Method Article
Bilayer Microfluidic Device for Combinatorial Plug Production
In This Article
Summary
The fabrication of a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-based bilayer device for the production of combinatorial libraries in water-in-oil emulsions (plugs) is presented here. The necessary hardware and software required to automate plug production are detailed in the protocol, and the production of a quantitative library of fluorescent plugs is also demonstrated.
Abstract
Droplet microfluidics is a versatile tool that allows the execution of a large number of reactions in chemically distinct nanoliter compartments. Such systems have been used to encapsulate a variety of biochemical reactions - from incubation of single cells to implementation of PCR reactions, from genomics to chemical synthesis. Coupling the microfluidic channels with regulatory valves allows control over their opening and closing, thereby enabling the rapid production of large-scale combinatorial libraries consisting of a population of droplets with unique compositions. In this paper, protocols for the fabrication and operation of a pressure-driven, PDMS-based bilayer microfluidic device that can be utilized to generate combinatorial libraries of water-in-oil emulsions called plugs are presented. By incorporating software programs and microfluidic hardware, the flow of desired fluids in the device can be controlled and manipulated to generate combinatorial plug libraries and to control the composition and quantity of constituent plug populations. These protocols will expedite the process of generating combinatorial screens, particularly to study drug response in cells from cancer patient biopsies.
Introduction
Microfluidics allows for the manipulation of small amounts of fluids in microchannels1. The scale of operation of typical microfluidic devices is tens to hundreds of micrometers which allows the miniaturization of chemical and biological reactions, thereby enabling such reactions to be carried out with relatively small quantities of reagents. Initially, microfluidic devices were fabricated with materials such as silicon2 and glass3. Although they are still in use4, they pose certain issues, such as solvent compatibility, high cost of manufacture, and difficulties in integrating controls for fluid flow5,6. PDMS-based fabrication methodologies, termed soft-lithography, offer an inexpensive alternative for the rapid prototyping of devices7 and an avenue to fabricate complex multilayered devices8. The addition of valves and pumps to PDMS devices allows for the ability to control the routing and speed of fluids in devices9,10. Several methods to design and actuate microvalves in a reversible or irreversible manner have been developed - for example, bimetallic valves made from silicon and aluminum, which are thermally actuated11 or using gas generated from an electrochemical reaction to deflect a silicon nitride membrane12. Gu et al. demonstrate the use of the mechanical pins of a Braille display to apply pressure on microchannels to regulate flow13. One set of microvalves that has gained popularity is the pneumatic PDMS-based valves pioneered by the group of Stephen Quake14. Typically, such valves are composed of two orthogonal microchannels - a flow channel and a control channel. Upon pressurization of the control channel, a thin PDMS membrane deflects upon the flow channel, closing it off and thereby interrupting fluid flow. Once depressurized, the membrane relaxes, thereby opening the flow channel and allowing the resumption of fluid flow. PDMS valves thereby allow flow regulation in a robust and reversible manner since the control channel can be pressurized and depressurized multiple times15. Additionally, since such valves can be actuated by the application of pressure, they open up avenues for digital control and automation16. Furthermore, as they are of the same material, they can be integrated seamlessly into the fabrication of PDMS-based devices using soft-lithography techniques8,17,18. These features make PDMS valves an attractive choice for flow regulation in microfluidic devices. Thorsen et al. used the principle of such valves to design a fluidic multiplexer - a combinatory array of pneumatic valves - to address nearly a thousand input flow channels with twenty control channels19. This principle has been extended to selectively route fluids to in-chip microfluidic chemostats such that unique reactions can be carried out simultaneously in each reactor20,21,22,23. However, such microreactors, while useful in optimizing the usage of limited reagents, cannot parallelize multiple reactions and are not sufficient for high-throughput studies.
Droplet microfluidics is a subcategory of microfluidics that involves the production of droplets through the manipulation of immiscible, multiphasic liquid flow in microfluidic devices24. Droplet formation involves the breakup of a continuous fluid by the introduction of an immiscible fluid, resulting in a pinch-off due to instability in the interfacial energy and in the formation of an emulsion25. Surfactants aid in the formation of rounded droplets when emulsions leave the microchannel by stabilizing the interfacial energies26. Larger droplets, called plugs, are less stable and can be collected in a holding compartment (such as a length of tubing) as an array of aqueous compartments spaced on either side by one or more immiscible liquids27. In addition to miniaturization and compartmentalization, droplet microfluidics also offers increased throughput of biological reactions, as a large number of monodisperse droplets can be produced - each serving as a nanoreactor28. Droplets, once generated, can also be subjected to further manipulations, such as splitting29,30, fusion31,32, sorting33,34, and assemblage into higher order structures35,36. Droplet microfluidics has revolutionized several scientific fields and technologies - from PCR37 to single-cell transcriptomics38, from drug-discovery39,40 to virology41, from next-generation sequencing42 to chemical synthesis43.
Integration of PDMS-based soft-lithography and microvalves with droplet technology is a potent combination that allows for the regulation of fluid flow in microchannels and subsequent control over droplet contents. Depending on the opening and closing of channels, it is possible to produce distinct populations of droplets, each with a specific composition. Such a platform could miniaturize, compartmentalize, and parallelize biochemical reactions and therefore be a useful technique for combinatorial screening44. Combinatorial screening is a high-throughput method to generate tens of thousands of combinations of selected reagents to produce libraries which consist of individual populations of known composition. Combinatorial screening has been used to discover synergistic effects between drugs and antibiotics for bacterial growth inhibition45. In the field of cancer therapy, combinatorial screening has been used to test combinations of anti-cancer drugs for a given patient thereby advancing personalized therapy46,47. Mathur et al. have built on this technology by integrating a combinatorial DNA barcoding approach to assess transcriptome changes in high-throughput drug screening48. Thus, combinatorial screening is a powerful yet nascent technology, and there is a need for developing diverse microfluidic technologies to execute and facilitate such screening procedures.
The goal of this manuscript is to present a complete set of protocols for the fabrication of a bilayer microfluidic device capable of generating a combinatorial library of water-in-oil plugs and describe the hardware and software needed for the operation of such a device. The fluid flow is regulated using pressure-controlled PDMS-based pneumatic valves, which are in turn controlled by a custom LabVIEW program. Flow of reagents in the device is achieved using commercially available pressure pumps. An eight-inlet prototype is presented wherein a plug is formed by the contents of three inlets, each containing an aqueous reagent. The aqueous phase meets a continuous oil phase, and plugs are produced at a T-junction with a frequency of 0.33 Hz. The functioning of the system is demonstrated by producing a quantitative library containing three distinct populations of fluorescent plugs. This technology and set of protocols will help to expedite the production of combinatorial libraries for high-throughput screening purposes.
Protocol
1. Soft lithography
NOTE: The microfluidic device is composed of two layers, flow layer and control layer (Figure 1A), and each layer is molded from individually patterned wafers using a positive and negative photoresist respectively (Refer to Table of Materials for details of photoresist and developers).
- Perform wafer fabrication for the flow layer as described below.
- Dehydrate a silicon wafer (100 mm diameter, <1-0-0> oriented, 525) overnight (12-16 h) at 250 °C.
- Allow the wafer to cool before proceeding to spin-coating. Apply 3-4 mL of the positive photoresist to the center of the wafer.
- Spin for 40 s at 1400 rpm (344 rpm/s) to obtain a feature height of 45 µm.
- Soft bake on a hotplate using a temperature ramp, increasing at the rate of 450 °C /h, from 35 °C to 105 °C. This step can also be carried out on microfiber tissues to prevent direct contact and minimize the bubbling of the photoresist. Remove the wafer from the hotplate and allow it to cool on microfiber tissues.
- Place the photomask (commercially produced) corresponding to the flow layer (emulsion side down) onto the resist-coated silicon wafer and expose it under a UV lamp, at 10 mW/cm2, until a total exposure of 200 mJ/cm2 is reached.
- Use two hotplates - one at 65 °C and the other at 95 °C - to perform a post-exposure bake - for 1 min and 7 min respectively - on the plates.
- Develop the wafer by transferring it to a Petri dish filled with developer for positive photoresist. Agitate the Petri dish by shaking it on a benchtop shaker with the wafer completely submerged and refresh the developer solution periodically until the wafer is completely developed, and the features can be clearly seen.
- Use demineralized water to rinse off residual resist from the wafer and check under a stereo microscope for any residues inside the channels. Remove residues by returning the wafer to the developer solution or carefully adding the developer to the wafer with a micropipette. Once completed, dry the wafer using a nitrogen spray gun.
- Reflow the wafer by placing it on a hotplate set to 110 °C for 25 min. This process results in rounded features.
- Proceed to silanization of the wafer as detailed in step 1.3.
NOTE: Hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS) vapor deposition can also be carried out on the silicon wafers prior to application of the resist to improve adhesion between the resist and the wafer.
- Perform Wafer fabrication for the control layer as described below.
- Take another silicon wafer and dehydrate by placing it on a hotplate set at 110 °C for 15 min.
- Remove the wafer and allow it to cool to room temperature before proceeding with spin coating.
- Apply 5 mL of the negative photoresist to the center of the wafer.
- Use the following spin protocol to obtain a feature height of 40 µm: 5 s at 500 rpm (100 rpm/s acceleration), 33 s at 1400 rpm (300 rpm/s), and finally decelerate to 0 rpm for 5 s at 300 rpm/s.
- Soft bake using two separate hotplates set to 65 °C and 95 °C for 1 min and 15 min respectively. Remove the wafer from the hotplate and allow it to cool on microfiber tissues.
- Place the photomask (commercially produced) corresponding to the control layer (emulsion side down) onto the resist-coated wafer and expose the wafer under a UV lamp, set at 15 mW/cm2, until a total exposure of 250 mJ/cm2 is reached.
- Use two hotplates - one at 65 °C and the other at 95 °C - and perform a post-exposure bake of the wafer for 2 min and then 5 min respectively. Remove the wafer from the hotplate and allow it to cool on microfiber tissues.
- Develop the wafer by transferring it to a Petri dish filled with developer for negative photoresist for 4 min. Refresh the developer and continue the process for 4 min more.
- Rinse the wafer with isopropanol to remove residual photoresist and use a stereo microscope to check the wafer for any residue inside the channels.
- Remove residues by returning the wafer to the developer solution or carefully adding the developer to the wafer with a micropipette. Once completed, dry the wafer using a nitrogen spray gun.
- Once fully developed, hard bake the photoresist by placing the wafer on a hotplate set at 95 °C for 10 min.
- Proceed to silanization as detailed in step 1.3.
- Carry out silanization as described below.
- Place the wafer in a desiccator. Place a glass bottle in the desiccator and add 4-5 drops of 1,1,3,3 tetramethyldisiloxane.
CAUTION: 1,1,3,3 tetramethyldisiloxane is not toxic but is flammable. Other silanes can be used, but they might be toxic. It is recommended to carry out silanization in a fume hood while wearing necessary Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) such as lab coat, glasses, and nitrile gloves. - Pull the vacuum for 15 min and seal the desiccator for 12-16 h to allow the silane to deposit on the wafer.
- Open the desiccator and dispose of the glass bottle. Place the wafer in a clean Petri dish.
- Place the wafer in a desiccator. Place a glass bottle in the desiccator and add 4-5 drops of 1,1,3,3 tetramethyldisiloxane.
- Perform microfluidic device fabrication as described below.
NOTE: The following protocol has been adapted from previous works23.- Prepare two separate PDMS solutions - one for the flow layer and one for the control layer. For each solution, mix the base agent and curing agent of the PDMS kit in a beaker and stir using a mixing rod. The control layer requires 10 g of base agent and 0.5 g of curing agent (20:1 ratio) while the flow layer requires 40 g of the base agent and 8 g of the curing agent (5:1 ratio).
- Degas the PDMS solutions in a desiccator until the solutions are gas-free.
- Place the silanized flow layer wafer in a Petri dish covered with foil and pour the corresponding PDMS solution over the wafer. Place the Petri dish back in the desiccator and pull the vacuum to degas further (for approximately 20 min).
- Spin coat the silanized control layer wafer with its corresponding PDMS solution. Pour 3-4 mL of the solution onto the center of the wafer and spin for 20 s at 1500 rpm at 408 rpm/s. Place the wafer on a level surface in a closed Petri dish for 20 mins.
- Place both the flow and control layers in an oven at 80 °C for 18-20 min. Periodically monitor the two layers to check if they are cured. The layers are ready when they are tough enough to be malleable yet slightly sticky, as this improves the bonding between the two layers.
- Cut out the PDMS around each of the devices on the flow layer wafer with a scalpel. Make sure to not cut too close to the features and leave approximately 2 cm of space between the feature and the edges of the PDMS. Once detached from the silicon wafer, cover the PDMS block with tape on the feature side to avoid any dust contamination.
- Once all PDMS blocks have been cut out, place them one by one on the corresponding control layer wafer performing a rough alignment by eye.
- After all the blocks have been placed on their corresponding areas on the control layer, adjust the position of each of the blocks such that the control valves overlap over the corresponding flow channels to complete the alignment. This can also be carried out with the help of a stereo microscope.
- Remove air pockets between the two layers by applying pressure. If the air pocket is on or near a feature, take care to not collapse the channels while applying pressure.
- Place the devices in the 80 °C oven and leave them to bond for 12-16 h. Place 100 g weights on each of the devices to improve the bonding between the two layers.
- Take the wafer out and cut out each individual device. Peel the devices off the control layer wafer and cover the feature side with tape.
- Place each individual device on a cutting mat with the feature side facing upwards and punch a hole for each of the eight flow layer inlets, eight control layer channel inlets, the oil inlets, and the outlet using a 0.75 mm biopsy punch with the feature side facing upwards.
- Load the plasma asher with a microscope slide and a single device with the tape removed and the feature side facing upwards. Perform the oxygen plasma ashing with a power of 30 W for a duration of 20 s.
- Take the device and the glass slide out as soon as the ashing is complete and place the device with the feature side downwards onto the slide. The adhesion between PDMS and glass should be immediately visible to the naked eye. Apply pressure to any regions with air pockets to squeeze the air out.
- Place the devices on a hotplate set to 110 °C for 60 min with a weight on top to improve the bonding of the PDMS to the glass.
2. Hardware setup
NOTE: A schematic of the connections to the microfluidic device is shown in Figure 1B and a realization of such a scheme using the necessary hardware is shown in Figure 2.
- Set up the Pneumatic valves as described below.
NOTE: Each control channel, which regulates a PDMS valve on the chip is in turn controlled by a single solenoid valve. The prototype presented here consists of eight control channels (Figure 1A), and hence eight solenoid valves are required.- The solenoid valves are controlled using a custom LabVIEW software program (Main Interface Program; Figure 3 and Supplementary File 1, Supplementary File 2, Supplementary File 3, Supplementary File 4). This program sends MODBUS commands via a TCP connection (Supplementary File 5, Supplementary File 6), to a WAGO controller. Connect the WAGO device to the computer with the LabVIEW program using an ethernet cable. Proceed to connect the solenoid valves sequentially to the ports on the WAGO controller. For a more detailed description, please refer to previously described protocols23.
- Connect the solenoid valve array to a compressed air source using 1/4 in tubing and set the pressure of the valve array to 3.5 bar. In this system, the eight valves marked 9-16 were used.
- Set up pressure regulators as described below.
NOTE: A commercially available pressure pump is used to control fluid flow (Figure 2). An eight-port and a four-port pump set were used to accommodate eight aqueous inlets and two oil inlets in the device. The pressure of each port is regulated via software that is provided by the manufacturers.- Connect the pressure pump to a compressed air source ensuring that the supplied pressure does not exceed the maximum pressure permitted by the pump (2.2 bar for both the eight-port and the four-port controllers).
- Connect the pressure pumps to a computer using a USB-connector.
- Once the pumps are switched on, they should be visible in the corresponding software. Set the pressures to zero while setting up the pumps.
- Connect a male luer to 3/32 in barb connector to each of the 12 female luer lock output ports on the controllers.
- Connect a piece of soft tubing (OD: 3 mm, ID: 1 mm, L: 15 cm) to the barb. Connect another male luer to 3/32 in barb connector to the other end of the soft tubing.
- Connect a luer stub (23 G, 0.5 in) to the barb connector. At this point, the pressure regulator is set up and ready to be used.
3. Microfluidic device setup
- Connect the control channel tubing as described below (Figure 2).
- For each control channel, cut a length of PolyTetraFluoroEthylene (PTFE) tubing (OD: 0.042 in, ID: 0.022 in). Insert the pin of a 23 G, 0.5 in luer stub at one end.
- Connect the luer stub to a male luer to 3/32 in barb nylon connector. Insert the barb of the connector into a length of polyurethane tubing (OD: 4 mm, ID: 2.5 mm). Connect the other end of the polyurethane tubing directly to a solenoid valve.
- Fill a syringe with water and connect a 23 G, 0.5 in luer stub at the end.
- Connect the free end of the PTFE tubing to this syringe and inject water until approximately halfway through the tubing.
- Disconnect the tubing from the syringe and insert the free end of the tubing into a punched hole of the corresponding control channel (Figure 1A-C1-8). Repeat until each control channel has been connected to its corresponding solenoid valve.
NOTE: In this paper, the solenoid valves 9-16 were connected to the control channels corresponding to C1 to C8, respectively. While these can be connected in any manner, it is important to remember the order and sequence of the connections, especially while operating the Main Interface program. - Use the Main Interface program (Figure 3) to open all the solenoid valves (Pressurize all control channels). This will push the fluid from the tubing into the control channels of the microfluidic device and thereby filling it up. An example of pressurized and depressurized valves is shown in Figure 4.
- Connect reagents and prime the device as described below.
- Ensure that all control channels are pressurized by pressing the Pressurize all Control Channels button in the Main Interface program (Figure 3).
- For each of the aqueous reagents, cut a segment of PTFE tubing (OD: 0.042 in, ID: 0.022 in) long enough to connect the pumps to the inlets of the microfluidic device inlets. Connect one of the tubing to the luer stub from step 2.2.6.
- Fill a syringe with the required reagent and connect a 23 G, 0.5 in luer stub at the end.
- Inject the reagent into the corresponding PTFE tubing until the tubing is full. Take care that the reagent does not enter the output port on the pump set.
- Insert the free end of the tubing into a corresponding inlet in the microfluidic chip.
- Apply a pressure of 400 mbar to each of the inlet aqueous reagents using the software provided.
- Sequentially depressurize the control channels individually using the Main Interface program (Figure 3) to ensure that all the reagents have reached the T-junction of the device. Actuate individual valves , if needed, by pressing the corresponding buttons on the program in the box Control Channels Manual Pressurization.
- Repeat steps 3.2.3 to 3.2.5 for the oil reagents. Apply a pressure of 400 mbar to each of the inlet oil reagents.
- Simultaneously depressurize all the control channels by pressing Depressurize All Control Channels (Figure 3) until all the air has been removed from the device. This is observable by the naked eye or under a microscope.
- Pressurize all the control channels by pressing Pressurize All Control Channels button (Figure 3). At this stage, all reagents have been connected and the device is primed and ready to use.
- Program and execute the experiment as described below.
- Encode the composition, sequence, and replicates of each plug population to be produced in a .csv file as shown in Supplementary File 7 which serves as the input for the Automatic Experiment in the Main Interface program (Figure 3). Mark the necessary control channels with a 0 if its corresponding to an inlet needs to be open and a 1 if it needs to be closed. Each row in the .csv file corresponds to one distinct plug population.
- Load the .csv on to the Main Interface program by clicking on the Folder button in the Experiment File tab.
- Enter the relevant fields in the program such as Iterations of experiment (to determine how many times the given sequence of plugs are produced), Time of depressurization (to determine how long the inlet channels need to be open and the corresponding control channel needs to be depressurized in milliseconds), Time of pressurization (to determine how long the inlets need to be closed between sequences of plug population in milliseconds).
- Select the inlet channel(s) corresponding to barcode production in the Barcode Inlets (up to 3 channels) section along with the duration for which they need to be open (Time for Barcoding (ms)). Alternatively, these barcodes can also be hardcoded into the input .csv file as shown in Supplementary File 7.
- Reduce the pressure of the inlet oil reagents to 200 mbar.
- Connect a PTFE tubing (OD: 0.042 in, ID: 0.022 in) of the desired length at the outlet to collect the plugs. In order to ensure uniform plug production, use tubing of approximately 100 cm prefilled with plugs for collection. This is to neutralize the difference in pressure at the outlet which is exerted by the collection of plugs in the tubing.
- Press Run Experiment to start the program and plug production.
- Perform data recording and analysis as described below (see Figure 5).
NOTE: This section specifically outlines a method for analyzing fluorescent plugs. Depending on the nature of the plugs generated, this section can be altered as required.- Fill a syringe with oil (either mineral oil or fluorinated oil) and connect a 23 G 0.5 in luer stub at the end. Fasten the syringe to a pump.
- Connect one of the ends of the filled collection tubing to the luer stub on the syringe. Affix the other end of the filled collection tubing above the objective lens of a microscope.
- Place a waste reservoir below the end of the tubing near the objective.
- Focus the microscope on a given region of the tubing and set it to record fluorescence in the desired channel(s).
- Set the pump to a flow rate of 50 µL/min.
- Record the video of the fluorescent channel as an .avi file.
- Analyze the .avi file using the provided python script (Supplementary File 8) to extract the average fluorescence in a predefined region of interest (ROI) per frame of the .avi file (an example of which is given in Supplementary File 9).
- Use the provided customized R script (Supplementary File 10) to extract the conditions and plot the raw data and the peak heights.
NOTE: The R script in Supplementary File 10 was used for analysis in this paper. The custom-made R functions used in this script to cut data, detect conditions using barcodes, and analyze the peak heights for individual plugs and plotting are provided in Supplementary File 11.
Results
One of the crucial features of the microfluidic chip are the PDMS valves and their ability to regulate fluid flow was characterized as it influences the operational paradigm of the device. To this end, the flow rate of distilled water (measured using a commercial flow rate sensor) through the inlet channels was recorded as a function of different input pressures whilst periodically pressurizing (3.5 bar for 2000 ms) and depressurizing (1000 ms) the PDMS valves (Figure 6A). It was observed that the valves were able to regulate fluid flow until approximately 800 mbar of input pressure, as indicated by the drop in flow rate to zero when the valves are actuated (Figure 6 B-D). This validates the use of such PDMS-based valves to regulate the flow of reagents inside the channels. Furthermore, at 1200 mbar, the input pressure is too high for the valves to regulate the flow, as is evidenced by the flow rate not reducing to zero (Figure 6E). Whilst the duration of pressurization and depressurization of the PDMS valves can be modified, the rate of change of fluid flow upon the current conditions of pressurization (2000 ms) and depressurization (1000 ms) was calculated. For an input pressure of 400 mbar, the flow can be switched on and off at the rate of 1.26 Hz and 1.44 Hz respectively (Figure 6C).
Previous iterations of a similar combinatorial high-throughput microfluidic device also incorporated a waste channel coupled to every flow channel46,47. These devices were operated in a constant flow rate regime (where reagents were injected into the device at constant flow rates rather than constant pressure), and the waste channels were programmed to open when their corresponding inlet channels were closed to alleviate any pressure build-up. Such channels, while useful, result in a loss of reagents as the contents of the waste channel do not contribute toward plug formation. Furthermore, additional control channels - and thereby additional pumps - are also required to regulate the opening and closing of the waste channels. In the prototype presented here, the waste channels were removed, and an operational paradigm was established that allows for reduced wastage of reagents and a scale-down of design and operational complexity. This involves injecting the aqueous reagents in constant pressure mode as opposed to constant flow rate mode. To better understand the two regimes, the relationship between pressure and flow rate in the channels during valve actuation was assessed in each case (using the same setup as shown in Figure 6A), the results of which are shown in Figure 7. In Figure 7A, the flow rate of distilled water was measured while being injected at a constant pressure (300 mbar) and it was observed that during valve actuation, the flow rate drops to zero and upon depressurization of the valve the flow rate recovers to pre-actuation levels. However, in a constant flow rate regime, wherein the pressure in the channels was recorded whilst injecting the distilled water at a constant flow rate (2.5 µL/min; Figure 7B), valve actuation did not result in complete inlet closure - evidenced by the flow rate not dropping to zero - and a build-up of pressure in the channel was observed. This is the pressure that is relieved by the opening of waste channels. Since a constant input pressure regime allows the operation of the device without back pressure upon valve actuation, thereby negating the need for waste channels, this regime was adopted for the operation of the microfluidic chip.
To demonstrate the functionality of the microfluidic device, a quantitative combinatorial library of fluorescent plugs was generated. To the eight inlets of the device, three aqueous reagents - fluorescein (50 µM) in four inlets (I1, I3, I5, I7), distilled water in three inlets (I4, I6, I8), one inlet with a blue color dye (I2; to act as a barcode) - and two oil reagents - fluorinated oil (FC-40) and mineral oil (MO) in inlets O1 and O2, respectively - were plugged in (Figure 1A, Figure 8A). The fluorinated oil serves as the carrier phase in which the aqueous plugs are dispersed, and the mineral oil aids in plug stability and minimizes adhesion of plug content to the walls, thereby minimizing cross-contamination between plugs46. With three inlets contributing to the composition of a single plug population, this configuration can generate three distinct fluorescent populations: FFF - composed of fluorescein from three channels, FFW - composed of fluorescein from two channels, and water from one channel, and FWW - composed of fluorescein from one channel and water from two channels. With this setup, there are 12 distinct conditions (plug populations produced with a distinct combination of three inlets) that can produce FWW plugs, 18 distinct conditions that can produce FFW plugs, and four distinct conditions that can produce FFF plugs. Therefore, the chip was programmed to produce these 34 different conditions with five different replicate plugs each, along with five replicates of barcode plugs separating them. It is recommended to intersperse the fluorescent plug populations with a barcode population, i.e., a set of colored (ideally non-fluorescent) plugs (in this case formed by opening the inlet channels corresponding to the blue dye and two distilled water channels) which are visible to the naked eye. It allows the user to monitor the plug production for issues such as plug break-up or fusion and helps in the downstream analysis of plugs. Therefore, a total of 340 plugs - 170 experimental plugs and 170 barcoding plugs separating the different conditions - were generated and collected in PTFE tubing, a sample of which is shown in Figure 8B. The time of depressurization and time of pressurization were set at 1000 ms and 2000 ms, respectively. The fluorescence of the plugs and their variability within and across the different experimental conditions were analyzed, the results of which are shown in Figure 8C,D. Figure 8C shows the fluorescence per frame of the .avi file generated in step 3.4.6, which highlights the 34 experimental conditions in consideration (demarcated by a blue line). The mean fluorescent value of peaks within a condition is shown in red, and the dashed lines indicate the standard error within that condition. The heights of the peaks of all the plugs in each population, obtained by subtracting the baseline fluorescence from the maximum fluorescence detected in each peak, were plotted in Figure 8D. The last peak in each condition was neglected for the calculations as it was a contaminated plug due to the intermixing of reagents at the T-junction (since the fluorescence of the plugs was recorded in reverse order of plug production, the first plug in a population during production is the last plug in a population during analysis). It was evident that the height of the FWW plugs is about one-third (mean = 40.9, standard deviation = 3.1) and that of the FFW plugs is about two-thirds (mean = 78.4, standard deviation = 5) of the height of the FFF plugs (mean = 117, standard deviation = 10). These results match the expected proportions of fluorescence in different populations of FFF/FFW/FWW plugs, which highlights the robustness of the device and its functioning.
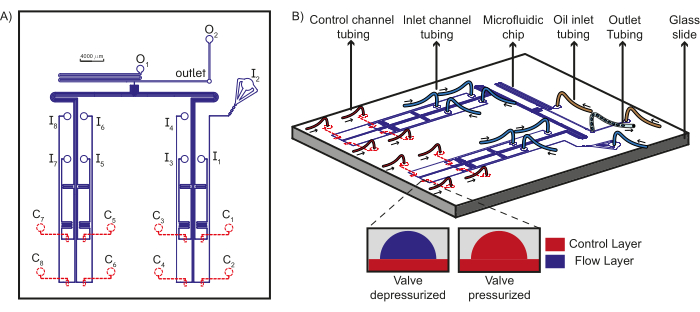
Figure 1: Schematic of the device design and microfluidic set up. (A) The flow layer of the chip is shown in blue and the control layer is shown in red. A total of eight unique aqueous reagents can flow through the inlets (I1-8) towards the T-junction, where they encounter the oil phases from the oil inlets (O1-2) to form plugs which are collected at the outlet. Each inlet flow channel is under the control of a unique control channel (C1-8). (B) Schematic of the microfluidic chip along with the tubing connections to the inlets, control channels, and oil reagents is shown along with the outlet tubing. Arrows indicate the direction of fluid flow in the tubing. The inset shows the working principle of PDMS valves. Dashed lines indicate that the control layer is beneath the flow layer. This figure has been modified from Dubuc et al49. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
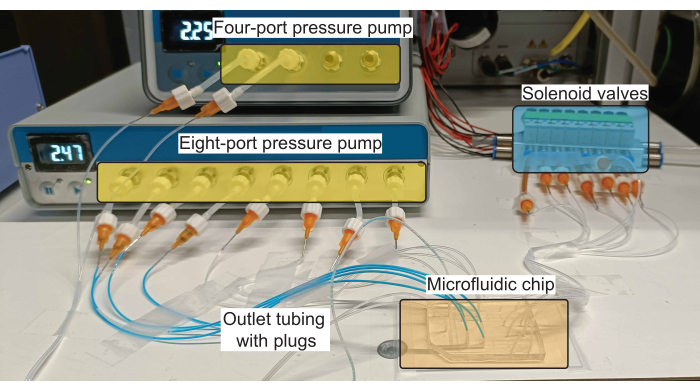
Figure 2: Schematic of the hardware setup for plug production. The pressure pumps control the flow of reagents (both aqueous and oil) in the inlet channels, and the solenoid valves control the actuation of the PDMS valves. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 3: The main interface program to control the microfluidic device. This custom-made program enables manual pressurization of individual pneumatic valves (white panel). It also allows the execution of a complete experiment (blue panel) where it accepts a .csv file with the desired plug populations and necessary parameters such as valve pressurization and depressurization times and displays the status of the experiment execution, including which control channels are pressurized and not, in real-time. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
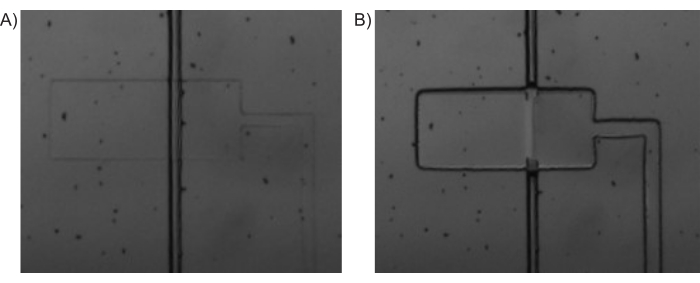
Figure 4: Pressure-driven valve actuation. Bright-field microscopy images of (A) PDMS-valve (horizontal) being depressurized and the inlet channel (vertical) being open and (B) PDMS-valve being pressurized and closing off the inlet channel. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
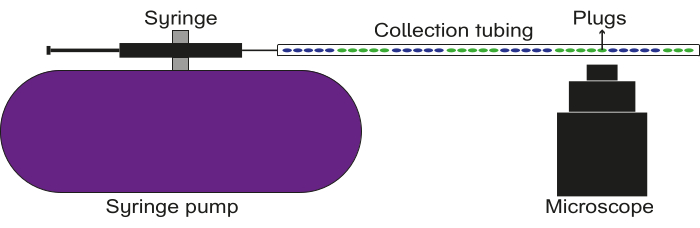
Figure 5: Schematic of the data recording setup. The collection tubing is connected to a syringe with oil, which is affixed to a pump. The plugs are flown through the collection tubing, and images/videos are captured using a fluorescence microscope. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
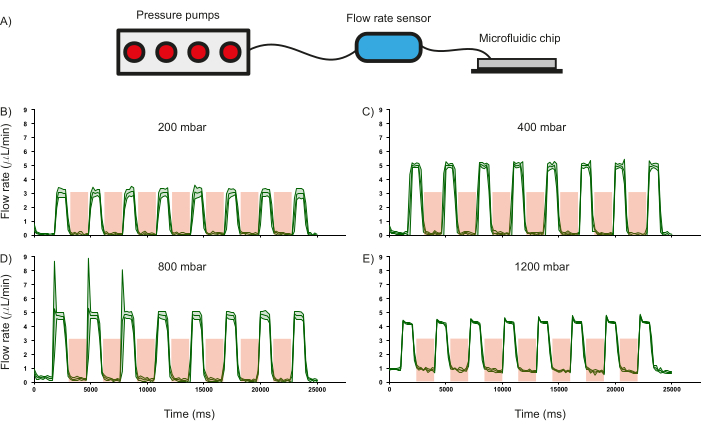
Figure 6: Effect of valve actuation on flow rate at a given input pressure. (A) Schematic of the hardware setup used to monitor flow rate in the microfluidic channels. The response of the flow rate in the channels when operated at different input pressures of (B) 200 mbar, (C) 400 mbar, (D) 800 mbar, and (E) 1200 mbar. Duration of valve actuation is shown in the red shaded region. Distilled water was used for all experiments. Standard deviation of three independent measurements is shown by the green shaded region. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
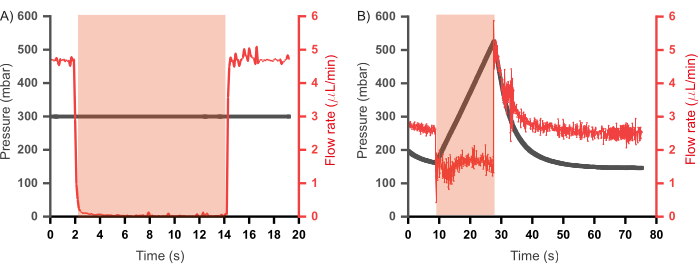
Figure 7: Relationship between pressure and flow rate of reagents in the inlet channels upon valve actuation. (A) In a constant input pressure regime (300 mbar) valve the flow rate reduces to zero upon valve actuation. (B) In a constant flow rate regime (2.5 µL/min) valve actuation results in rapid pressure build up in the channel until the valve is depressurized. Duration of valve actuation is shown in the red shaded region. Distilled water was used for all experiments. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
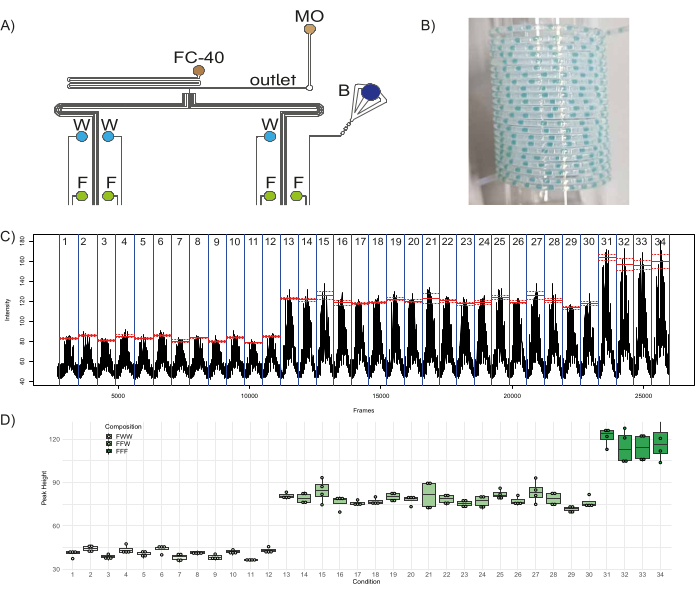
Figure 8: Production of fluorescent plug populations. (A) Schematic of the experimental setup depicting the connection of the different reagents to the device. Abbreviations: F = Fluorescein, W = distilled water, B = Blue food dye, FC-40 = fluorinated oil, and MO = mineral oil. (B) Sample picture of collection tubing containing plugs. (C) Raw data obtained from the analysis shows the average fluorescence intensity measured in a specified region of interest (ROI) vs the frame number of the video file. Red lines show the mean of the peak fluorescence for each condition (population of plugs produced with a specific combination of three inlets), and the dashed lines show the corresponding standard error. (D) Boxplots of the height of the peaks in the different conditions. Dots correspond to individual peaks, boxes for each condition range from the first to the third quartile of the distribution of the corresponding peaks, and the thick line is used for the median value. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Supplementary File 1: The main interface program for device operation. The control interface for manual pressurization of the control channels and running an automatic experiment in the eight-inlet device. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary File 2: Alternate main interface program for device operation. The control interface for running an eight-inlet device without a barcoding function. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary File 3: LabVIEW sub-program with global variables. SubVI of the main interface program listing and displaying the status of the global variables in the main interface program, namely the control channels. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary File 4: LabVIEW program to save values of global variables. SubVI of the main interface program that saves the current state of the valves as an array, which will be used to maintain the same state of the valves in case of the user being inactive for more than 30 seconds. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary File 5: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) LabVIEW program. SubVI for maintaining the TCP connection between the main interface program and the WAGO controller. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary File 6: TCP global variable LabVIEW sub-program. Program to store the TCP output variable. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary File 7: Input for carrying out automatic experiment. The .csv file encoding composition, sequence, and replicas of plug populations for carrying out experiments to produce quantitative fluorescent plugs, as detailed in this paper. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary File 8: Python script for analysis of fluorescent plug population. Custom python script to readout fluorescence values from the recording of plugs (.avi file). Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary File 9: Output of fluorescence analysis of plugs. Output from the Python script containing fluorescence values for a 5x5 ROI from the recording of the plugs. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary File 10: R program to read output file. Custom program used in this work to read the output fluorescent values and plot raw data, peak heights, and standard deviations. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary File 11: R functions for analyzing and plotting fluorescent data. Custom R functions which are used to 1. cut the raw data of the fluorescent values, 2. define different experimental conditions, 3. identify peaks from the given conditions, 4.plot the raw data and the detected conditions overlapped, and 5. plot the identified peaks and the raw data overlapped. Please click here to download this File.
Discussion
In this paper, a set of protocols for the fabrication and operation of a PDMS-based microfluidic device for the automated generation of combinatorial libraries in water-in-oil compartments called plugs has been presented. The combination of microfluidics with droplet technology provides a powerful technique to encapsulate small quantity of reagents in a large number of compartments, therefore opening avenues for large-scale combinatorial screening.
Previously, several technologies have been described to generate chemically distinct compartments using microfluidics, each with its advantages and limitations. Kulesa et al.50, described a strategy to encapsulate cells with barcodes in droplets using microtiter plates and merging these droplets using an electric field to create a combinatorial library. While such an approach can generate a lot of combinations of droplets, it is limited by the need for manual handling steps in the workflow. Tomasi et al.51 developed a microfluidic platform to merge a spheroid (free floating cell aggregates)-containing droplet with a stimulus droplet, thereby allowing the manipulation of the spheroid microenvironment. This method allows for the study of important phenomena such as cell-cell interactions and the effect of drugs, but it is relatively low throughput. Eduati et al.46 and Utharala et al.47 developed a microfluidic valve-based platform that can generate high-throughput combinatorial libraries in an automated fashion. However, in these studies, the valves are operated using a Braille device, which necessitates cumbersome alignment steps between the microvalve and the microfluidic chip. A key feature of the system described in this paper is the implementation of pneumatic PDMS valves to regulate the flow of fluid in the input channels. Since these valves are PDMS-based, they can be incorporated rather smoothly into the fabrication steps of the microfluidic chip. Additionally, they are a relatively straightforward option to control the flow of liquids in the inlet channels, as they can be actuated by applying pressure through an external gas source. Finally, the duration and sequence of pressurization and depressurization of these valves can be programmed, thereby automating the production of distinct populations of plugs in a high-throughput manner. Another important feature is the use of constant pressure regimes for the injection of reagents through the inlet, which allows one to opt out of incorporating waste channels to relieve any pressure accumulation that arises in a constant flow rate regime. This simplifies the device design, reduces the need for additional valves and hardware to control the valves of the waste channel, and minimizes reagent wastage.
While the fabrication of devices with PDMS is relatively uncomplicated, the implementation of such devices does require the usage of extensive hardware paraphernalia such as the pneumatic solenoid valves (to control the actuation of the PDMS valves), pressure pumps (to control the flow of inlet and oil reagents) and software programs (to regulate the solenoid valves). While they represent a significant investment, such a setup provides consistency and reliability for the successful operation of the device. Additionally, the hardware components and architecture outlined in this protocol are set up in a modular way. Therefore, alternatives can be used for some modules to reduce costs or to adapt them to a specific need. For example, there exists a variety of pumps that can be used based on utility, budget, availability, and convenience52,53,54. Additional components such as fluid reservoirs and temperature regulators can be incorporated for sensitive inlet reagents23. Furthermore, this design can be scaled up or down to address specific scientific needs. For example, in this paper, an eight-inlet prototype is described which allows eight unique reagents to be combined to produce plugs. This can be upscaled to a 16-inlet device which allows for a higher number of inlets and larger combinations thereof. Consequently, it will need extra control channels and solenoid valves to address the inlets, but such a prototype allows larger and more diverse combinatorial libraries to be generated. Finally, in this paper, each plug population is produced by the opening of three out of the eight aqueous inlets of the microfluidic device. It was observed that for such a configuration, a pressure of approximately 200 mbar for the oil reagents and 400 mbar for the aqueous reagents corresponded to a regime of plug production, which is driven solely by valve actuation. When higher pressures were applied to the oil(s), a breakup of plugs was observed, and the application of lower pressures led to a fusion of plugs. The optimal pressure regime for plug production depends on a wide range of factors, such as the number of inlets contributing to the formation of a plug, the nature and viscosity of the fluids, and the dimensions of the channels, and should be optimized as and when necessary.
One of the drawbacks of operating in a constant-pressure regime is that fluids with different viscosities have different flow rates under constant pressure. Therefore, it needs to be ensured that the aqueous reagents flowing through the inlets are of comparable viscosities. The use of fluids of different viscosities will affect not only fluid flow in the inlet channels but also plug formation at the T-junction, thereby compromising the composition of the plug populations. Another drawback is the contamination of a plug population from residual reagents at the T-junction. When the device switches between the production of different plug populations, the first/last plug in the sequence of each population tends to be contaminated by the previous or the following population. This can be overcome by producing extra replicates of each population and discounting the contaminated plug during analysis. Finally, there is also the potential for variation between individual devices arising from inconsistencies in fabrication and/or external sources (pressure fluctuations). This issue can be mitigated by reusing a single microfluidic chip multiple times and ensuring that a complete run of a combinatorial library is performed on a single chip to minimize the effect of these inconsistencies.
The microfluidic device and the accompanying set of operational protocols presented in this paper have been used to demonstrate the production of a quantitative combinatorial library of plugs. This platform can, therefore, rapidly generate combinatorial libraries of distinct plug populations in a high-throughput manner. As a result, such technologies can be used for a variety of screening purposes including, but not limited to, combinatorial drug screening on patient biopsy samples - whereby a small number of cells retrieved from a biopsy can be distributed in a large number of droplets and treated with a large combination of the anti-cancer drug to optimize individual therapy for a given patient sample - and therefore accelerate personalized cancer therapy46,48,55.
Disclosures
F. E. is a freelancer for TheraMe! AG. The authors declare they have no competing financial interests.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Stacey Martina of the NanoLab TuE for help with HMDS vapour deposition. This research was funded by the Institute for Complex Molecular Systems (ICMS) at TU/e and by the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO) Gravitation programme IMAGINE! (project number 24.005.009).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1,1,3,3 tetramethyldisiloxane | Merck Life Science NV | MFCD00008256 | |
| 4 channel digital input/output module | WAGO Kontakttechnik GmbH | 750-504 | |
| Acetone | Boom Labs | BOOMSKEUZW3 | |
| Analysis Software | Eindhoven University of Technology | https://github.com/SysBioOncology/BilayerMicrofluidicsAnalysis_JoVE | |
| AZ 40XT 11D | Merck Life Science NV | 212299 | Positive photoresist |
| AZ 726 MIF developer | Merck Life Science NV | 10055824960 | Developer for positive photoresist |
| Biopsy Punch, Rapid Core | World Precision Instruments Germany, GMBH | 504529 | 0.75 mm ID, W/Plunge |
| Blue food dye | PME | FC1036 | |
| Controller end module | WAGO Kontakttechnik GmbH | 750-600 | |
| Ethernet Controller | WAGO Kontakttechnik GmbH | 750-881 | |
| FC-40 | Merck Millipore | F9755-100ML | |
| Fluigent flow unit | Fluigent | FLU-S-D | |
| Fluigent pressure system | Fluigent | MFCS-EZ | 0 - 2 bar |
| Fluorescein | Merck Life Science NV | MFCD00005050 | |
| Hot plate | Torrey Pines Scientific | HP61 | |
| Inverted microscope | Nikon Instruments | Eclipse Ti-E | |
| Isopropanol | Boom Labs | BOOMSKEUZE3 | |
| LabVIEW (Software Version 20) | Eindhoven University of Technology | https://github.com/SysBioOncology/BilayerMicrofluidicsAnalysis_JoVE/tree/main/LabVIEW_8_inlet_device_ VERSION_1 | All files have been saved for LabVIEW version 20. It is advised to use this version or higher to open the files. |
| Luer stubs | Instech Laboratories, Inc. | LS23 | 23 ga, 0.5" |
| Male Luer to barb connectors | Cole Parmer | 45505-32 | 3/32" ID |
| MasterFlex PTFE tubing | Avator/VWR | 48634 | |
| Microscope Slides | VWR | 470150-480 | |
| Microscope slides, Plain | Corning | 2947-75X50 | |
| Mineral Oil | Merck Millipore | 330760-1L | |
| mr DEV 600 | Micro resist Technology | R815100 | Developer for negative photoresist |
| Oven | Thermo Scientific | Heraeus T6P 50045757 | |
| Oxygen plasma asher | Quorum Technologies | K1050X | |
| Photomask | CAD/Art Services, Inc. | ||
| Photomask Design | Eindhoven University of Technology (Adapted from Merten Lab, EPFL) | https://github.com/SysBioOncology/BilayerMicrofluidicsAnalysis_JoVE/blob/main/8_inlet_JoVE_device_design.dwg | |
| Pneumatic valve array | FESTO | 1x 8 valve array, Normally closed valves | |
| Silicon Wafers | Silicon Materials | <1-0-0>, 100 mm diameter, 525 μm thickness | |
| Single edge blades | GEM Scientific | ||
| Soft tubing | Fluigent | 1 mm ID, 3 mm OD | |
| Spin coater | Laurell Technologies Corporation | WS-650MZ-23NPPB | |
| Stereo microscope | Olympus Corporation | SZ61 | |
| SU-8 3050 | Kayakli Advanced Materials | Y311075 1000L1GL | Negative photoresist |
| Sylgard 184 Silicone Elastomer Kit (PDMS) | Dow | 1317318 | |
| Syringe | B Braun Injekt - F Fine Dosage Syringe | 10303002 | |
| UV-LED exposure system | Idonus | UV-EXP150S-SYS | |
| Vacuum pump | Vacuumbrand GmbH | MD1C | |
| Weighing scales | Sartorius | M-prove |
References
- Whitesides, G. M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature. 442 (7101), 368-373 (2006).
- Terry, S. C., Herman, J. H., Angell, J. B. A gas chromatographic air analyzer fabricated on a Silicon wafer. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices. 26 (12), 1880-1886 (1979).
- Mellors, J. S., Gorbounov, V., Ramsey, R. S., Ramsey, J. M. Fully integrated glass microfluidic device for performing high-efficiency capillary electrophoresis and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 80 (18), 6881-6887 (2008).
- Wlodarczyk, K. L., Hand, D. P., Maroto-Valer, M. M. Maskless, rapid manufacturing of glass microfluidic devices using a picosecond pulsed laser. Sci Rep. 9 (1), 20215 (2019).
- Nielsen, J. B., et al. Microfluidics: innovations in materials and their fabrication and functionalization. Anal Chem. 92 (1), 150-168 (2020).
- Nge, P. N., Rogers, C. I., Woolley, A. T. Advances in microfluidic materials, functions, integration, and applications. Chem Rev. 113 (4), 2550-2583 (2013).
- Duffy, D. C., McDonald, J. C., Schueller, O. J. A., Whitesides, G. M. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal Chem. 70 (23), 4974-4984 (1998).
- Unger, M. A., Chou, H. P., Thorsen, T., Scherer, A., Quake, S. R. Monolithic microfabricated valves and pumps by multilayer soft lithography. Science. 288 (5463), 113-116 (2000).
- Oh, K. W., Ahn, C. H. A review of microvalves. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering. 16 (5), R13 (2006).
- Au, A. K., Lai, H., Utela, B. R., Folch, A. Microvalves and micropumps for BioMEMS. Micromachines. 2 (2), 179-220 (2011).
- Jerman, H. Electrically-activated, normally-closed diaphragm valves. J. Micromech. Microeng. 4 (4), 210 (1994).
- Neagu, C. R., Gardeniers, J. G. E., Elwenspoek, M., Kelly, J. J. An electrochemical microactuator: principle and first results. J microelectromechanical sys. 5 (1), 2-9 (1996).
- Gu, W., Zhu, X., Futai, N., Cho, B. S., Takayama, S. Computerized microfluidic cell culture using elastomeric channels and Braille displays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101 (45), 15861-15866 (2004).
- Studer, V., et al. Scaling properties of a low-actuation pressure microfluidic valve. J Appl Phys. 95 (1), 393-398 (2004).
- Hansen, C. L., Sommer, M. O. A., Quake, S. R. Systematic investigation of protein phase behavior with a microfluidic formulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101 (40), 14431-14436 (2004).
- Ridgeway, W. K., Seitaridou, E., Phillips, R., Williamson, J. R. RNA-protein binding kinetics in an automated microfluidic reactor. Nucleic Acids Res. 37 (21), e142 (2009).
- Fu, A. Y., Chou, H. P., Spence, C., Arnold, F. H., Quake, S. R. An integrated microfabricated cell sorter. Anal Chem. 74 (11), 2451-2457 (2002).
- Liu, J., Enzelberger, M., Quake, S. A nanoliter rotary device for polymerase chain reaction. Electrophoresis. 23 (10), 1531-1536 (2002).
- Thorsen, T., Maerkl, S. J., Quake, S. R. Microfluidic large-scale integration. Science. 298 (5593), 580-584 (2002).
- Galas, J. C., Haghiri-Gosnet, A. M., Estévez-Torres, A. A nanoliter-scale open chemical reactor. Lab Chip. 13 (3), 415-423 (2013).
- Niederholtmeyer, H., Stepanova, V., Maerkl, S. J. Implementation of cell-free biological networks at steady state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 110 (40), 15985-15990 (2013).
- Yelleswarapu, M., et al. Sigma factor-mediated tuning of bacterial cell-free synthetic genetic oscillators. ACS Synth Biol. 7 (12), 2879-2887 (2018).
- van der Linden, A. J., et al. A multilayer microfluidic platform for the conduction of prolonged cell-free gene expression. J Vis Exp. (152), 59655 (2019).
- Shang, L., Cheng, Y., Zhao, Y. Emerging droplet microfluidics. Chem Rev. 117 (12), 7964-8040 (2017).
- Seemann, R., Brinkmann, M., Pfohl, T., Herminghaus, S. Droplet based microfluidics. Rep Prog Phys. 75, 016601 (2012).
- Baret, J. C. Surfactants in droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip. 12 (3), 422-433 (2012).
- Clausell-Tormos, J., et al. Droplet-based microfluidic platforms for the encapsulation and screening of mammalian cells and multicellular organisms. Chem Biol. 15 (5), 427-437 (2008).
- Umbanhowar, P. B., Prasad, V., Weitz, D. A. Monodisperse emulsion generation via drop break off in a coflowing stream. Langmuir. 16 (2), 347-351 (2000).
- Abate, A. R., Thiele, J., Weitz, D. A. One-step formation of multiple emulsions in microfluidics. Lab Chip. 11 (2), 253-258 (2011).
- Chen, Y., Gao, W., Zhang, C., Zhao, Y. Three-dimensional splitting microfluidics. Lab Chip. 16 (8), 1332-1339 (2016).
- Ahn, K., Agresti, J., Chong, H., Marquez, M., Weitz, D. A. Electrocoalescence of drops synchronized by size-dependent flow in microfluidic channels. Appl Phys Lett. 88 (26), 264105 (2006).
- Fidalgo, L. M., Abell, C., Huck, W. T. S. Surface-induced droplet fusion in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip. 7 (8), 984-986 (2007).
- Bernath, K., et al. In vitro compartmentalization by double emulsions: Sorting and gene enrichment by fluorescence activated cell sorting. Anal Biochem. 325 (1), 151-157 (2004).
- Aharoni, A., Amitai, G., Bernath, K., Magdassi, S., Tawfik, D. S. High-throughput screening of enzyme libraries: thiolactonases evolved by fluorescence-activated sorting of single cells in emulsion compartments. Chem Biol. 12 (12), 1281-1289 (2005).
- Deng, N. N., Yelleswarapu, M., Huck, W. T. S. Monodisperse uni- and multicompartment liposomes. J Am Chem Soc. 138 (24), 7584-7591 (2016).
- Deng, N. N., Yelleswarapu, M., Zheng, L., Huck, W. T. S. Microfluidic assembly of monodisperse vesosomes as artificial cell models. J Am Chem Soc. 139 (2), 587-590 (2016).
- Hindson, B. J., et al. High-throughput droplet digital PCR system for absolute quantitation of DNA copy number. Anal Chem. 83 (22), 8604-8610 (2011).
- Macosko, E. Z., et al. Highly parallel genome-wide expression profiling of individual cells using nanoliter droplets. Cell. 161 (5), 1202-1214 (2015).
- Shembekar, N., Chaipan, C., Utharala, R., Merten, C. A. Droplet-based microfluidics in drug discovery, transcriptomics and high-throughput molecular genetics. Lab Chip. 16 (8), 1314-1331 (2016).
- Wong, A. H., et al. Drug screening of cancer cell lines and human primary tumors using droplet microfluidics. Sci Rep. 7 (1), 9109 (2017).
- Jing, W., Han, H. Droplet microfluidics for high-resolution virology. Anal Chem. 94 (23), 8085-8100 (2022).
- Ding, Y., Choo, J., deMello, A. J. From single-molecule detection to next-generation sequencing: microfluidic droplets for high-throughput nucleic acid analysis. Microfluid Nanofluidics. 21 (3), 58 (2017).
- Nightingale, A. M., et al. A stable droplet reactor for high temperature nanocrystal synthesis. Lab Chip. 11 (7), 1221-1227 (2011).
- De Stefano, P., Bianchi, E., Dubini, G. The impact of microfluidics in high- throughput drug-screening applications. Biomicrofluidics. 16 (3), 031501 (2022).
- Tekin, E., et al. Prevalence and patterns of higher-order drug interactions in Escherichia coli. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 4, 31 (2018).
- Eduati, F., et al. A microfluidics platform for combinatorial drug screening on cancer biopsies. Nat Commun. 9 (1), 2434 (2018).
- Utharala, R., et al. A microfluidic Braille valve platform for on-demand production, combinatorial screening and sorting of chemically distinct droplets. Nat Protoc. 17 (12), 2920-2965 (2022).
- Mathur, L., et al. Combi-seq for multiplexed transcriptome-based profiling of drug combinations using deterministic barcoding in single-cell droplets. Nat Commun. 13 (1), 4450 (2022).
- Dubuc, E., et al. Cell-free microcompartmentalised transcription–translation for the prototyping of synthetic communication networks. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 58, 72-80 (2019).
- Kulesa, A., Kehe, J., Hurtado, J. E., Tawde, P., Blainey, P. C. Combinatorial drug discovery in nanoliter droplets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 115 (26), 6685-6690 (2018).
- Tomasi, R. F. X., Sart, S., Champetier, T., Baroud, C. N. Individual control and quantification of 3D spheroids in a high-density microfluidic droplet array. Cell Rep. 31 (8), 107670 (2020).
- White, J. A., Streets, A. M. Controller for microfluidic large-scale integration. HardwareX. 3, 135-145 (2018).
- Brower, K., et al. An open-source, programmable pneumatic setup for operation and automated control of single- and multi-layer microfluidic devices. HardwareX. 3, 117-134 (2018).
- Gonzalez-Suarez, A. M., Long, A., Huang, X. H., Revzin, A. A Compact control system to enable automated operation of microfluidic bioanalytical assays. Biosensors. 12 (12), 1160 (2022).
- Mathur, L., Ballinger, M., Utharala, R., Merten, C. A. Microfluidics as an enabling technology for personalized cancer therapy. Small. 16 (9), e1904321 (2020).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved