suficientemente nucleófilos como para atacar al grupo ciano. El pH alto puede ser perjudicial para los polisacáridos lábiles de base, y ni el CNBr ni el cianoéster activo formado inicialmente son lo suficientemente estables a un pH tan alto.
CDAP (1-ciano-4-dimetilaminopiridina tetrafluoroborato; Figura 1) fue introducido por Lees et al. para su uso como agente cianilante para la activación de polisacáridos5,6. Se encontró que CDAP, que es cristalino y fácil de manejar, activa los polisacáridos a un pH más bajo que el CNBr y con menos reacciones secundarias. A diferencia de CNBr, los polisacáridos activados por CDAP se pueden conjugar directamente con proteínas, simplificando el proceso de síntesis. Los polisacáridos activados por CDAP se pueden funcionalizar con una diamina (por ejemplo, diamina hexano) o una dihidrazida (por ejemplo, dihidrazida adípica, ADH) para fabricar polisacáridos derivados de aminoácidos o hidrazidas. Se utiliza una alta concentración del reactivo homobifuncional para suprimir la reticulación de polisacáridos. Los polisacáridos amino se pueden conjugar utilizando cualquiera de las innumerables técnicas utilizadas para la conjugación de proteínas. Los polisacáridos derivados de hidrazidas a menudo se acoplan a proteínas utilizando un reactivo de carbodiimida (por ejemplo, 1-etil-3-(3-dimetilaminopropil)carbodiimida (EDAC))7. La optimización adicional de la activación de polisacáridos CDAP ha sido descrita por Lees et al.8 y se incorpora al protocolo descrito aquí.
Descripción general de la conjugación CDAP
El protocolo CDAP se puede conceptualizar como dos fases: (1) la activación del polisacárido y (2) la conjugación del polisacárido activado con una proteína o ligando (Figura 2). El objetivo del primer paso es activar eficientemente el polisacárido, mientras que el objetivo del segundo es conjugar eficientemente con el polisacárido activado. El polisacárido activado une los dos pasos. Esta conceptualización ayuda a centrarse en los elementos críticos de cada paso. La Figura 2 amplía esta conceptualización, mostrando las reacciones de activación y acoplamiento deseadas, junto con las reacciones de hidrólisis y las reacciones secundarias.
Durante la fase de activación, las tres principales preocupaciones son la estabilidad del CDAP, la reacción del CDAP con los hidroxilos polisacáridos y la estabilidad del polisacárido activado(Figura 3). La hidrólisis cdAP aumenta con el pH, al igual que la hidrólisis del polisacárido activado y las reacciones secundarias. Sin embargo, la reacción CDAP con el polisacárido se facilita al aumentar el pH. La activación eficiente de polisacáridos con CDAP requiere un equilibrio entre 1) la reactividad del polisacárido y CDAP y 2) la hidrólisis y las reacciones secundarias tanto del reactivo como del polisacárido activado.
En el protocolo de activación cdAP original descrito por Lees et al.5,la activación CDAP de polisacáridos se llevó a cabo a temperatura ambiente en solución de pH 9 sin búfer. Se encontró que la tasa de activación era rápida bajo esta condición, y la activación se completaría en 3 minutos. La reacción también se acompañó de una hidrólisis rápida de CDAP, causando una rápida caída del pH de la solución de reacción sin búfer. Fue un desafío elevar rápidamente y mantener el pH de reacción en el valor objetivo en un período de tiempo tan corto. En el protocolo descrito, la activación se realizó mediante la adición de CDAP de una solución de stock de 100 mg/ml a la solución de polisacáridos sin búfer. El pH se elevó 30 s más tarde con "un volumen igual de 0,2 M de trietilamina". La proteína a conjugar se agregó después de 2,5 min a la reacción de activación. En particular, el pH del paso de activación no estaba bien controlado y lo más probable es que inicialmente excediera el pH objetivo. La reacción rápida que requería un ajuste rápido del pH hizo que el proceso de activación fuera difícil de controlar y difícil de escalar.
A diferencia del protocolo original, el protocolo modificado descrito aquí tiene dos mejoras importantes. En primer lugar, el pH de la solución de polisacáridos se ajusta previamente al pH de activación objetivo, utilizando DMAP como tampón, antes de la adición de CDAP. DMAP tiene un pKa de 9.5 y, por lo tanto, tiene un buen poder de amortiguación alrededor del pH 9, y a diferencia de muchos otros tampones, no se encontró que DMAP promueva la hidrólisis cdAP8. Además, DMAP ya es un proceso intermedio y, por lo tanto, no agrega un nuevo componente a la mezcla de reacción. El ajuste previo del pH antes de agregar CDAP elimina la gran oscilación del pH al comienzo de la reacción y permite un mantenimiento más eficiente del pH objetivo durante la reacción. La segunda mejora es realizar la reacción de activación a 0 °C, donde la tasa de hidrólisis cdAP es marcadamente más lenta que la de temperatura ambiente. Con la vida media del reactivo más larga a 0 °C, el tiempo de activación se incrementa de 3 min a 15 min para compensar la tasa de activación más lenta a la temperatura más baja. El mayor tiempo de reacción, a su vez, hace que sea más fácil mantener el pH de reacción. El uso de 0 °C también ralentiza la degradación de los polisacáridos sensibles al pH, lo que permite preparar conjugados de este tipo de polisacáridos. Las mejoras en el protocolo hacen que el proceso de activación sea menos frenético, más fácil de controlar, más reproducible y más susceptible de escalar.
Este artículo describe el protocolo mejorado para llevar a cabo la activación controlada cdAP del polisacárido a 0 °C y a un pH objetivo especificado y realizar la derivatización posterior de los polisacáridos activados con ADH. También se describe un ensayo de ácido trinitrobenceno sulfónico (TNBS), basado en el método de Qi et al.9,para la determinación del nivel de hidrazida en el polisacárido modificado. También se describe un ensayo modificado para hexosas basado en resorcinol y ácido sulfúrico10, que se puede utilizar para determinar una gama más amplia de polisacáridos. Para obtener más información sobre la activación y conjugación de CDAP, se remite al lector a las publicaciones anteriores5,6,8 de Lees et al.
Protocolo
NOTA: Prepare la solución de polisacáridos, la solución ADH, la solución DMAP y la solución de stock CDAP con anticipación antes de ejecutar los procedimientos de activación y funcionalización de polisacáridos. Coloque las soluciones y el equipo en una ubicación organizada, conveniente y lógica. La reacción descrita es para 10 mg de polisacárido y se puede escalar hacia arriba o hacia abajo. Se recomienda evaluar el protocolo a pequeña escala antes de escalar.
1. Preparar 5 mg/ml de solución de polisacáridos, 2 ml.
- Para polisacáridos liofilizados
- Permita que el recipiente de polisacáridos llegue a temperatura ambiente antes de abrirlo. Pesar 10 mg de polisacárido dentro de un tubo de tapón de rosca utilizando una balanza analítica. Utilice un eliminador estático para facilitar el muestreo y un pesaje más preciso del polvo.
- Agregue 2 ml de cloruro de sodio (NaCl) de 0,15 M al tubo para disolver el polisacárido. Tapa y vórtice el tubo.
NOTA: El cloruro de sodio no afecta la reacción CDAP, pero puede afectar la estructura secundaria del polisacárido. Algunos polisacáridos son más solubles a diferentes concentraciones de sal. - Mezcle el tubo mediante rotación de extremo a extremo durante 12-24 h, dependiendo del peso molecular del polisacárido, para permitir que el polisacárido se hidrate completamente. Si es necesario, caliente suavemente el tubo para promover la solubilización.
- Para polisacárido solubilizado en solución tamponada
NOTA: Para una activación eficiente de CDAP, la solución de polisacáridos no debe contener ningún tampón, especialmente ion fosfato. Siga el procedimiento a continuación para reemplazar el tampón con agua o una solución salina y para ajustar la concentración de polisacáridos a 5 mg / ml.- Obtener un dispositivo de filtro de espín centrífugo de 4 ml o 15 ml del límite de peso molecular (MWCO) apropiado.
NOTA: El MWCO es idealmente 5-10 veces más pequeño que el peso molecular del polisacárido. - Agregue un volumen de la solución de polisacárido tamponada que contiene ~ 20 mg del polisacárido al inserto del filtro. Llene hasta la marca completa con agua o una solución salina. Tapa bien el filtro. Mezclar de extremo a extremo varias veces.
- Centrífuga el dispositivo de filtro a la fuerza centrífuga sugerida por el fabricante. Asegúrese de que el tiempo de centrifugación sea lo suficientemente largo como para lograr una reducción de volumen de al menos 5 veces después de cada centrifugado. Descarta el flujo. Vuelva a montar el dispositivo de filtro.
- Vuelva a llenar el inserto del filtro hasta la marca completa con agua dulce o solución salina. Tapa bien el filtro. Mezcle el contenido en el filtro mediante rotación de extremo a extremo ~ 10 veces o mediante vórtice suave; repita el giro.
NOTA: El polisacárido puede acumularse en la parte inferior del inserto del filtro del dispositivo centrífugo, formando un gel. Se recomienda volver a mezclar el retentant dentro del inserto del filtro con la recarga fresca antes del siguiente giro. - Repita el ciclo de recarga y centrifugado durante un mínimo de 3 veces.
- Siga el ejercicio a continuación para recuperar el retentante de polisacáridos del inserto del filtro.
- Agregue agua dulce o solución salina al inserto del filtro para que el volumen sea de ~ 1 ml. Mezclar mediante pipeteo hacia arriba y hacia abajo o mediante vórtice suave.
- Transfiera todo el retentante mezclado a un tubo de 5 ml. Agregue 1 ml de agua dulce o solución salina al inserto del filtro. Enjuague el filtro mediante pipeteo hacia arriba y hacia abajo o mediante vórtice suave. Transfiera y combine todos los enjuagues con el polisacárido recuperado.
- Determinar la concentración de polisacáridos (ver el ensayo de polisacáridos en la sección 7.3). Diluir el polisacárido con agua adicional o solución salina a 5 mg/ml.
- Obtener un dispositivo de filtro de espín centrífugo de 4 ml o 15 ml del límite de peso molecular (MWCO) apropiado.
- Cuando se prepare la solución de polisacáridos, enfríe el tubo que contiene la solución de polisacáridos en un cubo de hielo.
2. Preparar 0,5 M de solución de dihidrazida ácida adípica (ADH), 10 ml.
- Pesar 0,87 g de ADH en una balanza analítica, y solubilizar en 8 mL de 0,1 M HEPES (ácido 4-(2-hidroxietil)-1-piperazinatanosulfónico), pH 8.
- Ajuste al pH objetivo con hidróxido de sodio (NaOH) de 1 M, monitoreado por un medidor de pH. Llevar a 10 ml con tampón adicional y volver a confirmar el pH.
3. Prepare la solución DMAP de 2,5 M, 10 ml.
NOTA: DMAP es tóxico y penetrará en la piel. Use guantes de nitrilo cuando realice el procedimiento.
- Pese cuidadosamente 3 g de DMAP en un tubo cónico de 50 ml. Añadir 5 ml de agua a DMAP y mezclar por vórtice durante 5 min para obtener una solución turbia (~ 7 mL).
- Durante la mezcla, agregue incrementos de 50 μL de ácido clorhídrico (HCl) de 10 N a la solución DMAP. Mezclar entre cada adición. Deje de agregar cuando la solución esté clara.
- Agregue 10 N NaOH en incrementos de 25 μL para llevar la solución DMAP a ~pH 8.
- Lleve la solución DMAP a 10 ml con agua para dar una solución de 2,5 m.
- Ajuste el pH de la solución DMAP de 2,5 M.
NOTA: El pH de la solución DMAP cambia con la concentración y la fuerza iónica. Este ejercicio consiste en ajustar el stock DMAP de 2,5 M a un pH específico para que cuando se mezcle con 10 volúmenes de polisacárido, la solución resultante esté cerca del pH objetivo para la activación.- Preparar una serie de tubos de 1,5 ml que contengan 1 ml de agua o la solución de NaCl, lo que se haya utilizado para preparar la solución de polisacáridos. Enfríe los tubos sobre hielo.
- Añadir 100 μL de DMAP a un tubo refrigerado. Vórtice y mida el pH con un medidor de pH. Luego, deseche el tubo medido.
- Si el pH medido no está cerca del valor objetivo, ajuste el pH de la culata DMAP con 1 M NaOH o HCl según corresponda. Repita los pasos 3.5.2 y 3.5.3 hasta que el pH medido esté cerca del pH objetivo.
4. Preparar 100 mg/ml de solución cdap stock
NOTA: El polvo de CDAP debe mantenerse bien cerrado y almacenado a -20 °C y dejarse llegar a temperatura ambiente antes de abrirlo. Use guantes de nitrilo cuando realice el procedimiento.
- Tara de un tubo de microcentrífuga de tapa a presión de 1,5 ml en una balanza analítica. Usando una espátula pequeña, pese 10-140 mg de CDAP en el tubo. Tenga en cuenta el peso real de CDAP.
- Determinar el volumen de acetonitrilo necesario para preparar 100 mg/ml cdAP. Abra el acetonitrilo en una campana extractora de humos.
- Usando una pipeta de volumen apropiada, extraiga y libere el acetonitrilo para equilibrar su vapor en la punta de la pipeta. Espere a que el disolvente gotee de la punta de la pipeta después de unos segundos y prepárese para transferirlo directamente al tubo CDAP. Extraiga el volumen calculado de acetonitrilo y transfiéralo directamente al tubo CDAP. Cierre la tapa.
NOTA: El acetonitrilo también se puede transferir al tubo CDAP utilizando una jeringa Hamilton o su equivalente de tamaño adecuado. - Vórtice para solubilizar completamente el CDAP. Coloque el tubo CDAP en un cubo de hielo.
NOTA: CDAP es estable en acetonitrilo en el frío. Las existencias solubles podrán mantenerse a -20 °C durante >1 semana. Sin embargo, es preferible preparar soluciones CDAP frescas.
5. Activación de polisacáridos y funcionalización de hidrazida
- Asegúrese de que todos los siguientes artículos estén listos y las soluciones enfriadas en hielo antes de comenzar la activación: 2 ml de una solución de polisacáridos de 5 mg / ml en un recipiente de boca ancha de fondo plano que contenga una barra de agitación, colocada encima de un agitador magnético; Solución cdap de 100 mg/ml; Solución de stock DMAP de 2,5 M; un medidor de pH con una sonda de pH semimicro, como la sonda de 6 mm de diámetro, calibrada para 0 °C de acuerdo con las instrucciones del fabricante; una pipeta de 100 μL lista para usar; un temporizador despejado y listo para usar; un cabezal dispensador automático colocado o una pipeta de 10 μL lista para usar; Solución ADH de 0,5 M.
- Ajuste previo del pH del polisacárido al pH objetivo utilizando DMAP.
- Coloque la sonda de pH en la solución de polisacáridos y déjela en la solución durante todo el procedimiento de activación.
- Transfiera 200 μL de la solución de material DMAP a la solución de polisacáridos mediante adición en gota bajo agitación. Ajuste el pH de la solución al pH de activación objetivo. Agregue 0.1 M HCl para reducir el pH y 0.1 M NaOH para aumentar el pH. Evite exceder el pH objetivo en más de 0.1 unidades de pH y mantenga la reacción fría en un baño de agua helada durante la duración de la activación.
- Activación de CDAP
- Pipeta 100 μL CDAP arriba y abajo para equilibrar el vapor en la punta de la pipeta. Transfiera 100 μL de CDAP a la solución de polisacáridos con agitación.
NOTA: Esta activación utiliza 1 mg de CDAP para 1 mg de polisacárido como proporción inicial. La proporción se puede aumentar o disminuir al optimizar la activación. - Inicie el temporizador y supervise el cambio de pH durante toda la activación. Mantenga la reacción en el pH objetivo agregando rápidamente incrementos de 10 μL de 0.1 M NaOH a la reacción, con la ayuda de un dispensador autotitulador (o pipeta).
NOTA: Puede ayudar a reducir el tiempo de respuesta del pH para agitar con una sonda de pH suavemente. El pH cae más rápidamente al principio, y puede ser necesario agregar el NaOH de 0.1 M con más frecuencia. A medida que avanza la reacción, la disminución del pH se vuelve más lenta y la adición se vuelve menos frecuente. El pH debe permanecer esencialmente sin cambios cuando se acerca el tiempo de activación óptimo, que es de 10-15 minutos para la activación del pH 9.
- Pipeta 100 μL CDAP arriba y abajo para equilibrar el vapor en la punta de la pipeta. Transfiera 100 μL de CDAP a la solución de polisacáridos con agitación.
- Funcionalización de ADH
- Cuando se alcance el tiempo óptimo de activación, agregue 2 ml de 0,5 M de ADH de una sola vez al polisacárido activado bajo agitación. Compruebe que el pH está en el rango objetivo (pH 8-9 para ADH).
NOTA: Una adición con mezcla rápida minimiza la probabilidad de que ambos extremos de la dihidrazida reaccionen con el polisacárido activado, evitando la reticulación de polisacáridos. - Continúe revolviendo la mezcla de reacción durante al menos 1 h. Transfiera la mezcla de reacción a 4 °C, pero 0-20 °C es aceptable.
NOTA: La reacción de funcionalización de ADH no depende en gran medida de la temperatura. Como el gran exceso de dihidrazida actúa como reactivo de enfriamiento, no es necesario apagar aún más el polisacárido activado. Sin embargo, cuando se conjugan directamente proteínas, la reacción debe apagarse, típicamente con 1 M de glicina, pH 8-9.
- Cuando se alcance el tiempo óptimo de activación, agregue 2 ml de 0,5 M de ADH de una sola vez al polisacárido activado bajo agitación. Compruebe que el pH está en el rango objetivo (pH 8-9 para ADH).
6. Purificación del polisacárido funcionalizado con ADH por diálisis
NOTA: El producto crudo de la reacción de funcionalización de ADH contiene una alta concentración de ADH (0,5 M), que se puede eliminar de manera más eficiente mediante diálisis extensa. La filtración en gel, ya sea con una columna o un dispositivo de desarenado de espín, no es tan eficiente, especialmente cuando se requiere eliminar el contaminante ADH residual.
- Determinar el MWCO de la membrana de diálisis. Utilice un corte de 3 kDa para polisacáridos más pequeños.
NOTA: El MWCO de la membrana de diálisis es idealmente 5-10 veces más pequeño que el MW del polisacárido. - Elija el formato de diálisis deseado (casetes o tubos) y la capacidad correcta del dispositivo. Asegúrese de que la capacidad del dispositivo sea 2 veces mayor que el volumen de muestra. Consulte las instrucciones de uso del dispositivo por parte de los fabricantes.
- Hidratar la membrana de diálisis en agua antes de usarla. Transfiera la solución cruda de polisacárido derivatizado al dispositivo de diálisis de acuerdo con las instrucciones del fabricante.
NOTA: Use guantes de nitrilo para evitar el contacto con DMAP. - Dializar en un recipiente lleno de 2-4 L de 1 M de NaCl y una barra de agitación. Coloque el recipiente en una placa de agitación en una cámara frigorífica o dentro de un refrigerador. Revuelva el dializador suave y continuamente durante la diálisis.
- Después de dializar durante al menos 4 h, cambie a NaCl fresco de 1 M y dializar durante al menos 12 h. Dializar contra 2 cambios de solución salina de 0,15 M, cada uno durante al menos 12 h. Si lo desea, dializar contra 2 cambios de agua.
- Verifique si se elimina toda la ADH probando el dializador durante la noche utilizando una prueba rápida de TNBS.
- Obtenga 3 tubos de borosilicato, etiquételos como control negativo (ctrl), ctrl positivo y muestra, respectivamente.
- Al tubo ctrl negativo, agregue 975 μL de borato de 0.1 M, pH 9.
- Al tubo ctrl positivo, agregue 100 μL de 0.05 mM ADH (0.1 mM hidrazida) y 875 μL de 0.1 M borato, pH 9.
- Al tubo de muestra, agregue 500 μL del dializador nocturno y 475 μL de borato de 0,1 M, pH 9.
- Agregue 25 μL de TNBS al 1% a los tres tubos. Mezclar bien. Colocar en la oscuridad durante 1 h.
- Compara la intensidad de color de los 3 tubos en 1 h. Asegúrese de que la intensidad del color del tubo de muestra esté entre la de la ctrl positiva y la ctrl negativa, lo que indica que el contaminante ADH ha bajado a 0.01 mM o menos. Dializar una vez más.
NOTA: Es prudente reducir el nivel del contaminante ADH tanto como sea posible para que la hidrazida ADH representa menos del 1% de la hidrazida total en el polisacárido de hidrazida purificado. - Recuperar el polisacárido derivatizado de la diálisis. Determinar la concentración de los polisacáridos e hidrazidas. Calcular la relación hidrazida/polisacárido (ver sección 7). Si el polisacárido dializada debe concentrarse a 5-10 mg/ml, consultar la sección 1.2.
7. Análisis de polisacáridos derivados de hidrazidas
NOTA: El propósito del análisis descrito aquí es determinar la concentración de polisacáridos, la concentración de hidrazidas y el nivel de derivatización de hidrazidas en términos de la relación hidrazida/polisacárido.
- Preparación de muestras
NOTA: Los polisacáridos que se ensayan deben estar libres de impurezas de carbohidratos, aminas o hidrazidas de bajo peso molecular. Las muestras liofilizadas deben estar secas y sin sal para garantizar una medición precisa del peso. Por lo general, ~ 1 ml de una solución de 1-2 mg / ml es adecuada para los ensayos.- Pesar al menos 10 mg de la muestra de polisacáridos liofilizados en una balanza analítica, utilizando una espátula no estática o un eliminador estático. Disolver el polisacárido en agua o solución salina a una concentración (por ejemplo, 2 mg/ml) para que las señales del ensayo caigan dentro del rango lineal de la curva estándar.
- Mezcle de extremo a extremo y deje suficiente tiempo para que la muestra se disuelva por completo. Realizar hidratación durante la noche en función del peso molecular del polisacárido.
- Ensayo de polisacáridos: método de resorcinol/ácido sulfúrico
NOTA: El ensayo apropiado para los polisacáridos dependerá de la composición de carbohidratos de los polímeros. El ensayo original de resorcinol/ácido sulfúrico estaba destinado a los azúcares de hexosa10. El ensayo se modificó aquí elevando la temperatura del paso de calentamiento de 90 ° C a 140 ° C. A esta temperatura más alta, el ensayo pierde cierta especificidad, pero se puede utilizar para analizar muchos azúcares. Sin embargo, todavía es necesario determinar la idoneidad del ensayo para un polisacárido en particular. Se recomiendan triplicados para cada punto, pero puede ser necesario algún alojamiento debido a la capacidad del bloque de calefacción.- Preparar ácido sulfúrico al 75%
NOTA: El ácido sulfúrico concentrado es extremadamente corrosivo y puede causar quemaduras graves. Realice este procedimiento en una campana de humos químicos. ¡Siempre vierta ácido concentrado en agua, no al revés!- Agregue 50 ml de agua a una botella de vidrio de 200 ml. Coloque la botella en un baño de agua fría. Agregue lentamente 150 ml de ácido sulfúrico. Tapa la botella para que se ventile.
- Permita que la solución se equilibre a temperatura ambiente. Use la solución dentro de los 3 meses.
- Preparar estándares de carbohidratos
- Preparar la solución de polisacárido sin modificar a 1 mg/ml para ser utilizada como estándar. Alternativamente, use una mezcla de azúcares individuales en la proporción que se encuentra en la unidad de repetición del polisacárido, a 1 mg / ml de la concentración total de azúcar, como estándar.
NOTA: Aunque la mezcla de azúcar generalmente dará el mismo resultado que el polímero de carbohidratos de composición de azúcar idéntica, esto debe confirmarse experimentalmente.
- Preparar la solución de polisacárido sin modificar a 1 mg/ml para ser utilizada como estándar. Alternativamente, use una mezcla de azúcares individuales en la proporción que se encuentra en la unidad de repetición del polisacárido, a 1 mg / ml de la concentración total de azúcar, como estándar.
- Asegúrese de que el bloque calefactor con soportes de tubo para tubos de ensayo de 13 x 100 borosilicato esté funcionando. Use una almohadilla protectora debajo y alrededor del bloque calefactor en caso de derrames de ácido. Precaliente el bloque calefactor a 140 °C durante un mínimo de 1 h para lograr una temperatura estable y uniforme a través de todos los bloques utilizados.
- Etiquete 13 x 100 tubos de ensayo de borosilicato, triplicado para cada estándar y cada muestra. Agregue 0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 μg (o μL) del estándar de carbohidratos de 1 mg / ml a los tubos estándar etiquetados correspondientemente. Agregue agua a cada tubo para llevar el volumen a 100 μL.
NOTA: El color generado depende de azúcares específicos. Como algunos azúcares requieren más masa para generar el rango de absorbancia completo, las cantidades reales utilizadas para la curva estándar pueden variar. - Configure ensayos de muestra agregando un volumen que contenga ~ 5 μg del polisacárido derivatizado a tres tubos de muestra y lleve el volumen total a 100 μL con agua. Alternativamente, si se desconoce la concentración de polisacáridos en la muestra, realice una serie de diluciones de 4 veces. Pruebe 100 μL de cada dilución por triplicado.
- Preparar resorcinol fresco a 6 mg/ml en agua desionizada (dI) inmediatamente antes de su uso. Vórtice hasta que el resorcinol esté en solución. Añadir 100 μL de 6 mg/ml de resorcinol a cada tubo.
- Vierta cuidadosamente la cantidad estimada de ácido sulfúrico al 75% en un pequeño beaker.
NOTA: Use una bata de laboratorio, guantes de nitrilo y gafas de seguridad. Tenga cuidado con los goteos, derrames y salpicaduras. Mantenga las toallas de papel húmedas a mano para limpiar cualquier goteo. A medida que la actividad del ácido sulfúrico cambia en la exposición prolongada al aire, use una mezcla uniforme de ácido sulfúrico para todo el ensayo. - Usando un pipettor repetidor, agregue uniformemente 300 μL de ácido sulfúrico al 75% a cada tubo. Vórtice los tubos vigorosamente para mezclar bien, apuntando el tubo hacia lejos mientras vórtice. Coloque los tubos en un bloque de calentador a un ritmo constante en orden secuencial. Una vez que todos los tubos estén dentro, configure el temporizador durante 3 minutos inmediatamente.
- A los 3 minutos, retire los tubos a un ritmo constante en el mismo orden y colóquelos directamente en una rejilla en un baño de agua helada. Deje los tubos hasta que estén helados. Retire los tubos y deje que se equilibren a temperatura ambiente durante ~ 5 minutos para evitar la condensación en la cubeta durante la lectura.
- Configure un espectrofotómetro UV/VIS para leer la absorbancia a 430 nm utilizando una cubeta de longitud de trayectoria de 10 mm. En blanco con un tubo estándar cero. Lea la absorbancia de todos los tubos a 430 nm.
NOTA: Las cubetas de plástico desechables son convenientes de usar. - Construya una curva estándar trazando μg de carbohidratos estándar vs. A430. Consulte la Figura 4 para una curva estándar típica que utiliza la glucosa como estándar de referencia.
- Utilice los tubos de ensayo de muestra con valores de A430 que caigan dentro del rango lineal de la curva estándar, calcule la cantidad de μg del polisacárido desconocido en los tubos de ensayo de muestra a partir de la ecuación de curva estándar. Determine la concentración del polisacárido desconocido a partir del volumen del agregado desconocido, teniendo en cuenta las diluciones. Convierta la concentración a unidades de repetición mg/mL o μM según sea necesario.
- Preparar ácido sulfúrico al 75%
- Ensayo de hidrazida con ácido trinitrobenceno sulfónico (TNBS)
- Preparar NaCl al 0,9% que contenga azida sódica al 0,02% (tampón de muestra) disolviendo 9 g de NaCl y 200 mg de azida de sodio en dI H2O a un volumen final de 1 L.
- Preparar 0,1 M de borato de sodio, pH 9 (tampón de ensayo), mezclando 100 mL de borato de sodio de 0,5 M, pH 9, con 400 mL de dI H2O. Confirme que el pH de la solución es de 9 ± 0,1; ajustar si es necesario.
- Preparar TNBS al 1% diluyendo 200 μL de solución de ácido sulfónico trinitrobenceno al 5% al 5% a 1 mL con dI H2O. Marque el tubo como 1% TNBS y guárdelo a 4 °C en la oscuridad durante una semana.
- Preparar 50 mM de stock de ADH (equivalente a 100 mM de hidrazida).
- Pesar 871 mg de polvo de dihyrazide adípico (ADH) usando una balanza analítica. Disuelva el polvo en una botella de reactivo agregando un tampón de muestra a 100 ml con la ayuda de una balanza de carga superior.
- Etiquete la botella como hidrazida de 100 mM/50 mM de ADH. Tapa bien el frasco y guárdalo a 4 °C durante 1 año.
- Prepare estándares de hidrazida (0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 y 0.6 mM de hidrazida).
- Prepare los 6 estándares de hidrazida diluyendo el stock de hidrazida de 100 mM con tampón de muestra con la ayuda de una balanza de carga superior. Prepare 100 ml de cada estándar para minimizar el error de concentración. Cierre herméticamente las botellas y guárdelo a 4 °C durante 1 año.
- Configuración de reacciones de ensayo
NOTA: El ensayo TNBS se ejecuta a un volumen de reacción de 1 ml. Cada tubo de ensayo consta de 100 μL de una muestra (o un estándar), 875 μL de tampón de ensayo y 25 μL de solución de TNBS al 1%. Todas las reacciones del ensayo (tanto para muestras como para estándares) se configuran por triplicado.- Etiquete 3 tubos de vidrio de borosilicato (12 x 75 mm) para cada estándar, incluido el estándar cero. Clasonda y organice los tubos estándar en el estante de tubos en orden de concentración creciente. Utilice una micropipeta calibrada de 100 μL o 200 μL para agregar con precisión 100 μL de los estándares a cada tubo correspondiente. Para el estándar cero, utilice 100 μL de búfer de muestra.
- Etiquete 3 tubos de vidrio de borosilicato (12 x 75 mm) para cada muestra diluida que se ensaye. Clasonda y organice los tubos de muestra en el bastidor de tubos en consecuencia. Utilice una micropipeta calibrada de 100 μL o 200 μL para agregar con precisión 100 μL de la muestra a cada tubo de muestra correspondiente.
- Utilice una micropipeta calibrada de 1000 μL para agregar con precisión 875 μL de tampón de ensayo a todos los tubos de ensayo: los estándares y las muestras.
- Para iniciar la reacción del ensayo, use una micropipeta calibrada de 100 μL para agregar con precisión 25 μL de TNBS al 1% a cada tubo de ensayo. Comience desde los tubos estándar cero, muévase a los tubos estándar en orden de concentración creciente, luego a los tubos de muestra de acuerdo con el orden predeterminado. Cambie las puntas al iniciar un nuevo estándar o una nueva muestra y mantenga el tiempo dedicado a agregar TNBS a todos los tubos dentro de los 5 minutos.
- Vórtice todos los tubos de ensayo durante 2 s a alta velocidad o a una configuración de velocidad que permita que el líquido dentro del tubo de ensayo se arremolina hacia arriba para alcanzar una altura de 1/2 pulgada desde la abertura del tubo.
- Registre la hora de inicio del ensayo y configure el temporizador en 2 h. Coloque el bastidor de tubos de ensayo en la oscuridad a temperatura ambiente durante 2 h. Cuando termine el tiempo, vórtice todos los tubos una vez más y proceda a la recopilación de datos.
- Recogida de datos
- Deje que el espectrofotómetro UV/VIS se caliente y la línea de base se estabilice. Establezca la longitud de onda de detección en 500 nm para el ensayo de hidrazida. Utilice una cubeta de cuarzo de 1 ml de longitud de trayectoria de 1 cm para todas las mediciones de absorbancia para todo el ensayo.
- Comience la recopilación de datos transfiriendo un ensayo estándar cero a la cubeta; en blanco el instrumento (ajuste la absorbancia a cero).
- Realice una sola lectura en cada tubo y registre los valores de absorbancia en una tabla de datos. Retire cualquier líquido residual de la cubeta antes de leer una nueva muestra. Comience desde los estándares cero, pase a los estándares de concentración creciente y luego a las muestras. Una vez iniciado, realice todos los pasos de manera eficiente sin detenerse y lea todos los tubos en 10 minutos.
- Análisis de datos de muestra
- Cree una curva estándar trazando mM hydrazide standard vs. A500. Encuentre la ecuación de curva estándar en forma de y = ax + b, donde y representa mM hidrazida y x representa A500. Consulte la Figura 4 para ver una curva estándar típica.
- Calcule la hidrazida mM en las muestras utilizando la ecuación de la curva estándar, ajustando los factores de dilución. Elija solo los tubos de ensayo de muestra con valores A500 que caigan dentro del rango lineal de la curva estándar para el cálculo.
- Calcular la relación molar de hidrazida/polisacárido usando la ecuación (1).
Hidrazida/polisacárido = h/c × MW (1)
Donde h es la hidrazida mM, c es la concentración de mg/ml del polisacárido, y MW es el peso molecular del polisacárido en kDa. - Calcular la densidad de etiquetado de hidrazida por 100 kDa de polisacárido utilizando la ecuación (2).
Densidad de etiquetado por polisacárido de 100 kDa = h / c × 100 (2)
Donde h es la hidrazida mM, y c es la concentración de mg/ml del polisacárido.
NOTA: Para mayor comodidad, se puede considerar que los polisacáridos tienen un peso molecular de 100.000 daltons. Esto permite considerar una "densidad de etiquetado" al comparar el nivel de derivatización de varios polisacáridos. - Calcule la densidad de etiquetado de hidrazida como porcentaje de peso ADH.
- Determinar la concentración efectiva de mg/ml de ADH mediante la ecuación (3).
mg/mL ADH = (mM hidrazida / 1000) × 174 (3)
donde 174 es el MW de ADH. - Calcular el peso % ADH mediante la ecuación (4).
peso % ADH = (mg/mL ADH) / (mg/mL polisacárido) × 100 (4)
- Determinar la concentración efectiva de mg/ml de ADH mediante la ecuación (3).
Resultados
Para ilustrar la activación y derivatización de un polisacárido utilizando la química CDAP, el dextrano se activó a 0,25 y 0,5 mg cdAP/mg de dextrano. Para cada reacción, se enfrió una solución de dextrano de 10 mg/ml en agua sobre hielo, y se añadió1/10 º volumen de una culata DMAP de 2,5 M (preparada como se describe en la sección 3). La solución final se llevó a pH 9 mediante la adición de 0,1 M de NaOH en alícuotas de 10 μL. La solución se enfrió y se agitó, se agregó CDAP y se mantuvo el pH a pH 9 agregando alícuotas de 10 μL de 0,1 M de NaOH durante 15 min. Solo se agregaron 0,25 mL de 0,5 M de ADH a pH 9 (menos de la cantidad habitual) y se permitió que la reacción continuara durante la noche a 4 °C.
El dextrano etiquetado se dializó secuencialmente contra 1 M NaCl, 0,15 M NaCl y agua como se describe en la sección 6. A continuación, se ensayó el ADH-dextrano para el dextrano mediante el ensayo de resorcinol/ácido sulfúrico (sección 7.2). Una curva estándar típica que utiliza la glucosa como el estándar de azúcar se muestra en la Figura 4A. El contenido de hidrazida se determinó mediante el ensayo TNBS descrito en la sección 7.3. Una curva estándar típica de hidrazida usando ADH como estándar se da en la Figura 4B.
Los cálculos representativos de la activación del dextrano en los dos niveles de activación se muestran en la Figura 4A,B. Los datos se presentan como hidrazidas por 100 kDa de polímero de dextrano y como porcentaje en peso de ADH a dextrano, como se describe en las secciones 7.9.3.4 y 7.9.3.5, respectivamente, en la Figura 4C. El grado de derivatización se duplicó aproximadamente a medida que se duplicó la relación CDAP.
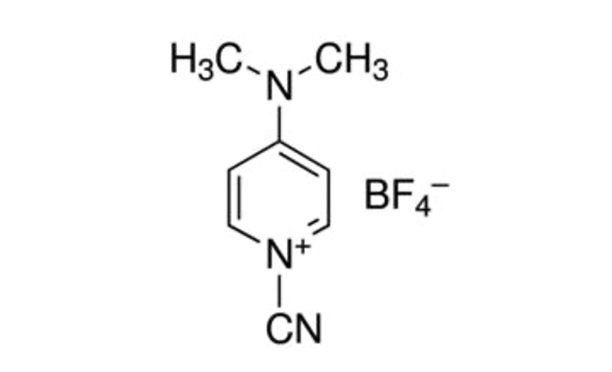
Figura 1: Estructura química del CDAP. CDAP = 1-ciano-4-dimetilaminopiridina tetrafluoroborato. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
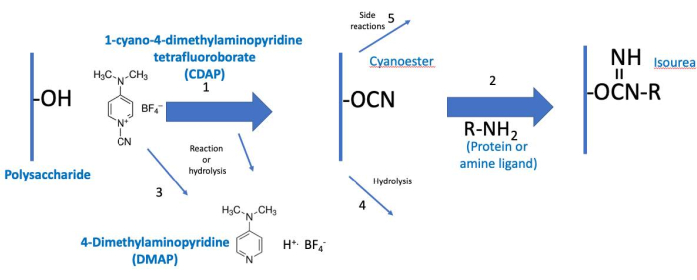
Figura 2: Proceso de activación y conjugación de CDAP. El proceso se divide conceptualmente en dos fases, con el polisacárido activado común a ambas. En condiciones básicas, CDAP activa hidroxilos polisacáridos, liberando DMAP (reacción 1). La hidrólisis CDAP también libera DMAP (reacción 3). Aunque se muestra un ciano-éster, este puede no ser el intermediario real. El intermedio se conoce, por lo tanto, como polisacárido "activado" (CDAP). Durante la primera fase de activación, el polisacárido activado puede hidrolizarse (reacción 4) o sufrir reacciones secundarias (reacción 5). En la segunda fase de conjugación (reacción 2), el polisacárido activado reacciona con una amina para formar un enlace isourea estable además de las reacciones 4 y 5. Abreviaturas: CDAP = 1-ciano-4-dimetilaminopiridina tetrafluoroborato; DMAP = 4-dimetilaminopiridina; R-NH2 = amina. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
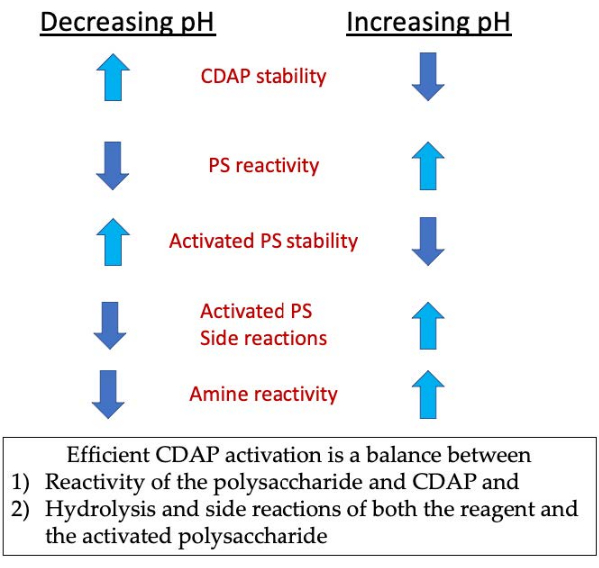
Figura 3: Activación y conjugación de CDAP. El proceso requiere equilibrar la reactividad del CDAP con el polisacárido, la estabilidad del CDAP y el polisacárido activado, así como la reactividad del polisacárido activado con la de la amina. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
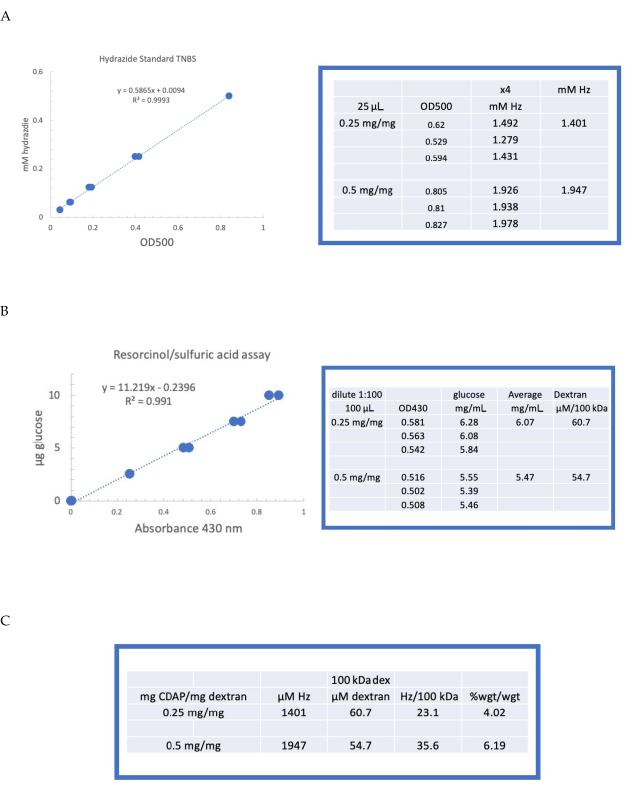
Figura 4: Resultados representativos para la activación CDAP de dextrano. Curvas estándar típicas para los ensayos (A) resorcinol/ácido sulfúrico y (B) TNBS. Se muestran los resultados del ensayo para el dextrano activado con 0,25 y 0,5 mg de CDAP/mg de dextrano. La glucosa se utilizó como estándar para el ensayo de resorcinol. El dextrano, en mg/ml, se divide por 100 kDa para dar una concentración molar. La concentración de hidrazida se determina utilizando ADH como estándar y los resultados expresados como μM Hz. (C) Cálculo de hidrazida: proporciones de dextrano. El nivel de derivatización se calculó como hidrazidas por 100 kDa de dextrano para facilitar la comparación entre polímeros de diferentes pesos moleculares medios. La relación % en peso de g ADH/g dextrano se calculó utilizando un MW de 174 g/mol para ADH. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
Discusión
CDAP es un reactivo conveniente para derivar y conjugar polisacáridos. Este artículo describe el método general para utilizar CDAP para derivar los polisacáridos con hidrazidas (PS-ADH) e incorpora mejoras publicadas recientemente8. En primer lugar, la técnica enfatiza la importancia de mantener el pH objetivo para controlar el proceso de activación. Encontramos que si bien muchos búferes comunes interfieren con la reacción de activación de CDAP, DMAP podría usarse con éxito como búfer para administrar el pH8. Además, DMAP ya es un subproducto de reacción de la activación de CDAP. Finalmente, el almacenamiento en búfer de la solución de polisacáridos con DMAP antes de agregar el CDAP facilita la orientación precisa y el mantenimiento del pH de reacción. Como describimos, es útil ajustar el pH de la solución de stock DMAP concentrada de tal manera que cuando se diluya, alcance el pH objetivo. En segundo lugar, realizar el proceso en frío ralentizó el tiempo de reacción, haciendo que el proceso de activación fuera menos frenético y más indulgente. La temperatura más baja disminuyó la tasa de hidrólisis de CDAP, y el tiempo óptimo de activación a pH 9 aumenta de ~ 3 min a ~ 15 min. Además, se requiere menos CDAP para lograr el mismo nivel de activación que cuando se realiza a temperatura ambiente.
Los polisacáridos derivados de ADH se pueden conjugar con proteínas utilizando carbodiimidas (por ejemplo, EDAC)7. Por ejemplo, varias vacunas autorizadas contra Haemophilus influenzae b (Hib) utilizan el polirribosilribitolfosfato (PRP) derivado con ADH para conjugar con toxoide tetánico utilizando EDAC. CNBr se empleó inicialmente, pero CDAP es un reactivo mucho más fácil de usar para este propósito. En nuestra experiencia, un buen rango objetivo para la derivatización de ADH es 10-30 hidrazidas por polisacárido de 100 kDa o ~ 1-3% de ADH en peso.
El mismo proceso se puede utilizar para derivar polisacáridos con aminas primarias sustituyendo la ADH por una diamina. Se recomienda utilizar hexano diamina para derivar polisacáridos con aminas8. El polisacárido nominado (PS-NH2)puede ser conjugado utilizando reactivos desarrollados para la conjugación de proteínas11. Típicamente, el PS-NH2 se deriva con una maleimida (por ejemplo, succinimidil 4-[N-maleimidometil]ciclohexano-1-carboxilato (SMCC) o N-γ-maleimidobutiril-éster de oxisuccinimida (GMBS)), y la proteína es tiolada (por ejemplo, con succinimidil 3-(2-piridilditio)propionato (SPDP)). La química tiol-maleimida es muy eficiente.
Las proteínas también se pueden acoplar directamente a los polisacáridos activados por CDAP a través de la ɛ-amina en las lisinas. Si bien el protocolo de activación utilizado es generalmente similar al descrito aquí, es necesario optimizar el nivel de activación, la concentración de polisacáridos y proteínas, así como la relación proteína:polisacárido5,6,8.
El dextrano es uno de los polisacáridos más fáciles de activar con CDAP debido a su densidad relativamente alta de grupos hidroxilo, pero algunos polisacáridos, como el antígeno Vi, pueden ser un desafío. En consecuencia, no existe un único "mejor" protocolo para la conjugación cdAP directamente a las proteínas. Sugerimos primero desarrollar un protocolo para lograr niveles adecuados de activación, según lo determinado por el grado de derivatización de la hidrazida, y luego proceder a la conjugación directa de proteínas al polisacárido activado por CDAP.
Divulgaciones
Andrew Lees es fundador y propietario de Fina Biosolutions. Posee varias patentes relacionadas con la química CDAP y se beneficia de la licencia de los conocimientos de química y conjugación CDAP.
Agradecimientos
El trabajo descrito aquí fue financiado por Fina Biosolutions LLC.
Materiales
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acetonitrile | Sigma | 34851 | |
| Adipic acid dihydrazide | Sigma | A0638 | MW 174 |
| Amicon Ultra 15 10 kDa | Millipore | UFC901008 | MW cutoff can be 30 kDa for 200 kDa PS |
| Analytical balance | |||
| Autotitrator or electronic pipet | |||
| Beaker 2-4 L | |||
| CDAP | SAFC | RES1458C | Sigma |
| DMAP | Sigma | 107700 | MW 122.2 |
| Flake ice | |||
| HCl 1 M | VWR | BDH7202-1 | |
| Micro stir bar | VWR | 76001-878 | |
| Microfuge tube (for CDAP) | VWR | 87003-294 | |
| NaCl | VWR | BDH9286 | |
| NaOH 1 M | Sigma | 1099130001 | |
| NaOH 10 M | Sigma | SX0607N-6 | |
| pH meter | |||
| pH probe | Cole Parmer | 55510-22 | 6 mm x 110 mm Epoxy single junction |
| pH temperature probe | |||
| Pipets & tips | |||
| Saline or PBS | |||
| Small beaker 5-20 mL | VWR | 10754-696 | A 10 mL beaker allows room for pH probe & pipet |
| Small ice bucket | |||
| Small spatula | |||
| Stir plate | |||
| Resorcinol assay | |||
| Combitip | Eppendorf | 10 ml | |
| DI water | |||
| Dialysis tubing | Repligen | 132650T | Spectra/Por 6-8kDa |
| Dialysis tubing clips | Repligen | 142150 | |
| Heating block | |||
| Nitrile gloves | VWR | ||
| Repeat pipettor | Eppendorf | M4 | |
| Resorcinol | Sigma | 398047 | |
| Sugar standard | As appropriate | ||
| Sulfuric acid 75% | VWR | BT126355-1L | |
| Timer | |||
| TNBS assay | |||
| Adipic dihydrazide | Sigma | A0638 | MW 174 |
| Borosilcate test tubes 12 x 75 | VWR | 47729-570 | |
| Sodium borate, 0.5 M pH 9 | Boston Biologicals | BB-160 | |
| TNBS 5% w/v | Sigma | P2297 | MW 293.17 |
Referencias
- Ellis, R. W., Granoff, D. M. . Development and clinical uses of Haemophilus B conjugate vaccines. , (1994).
- Goebel, W. F., Avery, O. T. Chemo-immunological studies on conjugated carbohydrate-proteins. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 50 (4), 533-550 (1929).
- Mond, J. J., Vos, Q., Lees, A., Snapper, C. M. T cell independent antigens. Current Opinion in Immunology. 7 (3), 349-354 (1995).
- Cruse, J. M., Lewis, R. E. . Conjugate Vaccines. 10, (1989).
- Lees, A., Nelson, B. L., Mond, J. J. Activation of soluble polysaccharides with 1-cyano-4-dimethylaminopyridinium tetrafluoroborate for use in protein-polysaccharide conjugate vaccines and immunological reagents. Vaccine. 14 (3), 190-198 (1996).
- Shafer, D. E., et al. Activation of soluble polysaccharides with 1-cyano-4-dimethylaminopyridinium tetrafluoroborate (CDAP) for use in protein-polysaccharide conjugate vaccines and immunological reagents. II. Selective crosslinking of proteins to CDAP-activated polysaccharides. Vaccine. 18 (13), 1273-1281 (2000).
- Schneerson, R., Barrera, O., Sutton, A., Robbins, J. B. Preparation, characterization, and immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-protein conjugates. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 152 (2), 361-376 (1980).
- Lees, A., Barr, J. F., Gebretnsae, S. Activation of soluble polysaccharides with 1-cyano- 4-dimethylaminopyridine tetrafluoroborate (CDAP) for use in protein-polysaccharide conjugate vaccines and immunological reagents. III Optimization of CDAP activation. Vaccines. 8 (4), 777 (2020).
- Qi, X. -. Y., Keyhani, N. O., Lee, Y. C. Spectrophotometric determination of hydrazine, hydrazides, and their mixtures with trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Analytical biochemistry. 175 (1), 139-144 (1988).
- Monsigny, M., Petit, C., Roche, A. C. Colorimetric determination of neutral sugars by a resorcinol sulfuric acid micromethod. Analytical biochemistry. 175 (2), 525-530 (1988).
- Hermanson, G. . Bioconjugate Techniques. 3rd ed. , (2013).
Erratum
Formal Correction: Erratum: Activation and Conjugation of Soluble Polysaccharides using 1-Cyano-4-Dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP)
Posted by JoVE Editors on 7/09/2021. Citeable Link.
An erratum was issued for: Activation and Conjugation of Soluble Polysaccharides using 1-Cyano-4-Dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP). A figure was updated.
Figure 4 was updated from:

Figure 4: Representative results for CDAP activation of dextran. Typical standard curves for the (A) resorcinol/sulfuric acid and (B) TNBS assays. The assay results for dextran activated with 0.25 and 0.5 mg CDAP/mg dextran are shown. Glucose was used as the standard for the resorcinol assay. Dextran, in mg/mL, is divided by 100 kDa to give a molar concentration. The hydrazide concentration is determined using ADH as the standard and the results expressed as µM Hz. (C) Calculation of hydrazide: dextran ratios.The level of derivatization was calculated as hydrazides per 100 kDa of dextran to facilitate the comparison between polymers of different average molecular weights. The % weight ratio of g ADH/g dextran was calculated using a MW of 174 g/mole for ADH. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
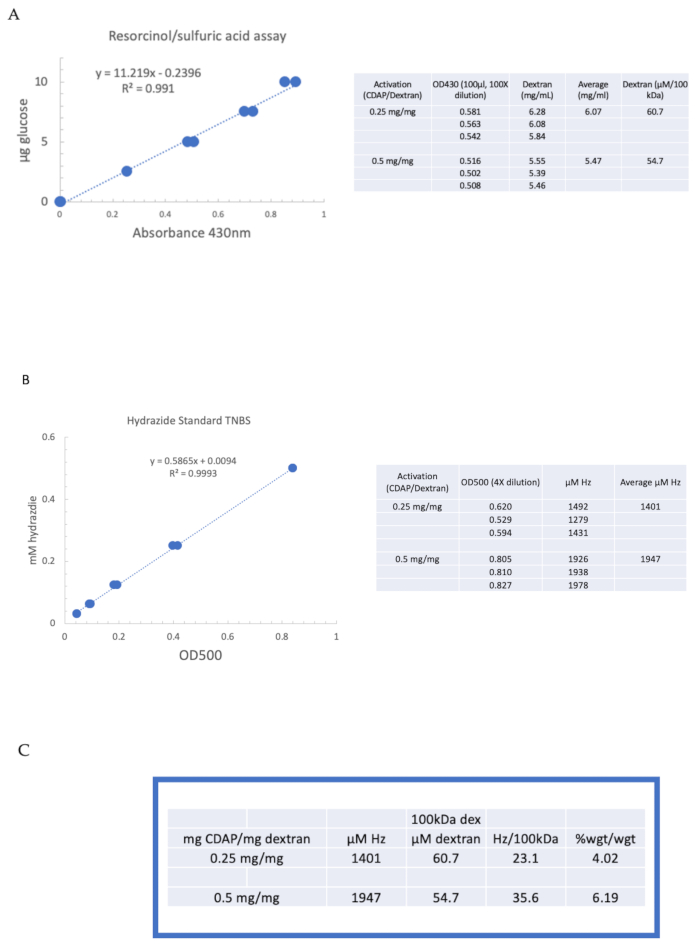
Figure 4: Representative results for CDAP activation of dextran. Typical standard curves for the (A) resorcinol/sulfuric acid and (B) TNBS assays. The assay results for dextran activated with 0.25 and 0.5 mg CDAP/mg dextran are shown. Glucose was used as the standard for the resorcinol assay. Dextran, in mg/mL, is divided by 100 kDa to give a molar concentration. The hydrazide concentration is determined using ADH as the standard and the results expressed as µM Hz. (C) Calculation of hydrazide: dextran ratios.The level of derivatization was calculated as hydrazides per 100 kDa of dextran to facilitate the comparison between polymers of different average molecular weights. The % weight ratio of g ADH/g dextran was calculated using a MW of 174 g/mole for ADH. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Reimpresiones y Permisos
Solicitar permiso para reutilizar el texto o las figuras de este JoVE artículos
Solicitar permisoExplorar más artículos
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados