Method Article
Robust Detection of Gene Amplification in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Samples by Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
In This Article
Summary
This protocol provides a reproducible method to visualize gene amplification in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue specimens.
Abstract
Focal gene amplification, such as extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA), plays an important role in cancer development and therapy resistance. While sequencing-based methodologies enable an unbiased identification of ecDNA, cytogenetic-based techniques, such as fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), remain time and cost-effective for identifying ecDNA in clinical specimens. The application of FISH in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples offers a unique avenue for detecting amplified genes, particularly when viable specimens are not available for karyotype examination. However, there is a lack of consensus procedures for this technique. This protocol provides comprehensive, fully optimized, step-by-step instructions for conducting FISH to detect gene amplification, including ecDNA, in FFPE tissue samples which present unique challenges that this protocol aims to overcome and standardize. By following this protocol, researchers can reproducibly acquire high-quality imaging data to assess gene amplification.
Introduction
The study of focal oncogene amplification is crucial as it drives cancer formation, progression, and therapy resistance1. Importantly, oncogenes and immunoregulatory genes may amplify as extrachromosomal DNAs (ecDNA), whose asymmetric inheritance promotes genetic heterogeneity in cancer2,3. ecDNA has been linked to therapy resistance and unfavorable clinical outcomes4,5,6.
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue specimens represent a vast archival resource in pathology laboratories, offering abundant information for retrospective studies. However, extracting molecular data from FFPE specimens through PCR or sequencing is challenging due to nucleic acid fragmentation, degradation, and cross-linking during fixation7. Among the array of techniques available for molecular analysis of FFPE tissues, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) has proven effective for visualizing specific DNA sequences8.
Despite the advancement of modern molecular diagnostic techniques, the ability of FISH to visualize and quantify gene amplification at the single-cell level provides valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis and clinical outcomes. By using fluorescently labeled probes complementary to the target gene of interest, FISH can conveniently resolve the localization of an oncogene and may infer the form of oncogene amplification (such as ecDNA) within individual cells, which is otherwise impossible or expensive through other technologies. Therefore, FISH offers an economical way to assess tumor heterogeneity and clonal evolution9. Furthermore, advances in automation, imaging, and computational analysis have facilitated high-throughput analysis of FISH data, enabling robust quantification of gene amplification across large tissue cohorts10.
However, applying FISH to FFPE tissue presents inherent challenges, including cross-linking artifacts and background autofluorescence. Overcoming these obstacles requires careful optimization of each procedure to ensure accurate and reproducible results. This paper provides a step-by-step, fully optimized protocol for applying FISH to investigate gene amplification in FFPE tissue samples. Using a probe targeting the ERBB2 (HER2) gene locus, we demonstrate that FISH can robustly detect ERBB2 amplification status in FFPE samples from breast cancer patients. It is even possible to estimate whether ERBB2 is amplified as ecDNAs. By synthesizing existing literature and our experimental findings, we elucidate the methodological considerations, technical challenges, and potential pitfalls of FISH-based analysis. We also discuss the clinical relevance of gene amplification profiling in various cancer types, highlighting its prognostic significance and potential for personalized therapeutic strategies.
In summary, this paper underscores the importance of FISH as a valuable tool for studying gene amplification in FFPE tissue specimens, offering unparalleled insights into tumor biology and guiding clinical decision-making in oncology. With continued refinement and integration with complementary molecular assays, FISH-based analysis stands poised to further enhance our understanding of cancer pathogenesis and improve patient outcomes in the era of precision medicine.
Protocol
This research protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. Informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to surgery.
1. Reagents and materials preparation
- Prepare the 0.2 N sodium chloride (HCl) solution in a fume hood by slowly adding 8.212 mL of HCl (37% w/w or 12.1 N) to 491.788 mL of ddH2O. Store at room temperature (RT).
CAUTION: Slowly add acid to water. Do not add water to acid. - Prepare 10 mM citric acid solution (pH 6.0) by dissolving 1.47 g of Tri-sodium citrate (dihydrate) in 400 mL of ddH2O. Use HCl to adjust to pH 6.0, and then bring the final volume to 500 mL with ddH2O. Store the buffer at RT.
- Prepare the 10% Tween-20 solution by adding 100 µL of Tween-20 to 900 µL of ddH2O. Store it at RT.
- Prepare the 10% IGEPAL solution by adding 5 mL of IGEPAL CA-630 to 45 mL of ddH2O. Store it at RT.
- Prepare the 20x SSC (pH 7.0, 3 M NaCl, 0.3 M Sodium Citrate) solution by dissolving 44.1 g of Tri-sodium citrate (dihydrate) and 87.65 g of sodium chloride (NaCl) in 900 mL of ddH2O. Use HCl to adjust to pH 7.0, and then bring the final volume to 1000 mL with ddH2O. Store the buffer at RT.
- Prepare the 2x SSC solution by adding 100 mL of 20x SSC to 900 mL of ddH2O. If necessary, add 0.5 mL of preservative (Table of Materials). Store it at RT.
- Prepare the probe hybridization buffer by mixing 910 µL of ddH2O, 500 µL of 20x SSC, 50 µL of 10% Tween-20, 40 µL of RNase A, 1 mL of 50% dextran sulfate, and 2.5 mL of formamide. Aliquot into 1 mL and store them at -20 ˚C.
- Prepare the 0.4x SSC with 0.3% IGEPAL solution by mixing 100 mL of 2x SSC, 15 mL of 10% IGEPAL, and 385 mL of ddH2O. Store it at RT.
- Prepare the 2x SSC with 0.1% IGEPAL solution by adding 5 mL of 10% IGEPAL to 495 mL of 2x SSC solution. Store it at RT.
- Freshly prepare the Proteinase K digestion buffer before use by adding 1 µL of Proteinase K to 99 µL of Tris-EDTA buffer.
- Prepare 1 mg/mL DAPI storage stock by dissolving 1 mg of DAPI into 1 mL of ddH2O. Store it at -20 °C and away from light. Prepare the DAPI working solution by adding 1 µL of the DAPI storage stock to 999 µL of 2x SSC solution. Keep away from light till use.
2. Sample pretreatment
NOTE: The slide used here contains the specimen.
- Age the slide at 60-90°C for 20 min or overnight (Figure 1).
NOTE: This step facilitates paraffin melting. Usually, 20 min of heating is sufficient. It can be extended to overnight to accommodate the schedule. - Deparaffinize the slide by immersing it into xylene or its substitutes in a Coplin jar for 10 min. Repeat this step with fresh xylene or its substitutes. Perform all the following pretreatment and washing steps in a Coplin jar.
NOTE: Xylene substitutes are safe and eco-friendly alternatives to xylene. One of the substitutes (see Table of Materials) performs as well as xylene, if not better. Although xylene substitutes produce less odor than xylene, using it inside a fume hood is recommended. If xylene substitutes are not accessible, all procedures are compatible with xylene-based deparaffinization without any changes. - Wash off the xylene substitute with 100% ethanol for 5 min.
- Rehydrate the slide with 70% ethanol immersion for 5 min.
- Immerse the slide into 0.2 N hydrochloric acid (HCl) at RT for 20 min.
NOTE: HCl effectively extracts acid-soluble proteins, such as basic nuclear proteins, to improve DNA accessibility to FISH probes11. - Immerse the slide into 10 mM of hot citric acid solution and incubate at 90-95 °C for 20 min.
NOTE: Citric acid treatment under high temperatures similarly extracts acid-soluble proteins. Both acid treatments are thought to extract extracellular matrix proteins to decrease autofluorescence12. It is recommended that the citric solution be preheated to the desired temperature range before being applied to the slide. Microwave can be a convenient way to do so. A water bath, such as with a sous vide cooker, is the most effective and economical solution for high-temperature incubation. - Rinse the slide briefly in 2x SSC to neutralize pH.
- Digest the tissue by adding 100-200 µL (enough to completely cover the tissue depending on the size of the section) of Proteinase K digestion buffer and incubate at RT for 1 min.
NOTE: Proteinase K digestion further increases the accessibility for FISH probes and reduces autofluorescence. The time of digestion should be optimized based on the tissue types. In most cases, 1 min of digestion is sufficient. Over-digestion leads to halo-shaped nuclei morphology, and the digestion time should be reduced. - Immediately stop Proteinase K digestion and dehydrate the slide by immersing it into 70% ethanol for 2 min, followed by 85% and 100% ethanol treatment for 2 min each.
3. FISH and imaging
- Prepare the FISH hybridization mix by diluting 2 µL of FISH probe stock with 8 µL of hybridization buffer, then apply it to the slide. Cover the sample with a coverslip.
NOTE: The total FISH probe stock used ranges from 0.5-4 µL, depending on the image quality. If the signal is too low, increase the probe input. Reduce the FISH probe input if the background is too high, especially when fluorescent debris outside the nuclei is observed. The hybridization buffer can either be the one provided with the commercially purchased probes or prepared as in the section 1. - Place the slides onto a hot plate, such as a slide moat hybridization system, to denature DNA at 75 °C for 2-5 min. Then, transfer the slide onto another hot plate set at 37 °C to hybridize overnight.
NOTE: If the hot plate has a water tray or reservoir to maintain the humidity during hybridization, sealing the coverslip with rubber cement is unnecessary. - After hybridization, dip the slide into 40-60 °C warmed 0.4x SSC with 0.3% IGEPAL CA-630 washing buffer, then carefully remove the coverslip. Continue the washing twice for 5 min each in the dark, with agitation for the first 10-15 s.
NOTE: Dipping the slide into the washing buffer helps gently release the coverslip. - Wash the slide by in SSC with 0.1% IGEPAL CA-630 for 5 min at RT in the dark, with agitation for the first 10-15 s.
- To quench autofluorescence, treat the slide with the autofluorescence quenching kit (see Table of Materials) by applying 150 µL of reagent (50 µL + 50 µL + 50 µL of reagents A, B, C) for 2-5 min, then wash it with 2x SSC for 5 min.
NOTE: This is an optional step. Tissue autofluorescence primarily originates from extracellular matrix components, such as collagen and elastin. It is also significantly influenced by lysosomes and mitochondria due to their lipofuscin, NADPH, and flavin coenzyme content. Aldehyde fixation and blood cell presence may also increase autofluorescence well13,14. - Stain the slide with DAPI for 10 min. Rinse the slide with 2x SSC buffer for 5 min.
NOTE: If the slide is not treated by the autofluorescence quenching kit, DAPI staining can be reduced to 2 min. - Quickly dip the slide into deionized water for no more than 1 s, then quickly dry it by absorbing extra moisture with a paper towel.
NOTE: This is an optional step. Deionized water treatment effectively prevents salt crystal deposition of SSC buffer on the slide and improves imaging quality. However, under such low ion conditions, hydrogen bonds between the FISH probe and targeted DNA are weakened, leading to probe dissociation and signal loss. Therefore, maintaining the water treatment step for a very short time is crucial. - Dry the slide, then mount it with antifade mounting media. Seal the coverslip with nail polish before imaging.
NOTE: If the slide is treated by autofluorescence quenching reagent, mount the slide with an antifade mounting medium per the manufacturer's instruction. Moreover, depending on the type of mounting media, hardening or non-hardening, the sample must be cured for 1-24 h before sealing and imaging. It is recommended that the sample be cured at least overnight to achieve the best refractive index for imaging. - Use a 60× oil lens to capture fluorescence signal. Use the DAPI channel to adjust the focus. Ensure to obtain multiple Z-stacks. Typically, 5-10 z-stacks with a 1-µm interval are sufficient. Perform a maximum 3D projection to achieve the best resolution. Apply deconvolution or other background-clearing algorithms to further improve the image quality.
Results
We used FFPE samples from both HER2-positive and negative breast cancers to demonstrate the result of FISH imaging. Amplification of HER2 (encoded by the ERBB2 gene) is a favorable marker due to the availability and effectiveness of HER2 molecular targeting therapies. On the contrary, patients with triple-negative breast cancers, which lack expression of HER2, estrogen receptor (ER), and progesterone receptor (PR), face poor outcomes due to limited therapeutic options. Therefore, determining the HER2 status is crucial in breast cancer research and treatment15.
In the triple-negative breast cancer sample, most nuclei display two distinct dots representing HER2/ERBB2 FISH signals. Some nuclei may only have one dot due to sectioning bias (Figure 2, left). In contrast, HER2-positive samples present abundant FISH signals with two different patterns. One pattern shows scattered dots throughout the nucleus (Figure 2, middle). This pattern is a characteristic of ecDNA morphology, as ecDNAs may not occupy a unique and organized nuclear territory16. Furthermore, ecDNAs' asymmetric segregation during mitosis drives copy number variation, leading to signal heterogeneity among nuclei17. Some nuclei may show occasional clusters, indicative of ecDNA hubs18 (Figure 2, right). The other type of HER2 amplification primarily displays rod-shaped, condensed aggregates. This morphology likely indicates chromosome-based amplification, such as homogeneously staining regions (HSR)19 or through the breakage-fusion-bridge (BFB) cycle20. Notably, ecDNA, HSR, and BFB amplification can co-exist in the same nucleus. Therefore, examining multiple nuclei is recommended to infer the form of focal amplification.
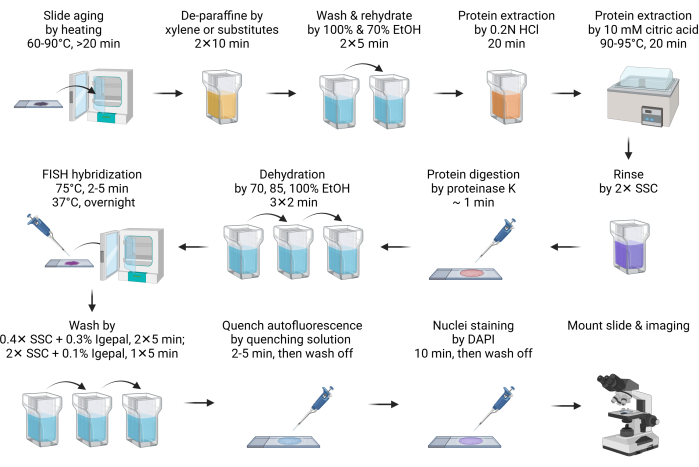
Figure 1: Schematic for FISH in FFPE samples. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
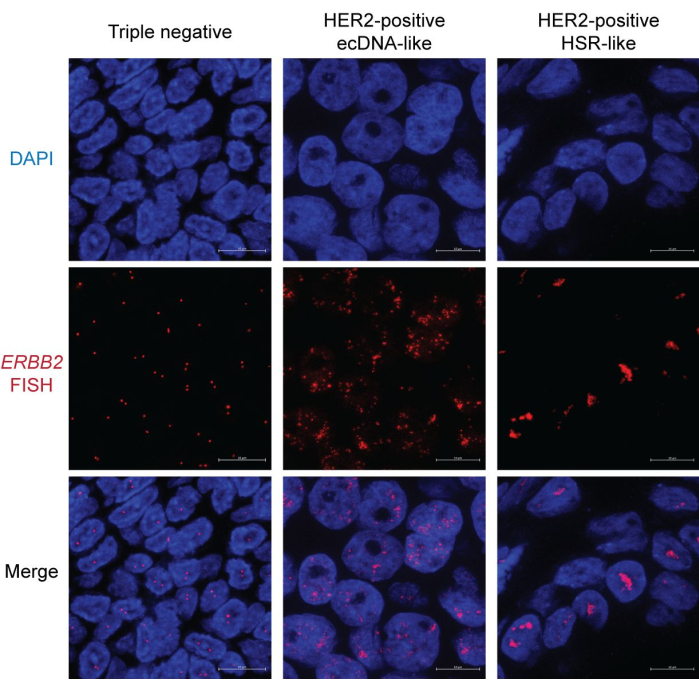
Figure 2: Representative FISH image in breast cancer FFPE samples. Magnification: 600x; Scale bar: 10 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
FISH is a fast and affordable option for cytogenetic diagnosis. Especially in determining whether ecDNA is present in cancer, FISH evidence remains the gold standard1. FISH in FFPE tissue allows rapid determination of gene status in a patient's biopsy specimens, allowing for quicker diagnosis and tracking changes throughout the disease's progress. This technique is particularly valuable for testing clinical samples that have already been collected for pathology.
This protocol involves several critical steps. The first step is thorough deparaffinization. Residual paraffin can disrupt FISH hybridization. If the sample still appears waxy after step 2, it should be treated again with fresh xylene or its substitutes.
Second, protein extraction and digestion are critical. These processes not only enhance the DNA's accessibility to the FISH probe but also significantly reduce auto-fluorescence. This protocol includes three deproteinization steps. While the treatment with 0.2 N HCl and 10 mM citric acid is straightforward, the proteinase K digestion may require optimization. Over-digestion is the most common error when using proteinase K, resulting in halo-shaped nuclei. Shortening the digestion time will improve the nuclei morphology. Additionally, it is recommended not to digest more than four samples simultaneously to minimize the time difference between the first and the last sample. It is important to note that even an intact nucleus may appear as a halo under high-magnification and high-resolution microscopy. This is because the nucleus is not on the same focal plane. Therefore, it is suggested to take multiple Z-stacks and perform a max projection to inspect the nuclear morphology.
Lastly, quenching autofluorescence is recommended. Although acid extraction and proteinase K digestion can significantly reduce protein-derived background, fluorescent metabolites may still affect the imaging quality.
While FISH offers unparalleled spatial resolution in identifying focal gene amplification, it has limitations. First, the content and throughput are low compared to PCR or next-generation sequencing (NGS) based approaches. Typically, one to three FISH probes of different colors can be applied to a single slide without specialized equipment. Nonetheless, advancements in automation technologies have made high-content and high-throughput FISH, such as in situ sequencing21, feasible. Second, the FISH probe design requires prior information. The ongoing efforts to identify recurrent focal amplification events in cancer have enabled the creation of pre-designed FISH panels for laboratory and clinical applications. For instance, MYC-family oncogenes are frequently amplified as ecDNA in small-cell lung cancer to mediate chemotherapy resistance. Therefore, a FISH panel targeting MYC, MYCL, and MYCN genes can expedite the determination of treatment responses in biopsies. In comparison, NGS allows a more unbiased screening of genes of interest. However, among NGS-based technologies, only whole-genome sequencing with computation-expensive analysis22 can characterize ecDNA.
In summary, we present robust and comprehensive instructions for investigating focal gene amplification in FFPE samples. By examining the FISH signal pattern, it becomes unequivocally clear whether and how a gene locus is amplified. We anticipate the integration of machine learning into the image analysis23 of interphase nuclei to extract cytogenetic information regarding copy number and the form of amplification (chromosome or ecDNA), thereby streamlining the molecular diagnosis process and enhancing our understanding of pathogenetic mechanisms in cancer.
Disclosures
S.W. is a member of the scientific advisory board of Dimension Genomics Inc.
Acknowledgements
S.W. is a scholar of and is supported by the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (RR210034)
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| DAPI | Tocris Bioscience | 5748 | Nucleus staining |
| Dextran sulfate 50% solution | EMD Millipore Sigma | S4030 | Probe hybridization buffer |
| ERBB2 (HER2) FISH Probe | Empire Genomics | ERBB2-20-RE | FISH probe |
| Ethanol | Decon Labs | 2716 | Dehydrating and hydrating tissue |
| Formamide | Thermo Scientific Chemicals | 205821000 | Probe hybridization buffer |
| Formula 83 (Xylene substitute) | CBG Biotech | CH0104A | Removing paraffin |
| Hydrochloric acid | Fisher Chemical | A144-500 | Sample pretreatment |
| IGEPAL CA-630 | Thermo Scientific Chemicals | J19628K2 | Slide washing |
| Proclin 300 | Sigma-Aldrich | 48914-U | Preservative for SSC buffer (optional) |
| Proteinase K (800 units/mL) | New England Biolabs | P8107S | Protein digestion |
| RNase A (20 mg/mL) | New England Biolabs | T3018L | Probe hybridization buffer |
| Slide Moat Hybridization System | Boekel Scientific | 280001 | Sample denature and hybridization. Alternative hot plates are acceptable. |
| Sodium chloride | Fisher Chemical | S2713 | SSC buffer |
| Sodium citrate dihydrate | Fisher BioReagents | FLBP3271 | SSC buffer and sample pretreatment |
| Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer | Fisher BioReagents | BP2473500 | Proteinase K digestion buffer |
| Tween-20 | Fisher BioReagents | BP337-500 | Probe hybridization buffer |
| Vectashield antifade mounting media | Vector Laboratories | H190010 | Slide mounting |
| Vector TrueVIEW | Vector Laboratories | SP8400 | Autofluorescence quenching kit |
References
- ICGC/TCGA Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes Consortium. Pan-cancer analysis of whole genomes. Nature. 578 (7793), 82-93 (2020).
- Wu, S., Bafna, V., Chang, H. Y., Mischel, P. S. Extrachromosomal DNA: An emerging hallmark in human cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 17, 367-386 (2022).
- Luebeck, J., et al. Extrachromosomal DNA in the cancerous transformation of Barrett's oesophagus. Nature. 616 (7958), 798-805 (2023).
- Nathanson, D. A., et al. Targeted therapy resistance mediated by dynamic regulation of extrachromosomal mutant EGFR DNA. Science. 343 (6166), 72-76 (2014).
- Kim, H., et al. Extrachromosomal DNA is associated with oncogene amplification and poor outcome across multiple cancers. Nat Genet. 52 (9), 891-897 (2020).
- Pal Choudhuri, S., et al. Acquired cross-resistance in small cell lung cancer due to extrachromosomal DNA amplification of MYC paralogs. Cancer Discov. 14 (5), 804-827 (2024).
- Greytak, S. R., Engel, K. B., Bass, B. P., Moore, H. M. Accuracy of molecular data generated with FFPE biospecimens: Lessons from the literature. Cancer Res. 75 (8), 1541-1547 (2015).
- Chrzanowska, N. M., Kowalewski, J., Lewandowska, M. A. Use of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in diagnosis and tailored therapies in solid tumors. Molecules. 25 (8), 1864(2020).
- Cui, C., Shu, W., Li, P. Fluorescence in situ hybridization: Cell-based genetic diagnostic and research applications. Front Cell Dev Biol. 4, 89(2016).
- Finn, E. H., Misteli, T. A high-throughput DNA FISH protocol to visualize genome regions in human cells. STAR Protoc. 2 (3), 100741(2021).
- Watters, A. D., Bartlett, J. M. S. Fluorescence in situ hybridization in paraffin tissue sections. Mol Biotechnol. 21 (3), 217-220 (2002).
- Richardson, S. O., et al. One-fits-all pretreatment protocol facilitating fluorescence in situ hybridization on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded, fresh frozen and cytological slides. Mol Cytogenet. 12, 27(2019).
- Monici, M. Cell and tissue autofluorescence research and diagnostic applications. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 11, 227-256 (2005).
- Davis, A. S., et al. Characterizing and diminishing autofluorescence in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human respiratory tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 62 (6), 405-423 (2014).
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 490 (7418), 61-70 (2012).
- Liang, Z., et al. Chromatin-associated RNA dictates the ecDNA interactome in the nucleus. bioRxiv. , (2023).
- Lange, J. T., et al. The evolutionary dynamics of extrachromosomal DNA in human cancers. Nat Genet. 54 (10), 1527-1533 (2022).
- Hung, K. L., et al. ecDNA hubs drive cooperative intermolecular oncogene expression. Nature. 600 (7890), 731-736 (2021).
- Storlazzi, C. T., et al. Gene amplification as double minutes or homogeneously staining regions in solid tumors: origin and structure. Genome Res. 20 (9), 1198-1206 (2010).
- Guerin, T. M., Marcand, S. Breakage in breakage-fusion-bridge cycle: an 80-year-old mystery. Trends Genet. 38 (7), 641-645 (2022).
- Nguyen, H. Q., et al. 3D mapping and accelerated super-resolution imaging of the human genome using in situ sequencing. Nat Methods. 17 (8), 822-832 (2020).
- Deshpande, V., et al. Exploring the landscape of focal amplifications in cancer using AmpliconArchitect. Nat Commun. 10 (1), 392(2019).
- Rajkumar, U., et al. EcSeg: Semantic segmentation of metaphase images containing extrachromosomal DNA. iScience. 21, 428-435 (2019).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved