A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Exploring Biomolecular Interaction Between the Molecular Chaperone Hsp90 and Its Client Protein Kinase Cdc37 using Field-Effect Biosensing Technology
In This Article
Summary
Field-effect biosensing (FEB) is a label-free technique for detecting biomolecular interactions. It measures the electric current through the graphene biosensor to which the binding targets are immobilized. The FEB technology was used to evaluate biomolecular interactions between Hsp90 and Cdc37 and a strong interaction between the two proteins was detected.
Abstract
Biomolecular interactions play versatile roles in numerous cellular processes by regulating and coordinating functionally relevant biological events. Biomolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, fatty acids, nucleic acids, and enzymes are fundamental building blocks of living beings; they assemble into complex networks in biosystems to synchronize a myriad of life events. Proteins typically utilize complex interactome networks to carry out their functions; hence it is mandatory to evaluate such interactions to unravel their importance in cells at both cellular and organism levels. Toward this goal, we introduce a rapidly emerging technology, field-effect biosensing (FEB), to determine specific biomolecular interactions. FEB is a benchtop, label-free, and reliable biomolecular detection technique to determine specific interactions and uses high-quality electronic-based biosensors. The FEB technology can monitor interactions in the nanomolar range due to the biocompatible nanomaterials used on its biosensor surface. As a proof of concept, the protein-protein interaction (PPI) between heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) and cell division cycle 37 (Cdc37) was elucidated. Hsp90 is an ATP-dependent molecular chaperone that plays an essential role in the folding, stability, maturation, and quality control of many proteins, thereby regulating multiple vital cellular functions. Cdc37 is regarded as a protein kinase-specific molecular chaperone, as it specifically recognizes and recruits protein kinases to Hsp90 to regulate their downstream signal transduction pathways. As such, Cdc37 is considered a co-chaperone of Hsp90. The chaperone-kinase pathway (Hsp90/Cdc37 complex) is hyper-activated in multiple malignancies promoting cellular growth; therefore, it is a potential target for cancer therapy. The present study demonstrates the efficiency of FEB technology using the Hsp90/Cdc37 model system. FEB detected a strong PPI between the two proteins (KD values of 0.014 µM, 0.053 µM, and 0.072 µM in three independent experiments). In summary, FEB is a label-free and cost-effective PPI detection platform, which offers fast and accurate measurements.
Introduction
Biomolecular interactions:
Proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in numerous molecular pathways such as cell metabolism, cell structure, cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and more. While some proteins perform their function(s) independently, most proteins interact with other proteins using a binding interface to coordinate proper biological activity1.
Biomolecular interactions can mainly be classified based on the distinct structural and functional characteristics of proteins involved2, for example, based on the protein surfaces, the complex stability, or the persistence of interactions3. Identifying essential proteins and their roles in biomolecular interactions is vital for understanding biochemical mechanisms at the molecular level4. Currently, there are various approaches to detect these interactions5: in vitro6, in silico7, in live cells8, ex vivo9, and in vivo10 with each having its own strengths and weaknesses.
The in vivo assays are performed using the whole animal as an experimental tool11, and the ex vivo assays are performed on tissue extracts or whole organs (e.g., heart, brain, liver) in a controlled external environment by providing minimal alterations in natural conditions. The most common application of in vivo and ex vivo studies is to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and toxicity effects of potential pharmacological agents before human trials by ensuring their overall safety and efficacy12.
Biomolecular interactions can also be detected within living cells. Imaging live cells allow us to observe dynamic interactions as they execute the reactions of a particular biochemical pathway13. Moreover, detection techniques, such as bioluminescence or fluorescence resonance energy transfer, can provide information about where and when these interactions occur within the cell14. Although detection in live cells offers crucial details, these detection methodologies rely on optics and labels, which may not reflect the native biology; they are also less controlled than in vitro methods and require specialized expertise to perform15.
The in silico computational methods are primarily used for large-scale screening of target molecules before the in vitro experiments. Computational prediction methods, computer-based databases, molecular docking, quantitative structure-activity relationships, and other molecular dynamics simulation approaches are among the well-established in silico tools16. Compared to laborious experimental techniques, the in silico tools can easily make predictions with high sensitivity, but with reduced accuracy in predictive performance17.
In vitro assays are performed with microorganisms or biological molecules outside of their standard biological context. Portraying biomolecular interactions through in vitro methods is critical to understanding protein functions and the biology behind the complex network of cell functioning. The preferred assay methodology is chosen according to the protein's intrinsic properties, kinetic values, and the mode and intensity of interactions18,19.
The Hsp90/Cdc37 interaction:
The chaperone-kinase pathway, connecting Hsp90 and Cdc37, is a promising therapeutic target in tumor biology20. Hsp90 plays a central role in cell cycle control, protein assembly, cell survival, and signaling pathways. Proteins that rely on Hsp90 for their functions are delivered to Hsp90 for complexation through a co-chaperone, such as Cdc37. The Hsp90/Cdc37 complex controls the folding of most protein kinases and serves as a hub for a multitude of intracellular signaling networks21. It is a promising anti-tumor target due to its elevated expression in various malignancies, including acute myeloblastic leukemia, multiple myeloma, and hepatocellular carcinoma22,23.
Commonly used in vitro biomolecular interaction detection techniques
Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) is a technique relying on antigen-antibody specificity to identify biologically relevant interactions24. The primary disadvantage of this method is its inability to detect low-affinity interactions and kinetic values24. Biophysical methods such as isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), surface plasmon resonance (SPR), biolayer interferometry (BLI), and FEB technology are preferred to determine the kinetic values.
ITC is a biophysical detection method based on the determination of binding energy along with a complete thermodynamics analysis to characterize biomolecular interactions25. The primary advantage of ITC is that it does not require any labeling or fixation of the target protein. The main difficulties encountered by ITC are the high concentration of target protein required for one experiment and the difficulty in analyzing non-covalent complexes due to small binding enthalpies26. Both SPR and BLI are label-free biophysical techniques that rely on the immobilization of the target molecule on the sensor surface, followed by subsequent injections of the analyte over the immobilized target27,28. In SPR, alterations in the refractive index during biomolecular interactions are measured27; in BLI, the interference in reflected light is recorded in real-time as a change in wavelength as a function of time28. Both SPR and BLI share common advantages of offering high specificity, sensitivity, and detection capabilities29. In both methods, the target protein is immobilized on biosensor surfaces, and hence, there may be some loss of the native conformation of the target, which makes it difficult to discriminate between specific vs. non-specific interactions30. BLI uses expensive disposable fiber-optic biosensors to immobilize the target, and is, therefore, a costly technique31. Compared to these well-established biomolecular detection tools, FEB technology offers a reliable and label-free platform by using low nanomolar concentrations for biomolecular detection in real-time with kinetic characterization. The FEB technology also overcomes the bubbling challenges faced in ITC and is more cost-effective compared to SPR or BLI.
The field-effect transistor (FET) based biosensors is an emerging field for detecting biomolecular interactions by offering varied biomedical applications. In the FET system, targets are immobilized to the biosensor chips and interactions are detected by changes in conductance32. The unique feature to be considered in the development of an efficient electronic biosensor is the physicochemical properties such as the semi-conductive nature and chemical stability of the coating material used to fabricate the sensor surface33. Conventional materials like silicon used for FET have limited the sensitivity of sensors because it requires oxide layers sandwiched between the transistor channel and a specific environment for proper functioning34. Moreover, silicon transistors are sensitive to high salt environments, thus making it hard to measure biological interactions in their natural environment. The graphene-based biosensor is presented as an alternative as it offers excellent chemical stability and electric field. Since graphene is a single atomic layer of carbon, it is both extremely sensitive as a semi-conductor and chemically compatible with biological solutions; both of these qualities are desirable to generate compatible electronic biosensors35. The remarkable ultrahigh loading potential of biomolecules offered by graphene-coated biosensors lead to the development of graphene-based biosensors FEB technology.
Principle of FEB technology: FEB is a label-free biomolecular detection technique that measures the electric current through the graphene biosensor to which the binding targets are immobilized. Interactions between the immobilized protein and the analyte result in alterations in current that are monitored in real-time, enabling accurate kinetic measurements36.
Instrumentation: The FEB system comprises a graphene field-effect transistor (gFET) sensor chip and an electronic reader that applies a constant voltage throughout the experiment (Figure 1). The analyte is applied in solution to the target protein immobilized on the biosensor surface. When an interaction occurs, an alteration in the current is measured and recorded in real-time. As the analyte concentration increases, the fraction of bound analyte will also increase, causing higher alternations in the current. Using the automated analysis software provided with the instrument (Table of Materials), I-Response is measured and recorded in terms of biosensing units (BU)37. I-Response is defined as the alteration in the current (I) through the biosensor chip measured in real-time upon the interaction of the immobilized target with the analyte. The FEB automated analysis software can analyze both the I-Response and C-Response to dynamic interaction events, where the C-Response records the alterations in the capacitance (C). The variations in both the I-Response and C-Response correspond directly to the fraction of bound analyte and can be further analyzed to generate KD values. The automated analysis software's default preference is I-Response.
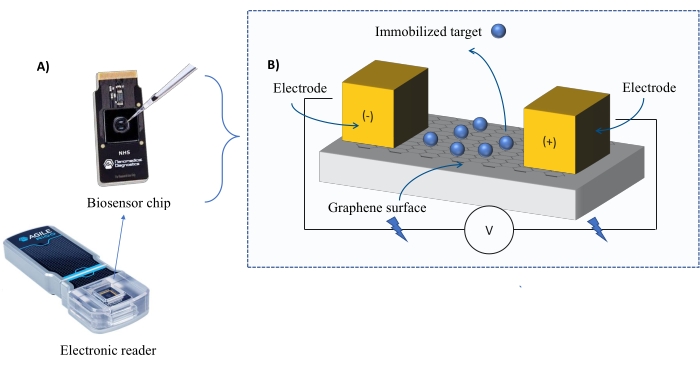
Figure 1: Overview of the experimental setup. (A) Graphene-based chip and an electronic reader. (B) An overview of the chip components. The chip is attached to two electrodes that supply current to the system. The surface of the chip is covered with graphene, which when activated can bind the target. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Methodology:
Initially, the activated biosensor chip is inserted into the FEB device (Figure 1) followed by the execution of the steps outlined below: (1) Calibration: The experiment starts with system calibration using 1x phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH = 7.4) to create the baseline equilibration response. (2) Association: The analyte is introduced in the chip, and the I-Response is monitored until binding saturation is reached. (3) Dissociation: The analyte is dissociated using 1x PBS. (4) Regeneration: Remnants of the analyte are removed using 1x PBS. (5) Washing: A total of five washes are performed using 1x PBS for the thorough removal of the bound and unbound analytes from the chip.
Analysis:
Data analysis is performed using the fully automated software provided with the instrument. The automated analysis software generates a Hill fit plot with a KD value. The Hill fit plot describes the association of an analyte to the target protein as a function of analyte concentrations. The concentration at which a half-maximal response is achieved is proportional to the KD value. A low KD value represents high binding affinity and vice versa.
To validate the data obtained from the FEB experiment, I-Responses are extracted from each readout point for each analyte concentration using the data review/export software and can be exported to other statistical analysis software (see Table of Materials) as explained below.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
NOTE: The recombinant proteins used in this study, Hsp90 and Cdc37, were commercially obtained (see Table of Materials).
1. Chip activation
NOTE: All materials to be used in the experiment are listed in the Table of Materials. Filter all prepared solutions through a sterile 0.2 μm filter.
- Prepare 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) carbodiimide (EDC) solution by adding 2 mg of EDC to 2.5 mL of 1 M 2-(N-morpholino) ethane sulfonic acid (MES) buffer (pH = 6.0) in a 15 mL tube. Prepare N-Hydroxysulfosuccinimide (sulfo-NHS) solutions by adding 6 mg of sulfo-NHS to 2.5 mL of 1 M MES buffer (pH = 6.0) in a separate 15 mL tube. Aliquot 50 µL of each solution in independent tubes and store at -20 °C for future use.
- Mix equal volumes of EDC sand sulfo-NHS solution (50 µL of EDC + 50 µL of sulfo-NHS) by pipetting up and down (do not vortex).
NOTE: The mixed solution of EDC/sulfo-NHS must be used within 30 min to maintain effective cross-linking for proper chip functionalization. - Place the biosensor chip (5.7 cm x 2.4 cm; see Table of Materials) supplied by the company in a glass Petri dish with a fitted lid. All the functionalization steps involved in chip activation are suggested to be done within the Petri dish. Apply 50 µL of 1 M MES buffer (pH = 6.0) to the biosensor chip, incubate for 1 min at room temperature, and then aspirate the buffer.
- Apply 50 µL of EDC/sulfo-NHS solution immediately to the sensor chip. Cover the Petri dish and incubate for 15 min at room temperature. Aspirate EDC/sulfo-NHS solution from the chip.
- Rinse the chip once with 50 µL of 1 M MES buffer (pH = 6.0); aspirate the MES buffer.
2. Target protein immobilization
- Rinse the chip 2x with 50 µL of 1x PBS (pH = 7.4). Aspirate the PBS from the chip and add the target molecule, Hsp90 (50 µL; 500 nM).
NOTE: Buffer mismatch may ruin the entire experiment; hence, before the experiment, it is important to make sure that the target molecule is in the same buffer as that used for calibration (e.g., 1x PBS (pH = 7.4)). If needed, perform a buffer exchange by overnight dialysis before the experiment. In this experiment, overnight dialysis was performed for both recombinant proteins, Hsp90 and Cdc37, against 1x PBS (pH = 7.4; see Table of Materials) with proper buffer exchange at 4 °C. The concentration of the target material (Hsp90 in this case) may vary according to different experimental protocols and the nature of target materials (protein/peptide/ligands). - Cover the glass Petri dish and incubate for 30 min at room temperature. Aspirate the solution containing the target molecule and rinse 3x with 50 µL of 1x PBS (pH = 7.4). Aspirate the 1x PBS (pH = 7.4) solution from the chip.
- Add 50 µL of Quench 1 (3.9 mM amino-PEG5-alcohol in 1x PBS (pH = 7.4)) solution to the chip. Cover the glass Petri dish and incubate for 15 min at room temperature. Aspirate the Quench 1 solution from the chip.
- Add 50 µL of Quench 2 (1 M ethanolamine (pH = 8.5)) solution to the chip. Cover the glass Petri dish and incubate for 15 min at room temperature. Aspirate Quench 2 solution from the chip and rinse the chip 5x using 50 µL of 1x PBS, leaving the last PBS droplet on the sensor.
3. Preparing analyte samples
- Prepare analyte dilution series for Cdc37 in the desired concentration range. For the first experiment, the following concentrations were used: 25 nM, 50 nM, 100 nM, 200 nM, 400 nM, 800 nM, 1,000 nM, 2,000 nM, 3,000 nM, and 5,000 nM. For the second experiment, a different set of concentrations ranging from 0.4 nM to 200 nM was used.
- Design the experiment to include at least eight different analyte concentrations to obtain a reliable KD value. Prepare the different dilutions of the analyte protein in the same buffer as that used for calibration and target protein; here it is 1x PBS (pH = 7.4).
4. Loading of the activated biosensor chip into the FEB device
NOTE: The FEB device consists of a reader featured with LED light indications and a cartridge to insert the biosensor chip.
- After target protein immobilization, insert the activated chip into the cartridge of the device, which is connected via USB to a computer. After the chip insertion, a green LED light will be displayed on the reader indicating that the FEB device is ready for the experiment. Install the automated software (see Table of Materials) supplied by the company on the computer, to which the FEB device is connected, to monitor the experiment step by step as described below.
5. Run the experiment
- Press the Run Experiment module on the automated software and choose 10 Points with Regeneration or any other desired protocol. Fill in the following details: operator name, experiment name, date (e.g., Yana, Hsp90 + Cdc37, 14.03.2021); regeneration buffer (e.g., PBS buffer); immobilized target (e.g., Hsp90); analyte in solution (e.g., Cdc37). See Supplementary Figure S1 for details.
- Press the Begin the Experiment button displayed on the software and follow the instructions shown by the automated software as described below.
NOTE: The software is fully automated, user-friendly, and guides the user throughout the experiment step by step. A pop-up window will appear on the screen with instructions to proceed further at each step of the experiment. The software will provide instructions for each repetitive step consecutively from calibration, analyte association, dissociation, regeneration, and wash (5x) for each analyte concentration throughout the experiment. - Perform instrument calibration. To do so, aspirate the remaining PBS solution from the chip and apply 50 µL of calibration buffer (1x PBS; pH = 7.4). Press the Continue button and wait for 5 min until the calibration step is finished. The software displays the endpoint determined for the calibration step (5 min) with a warning alarm to follow-up.
- Next, perform an analyte association. To do so, aspirate the calibration buffer from the chip and apply 50 µL of the lowest analyte concentration (25 nM of Cdc37). Press the Continue button and wait for 5 min until the association step is finished. The software displays the endpoint for the association step (5 min) with a warning alarm to proceed.
- Perform an analyte dissociation. To do so, aspirate the analyte solution from the chip and apply 50 µL of the dissociation buffer (1x PBS; pH = 7.4). Press the Continue button and wait for 5 min until the dissociation step duration (5 min) is finished. The software displays the endpoint for the dissociation step (5 min) with a warning alarm to follow-up.
- Next, perform chip regeneration. Aspirate the dissociation solution from the chip and apply 50 µL of regeneration buffer (1x PBS; pH = 7.4). Press the Continue button and wait for 30 s until the regeneration step duration (30 s) is finished. The software displays the endpoint for the regeneration step (30 s) with a warning alarm to follow-up.
- Finally, wash the chip. Aspirate the regeneration solution from the chip and apply 50 µL of wash buffer (1x PBS; pH = 7.4) to the chip. Aspirate the solution from the chip and repeat this 5x. Leave the last drop of wash buffer on the chip and press the Continue button and wait for 30 s until the wash step duration is finished in the software display.
NOTE: The software displays the endpoint for the wash step (30 s) with a warning alarm to proceed with the next cycle of the experiment. - Repeat the steps for each analyte concentration used; the five steps of calibration, analyte association, dissociation, regeneration, and wash (5x) constitute one cycle. For the experiment shown here, we performed 10 cycles for 10 analyte concentrations (ranging from 25 nM to 5,000 nM or 0.4 nM to 200 nM; Figure 2).
6. Analysis
- Press the Analysis button seen at the top of the automated analysis software at the end of the experiment. A display window containing all the experimental points will appear. In the window, ensure that the analyte concentrations used for the prescribed protocol are correct.
- Press the Run Analysis button to generate the KD value automatically. The software generates a Hill fit plot by plotting the analyte concentrations against the corresponding I-Responses from which the dissociation constant at equilibrium, KD value, is calculated.
- Export the raw data for analysis in other statistical analysis software by using the data review/export software as described below.
- Copy the R1R file created automatically at the end of the experiment (e.g., Hsp90 + Cdc37 14.03.2021) to a new folder on the desktop. Open the Data Review/Export software supplied by the company (see Supplementary Figure S2A).
- Click on Data Processing > Process R1R files > OK on the home screen of the data review/export software.
- Select the folder containing R1R files created on the desktop in step 6.3.1. and press the OK button. This creates a copy of the original R1R data, to review and edit the data without overriding the original file.
- Press the data processing icon seen at the home screen of the data review/export software. Press Load Processed R1R Files > OK. Select the same folder created in step 6.3.1 containing processed R1R files. Press OK. At this step, the folder containing the experiment files is ready to be reviewed.
- At the home screen of data review/export software, press Data Analysis. Select Calibration > Calibrate edited R1R files > OK (see Supplementary Figure S2B). This step calibrates all the data points according to the first calibration step, to create a baseline.
- At the home screen of data review/export software, press Data Analysis. Select Review and Edit R1R Files > OK. Review the data points, delete points, or add steps by using the Delete/Add Step button. Make sure all the steps are in the correct place, e.g., the calibration step is on the baseline, the association step is at the peak (see Supplementary Figure S3), and then press the Save button to save all the changes made.
- At the home screen of data review/export software, press Data Analysis. Select Analyze/Plot Data, choose the steps to export (see Supplementary Figure S4). Add each association step (e.g., step 2, step 7, and so on) after subtracting the calibration step (e.g.,step 1, step 6, and so on) to the export list before exporting the data.
- Press Export this Data. The software generates a spreadsheet file containing the I-Response for each analyte concentration data point from each transistor (if all transistors are working, we will have three different I-response values for each concentration point). Use this spreadsheet file to further analyze the data in the statistical software.
- Open the statistical analysis software. Create an XY table with three Y values; press Create. The data for this table (X, Y values) is copied from the spreadsheet file created in step 6.3.8. The x-axis corresponds to analyte concentration (depending on the concentration used), and the three Y values correspond to the I-Responses, obtained from the Data Review/Export software supplied by the company.
- Press Analyze this Data. Choose XY Analyses > Nonlinear Regression (Curve Fit) > Binding Saturation > One Site > Total. The software will automatically analyze the data, generate the KD value, and create a graph of the data points.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Results from experiment 1:
The target protein Hsp90 (500 nM) was immobilized to the chip following the target immobilization protocol as described above. For the first experiment, 10 concentrations of the analyte protein, Cdc37, ranging from 25 nM to 5,000 nM, were prepared based on the data available in the literature (see Table 1).
The steps of the experiment can be monitored in real-time by following the alterations occurring in the I-Response (
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
In this study, the feasibility of using the FEB technology (a real-time kinetic characterization approach) was evaluated to determine the biomolecular interaction between Hsp90 and Cdc37. The initial exploratory experiment (first experiment) suggested that choosing the proper analyte concentrations is a critical part of the experiment and that the experiment should be designed by including concentration points above and below the KD value, which were predicted based on the data available in the literature.
...Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from the Binational Science Foundation (BSF) to S.K.S. and N.Q.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Automated analysis software | Agile plus software, Cardea (Nanomed) | NA CAS number: NA | Referred to in the text as the automated analysis software supplied with the instrument. Generates automated analysis. |
| COOH-BPU (Biosensing Processing Unit) | Agile plus software, Cardea (Nanomed) | NA CAS number: NA | biosensor chip |
| Data review software | Datalign 1.0, Cardea (Nanomed) | NA CAS number: NA | Referred to as the supplied data review software in the text. Supplied with the instrument and allows to review and export the information data points. |
| Dialysis bag | CelluSep, Membrane filtration products | T2-10-15 CAS number: NA | T2 tubings (6,000-8,000 MWCO), (10 mm fw, 6.4mm Ø, 0.32ml/cm, 15m) |
| EDC (1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) carbodiimide) | Cardea (Nanomed) | EDC160322-02 CAS number: 25952-53-8 | White powder |
| ITC (Isothermal titration calorimetry) system | Microcal-PEAQ-ITC (Malvern, United Kingdom) | NA CAS number: NA | |
| MES (2-(N-morpholino) ethane sulfonic acid) buffer | Merck | M3671-50G CAS number: 4432-31-9 | White powder |
| NHS (N-Hydroxysulfosuccinimide) chips | Cardea (Nanomed) | NA CAS number: NA | Graphene-based chip |
| PBS (Phosphate-buffered saline) X 10 | Bio-Lab | 001623237500 CAS number: 7758-11-4 | Liquid transparent solution |
| Pipete | Thermo Scientific | 11855231 CAS number: NA | Finnpipette F3 5-50 µL, yellow |
| Quench 1 (3.9 mM amino-PEG5-alcohol in 1 X PBS) | Cardea (Nanomed) | 0105-001-002-001 CAS number: NA | Liquid, transparent solution |
| Quench 2 (1 M ethanolamine (pH=8.5)) | Cardea (Nanomed) | 0105-001-003-001 CAS number: NA | Liquid, transparent solution |
| Recombinant protein Cdc37 | Abcam | ab256157 CAS number: NA | |
| Recombinant protein Hsp90 beta | Abcam | ab80033 CAS number: NA | |
| Spreadsheet | Excel, Microsoft office | NA CAS number: NA | |
| Statistical software | GraphPad, Prism | NA CAS number: NA | Referred to as the other statistical software. Sigma plot, phyton or other statistical programes may also be used |
| Sulfo-NHS | Cardea (Nanomed) | NHS160321-07 CAS number: 106627-54-7 | White powder |
| Tips | Alex red | LC 1093-800-000 CAS number: NA | Tip 1-200 µl, in bulk, 1,000 pcs |
References
- Tuncbag, N., Gursoy, A., Guney, E., Nussinov, R., Keskin, O. Architectures and functional coverage of protein-protein interfaces. Journal of Molecular Biology. 381 (3), 785-802 (2008).
- Berggård, T., Linse, S., James, P. Methods for the detection and analysis of protein–protein interactions. Proteomics. 7 (16), 2833-2842 (2007).
- Magliery, T. J., et al. Detecting protein-protein interactions with a green fluorescent protein fragment reassembly trap: Scope and mechanism. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 127 (1), 146-157 (2005).
- Xing, S., Wallmeroth, N., Berendzen, K. W., Grefen, C. Techniques for the analysis of protein-protein interactions in vivo. Plant Physiology. 171 (2), 727-758 (2016).
- Nguyen, T. N., Goodrich, J. A. Protein-protein interaction assays: Eliminating false positive interactions. Nature Methods. 3 (2), 135-139 (2006).
- Fernández-Suárez, M., Chen, T. S., Ting, A. Y. Protein-protein interaction detection in vitro and in cells by proximity biotinylation. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 130 (29), 9251-9253 (2008).
- Jiang, M., Niu, C., Cao, J., Ni, D. -A., Chu, Z. In silico-prediction of protein–protein interactions network about MAPKs and PP2Cs reveals a novel docking site variants in Brachypodium distachyon. Scientific Reports. 8 (1), 15083(2018).
- Yazawa, M., Sadaghiani, A. M., Hsueh, B., Dolmetsch, R. E. Induction of protein-protein interactions in live cells using light. Nature Biotechnology. 27 (10), 941-945 (2009).
- Wang, W., Goodman, M. T. Antioxidant property of dietary phenolic agents in a human LDL-oxidation ex vivo model: Interaction of protein binding activity. Nutrition Research. 19 (2), 191-202 (1999).
- Xing, S., Wallmeroth, N., Berendzen, K. W., Grefen, C. Techniques for the analysis of protein-protein interactions in vivo. Plant Physiology. 171 (2), 727-758 (2016).
- Qvit, N., Disatnik, M. -H., Sho, E., Mochly-Rosen, D. Selective phosphorylation inhibitor of delta protein kinase C–Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase protein–protein interactions: Application for myocardial injury in vivo. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 138 (24), 7626-7635 (2016).
- Alam, M. N., Bristi, N. J., Rafiquzzaman, M. Review on in vivo and in vitro methods evaluation of antioxidant activity. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 21 (2), 143-152 (2013).
- Paulmurugan, R., Gambhir, S. S. Novel fusion protein approach for efficient high-throughput screening of small molecule–mediating protein-protein interactions in cells and living animals. Cancer Research. 65 (16), 7413-7420 (2005).
- Boute, N., Jockers, R., Issad, T. The use of resonance energy transfer in high-throughput screening: BRET versus FRET. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 23 (8), 351-354 (2002).
- Deriziotis, P., Graham, S. A., Estruch, S. B., Fisher, S. E. Investigating protein-protein interactions in live cells using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (87), e51438(2014).
- Ekins, S., Mestres, J., Testa, B. In silico pharmacology for drug discovery: Methods for virtual ligand screening and profiling. British Journal of Pharmacology. 152 (1), 9-20 (2007).
- Valerio, L. G. Application of advanced in silico methods for predictive modeling and information integration. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology. 8 (4), 395-398 (2012).
- Piehler, J. New methodologies for measuring protein interactions in vivo and in vitro. Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 15 (1), 4-14 (2005).
- Ideker, T., Sharan, R. Protein networks in disease. Genome Research. 18 (4), 644-652 (2008).
- Lu, H., et al. Recent advances in the development of protein–protein interactions modulators: mechanisms and clinical trials. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 5 (1), 213(2020).
- Jarosz, D. Hsp90: A global regulator of the genotype-to-phenotype map in cancers. Advances in Cancer Research. 129, 225-247 (2016).
- Johnson, V. A., Singh, E. K., Nazarova, L. A., Alexander, L. D., McAlpine, S. R. Macrocyclic inhibitors of Hsp90. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 10 (14), 1380-1402 (2010).
- Mahalingam, D., et al. Targeting HSP90 for cancer therapy. British Journal of Cancer. 100 (10), 1523-1529 (2009).
- Stewart, A., Fisher, R. A. Co-Immunoprecipitation: Isolation of protein signaling complexes from native tissues. Methods in Cell Biology. 112, 33-54 (2012).
- Pierce, M. M., Raman, C. S., Nall, B. T. Isothermal titration calorimetry of protein-protein interactions. Methods. 19 (2), San Diego, Calif. 213-221 (1999).
- Paketurytė, V., et al. Inhibitor binding to carbonic anhydrases by isothermal titration calorimetry. Carbonic Anhydrase as Drug Target. , Springer International Publishing. 79-95 (2019).
- Grote, J., Dankbar, N., Gedig, E., Koenig, S. Surface plasmon resonance/mass spectrometry interface. Analytical Chemistry. 77 (4), 1157-1162 (2005).
- Kumaraswamy, S., Tobias, R. Label-free kinetic analysis of an antibody–antigen interaction using biolayer interferometry. Methods in Molecular Biology. , 165-182 (2015).
- Wallner, J., Lhota, G., Jeschek, D., Mader, A., Vorauer-Uhl, K. Application of bio-layer interferometry for the analysis of protein/liposome interactions. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 72, 150-154 (2013).
- Singh, A. N., Ramadan, K., Singh, S. Experimental methods to study the kinetics of protein–protein interactions. Advances in Protein Molecular and Structural Biology Methods. , 115-124 (2022).
- Frenzel, D., Willbold, D. Kinetic titration series with biolayer interferometry. PLoS One. 9 (9), 106882(2014).
- Vu, C. -A., Chen, W. -Y. Field-effect transistor biosensors for biomedical applications: Recent advances and future prospects. Sensors. 19 (19), 4214(2019).
- Bergveld, P. A critical evaluation of direct electrical protein detection methods. Biosensors & Bioelectronics. 6 (1), 55-72 (1991).
- Lowe, B. M., Sun, K., Zeimpekis, I., Skylaris, C. K., Green, N. G. Field-effect sensors – from pH sensing to biosensing: sensitivity enhancement using streptavidin–biotin as a model system. The Analyst. 142 (22), 4173-4200 (2017).
- Goldsmith, B. R., et al. Digital biosensing by foundry-fabricated graphene sensors. Scientific Reports. 9 (1), 434(2019).
- Afsahi, S., et al. Novel graphene-based biosensor for early detection of Zika virus infection. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 100, 85-88 (2018).
- Afsahi, S. J., et al. Towards novel graphene-enabled diagnostic assays with improved signal-to-noise ratio. MRS Advances. 2 (60), 3733-3739 (2017).
- Roe, S. M., et al. The mechanism of Hsp90 regulation by the protein kinase-specific cochaperone p50cdc37. Cell. 116 (1), 87-98 (2004).
- Gaiser, A. M., Kretzschmar, A., Richter, K. Cdc37-Hsp90 complexes are responsive to nucleotide-induced conformational changes and binding of further cofactors. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 285 (52), 40921-40932 (2010).
- Popescu, A. I., Găzdaru, D. M., Chilom, C. G., Bacalum, M. Biophysical interactions: Their paramount importance for life. Romanian Reports in Physics. 65 (3), 1063-1077 (2013).
- Surya, S., Abhilash, J., Geethanandan, K., Sadasivan, C., Haridas, M. A profile of protein-protein interaction: Crystal structure of a lectin-lectin complex. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 87, 529-536 (2016).
- Velazquez-Campoy, A., Freire, E. ITC in the post-genomic era...? Priceless. Biophysical Chemistry. 115 (23), 115-124 (2005).
- Concepcion, J., et al. Label-free detection of biomolecular interactions using bioLayer interferometry for kinetic characterization. Combinatorial Chemistry & High Throughput Screening. 12 (8), 791-800 (2009).
- Helmerhorst, E., Chandler, D. J., Nussio, M., Mamotte, C. D. Real-time and label-free bio-sensing of molecular interactions by surface plasmon resonance: A laboratory medicine perspective. The Clinical Biochemist. Reviews. 33 (4), 161-173 (2012).
- Jacob, N. T., et al. Synthetic molecules for disruption of the MYC protein-protein interface. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 26 (14), 4234-4239 (2018).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved