A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
A Photodynamic Approach to Study Function of Intracellular Vesicle Rupture
In This Article
Summary
AlPcS2a-mediated chromophore-assisted laser inactivation (CALI) is a powerful tool for studying spatiotemporal damage of intracellular vesicles (IVs) in live cells.
Abstract
Intracellular vesicles (IVs) are formed through endocytosis of vesicles into cytoplasm. IV formation is involved in activating various signal pathways through permeabilization of IV membranes and the formation of endosomes and lysosomes. A method named chromophore-assisted laser inactivation (CALI) is applied to study the formation of IVs and the materials in controlling IV regulation. CALI is an imaging-based photodynamic methodology to study the signaling pathway induced by membrane permeabilization. The method allows spatiotemporal manipulation of the selected organelle to be permeabilized in a cell. The CALI method has been applied to observe and monitor specific molecules through the permeabilization of endosomes and lysosomes. The membrane rupture of IVs is known to selectively recruit glycan-binding proteins, such as galectin-3. Here, the protocol describes the induction of IV rupture by AlPcS2a and the use of galectin-3 as a marker to label impaired lysosomes, which is useful in studying the downstream effects of IV membrane rupture and their downstream effects under various situations.
Introduction
Endosomes, a type of intracellular vesicle (IV), are formed by endocytosis and then mature into lysosomes. Various intracellular signal pathways are involved in the formation of IVs; additionally, different intrinsic and extrinsic stimuli can damage IVs (e.g., pathogens can escape from the bounded membrane during infection and enter into cytoplasm1). This is usually accompanied by the rupture of endocytotic vesicles2. Therefore, the techniques for targeting and damaging IVs can be used in related studies3.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a light-dependent therapy to combat diseases by killing tumors or pathogens4. In PDT, targeted cells are labeled with non-toxic chromophores, called photosensitizers, that can be locally activated by light illumination5,6. Photosensitizers absorb energy from light and transform into an excited singlet state, leading to the long-lived excited triplet state. Photosensitizers of the triplet state can undergo electron or energy transfer and form reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the presence of oxygen, and can spatially destroy labeled cells within the illumination region7. The consequence varies depending on the power of light8. By controlling the concentration of photosensitizers and the intensity of light illumination, targeted biomolecules can be selectively inactivated without cell lysis, termed as chromophore-assisted light inactivation (CALI)9. With the significant development of photosensitizers that can selectively label various subcellular targets, CALI has become a valuable tool to control light-mediated inactivation of biomolecules for small biomolecules such as nucleotides and proteins, as well as organelles such as mitochondria and endo-lysosomes3,10,11,12,13.
Compared to CALI, chemical or physical methods are also used to impair membranes, such as bacterial toxin14,15 and Leu-Leu-OMe16 treatment for lysosomal damage. However, these methods display bulk impairment of IVs within cells. Robust photosensitizers (i.e., Al(III) phthalocyanine chloride disulfonic acid (AlPcS2a)) are used in CALI; AlPcS2a, targeting the lysosomes through endocytosis, is used to rupture endosomes or lysosomes in a controlled region17. AlPcS2a is a cell membrane-impermeable phthalocyanine-based chromophore that binds to lipid on plasma membrane and is internalized through endocytosis and eventually accumulates within the lysosome through the endocytic pathway18. It absorbs light within a near-infrared spectral region and generates singlet oxygen, a major ROS generated by excited AlPcS2a18. Singlet oxygen decaying rapidly limits its diffusion and reaction distance within a tiny region in cells (approximately 10-20 nm)19. By adjusting the duration of AlPcS2a incubation and light illumination, spatiotemporal control of the damage of IVs within a subcellular area is allowed. CALI therefore becomes a powerful tool for examining the consequences of IV damage, and the formation and regulation of IVs.
In this study, a specific protocol of CALI using AlPcS2a as a photosensitizer is addressed. This protocol can be applied to various types of IVs, including endosomes and lysosomes, and used to examine the follow-up responses after membrane rupture. HeLa cells expressing fluorophore-conjugated galectin-316,20 revealed after lysosome rupture are used to demonstrate this protocol.
Protocol
1. AlPcS2a stock preparation
- Dissolve 10 mg of AlPcS2a in 400 µL of 0.1 M NaOH. To improve solubility, heat the solution at 50 °C and vortex.
- Mix the solution with 4 mL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Then, filter the solution with a 0.22 µm filter to remove the insoluble precipitates.
- Measure the concentration of the solution through a UV-Vis spectrophotometer. The extinction coefficient of AlPcS2a at 672 nm is 4 x 104 cm-1 M-1. Dilute the AlPcS2a solution with PBS to make a 1 mM solution. Make 1 mL aliquots and store at -20 °C.
2. Transfection
NOTE: Gal3-GFP is applied as an indicator for live-cell imaging of lysosomal rupture.
- Maintain HeLa cell culture in DMEM supplemented with 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS). After washing the cells with PBS, trypsinize the cells, then resuspend the cells in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS.
NOTE: The method is applicable for most of the attached cell lines, including HeLa and A549 cell lines. In principle, despite not testing suspension cells, CALI assays could be performed with them. - Dilute 300 ng of Gal3-GFP plasmid in 25 µL of reduced serum medium, and then add 0.6 µL of P3000 reagent. Gently mix. Dilute 0.45 µL of Lipofectamine 3000 reagent in 25 µL of reduced serum medium. Gently mix.
- Incubate for 5 min at room temperature. Mix diluted DNA and diluted Lipofectamine 3000, and then incubate for 10 min at room temperature.
- Mix the DNA-Lipofectamine mixture, 3 x 105 suspended HeLa cells, and 200 µL of DMEM+10% FBS, and then seed the cells on the central glass region of a 35 mm glass button dish.
3. AlPcS2a staining
- To allow cell attachment, incubate the cells at 37 °C in the incubator supplied with 5% CO2 for at least 4 h.
- Dilute AlPcS2a in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS to make a 1 µM AlPcS2a solution. Pre-warm the AlPcS2a-containing medium in a 37 °C water bath. Replace the culture medium with the AlPcS2a-containing medium.
- Incubate the cells at 37 °C in the incubator supplied with 5% CO2 overnight (16-18 h).
- The following day, wash the cells twice with PBS to remove extracellular AlPcS2a. Replace the medium with fresh medium, and then incubate at 37 °C for 4 h to allow residual dye along the endocytic pathway to accumulate into lysosomes.
NOTE: To stain endosomes, incubate cells in 1 µM AlPcS2a in DMEM containing 10% FBS for 15 min at 37 °C. Next, wash cells twice with PBS and incubate them in pre-warmed medium before imaging .
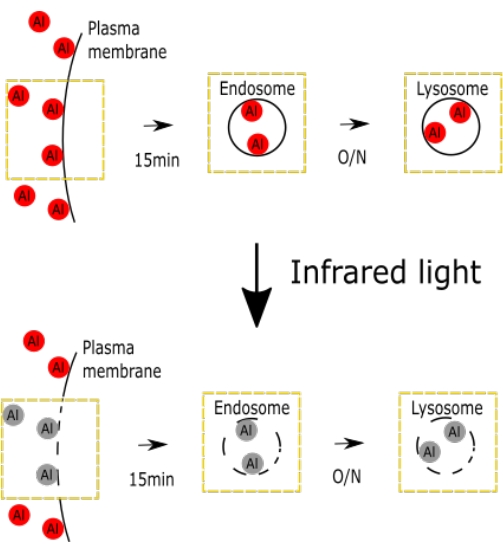
Figure 1. A schematic figure representing the selective IV damage with AlPcS2a. The figure shows the schematics of selective IV damage. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
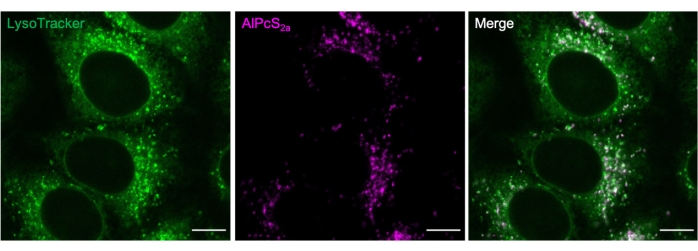
Figure 2. Lysosomal staining with AlPcS2a. Lysosomes labeled overnight with 1 µM AlPcS2a in HeLa cells are positively stained with 50 nM green fluorescent dye. Scale bar: 10 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Sample imaging and light illumination
NOTE: IV damage within a subcellular region of a single cell or all the AlPcS2a-labeled cells in a culture dish can be performed. Bulk illumination of the whole culture dish allows quantitative study of this damage, including biochemical studies.
- Manipulate single cells by damaging lysosomes within a single cell, as described below.
- Place the culture dish on the stage of a confocal microscope. Use the 488 nm and 561 nm lasers for exciting GFP and AlPcS2a, respectively.
- Circle a 5 x 5 µm2 region of interest (ROI) on the AlPcS2a-labeled vesicles which are selected to be damaged.
- Pulse illuminate the ROI with a 633 nm laser of 0.21 mW for 70 repeats. Monitor the formation of Gal3 puncta as an indicator of lysosomal membrane permeabilization.
- Damage all labeled cells in a culture dish as described below.
- Place the culture dish on a platform. Illuminate the dish with 660 nm of collimated LED light (near-infrared light is ideal base on the excitation spectrum of AlPcS2a).
- Place the culture dish on the microscope and monitor the indicators of membrane permeabilization as mentioned in step 4.1.3.
- Assess injury of IVs using the following indicators.
- The contents of endosome or lysosome are most highly glycosylated, which are exposed to cytosol upon IV rupture. Rapidly label these using cytosolic glycan-binding galectins, including galectin-1, galectin-3, galectin-8, and galectin-916,20.
- The size of the wound can be determined by the release of membrane-impermeable dye as described in21.
- The difference between endosomes and lysosomes are their luminal pH value. Lysosomal rupture perturbs the luminal pH, which can be measured by using pH-sensitive dye, such as FITC-dextran3.
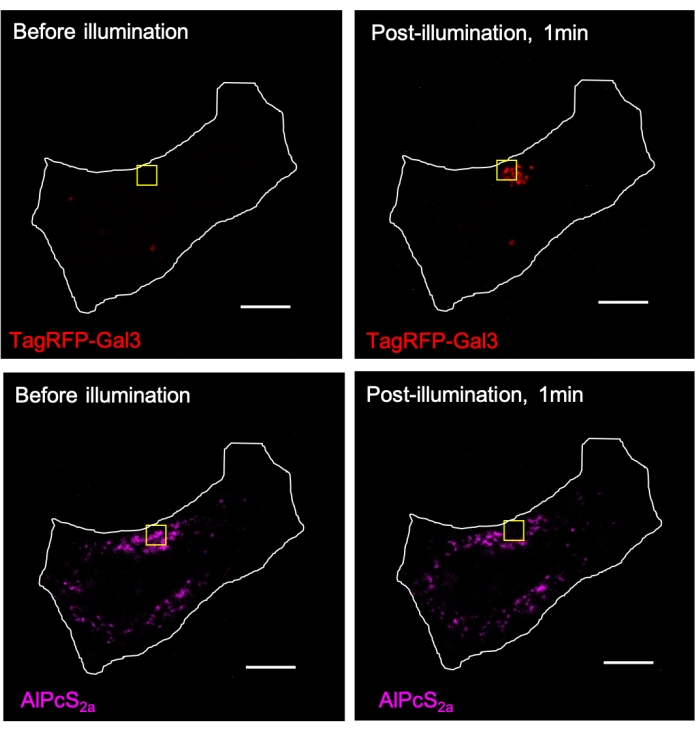
Figure 3. AlPcS2a-mediated CALI induces local recruitment of TagRFP-galectin-3 (Gal3) to the lysosomes within the illumination region. Lysosomes in TagRFP-galectin-3-expressed HeLa cells were stained overnight with 1 µM AlPcS2a, followed by focusing illumination with near-infrared light (633 nm) within the yellow square. AlPcS2a signal within the yellow square is photobleached, accompanied by the formation of TagRFP-galectin-3 puncta. Scale bar: 10 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
A schematic figure representing the AlPcS2a-induced damage of IV, including endosome and lysosome, has been shown (Figure 1).
Commercially available markers can be used to determine the AlPcS2a staining conditions. For example, AlPcS2a puncta and green fluorescent dye22 colocalization (Figure 2).
Fluorophore-labeled galectin-3 can be applied as an ind...
Discussion
AlPcS2a binds to the plasma membrane, then is internalized by endocytosis and eventually accumulates in lysosomes. AlPcS2a can thus be localized in the subcellular compartments by adjusting the incubation duration. A limitation of this methodology is that only a sub-population of IVs could be labeled by AlPcS2a through endocytosis because there are many other membrane sources of IVs, such as ER and Golgi apparatus. In addition, the selective labeling of AlPcS2a into early or la...
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Academia Sinica Inflammation Core Facility, IBMS for research support. The core facility is funded by the Academia Sinica Core Facility and Innovative Instrument Project (AS-CFII-111-213). The authors thank the Common Equipment Core Facility of the Institute of Biomedical Sciences (IBMS), Academia Sinica (AS) for assisting the image acquisition.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Reagent | |||
| Al(III) Phthalocyanine Chloride Disulfonic acid (AlPcS2a) | Frontier Scientific | P40632 | |
| Culture dish | ibidi | 812128-200 | |
| Culture Medium | DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and 100 U/mL penicillin G and 100 mg/mL Streptomycin | ||
| DMEM | Gibco | 11965092 | |
| FBS | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A4736301 | |
| Gal3-GFP plasmid | addgene | ||
| Lipofectamine 3000 kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | L3000008 | |
| LysoTracker Green DND-26 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | L7526 | green fluorescent dye |
| Multiwall plate | perkinelmer | PK-6005550 | |
| NaOH | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Q15895 | |
| OptiMEM | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 31985070 | |
| Penicillin-streptomycin | Gibco | 15140163 | |
| Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS) | Gibco | 21600-069 | 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10mM Na2HPO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4 |
| Cell line | |||
| HeLa Cell Line | ATCC | CCL-2 | The methods are applicable for most of the attached cell lines. Conditions must be determined individually. |
| Equipments | |||
| 0.22 µm Filter | Merck | SLGV013SL | |
| Collimated LED Light (660nm) | Thorlabs | M660L3-C1 and DC2100 | Near-infared light is ideal base on the excitation spectrum of AlPcS2a. |
| Confocal microscopy | Carl Zeiss | LSM 780 | An incubation system is required for long-term imaging. |
| NanoDrop 2000/2000c Spectrophotometers | Thermo Fisher Scientific | ||
| Red LED light | Tholabs | M660L4-C1 |
References
- Cossart, P., Helenius, A. Endocytosis of viruses and bacteria. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 6 (8), 016972 (2014).
- Daussy, C. F., Wodrich, H. 34;Repair me if you can": membrane damage, response, and control from the viral perspective. Cells. 9 (9), 2042 (2020).
- Hung, Y. H., Chen, L. M., Yang, J. Y., Yang, W. Y. Spatiotemporally controlled induction of autophagy-mediated lysosome turnover. Nature Communications. 4, 2111 (2013).
- Sharma, S. K., et al. Photodynamic therapy for cancer and for infections: what is the difference. Israel Journal of Chemistry. 52 (8-9), 691-705 (2012).
- Kübler, A. C. Photodynamic therapy. Medical Laser Application. 20 (1), 37-45 (2005).
- De Rosa, F. S., Bentley, M. V. Photodynamic therapy of skin cancers: sensitizers, clinical studies and future directives. Pharmaceutical Research. 17 (12), 1447-1455 (2000).
- Hamblin, M. R. New photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Biochemical Journal. 473 (4), 347-364 (2016).
- Lavie, G., et al. A photodynamic pathway to apoptosis and necrosis induced by dimethyl tetrahydroxyhelianthrone and hypericin in leukaemic cells: possible relevance to photodynamic therapy. British Journal of Cancer. 79 (3-4), 423-432 (1999).
- Jay, D. G. Selective destruction of protein function by chromophore-assisted laser inactivation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 85 (15), 5454-5458 (1988).
- Grate, D., Wilson, C. Laser-mediated, site-specific inactivation of RNA transcripts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 96 (11), 6131-6136 (1999).
- Lin, J. Y., et al. Optogenetic inhibition of synaptic release with chromophore-assisted light inactivation (CALI). Neuron. 79 (2), 241-253 (2013).
- Hsieh, C. W., Yang, W. Y. Triggering mitophagy with photosensitizers. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1880, 611-619 (2019).
- Yang, J. Y., Yang, W. Y. Spatiotemporally controlled initiation of Parkin-mediated mitophagy within single cells. Autophagy. 7 (10), 1230-1238 (2011).
- Molinari, M., et al. Vacuoles induced by Helicobacter pylori toxin contain both late endosomal and lysosomal markers. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (40), 25339-25344 (1997).
- Prince, L. R., et al. Subversion of a lysosomal pathway regulating neutrophil apoptosis by a major bacterial toxin, pyocyanin. Journal of Immunology. 180 (5), 3502-3511 (2008).
- Aits, S., et al. Sensitive detection of lysosomal membrane permeabilization by lysosomal galectin puncta assay. Autophagy. 11 (8), 1408-1424 (2015).
- Prasmickaite, L., Hogset, A., Berg, K. Evaluation of different photosensitizers for use in photochemical gene transfection. Photochemistry and Photobiology. 73 (4), 388-395 (2001).
- Berg, K., et al. Photochemical internalization: a novel technology for delivery of macromolecules into cytosol. Cancer Research. 59 (6), 1180-1183 (1999).
- Moan, J., Berg, K. The photodegradation of porphyrins in cells can be used to estimate the lifetime of singlet oxygen. Photochemistry and Photobiology. 53 (4), 549-553 (1991).
- Thurston, T. L., Wandel, M. P., von Muhlinen, N., Foeglein, A., Randow, F. Galectin 8 targets damaged vesicles for autophagy to defend cells against bacterial invasion. Nature. 482 (7385), 414-418 (2012).
- Repnik, U., et al. L-leucyl-L-leucine methyl ester does not release cysteine cathepsins to the cytosol but inactivates them in transiently permeabilized lysosomes. Journal of Cell Science. 130 (18), 3124-3140 (2017).
- Griffiths, G., Hoflack, B., Simons, K., Mellman, I., Kornfeld, S. The mannose 6-phosphate receptor and the biogenesis of lysosomes. Cell. 52 (3), 329-341 (1988).
- Jia, J., et al. Galectin-3 Coordinates a cellular system for lysosomal repair and removal. Developmental Cell. 52 (1), 69-87 (2020).
- Chu, Y. P., Hung, Y. H., Chang, H. Y., Yang, W. Y. Assays to monitor lysophagy. Methods in Enzymology. 588, 231-244 (2017).
- Nguyen, L., Madsen, S. J., Berg, K., Hirschberg, H. An improved in vitro photochemical internalization protocol for 3D spheroid cultures. Lasers in Medical Science. 36 (8), 1567-1571 (2021).
- Daugelaviciene, N., et al. Lysosome-targeted photodynamic treatment induces primary keratinocyte differentiation. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology. B, Biology. 218, 112183 (2021).
- Hong, M. H., et al. Intracellular galectins control cellular responses commensurate with cell surface carbohydrate composition. Glycobiology. 30 (1), 49-57 (2019).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved