A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Unfractionated Bulk Culture of Mouse Skeletal Muscle to Recapitulate Niche and Stem Cell Quiescence
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
Skeletal muscle comprises multiple cell types, including resident stem cells, each with a special contribution to muscle homeostasis and regeneration. Here, the 2D culture of muscle stem cells and the muscle cell niche in an ex vivo setting that preserves many of the physiological, in vivo, and environmental characteristics are described.
Abstract
Skeletal muscle is the largest tissue of the body and performs multiple functions, from locomotion to body temperature control. Its functionality and recovery from injuries depend on a multitude of cell types and on molecular signals between the core muscle cells (myofibers, muscle stem cells) and their niche. Most experimental settings do not preserve this complex physiological microenvironment, and neither do they allow the ex vivo study of muscle stem cells in quiescence, a cell state that is crucial for them. Here, a protocol is outlined for the ex vivo culture of muscle stem cells with cellular components of their niche. Through the mechanical and enzymatic breakdown of muscles, a mixture of cell types is obtained, which is put in 2D culture. Immunostaining shows that within 1 week, multiple niche cells are present in culture alongside myofibers and, importantly, Pax7-positive cells that display the characteristics of quiescent muscle stem cells. These unique properties make this protocol a powerful tool for cell amplification and the generation of quiescent-like stem cells that can be used to address fundamental and translational questions.
Introduction
Movement, breathing, metabolism, body posture, and body temperature maintenance all depend on skeletal muscle, and malfunctions in the skeletal muscle can, thus, cause debilitating pathologies (i.e., myopathies, muscular dystrophies, etc.)1. Given its essential functions and abundance, skeletal muscle has drawn the attention of research labs worldwide that strive to understand the key aspects that support normal muscle function and can serve as therapeutic targets. In addition, skeletal muscle is a widely used model to study regeneration and stem cell function, as healthy muscle can fully self-repair after complete injury and degeneration, mostly due to its resident stem cells2; these are also called satellite cells and are localized under the basal lamina in the periphery of the muscle fibers3.
The core cells of adult skeletal muscle are the myofibers (long syncytial multinuclear cells) and the satellite cells (stem cells with myogenic potential that are quiescent until an injury activates them). The latter cells are the central cells of muscle regeneration, and this process cannot occur in their absence4,5,6,7. In their immediate microenvironment, there are multiple cell types and molecular factors that signal to them. This niche is gradually established throughout development and until adulthood8. Adult muscle contains multiple cell types (endothelial cells, pericytes, macrophages, fibro-adipogenic progenitors-FAPs, regulatory T cells, etc.)9,10 and extracellular matrix components (laminins, collagens, fibronectin, fibrillins, periostin, etc.)11 that interact with each other and with the satellite cells in the context of health, disease, and regeneration.
Preserving this complex niche in experimental settings is fundamental but challenging. Equally difficult is to maintain or return to quiescence, a cell state that is critical for satellite cells9. Several methods have been introduced to partially tackle these challenges, each with its advantages and disadvantages (detailed in the discussion section). Here, a method is presented that can partially overcome these two barriers. Muscles are initially harvested and then broken down mechanically and enzymatically before the heterogenous cell mixture is put into culture. Over the course of the culture, many cell types of the niche are detected, and satellite cells that have returned to quiescence are observed. As a last step of the protocol, the immunofluorescence steps that allow for the detection of each cell type through the use of universally accepted markers, are presented.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
All experiments complied with French and EU animal regulations at the Institut Mondor de Recherche Biomédicale (INSERM U955), notably the directive 2010/63/UE. Animals were kept in a controlled and enriched environment at the animal facilities with certification numbers A94 028 379 and D94-028-028; they were handled only by authorized researchers and animal caretakers, and they were visually inspected by animal housing personnel for signs of discomfort during their lifetime. They were euthanized by cervical dislocation prior to dissection. No interventional procedures were performed during the animals' lifetimes; thus, acquiring approval for the procedure from an Ethics Committee and the French Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Innovation was not necessary. Indeed, no ethics clearance is required for euthanization and post-mortem dissection according to the directive 2010/63/UE. The results presented in this manuscript are from the wild-type C57BL/6NRj line (see Table of Materials) and the transgenic Tg:Pax7-nGFP line12(bred by our team). The protocol was applied to male and female mice aged 8-12 weeks of age.
1. Reagent and equipment preparation pre-digestion
- Spray the dissection tools (straight and curved scissors, forceps, see the Table of Materials) with 70% ethanol, and dry them with paper. Coat a cork plate with aluminum foil, and keep 10 cm Petri dishes (one per animal) nearby. Have paper and 70% ethanol in reach.
NOTE: At the end of the dissection, rinse the dissection tools with water, then spray them with 70% ethanol, and dry them with paper. - Set a rotating water bath to 37 °C, and prepare the digestion mix (20 mL/animal) by combining DMEM with 1% penicillin-streptomycin, 0.5 U/mL collagenase, 3 U/mL dispase (see the Table of Materials), and 0.2% BSA in 50 mL tube(s).
- Pass the digestion mix through a 0.22 µm filter in a cell culture hood.
NOTE: It is recommended to prepare the digestion mix fresh every time.
2. Reagent and equipment preparation post-digestion
- Post-digestion, the mix can be frozen or cultured. For freezing, prepare 10% DMSO:90% fetal bovine serum (FBS), as well as a set of cryotubes (1 mL of cell suspension per 2 mL cryotube). For the culture, prepare culture medium (DMEM supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin, 4 ng/mL bFGF, and 20% FBS) and a set of 8-well plates. The plates must be coated before plating the cells (details are provided in step 7.1).
- For the staining, prepare 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (0.15 mL/well of the 8-well plate) and blocking solution (5% IgG-free bovine serum albumin [BSA] in PBS; 0.15 mL/well of the 8-well plate).
CAUTION: Do not breathe in the PFA powder; prepare and handle it under a chemical hood.
3. Dissection
- Spray the euthanized animal with 70% ethanol. Make a horizontal incision (left side of the body to the right side) with big scissors at the level of the abdomen, and cut around the waist. Pull the skin off of the hindlimbs to reveal the muscles (Figure 1A).
- Place the animal on the aluminum foil-covered cork plate, and pin down the opposite forelimb and hindlimb. Quickly remove all the hindlimb muscles (front and back) into a 10 cm Petri dish placed on ice (Figure 1B,C). Take special care to remove the adipose tissue from the areas around the quadriceps and the posterior muscles. Fascia, nerves, and tendons can also be removed at this point if this does not compromise the overall time spent on dissection.
NOTE: An optimal dissection time for both the hindlimbs should be around 15-20 min. It is advised that the dissection time does not exceed 30 min. - Add drops of DMEM to the muscles occasionally to keep them moist, but not too much, as this will render chopping difficult. Repeat for the other hindlimb. Once all the muscles of one animal are in the Petri dish (Figure 1D), chop them finely with scissors for 7-10 min to obtain a smooth homogenate (Figure 1E).
NOTE: In this protocol, DMEM supplemented with L-glutamine, pyruvate, and 4.5 g/L D-glucose is used.
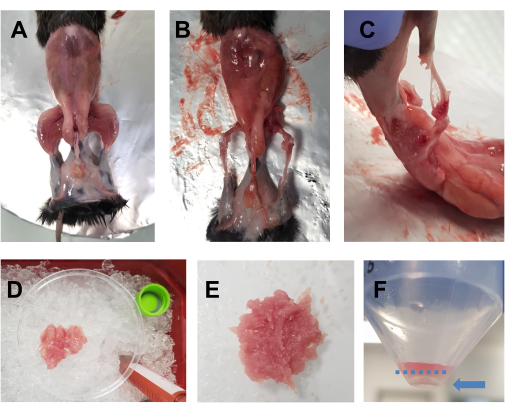
Figure 1: Pre-culture muscle preparation. (A) The skin is removed to reveal the hindlimb muscles, as described in step 3.1. (B,C) All the hindlimb muscles are harvested (B) around and (C) between the bones, as described in step 3.2. (D) The harvested muscles are placed in a 10 cm Petri dish on ice with DMEM drops to keep them moist, as described in step 3.3. (E) The muscles are finely chopped with scissors until a smooth paste is obtained with the consistency depicted in this image. (F) An image of the pellet after the final centrifugation; the blue arrow highlights the pellet, which is against the tube, under the dashed blue line. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Digestion
NOTE: At the end of the digestion, a centrifuge at 4 °C, a bucket of ice, three cell strainers (100 um, 70 um, 40 um), and three 50 mL tubes (per animal) are needed for section 5.
- Prepare and filter the digestion mix as described in step 1.2. Keep the mix on ice.
- Once all muscles are chopped, place the homogenate in a 50 mL tube with 20 mL of digestion mix. Wrap the edges of the lid with flexible film to prevent leaking, and place the tube in a 37 °C shaking water bath at a low to medium speed (50 rpm).
- After 1 h at 37 °C, open the lid, and mix by gently pipetting seven times up and down with a 10 mL pipette to obtain a homogenous mix. Apply new film around the lid, and place it back in the shaking water bath. After 1 h, remove the tube, and turn off the bath.
NOTE: For culture, use this incubation time to coat the plates as described in step 7.1 before moving to section 5.
5. Filtration
- Fill the digestion tube with cold DMEM (supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin) up to 50 mL. Mix by inverting the tube three times. Keep the DMEM in an ice bucket for the next steps.
- Place a 100 µm cell strainer on a new 50 mL tube. Pass the digested mix through the cell strainer into the new tube. Centrifuge at 600 x g for 5 min at 4 °C. Pour out the supernatant into a liquid waste container.
- Resuspend the pellet in 1 mL of cold DMEM (supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin). Fill the tube up to 50 mL with the same DMEM. NOTE: If the centrifuging is skipped, the next pellet will be more difficult to identify and maintain.
- Place a 70 µm cell strainer on a new 50 mL tube. Pass the centrifuged/resuspended mix through the cell strainer into the new tube. Centrifuge at 80 x g for 5 min at 4 °C.
NOTE: This step is not mandatory but is recommended to eliminate cell debris. - Place a 40 µm cell strainer on a new 50 mL tube. Pass the supernatant through the cell strainer into the new tube. Centrifuge at 600 x g for 5 min at 4 °C, pour the supernatant into a liquid waste container, and resuspend the pellet in FBS under the culture hood. The pellet is very small at this step (Figure 1F).
NOTE: Filtering through the 40 µm strainer removes debris, which would give a non-specific signal in the later staining of the cultures.
6. (Optional) Freezing
NOTE: Section 6 is optional. The protocol can be paused after filtering, but this can reduce the cell survival and culture success.
- Add DMSO to obtain a 10% DMSO:90% FBS ratio, and transfer to cryotubes (1 mL of resuspended pellet per 2 mL cryotube).
- Place the cryotube at −80 °C in a polystyrene box overnight. Move to −150 °C the next day for long-term storage.
NOTE: Short-term storage at −80 °C is also possible. - When starting the culture, thaw the cryotube quickly in a 37 °C water bath until the cell suspension has thawed. Mix with 4 mL of DMEM under the culture hood. Spin at 600 x g for 5 min at 4 °C. Pipette out the supernatant, and continue as described in step 7.2.
7. Culturing
NOTE: Frozen or fresh cell suspensions can be expected to fill 24-32 wells of three to four 8-well plates.
- Coat 8-well plates with the coating solution, which should be thawed at 4 °C or on ice (stock coating solution is normally kept at −20 °C). Add 0.4 mL of coating solution to one well, and pipette it from well to well. After transferring the coating solution through all the wells, it can be recollected and refrozen for future cultures. Keep the coated plates at 37 °C for 30 min before plating the cells.
- Add DMEM (supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin) supplemented with 4 ng/mL bFGF (see Table of Materials) to the FBS-cell suspension to obtain a 20% FBS:80% DMEM ratio.
NOTE: Even though the addition of bFGF can be beneficial in primary myoblast cultures and in satellite-like cell production in bulk cultures, its addition is optional, as its omission in bulk cultures of ~7 days does not severely compromise the cell yields. - Plate 0.4 mL of the suspension per well (from step 7.2) in the coated 8-well plates.
NOTE: Calculate 30 cm2 of culture per animal for frozen and fresh preparations. - Incubate the cultures at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for up to 10 days, changing the medium every day after the culture begins to change to a yellowish color (usually 5-7 days).
NOTE: To quantify cells in the S phase of the cell cycle13, add 10 µM EdU 2 h before fixation. To capture the first S phase, add 10 µM EdU from the plating, and fix at 40 h of culture.
8. Fixation
NOTE: Sections 8-10 should be conducted at room temperature unless otherwise stated.
- Pipette out the culture medium, and fix the cells with 4% PFA (0.15 mL/well).
CAUTION: Add PFA under a chemical hood.
NOTE: If all the wells are fixed at the same time, incubate with PFA at room temperature for 10 min. If the wells are fixed at different time points, add PFA to the wells to be fixed, and keep the plate in the incubator at 37 °C for 5 min. - Pipette out the PFA, and add PBS for 10 s (0.15 mL/well). Pipette out the PBS, and add fresh PBS for 5 min (0.15 mL/well).
NOTE: If all the wells are fixed at the same time, incubate with PBS at room temperature. If the wells are fixed at different time points, add PBS to the fixed wells, and keep the plate in the incubator at 37 °C for 5 min. Then, add 0.4 mL of PBS, and keep the plate in the incubator for up to 1 week.
9. Permeabilization and blocking
- When ready to stain, pipette out the PBS, and permeabilize with 0.5% TritonX 100 in PBS (0.15 mL/well) for 8 min. Pipette out the TritonX 100, rinse with PBS for 10 s (0.15 mL/well), pipette out the PBS, and wash with PBS for 5 min (0.15 mL/well).
- Block with 5% IgG-free BSA in PBS for 30-60 min (0.15 mL/well).
10. Staining
- Pipette out the BSA, and add the primary antibody mix diluted in PBS (0.15 mL/well) (see the Table of Materials; dilutions: anti-CD31 1:100, anti-FOSB 1:200, anti-GFP 1:1,000, anti-KI67 1:1,000, anti-MyHC 1:400, anti-MYOD 1:200, anti-MYOG 1:150, anti-PAX7 1:100, anti-PDGFRa 1:50) for overnight incubation at 4 °C.
NOTE: After the antibody incubation, collect the antibody mix, add sodium azide, and keep at 4 °C or −20 °C (as per the antibody manufacturer's instructions) for future reuse. - Pipette out the antibody mix, rinse with PBS for 10 s (0.15 mL/well), pipette out the PBS, and wash with PBS for 5 min (0.15 mL/well).
- Pipette out the washing PBS, add the secondary antibody mix (goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488, goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 555, goat anti-rat Alexa Fluor 647, goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 555, goat anti-chicken Alexa Fluor 488, all used at dilutions of 1:500-1,000) and nucleus marker (e.g., DAPI) diluted in PBS (0.15 mL/well) (see Table of Materials), and incubate for 1 h at room temperature, protected from light.
- Pipette out the secondary antibody mix, rinse with PBS for 10 s (0.15 mL/well), pipette out the PBS, wash with PBS for 5 min (0.15 mL/well), pipette out the PBS, and mount.
NOTE: If 8-well plates with removable separators are used, peel off the separators before mounting.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
This protocol allows for muscle cell culture while preserving the satellite cells and most cells from their endogenous niche. Figure 2 summarizes the main steps of the protocol, while essential parts of the dissection and digestion are presented in Figure 1. Dissection of the hindlimb musculature is recommended (Figure 1A-C), as this group of muscles is well studied and shares a developmental origin...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
Adult skeletal muscle function is underpinned by a finely orchestrated set of cellular interactions and molecular signals. Here, a method is presented that allows for the study of these parameters in an ex vivo setting that closely resembles the physiological microenvironment.
Several groups have reported in vitro methods to culture myogenic cells. These methods aimed to isolate satellite cells to study their myogenic progenitor properties. Two main approaches are used to iso...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
For Figure 2, templates from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com/) were used. The FR lab is supported by the Association Française contre les Myopathies - AFM via TRANSLAMUSCLE (grants 19507 and 22946), the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale - FRM (EQU202003010217, ENV202004011730, ECO201806006793), the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche - ANR (ANR-21-CE13-0006-02, ANR-19-CE13-0010, ANR-10-LABX-73), and the La Ligue Contre le Cancer (IP/SC-17130). The above funders had no role in the design, collection, analysis, interpretation, or reporting of this study or the writing of this manuscript.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| anti-CD31 | BD | 550274 | dilution 1:100 |
| anti-FOSB | Santa Cruz | sc-7203 | dilution 1:200 |
| anti-GFP | Abcam | ab13970 | dilution 1:1000 |
| anti-Ki67 | Abcam | ab16667 | dilution 1:1000 |
| anti-MyHC | DSHB | MF20-c | dilution 1:400 |
| anti-MYOD | Active Motif | 39991 | dilution 1:200 |
| anti-MYOG | Santa Cruz | sc-576 | dilution 1:150 |
| anti-Pax7 | Santa Cruz | sc-81648 | dilution 1:100 |
| anti-PDGFRα | Invitrogen | PA5-16571 | dilution 1:50 |
| b-FGF | Peprotech | 450-33 | concentration 4 ng/mL |
| Bovine serum albumin (BSA) – used for digestion | Sigma Aldrich | A7906-1006 | concentration 0.2% |
| BSA IgG-free, protease-free – used for staining | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 001-000-162 | concentration 5% |
| Cell strainer 40 um | Dominique Dutscher | 352340 | |
| Cell strainer 70 um | Dominique Dutscher | 352350 | |
| Cell strainer 100 um | Dominique Dutscher | 352360 | |
| Collagenase | Roche | 10103586001 | concentration 0.5 U/mL |
| Culture plate | Sarstedt | 94.6140.802 | |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | Euromedex | UD8050-05-A | |
| Dispase | Roche | 4942078001 | concentration 3 U/mL |
| Dissection forceps size 5 | Fine Science Tools | 91150-20 | |
| Dissection forceps size 55 | Fine Science Tools | 11295-51 | |
| Dissection scissors (big, straight) | Fine Science Tools | 9146-11 | ideal for chopping |
| Dissection scissors (small, curved) | Fine Science Tools | 15017-10 | |
| Dissection scissors (small, straight) | Fine Science Tools | 14084-08 | |
| Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) | ThermoFisher | 41966-029 | |
| EdU Click-iT kit | ThermoFisher | C10340 | |
| Fetal bovine serum – option 1 | Eurobio | CVF00-01 | |
| Fetal bovine serum – option 2 | Gibco | 10270-106 | |
| Matrigel | Corning Life Sciences | 354234 | coating solution |
| Parafilm | Dominique Dutscher | 090261 | flexible film |
| Paraformaldehyde – option 1 | PanReac AppliChem ITW Reagents | 211511.1209 | concentration 4% |
| Paraformaldeyde – option 2 | ThermoFisher | 28908 | concentration 4% |
| Penicillin streptomycin | Gibco | 15140-122 | |
| Shaking water bath | ThermoFisher | TSSWB27 | |
| TritonX100 | Sigma Aldrich | T8532-500 ML | concentration 0.5% |
| Wild-type mice | Janvier | C57BL/6NRj |
References
- Frontera, W. R., Ochala, J. Skeletal muscle: A brief review of structure and function. Calcified Tissue International. 96 (3), 183-195 (2015).
- Forcina, L., Cosentino, M., Musarò, A. Mechanisms regulating muscle regeneration: Insights into the interrelated and time-dependent phases of tissue healing. Cells. 9 (5), 1297(2020).
- Mauro, A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. Journal of Biophysical and Biochemical Cytology. 9 (2), 493-495 (1961).
- Lepper, C., Partridge, T. A., Fan, C. -M. An absolute requirement for Pax7-positive satellite cells in acute injury-induced skeletal muscle regeneration. Development. 138 (17), 3639-3646 (2011).
- McCarthy, J. J., et al. Effective fiber hypertrophy in satellite cell-depleted skeletal muscle. Development. 138 (17), 3657-3666 (2011).
- Murphy, M. M., Lawson, J. A., Mathew, S. J., Hutcheson, D. A., Kardon, G. Satellite cells, connective tissue fibroblasts and their interactions are crucial for muscle regeneration. Development. 138 (17), 3625-3637 (2011).
- Sambasivan, R., et al. Pax7-expressing satellite cells are indispensable for adult skeletal muscle regeneration. Development. 138 (17), 3647-3656 (2011).
- Hicks, M. R., Pyle, A. D. The emergence of the stem cell niche. Trends in Cell Biology. 33 (22), 112-123 (2022).
- Relaix, F., et al. Perspectives on skeletal muscle stem cells. Nature Communications. 12 (1), 692(2021).
- Gama, J. F. G., et al. Role of regulatory T cells in skeletal muscle regeneration: A systematic review. Biomolecules. 12 (6), 817(2022).
- Loreti, M., Sacco, A. The jam session between muscle stem cells and the extracellular matrix in the tissue microenvironment. NPJ Regenerative Medicine. 7 (1), 16(2022).
- Sambasivan, R., et al. Distinct regulatory cascades govern extraocular and pharyngeal arch muscle progenitor cell fates. Developmental Cell. 16 (6), 810-821 (2009).
- Pereira, P. D., et al. Quantification of cell cycle kinetics by EdU (5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine)-coupled-fluorescence-intensity analysis. Oncotarget. 8 (25), 40514-40532 (2017).
- Bismuth, K., Relaix, F. Genetic regulation of skeletal muscle development. Experimental Cell Research. 316 (18), 3081-3086 (2010).
- Yin, H., Price, F., Rudnicki, M. A. Satellite cells and the muscle stem cell niche. Physiological Reviews. 93 (1), 23-67 (2013).
- Lertkiatmongkol, P., Liao, D., Mei, H., Hu, Y., Newman, P. J. Endothelial functions of platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31). Current Opinion in Hematology. 23 (3), 253-259 (2016).
- Scholzen, T., Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 182 (3), 311-322 (2000).
- Abou-Khalil, R., Le Grand, F., Chazaud, B. Human and murine skeletal muscle reserve cells. Stem Cell Niche. 1035, 165-177 (2013).
- Pasut, A., Oleynik, P., Rudnicki, M. A. Isolation of muscle stem cells by fluorescence activated cell sorting cytometry. Methods in Molecular Biology. 798, 53-64 (2011).
- Liu, L., Cheung, T. H., Charville, G. W., Rando, T. A. Isolation of skeletal muscle stem cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Nature Protocols. 10 (10), 1612-1624 (2015).
- Montarras, D., et al. Direct isolation of satellite cells for skeletal muscle regeneration. Science. 309 (5743), 2064-2067 (2005).
- Qu, Y., Edwards, K., Barrow, J. Isolation, culture, and use of primary murine myoblasts in small-molecule screens. STAR Protocols. 4 (2), 102149(2023).
- Danoviz, M. E., Yablonka-Reuveni, Z. Skeletal muscle satellite cells: Background and methods for isolation and analysis in a primary culture system. Methods in Molecular Biology. 798, 21-52 (2011).
- Saclier, M., Theret, M., Mounier, R., Chazaud, B. Effects of macrophage conditioned-medium on murine and human muscle cells: analysis of proliferation, differentiation, and fusion. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1556, 317-327 (2017).
- Giordani, L., et al. High-dimensional single-cell cartography reveals novel skeletal muscle-resident cell populations. Molecular Cell. 74 (3), 609-621 (2019).
- Tabula Muris Consortium et al. Single-cell transcriptomics of 20 mouse organs creates a Tabula Muris. Nature. 562 (7727), 367-372 (2018).
- Brunetti, J., Koenig, S., Monnier, A., Frieden, M. Nanopattern surface improves cultured human myotube maturation. Skeletal Muscle. 11 (1), 12(2021).
- Denes, L. T., et al. Culturing C2C12 myotubes on micromolded gelatin hydrogels accelerates myotube maturation. Skeletal Muscle. 9 (1), 17(2019).
- LaFramboise, W. A., et al. Effect of muscle origin and phenotype on satellite cell muscle-specific gene expression. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 35 (10), 1307-1318 (2003).
- Azhar, M., Wardhani, B. W. K., Renesteen, E. The regenerative potential of Pax3/Pax7 on skeletal muscle injury. Journal of Generic Engineering and Biotechnology. 20 (1), 143(2022).
- Hardy, D., et al. Comparative study of injury models for studying muscle regeneration in mice. PLoS One. 11 (1), e0147198(2016).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved