Method Article
Alternatifi olarak dilaltı immünoterapi Akut Solunum Enfeksiyonları Karşı Koruma tetikleyebilecek
Bu Makalede
Özet
The present work illustrates the convenience of using sublingual immunotherapy to boost the innate immune response in the lungs and confer protection against acute pneumococcal pneumonia in mouse.
Özet
Sublingual route has been widely used to deliver small molecules into the bloodstream and to modulate the immune response at different sites. It has been shown to effectively induce humoral and cellular responses at systemic and mucosal sites, namely the lungs and urogenital tract. Sublingual vaccination can promote protection against infections at the lower and upper respiratory tract; it can also promote tolerance to allergens and ameliorate asthma symptoms. Modulation of lung’s immune response by sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) is safer than direct administration of formulations by intranasal route because it does not require delivery of potentially harmful molecules directly into the airways. In contrast to intranasal delivery, side effects involving brain toxicity or facial paralysis are not promoted by SLIT. The immune mechanisms underlying SLIT remain elusive and its use for the treatment of acute lung infections has not yet been explored. Thus, development of appropriate animal models of SLIT is needed to further explore its potential advantages.
This work shows how to perform sublingual administration of therapeutic agents in mice to evaluate their ability to protect against acute pneumococcal pneumonia. Technical aspects of mouse handling during sublingual inoculation, precise identification of sublingual mucosa, draining lymph nodes and isolation of tissues, bronchoalveolar lavage and lungs are illustrated. Protocols for single cell suspension preparation for FACS analysis are described in detail. Other downstream applications for the analysis of the immune response are discussed. Technical aspects of the preparation of Streptococcus pneumoniae inoculum and intranasal challenge of mice are also explained.
SLIT is a simple technique that allows screening of candidate molecules to modulate lungs’ immune response. Parameters affecting the success of SLIT are related to molecular size, susceptibility to degradation and stability of highly concentrated formulations.
Giriş
The overall goal of this work is to illustrate the benefits of sublingual immunotherapy for the treatment of acute respiratory infections (ARI) and present the advantages of this delivery route compared to other routes of administration, namely intranasal.
ARI cause millions of deaths every year especially in children under five. Streptococcus pneumoniae remains as one of the major etiological agents of bacterial pneumonia in infants and the elderly1,2. To present, the main available treatment relies on the use of antibiotics but resistant strains are continuously arising3,4.
SLIT induces broad responses at systemic and also mucosal level, particularly at the respiratory tract5. It has proven effectiveness against influenza infection, promoting long term protection with production of humoral and cellular responses6,7. Besides, it has been shown that prophylactic treatment with bacterial lysates delivered by sublingual route reduced exacerbations of chronic obstructive bronchitis in the elderly8 and prevented recurrent respiratory infections in children9. SLIT has been widely used for the treatment of allergies and asthma. Clinical studies had not only demonstrated its efficacy to modulate the immune response in the respiratory tract but also its safety10. Despite the growing interest of pharmaceutical companies and researchers in SLIT, the mechanisms involved in the induction of mucosal immune responses after sublingual delivery of compounds remain obscure. Recently, attention has been focused on the mechanisms promoting tolerance associated with allergen desensitization. It has been proposed that resident and recruited cells at the sublingual mucosa, like dendritic cells and macrophages, can promote tolerance after SLIT11-13. Dendritic cells of the oral mucosa can promote IFN-gamma and IL-10 producing T helper cells11 as well as recirculate to the distal genital mucosa and promote CD8+ T cells14. However, little is known about the impact of SLIT on innate cells or its capacity to improve pathogen clearance during acute respiratory infections.
The natural control of pneumococcal infection in the lungs greatly depends on the efficient and swift activation of local innate defences. We previously showed that enhancement of lungs’ innate immunity by a single intranasal dose of flagellin (FliC), a TLR5 and NLRC4 agonist, protects 75-100% of mice challenged with a lethal dose of a clinical isolate of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 1. This protection was shown to be dependent on local recruitment of GR1+ cells (likely polymorphonuclear neutrophils, PMNs) and not dependent on antibodies, B or T cells15.
Flagellin is the structural component of the bacterial flagellum. In its monomeric form it is recognized by two Pathogen Recognition Receptors (PRRs), TLR5 that senses extracellular FliC16 and NLRC4/NAIP5 inflammasome that detects intracellular flagellin17,18. When FliC is sensed by the PRRs an important inflammatory response is triggered. We and others have demonstrated that instillation of purified FliC from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium into the lungs drives swift production of chemokines and cytokines specially when recognized by the lungs’ epithelium that in turn orchestrate the recruitment of immune cells into the airways, mainly PMNs15,19-21. Although transient, the substantial neutrophil infiltration that takes place into the airways after nasal delivery of FliC could be a concern if moving towards clinical therapies for human use. Excessive inflammation could be detrimental for the lungs’ function. Moreover, it has been shown that intranasal delivery of immunostimulatory molecules may cause facial paralysis and/or brain toxicity22-24.
Sublingual immunotherapy offers a safer alternative to modulate the immune response in the respiratory tract compared to the intranasal route. It is non-invasive, painless, simple and has good patient compliance25. Furthermore, as mentioned before, it can induce protective responses in the respiratory mucosa without the risks associated to direct intranasal or intrapulmonary delivery of formulations. Sublingual route could be alternatively used to deliver molecules that have great effects onto the lung’s immune system but that have been proven to be toxic or to elicit great inflammation when administered intranasally. Besides these advantages, formulations for sublingual immunotherapy have lower cost of manufacture since non-sterile products can be delivered by this route and endotoxic shock is not a concern for SLIT. On the other hand, it is worth noticing that higher doses of the immunostimulatory compounds compared to those used by intranasal or parenteral routes are necessary to induce an immune response in the lungs; also highly concentrated solutions are needed when using the mouse model of SLIT since the anatomical site where the formulations are deposited is small.
Based on our previous published data, we developed a model of protection using sublingual immunotherapy with flagellin as model immunostimulant. We demonstrated that a single dose of flagellin induced 60% survival against invasive pneumococcal pneumonia caused by the serotype 1 strain while all mice in the control group died of infection within 5 days. Flow cytometry analysis showed that higher numbers of PMN are recruited into the airways of protected animals after sublingual treatment with flagellin suggesting that these cells might be involved in the mechanism of protection induced by sublingual immunotherapy.
This video shows in detail how to perform sublingual immunotherapy and also how to recover relevant tissue from the sublingual mucosa, draining lymph nodes as well as lungs and airways to perform further analysis. Additionally, it illustrates the general technique of cell preparation for FACS analysis and briefly shows how to prepare Streptococcus pneumoniae suspensions and how to perform intranasal infections in mouse to set up the acute infection model.
Protokol
Uruguay - hayvanları kapsayan Prosedürleri Hayvan Deney için Fahri Komisyonu ve Tıp Okulu, Universidad de La Republica Direktifi Kurulu tarafından onaylanmış 071140-000821-12 ve 08.052.010 ° protokolleri N ile uygun olarak yapıldı.
Terapötik madde, 1. dil altı uygulama
- Terapötik madde ihtiva eden bir çözelti hazırlamak test edilecek. Fare başına 10 ul maksimum bir hacme sahip yönetmek üzere, konsantre hale ayarlayın.
Not: Salmonella enterica serovar saflaştırılmıştır flagellin'in için S. ilk ölümcül dozu ile enfekte farede korumayı indüklemek için en uygun dozu typhimurium pneumoniae serotip 1 E1586,% 100 ölüme neden olan 10 ug / faredir. Çözelti, flagellin monomerlerin salınmasını sağlamak için 5 dakika boyunca 65 ° C 'de ısıtılması gerekmektedir. Flagellin arıtma hakkında daha fazla bilgi için başvuru 26 bkz.- Var, moleküler boyut, saflık, duyarlılık ve proteolize mukozaya yapışan maddelerin kullanımına göre farklı immüno-modülatör ajanlar olarak etkili konsantrasyonu. Her bir bileşik, etki için test edilecek için en uygun konsantrasyon ayarlayın. Burun içinden yol ile daha önce yapılan çalışmalar, belirli bir bileşik için yapılmıştır halinde, dil altı yol ile etkinliğini test etmek için bir başlangıç dozu 5-10 kat daha yüksek kullanın.
- 5.5 mg / kg Xylacine ile 110 mg / kg ketamin içeren bir kokteyl enjekte ederek farelerin Anesteziyoloji ve hayvanlar 7 ila 10 dakika bekletin.
- Yavaşça arka bacaklardan birinin Kapkaççı basarak uygun anestezi onaylayın; Eğer düzgün hayvan uyarana cevap olarak hareket etmeyecektir anestezi.
- Anestezi altında iken kuruluğunu önlemek için her fare gözleri üzerine veteriner merhem ince bir tabaka sürün.
NOT: Bir sistem donatmak eğer Izofloran gibi Đnhalatuar anestezik yerine de Ketamin / Xylacine kullanılabilirindüksiyon odası ve burun kozalakları ile ped kullanılabilir. Hayvanları anastetize ve sublingual yoldan imünostimülanı yönetmek indüksiyon odasına kullanın. Yutulduktan hemen önlemek ve tedavi edici bir bileşiğinin emilimine imkan vermek için anestezi altında tutmak için en az 15 dakika boyunca, bir uç konisinde, hayvanın bağlayın. - Immüno-uyarıcı veya kontrol çözeltiyi içeren çözeltinin Pipet; başparmak ve dominant olmayan el işaret parmağı kullanarak fare almak ve dikey konumda tutun.
- Biraz forseps açık, dil altında dominant el yerde kapalı forseps bir çift kullanarak ve orta ve yüzük parmaklarını kullanarak yerinde tutun dilini kaldırmak için.
- Pipet ve dilin ağız ve dorsal tarafına zemin üzerine solüsyonun verilmesi.
- Forseps çıkarın ve kafesin içine geri koyarak önce 3 ila 5 dakika boyunca fare dinlensin. Sağlamak için bu normotermi anestezi uygulanmış mikrofon korunure, bir kafes ısıtıcı sistemine kafesleri bağlayın. Böyle bir sistem mevcut değilse, yer farenin yatak üzerinde birbirine yakın gelen kafes içine tekrar aynı tedavi grubuna ait ve kısmen onları vücut ısısını korumaya yardımcı olmak için temiz kağıt levhalar ile bunları kapatın.
- Muamele ile uyarılan hücre popülasyonlarında değişiklikleri analiz etmek için bağışıklık düzenleyici maddenin uygulamasından sonra herhangi bir zaman noktasında, doku örneklerinin alınması.
Not: flagellin'in bu özel protokol yönetiminde muameleden önce 2 saat uygulandı. Tedavisi ve meydan okuma her bir terapötik madde ve patojen arasındaki uygun zamanı belirlemek üzere test edilebilir.
Streptococcus pneumoniae 2. Bakteriyel Süspansiyon hazırlanması ve burun içi bulaştırma
NOT: S. pneumoniae invaziv pnömoni, sepsis gibi yaşamı tehdit eden hastalıklara neden olabilir doğal bir patojendirve menenjit. Solunması veya mukozası ile temas halinde olduğunda iletim oluşabilir. Bu nedenle, S. ile temas etmiş olabilecek tüm örnekler pneumoniae sınıf II biyogüvenlik kabini kullanarak uygun bir Biyogüvenlik Seviye II tesisi ele alınmalıdır. Koruyucu giysiler, atık bertarafı ve uygulanabilecek ek güvenlik önlemleri için Tip II patojenlerin kullanılmasıyla ilgili kurumun Standart Çalışma Prosedürleri edin. Enfekte hayvanlar HEPA filtre ile donatılmış izolatörler tek tek havalandırılan kafeslerde tutulmalıdır. Anti-pnömokok aşıları ve antibiyotik tedavisi mevcuttur. Daha fazla bilgi için başvurular 27 ve 1 bkz.
- 15'te açıklandığı gibi hazırlanan bilinen Bakteri CFU sayısı bir Streptococcus pneumoniae çalışma stok süspansiyonu bir kısım çözülme.
- 2500 xg ve oda sıcaklığında 5 dakika boyunca santrifüj.
- Süpernatantı atın ve st 1 ml asarak bakteriyel pelet yıkayınerile tuzlu su çözeltisidir. Bakteri süspansiyonu, dilüsyonlarını veya hayvan meydan için hazırlanırken filtre ipuçlarını kullanın.
- Şekilde tekrar adım 2.2 tarif santrifüj.
- Süpernatant atılır ve 4x10 5 CFU / 50 ul bir süspansiyonunu elde etmek için steril tuz uygun hacimde pelletini. Bu doz, S. minimum bakteri dozuna denk düşen pneumoniae serotip önceki çalışmalara göre, 15, BALB / c farelerinde% 100 ölüme yol açar 1 E1586.
Not: farelerde pnömokok kökenli pnömoni bir model oluşturmak halinde en az bakteriyel doz mortalite% 100 bakteri suşu, serotip ve fare soyunun her bir kombinasyonu için belirlenmelidir neden olur. - Vorteks veya aşağı 5 kez yukarı pipetleme ve bakteri süspansiyonu homojenize.
- Yük steril bir filtre ucu kullanılarak bakteriyel süspansiyonun 50 | il ve anestezi uygulanmış bir farenin burun içine toplam hacmi aşılamak. Fare upri tutun2 dakika için ğa ve 2 dakika daha dorsal pozisyonda dinlendirin. Gözleri üzerine veteriner merhem sürün ve kafesine hayvanların dönmek; Anestezi altında iken normotermi korumak için emin olun.
NOT: Bu çalışmada, bakteriye karşı 15,28 daha önce tayin edildiği gibi akciğerlere toplam CFU en azından% 90 teslimini sağlamak için 50 ul bir hacim içinde gerçekleştirilmiştir. Kullanılabilir hayvanın daha küçük hacimlerde (örneğin, 20 ul) rahatsızlığı en aza indirmek için,. Bununla birlikte, ciğerlere girebilecek bakterilerin etkin bir dağıtım kontrol edilmelidir; Bu uygulama sonrasında akciğerlerinde 5 dakika hasat edilmesi ve kan-agar plakaları üzerine seri dilüsyonları kaplama ile akciğerlerin homojenatlarında CFU sayılması ile yapılabilir. - Kan agar plakaları üzerine 10 kat seri dilüsyonları kaplama ile enfeksiyon için, kullanılan bakteri süspansiyonu içinde CFU numaralarını kontrol edin. % 5 CO2 ile 37 ° C, O / N inkübe ve al yeşil bir halo özelliği gösteren mukoid koloni sayısınıfazlı hemolitik bakteri.
3. Doku Toplanması ve akış sitometrisi (FACS) analizi için örnek hazırlanması
3.1) Doku Toplama
- Servikal dislokasyon veya bir CO2 bölmesinde kullanılarak hayvan Euthanize; boynuna kadar göğüs boşluğunda tüm yol açıp boyun ve submandibular bölge ventral tarafında ortaya çıkarmak için ön ayakları boyunca bir kesi yapmak.
- Ince uçlu kavisli bir forseps ile hafifçe ağız kat dorsal yüzü ortaya çıkarmak için tükürük bezleri ve komşu yumuşak dokuyu yukarı çekin. 500 ml-% 10 Fetal Sığır Serumu, 10,000 U / ml ihtiva eden bir çözelti, 5 ml için, nazikçe çekerek alt çene ve alt çene aksesuar lenf düğümlerine ve tam RPMI (cRPMI içeren bir tüpe yerleştirin, ince kavisli ucu forseps kullanılarak bu olacak alt prosedüre göre penisilin ve 10 mg / ml streptomisin solüsyonu ve 5 ml L-glutamin, 200 mM) veya nükleik asit koruyucu çözeltisiDaha sonra gerçekleştirilebilir.
- Göğüs boşluğu diyafram bir kesi yapmak açmak için; sıçan dişli forseps bir çift dikkatle sternum xiphoid kıkırdak kelepçe kullanarak ve gerçek kaburga sternum manubrium karşılamak noktaya ulaşıncaya kadar tüm yol kadar yanlış kaburga başlayarak her iki dorsal tarafta kaburga kesti.
- Forseps ile sternum xiphoid kıkırdak tutarak, göğüs boşluğunun organların maruz hafifçe yukarı çekin.
- Tamamen birinci kaburga ve köprücük kemiğine keserek kaburga çıkarın. Timüs, kalp tabanına yakın toraks anteroventral kısmında bulunan iki lob beyaz bir yapı olarak görünür.
- Forseps bir çift ile sıkma tarafından lob birini alın ve onun alt yüz ve perikard arasındaki bağları kaldırmak için bir makas kullanın. İkinci lobunu kaldırmak için devam edin.
- Karın boşluğu belirlenmesi ve m medyan ekseni boyunca keserek açınuscular duvar organları ortaya çıkarmak. Forseps bir çift ile posterior vena kava ve aorta kesilmiş; emici bir doku ile kan fazlasının ayrılması.
- Alveol ikamet eden ve infiltre hücre popülasyonları bronkoalveoler lavaj (BAL) gerçekleştirmek analiz etmek. Trakea ve yemek borusu açığa çıkarmak için boynun ventral kısmında kaslar kesin; bunların yapıları lateral dorsal taraftan kesiler yapmak ayırmak için.
- Forseps ile trakea yukarı kaldırın ve Ca 2 + / Mg 2 + artı 1 mM EDTA olmadan 1 ml PBS ile dolu ince uçlu transfer pipet tanıtmak için bir neşter ile küçük bir kesi yapmak. Aşılamak ve toplam hacmin en az üç kez aspire; aspirat steril 1.5 ml tüp hücre süspansiyonu transfer ve buz üzerine yerleştirin ve.
- Önce sağ ventrikül içine Ca2 + / Mg2 + artı 1 mM EDTA içermeyen 5 ml PBS enjekte edilerek akciğerlere serpmek, parenkimde hücre popülasyonları analiz etmekkalbin.
Not: Bu akciğerlerin kan damarları içine mevcut olan kırmızı kan hücreleri ve bağışıklık hücrelerinin çoğu ortadan kaldırır. Perfüzyon doğru yapıldı ise, akciğerler renk beyaz pembe kayacak. - Sol ventrikül tabanından sıkma tarafından akciğerlerden kalbe yalıtmalı ve incelikle tamamen kaldırmak için makas ile kan damarlarını kesti. CRPMI veya alt analizi bağlı olarak nükleik asit koruyucu çözelti içinde perfüze akciğerlere almak ve yerleştirmek gerçekleştirilmelidir.
- Sublingual mukozada hücre popülasyonlarının analizi için, hayvanın baş izole ve adım 3.2.1 yapılan edilmemiş ise tükürük bezleri ve bitişik yumuşak doku çıkarın.
- Altçene eklemi ulaşana kadar ağız her tarafında bir kesi yapmak ve pimleri diseksiyon tahtada bunu düzeltmek kullanarak, ağız dil ve zemin ile birlikte alt çene ayrı. Dil yukarı çekin; Bir neşter kullanılarak bir kesi yapmak nerede baDilin se dil altı mukozasına ortaya çıkarmak için üçüncü azı ulaşana kadar ağzın zemini karşılamaktadır.
- Tamamen dilini çıkarın; 0.5 mm'lik biyopsi yumruk almak ve alt ön dişlerin yanına yerleştirin. Yavaşça ağız kat kadar sublingual doku ve basın dişeti sokulmasına Cut tamamen kesilmiştir.
- Şimdi sublingual doku çıkarılmasını tamamlamak için üçüncü molar yakın biyopsi yumruk yerleştirerek bir kez daha tekrarlayın. CRPMI veya nükleik asit koruyucu içeren temiz bir tüpe yerleştirin.
FACS analizi için 3.2) Numune hazırlama.
- , 24 oyuklu bir plakaya her bir fareden izole edilen Akci¤erlere doku aktarın ve yaklaşık 2 mm doku küçük parçalar elde edene kadar makas temiz bir çift ile kıyma. Tip II Kolajenaz, 30 mg, FBS'siz RPMI 1 ml 50 ug DNAse I ihtiva eden sindirim orta oyuk başına 1 ml ilave edilir. Pipet ve aşağı yukarı beş kez ve inkübe37 ° C,% 5 ila 40 dakika boyunca CO2.
- Dil altı dokuda hücre popülasyonlarının analizi için, dispaz, 2 adet, RPMI, 1 ml, 30 mg, tip II Kolagenaz, 50 ug DNAse I ihtiva eden biriyle 3.2.1 sindirim ortamı yerine. 50 rpm'de bir orbital sallayıcı içinde 37 ° C'de 20 dakika boyunca sindirim ortamının 500 ul bir fareden alınan doku inkübe edin.
- Inkübasyon, pipet ardından ve dokusunu en bozuldu 10 kere veya 30 saniye kadar kadar aşağı. 40 mikron steril bir hücre süzgecinden da hücre süspansiyonu filtre edin ve PBS 5 mi, 5 mM EDTA ile takviye ile yıkayın.
Not: hücre dışı matris ve lifli doku Tam sindirme elde edilmeyecektir. Bu artan hücre ölümü ve F genel sonucu etkileyen hücre dışı proteinlerin bozulmasına neden olur Ancak, kolajenaz ve / veya toz haline getirme ya da agresif dispase mevcudiyetinde daha uzun inkubasyon süreleri tavsiye edilmezACS analiz. - 400 xg, 5 dakika, 4 ° C'de santrifüj.
- BAL hücre popülasyonlarının analizi için, 4 ° C'de 400 x g'de 5 dak hücreleri santrifüj 3.2.4 adıma devam eder.
- Lenf düğümleri hücre popülasyonlarının analizi için, steril bir petri tabağına 70 mikron hücre süzgecinden yerleştirmek ve süzgeç içine cRPMI 1 ml lenf düğümleri birlikte koydu. 2 ml steril şırınga dalma çıkarın ve süzgecini en örgü karşı lenf düğümleri ezmek için bir havanda olarak kullanabilirsiniz. Taze cRPMI 1 ml hücre süzgecinden yıkayın ve steril bir tüpe petri hücreleri aktarın.
- Her numunenin temsili bir kısım alın ve canlı hücre sayısını belirlemek için Tripan Blue ile boyanır.
- 2x10 mi 7 hücre / süspansiyonunu oluşturan bir tüp içine sitometresi 50 ul PBS-5 mM EDTA,% 1 Sığır Serum Albumin-: FACS-EDTA içinde süspansiyon hücreleri.
- Yakl içeren 2X antikor karışımı hazırlayınMevcut FACS enstrümana göre yüzey belirteçleri ve florokromlar karşı antikorların opriate kombinasyonları. Hücre süspansiyonu ihtiva eden her tüpe 2X antikor karışımı 50 ul ekle.
Not: iyi miktarını belirlemek için, her fluorokrom-etiketli antikor titre başvuru 29 bkz detaylı bir protokol için kullanılır. - Karanlıkta buz üzerinde 30 dakika inkübe edin.
- FACS-EDTA, 3 ml bir kez yıkayın ve 4 ° C'de 5 dakika boyunca 400 x g'de santrifüj ile hücreler aşağı spin, aynı tampon 200 ul hücreleri tekrar süspansiyon ve Akış Sitometresi analiz.
Not: numune büyük bir sayı kullanılacaksa, yukarıda tarif edilen FACS analizi için boyama protokolü yerine sitometre tüpler U tabanlı, 96 oyuklu plakalar içerisinde gerçekleştirilir. Bununla birlikte, 96 oyuklu plakalar, yıkama adımları, her Washi ile, 4 ° C'de 5 dakika boyunca 400 xg'de hücreleri aşağı iplik 4 kez FACS-EDTA, 200 ul kadar ilave edilmesi ve tekrar tarafından gerçekleştirilmelidirng adım. - Bu noktada, daha sonraki sitometresi (sabitlenmesinden sonra 72 saat kadar) akış analizi için numuneler, tespit edin.
- Hücreleri sabitlemek için, FACS-antikorları ile işaretlendikten sonra PBS herhangi bir Ca2 + / Mg2 +, FBS'siz 1 mM EDTA içinde hücreleri yıkayın. Herhangi bir Ca2 + / Mg2 +, aynı tamponun 50 ul süspanse hipertonik (2X) ile, PBS içinde taze hazırlanmış% 4 paraformaldehid çözeltisi 50 ul ekle.
- Oda sıcaklığında 20 dakika boyunca inkübe edin ve FACS-EDTA içinde 3 kez yıkayın.
- 4 ° C'de 200 FACS ul EDTA ve mağaza hücrelerin tekrar ve en fazla 72 saat boyunca ışıktan korundu.
NOT: FSC-SSC sabitleme etkilenebilir. Tandem boyaları sabitleyici ajanlar varlığında bozulmuş olabilir çünkü tespit takdirde, numunelerin üretici ile floresan etiketli antikorların uyumluluğunu kontrol. Örnekleri enfekte hayvanlardan kaynaklandığı varsa tespit hayli zaman analy hiçbir kalıcı patojenler mevcut olmasını sağlamak için tavsiye edilirmicroaerosols numune alımı sırasında oluşturulabilir çünkü FACS makinesinde örnekleri şarkı.
4. Toplam RNA Ekstraksiyon, cDNA Sentezi ve Real Time PCR.
4.1), RNA ekstraksiyonu ve cDNA sentezi.
- Mekanik parçalama göre tercih edilen nükleik asit koruyucu bir solüsyon içerisinde dokuyu homojen (örneğin, bir rotor-stator homojenleştirici kullanılarak, dokuya ruptor boncuk vb çalkalama yüksek hız). 15 dakika 4 ° C'de 12,600 x g'de santrifüje doku çöküntüsü ortadan kaldırılmaktadır. Temiz bir tüpe süpernatant aktarın.
- Üretici talimatlarına uygun seçim yöntemi ile RNA ekstrakte edin.
NOT: hacimde yapmak ve -80 ° C'de RNAse serbest tüpler içinde saklayın, hemen izolasyondan sonra kullanılacak olacak değilse RNA, parçalanmaya yüksek duyarlıdır. Tekrarlanan donma ve çözülme kaçının. Tüpler her zaman eldiven ile ele alınması gerekir. Bir numune çözündükten sonralways buz üzerinde saklayın. - 260 nm'de nükleik asitlerin absorbansı ölçülür ve mg / ml konsantrasyonunu hesaplamak.
- DNAse I ilave edilerek karıştırın hazırlanması (1 bir numune için): ultra saf su 7.6 ul 10X DNAse I tampon maddesi 1 ul, 0.4 DNAse (amplifikasyon eğim) stok, 1 U / ul ul, 8.4 ul DNAse I toplam RNA'nın 1 ug ihtiva eden her bir örnek için karıştırın.
- 1 mg / ml bir konsantrasyonda RNA kullanarak ve bir şablon olarak toplam RNA'nın 1 ul ekleyerek retrotranscription reaksiyonu (RT-PCR) gerçekleştirir. Örnekler de seyreltilmiş ve konsantrasyon beklenenden daha düşük olması halinde, toplam RNA yerine daha büyük hacimde su ilave edin. Fenol izleri RT-PCR verimini etkileyebilecek yana tercih RNA ekstraksiyon protokolü fenol-kloroform karışımı katılan özel olarak ise, RNA eklerken nihai reaksiyon hacminin% 20'sinden fazla değildir.
- 4 ° C ya da I, 10 dakika süre ile oda sıcaklığında 15 dakika inkübece. (Inkübasyon süresi aşmayın !!)
- Her bir tüp, 25 mM EDTA, (Moleküler Biyoloji) 1 ul ilave edin ve DNAse I etkisiz hale getirmek için 10 dakika boyunca 65 ° C'de inkübe edin.
- (1 reaksiyon için) aşağıdaki gibi retrotranscription (RT) karışımı hazırlayın: 1 ul rastgele heksamer primerleri stok 0.2 mg / ml, 1 ul dNTP stok 10 mm, 4 ul 5X ir M-MLV-RT tamponu, 2 ul 0.1 M DTT, 1 ul RNAz OUT stok 40 U / ml ve 1 ul M-MLV stok 200 U / ul retrotranscriptase.
- RT-PCR, 10 ul, 10 ul DNAse I reaksiyon tüpüne karışımı ekleyin.
- Aşağıdaki programa göre, bir termal döngü PCR reaksiyonu yürütmek:
1X döngüsü: 10 dk, 25 ° C; 50 dakika, 37 ° C; 15 dakika, 70 ° C - Ultra saf su 80 ul ekleyerek 5: 1 cDNA seyreltin. -20 ° C'de saklayın.
4.2) Gerçek zamanlı PCR (qPCR).
- Taq P içeren 5 ul ana karışımı: (1 reaksiyon için) aşağıdaki gibi qPCR reaksiyon karışımı hazırlayınolymerase, SYBR Green boya, PCR Tampon, dNTP karışımı ve MgCl2 (aşağıya bakınız 4.2.2); Adım 4.1.10 gösterildiği gibi ileri primeri, 10 uM stok çözeltisi 0.9 ul, bir ters primerin 10 uM stok çözeltisi, 1.2 ul ultra-saf su, 0.9 ul, cDNA şablonunun 2 ul, daha önce seyreltilmiştir.
NOT: Bu bölümde kullanılan reaktif konsantrasyonu ve Çevrim protokolleri, "Materyaller ve Reaktifler: Tablo" de tarif edilen tepkime maddeleri ve araçlar ile özel olarak gerçekleştirilebilir için optimize edildi diğer markalar kullanılabilir, ancak reaksiyon hacmi, reaktif konsantrasyonları ve çevrim protokolü değişebilir. RT-qPCR gerçekleştirmeden önce üretici talimatları kontrol edin. - Aşağıdaki gibi QPCR enstrüman ayarlayın:
1X döngüsü: 15 dk, 95 ° C
40X çevrimi: 15 saniye, (bu noktada elde edimi fluoresans) yaklaşık 1 dakika, 60 ° C, daha sonra 95 ° C'dir.
Not: mRNA'nın nispi ölçümü için Ct yöntemi 30, e göre referencE geni Ct değerleri normalleştirme için seçilmelidir. Referans seçim gen ifadesi değişebilir belirli deney koşulları altında test edilmelidir ACTB, GAPDH veya 18S, genellikle referans olarak seçilen genlerin bazılarıdır. - Eşik değerini ayarlama ve verileri analiz.
Sonuçlar
Sublingual immünoterapi ile başarılı Akci¤erlere bağışıklık tepkisini modüle etmek üzere kullanılabilir. Biz, flagellin, TLR5 ve NLRC4 agonisti tek bir dozu, kemokinler CXCL1, CCL20 ve tuzlu suyla tedavi edilen kontrol grubu ile karşılaştırıldığında sitokin, IL-6 kodlayan mRNA'nın önemli ölçüde artmasına neden olduğunu göstermiştir. MRNA seviyelerinin indüksiyon SLIT'in sonra 8 saatte doruğa katlayın ve 20 saat (Şekil 1) sonra bazal düzeylere geri dönmektedir. SLIT'in S'dir. Pneumoniae ile 2 saat önce uygulandı burun içi enfeksiyona, ancak, CXCL1 ve IL 6 mRNA düzeyleri tedavi edilmemiş hayvanlarda (Şekil 2) ile karşılaştırıldığında SLIT'in sonra, hatta 24 saat regüle kaldı.
FACS ile BAL hücre popülasyonlarının ve akciğer dokusunun analizi dil altı yolu ile FLIC ile muamele edilmiş hayvanlar için akciğerin doku (Şekil 3), hava yollarında nötrofil sayısı artmıştır, ancak ortaya çıkardı.
Nihayet, pnömokok cebine hayatta kalma, daha önce dil altı yolu ile veya bir kontrol olarak salin solüsyonu ile FLIC ile tedavi edilen hayvanlarda karşılaştırılmıştır. Şekil 4'te gösterildiği gibi, flagellin ile SLĐT koruma teşvik edilmesi ve akut pnömokok kökenli pnömoniye karşı yaşamalarım arttırmıştır.
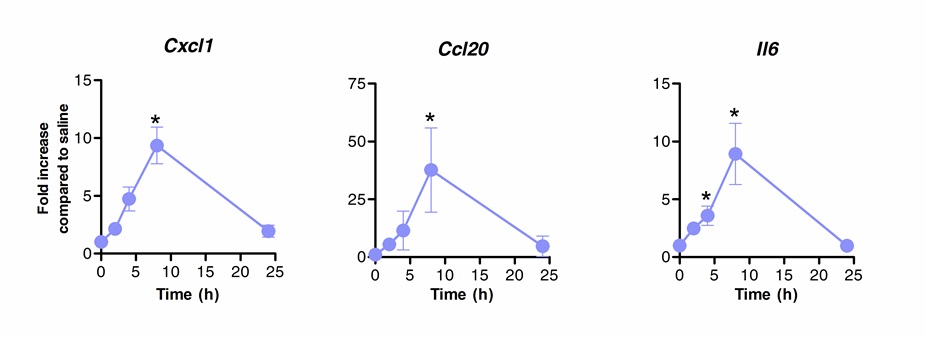
Flagellin ile sublingual immünoterapi Şekil sonra akciğerlerin transkripsiyonel profili 1. kinetiği. Sekiz ila 10 haftalık BALB / c fareleri (n = 4) olarak uygulandı dil altı yolu ile, flagellin ya da tuzlu su, 10 ug ile muamele edilmiştir. Akciğerler farklı zaman noktalarında toplandı ve nükleik asit koruyucu yerleştirildi. Tüm RNA çıkarılması uygulandı ve cDNA sentezlenmiştir. mRNA seviyeleri Tabl listelenen spesifik primerler kullanılarak, gerçek zamanlı PCR ile değerlendirildiE 1. miktar ölçümü normalizasyonu için ACTB mRNA seviyelerini kullanarak ACt yöntemi göre gerçekleştirilmiştir. Sonuçlar ± SEM ortalaması olarak salin ile tedavi edilmiş gruba kıyasla kat bir artış olarak gösterilmiştir. Yıldız Mann-Whitney testi kullanılarak hesaplanmıştır istatistiksel olarak anlamlı fark (p <0.05) göstermektedir. Sonuçlar Şekil 2, bağımsız deneyi temsil etmektedir.
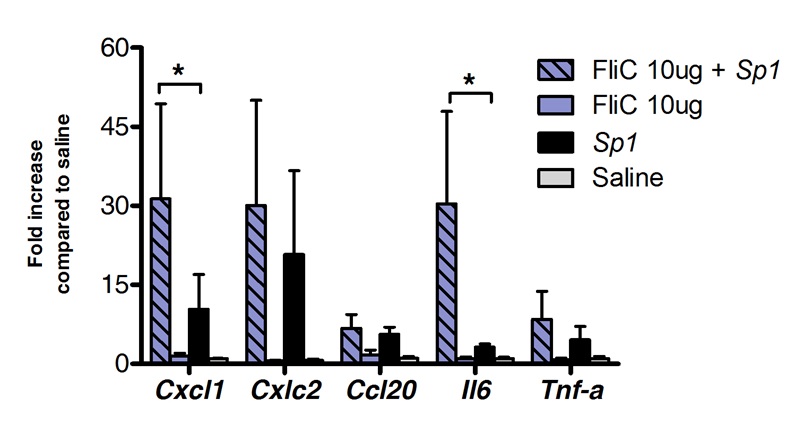
Ile, flagellin. Sekiz ila 10 haftalık BALB / c fareleri (n = 4, kontrol grubu için n = 7 tedavi gören grup için) sublingual immünoterapi sonra pnömokok kökenli pnömoni sırasında Şekil 2. akciğerleri transkripsiyonel profili, flagellin ya da tuz, 10 ug ile muamele edilmiştir anestezi altında dilaltı rota. 2 saat sonra 10 farenin neden olan en az ölümcül bir doz (MSD) ile intranazal yoldan tehdit edildiS. klinik izolatı% 0 mortalite 4x10 5 CFU / 50 ul karşılık gelen pneumoniae serotip 1 E1585. Akciğerler mücadeleden 24 saat sonra toplandı ve RNA ekstraksiyonu ve cDNA sentezi gerçekleştirilmiştir kadar nükleik asit koruyucu depolanmıştır. Gerçek zamanlı PCR ile gerçekleştirilmiştir (Tablo 1 'de astar listesine bakınız) ve nispi ölçümü normalizasyonu için ACTB mRNA seviyelerini kullanarak ACt yöntemi göre gerçekleştirilmiştir. Sonuçlar ± SEM ortalaması olarak salin ile tedavi edilmiş gruba kıyasla kat bir artış olarak gösterilmiştir. Yıldız Mann-Whitney testi kullanılarak hesaplanmıştır istatistiksel olarak anlamlı fark (p <0.05) göstermektedir.
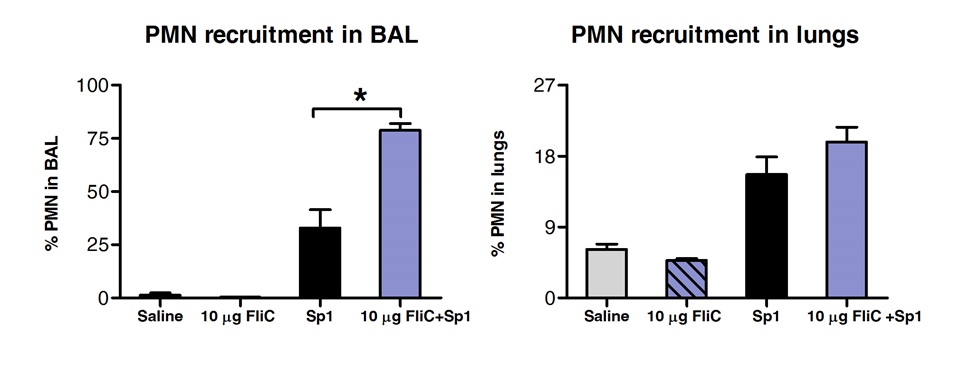
Polimorfonükleer nötrofil Şekil 3. Analiz (PMN) SLIT'in sonra akciğerlerin dokusunda ve hava yollarında işe. Eight'e10 haftalık BALB / c fareleri (n = 4) olarak uygulandı dil altı yolu ile, flagellin ya da tuzlu su, 10 ug ile muamele edilmiştir. 2 saat sonra farelerin S. MLD ile intranazal yoldan tehdit edildi pneumoniae serotip 1 E1585. Hücumdan 24 saat sonra, BAL yapıldı ve akciğerler FACS analizi için işlenmiştir. PMN Ly6G yüksek / CD11b yüksek / CD11c'nin negatif hücreler olarak tanımlanan ve FCS-SSC profiline göre yapılmıştır. Sonuçlar akciğerde ya da BAL'da toplam hücre sayıları açısından PMN yüzdesi olarak ifade edilmiştir. Barlar ± SEM medyan temsil eder. Yıldız tek yönlü Mann-Whitney testi kullanılarak hesaplanmıştır istatistiksel olarak anlamlı fark (p <0.05) göstermektedir.
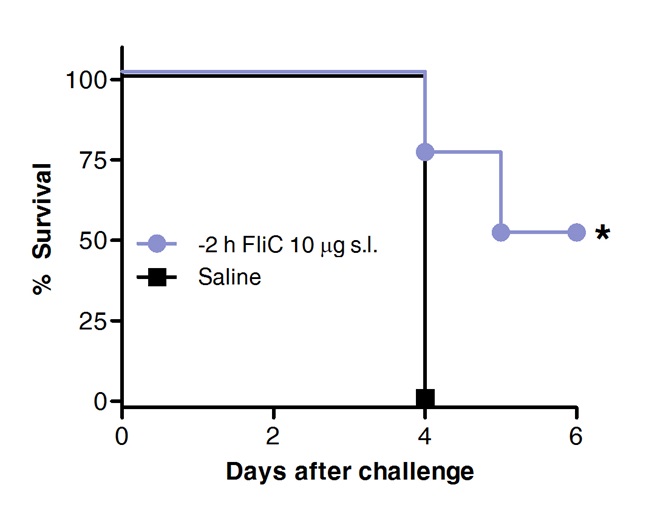
Flagelllin'ine ile Şekil 4. SLIT'in akut pnömokokal pnömoniye karşı fareleri korur. 10 Sekiz haftalık BALB / c fareleri (n = 8), anestezi altında dil altı yolu ile, flagellin ya da tuzlu su, 10 ug ile muamele edilmiştir. 2 saat sonra farelerin S. MLD ile intranazal yoldan tehdit edildi pneumoniae serotip 1 E1585. Hayatta kalma günlük olarak değerlendirildi. Kaplan-Meier eğrileri Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) testi açısından karşılaştırıldı. Yıldız istatistiksel olarak anlamlı fark (p <0.05) .Results 2 bağımsız deneyler temsilcisi olduklarını gösterir.
| İsim | Dizi 5'-3 ' | PCR Ürün uzunluğu (bp) |
| mB,-actin_F | GCTTCTTTGCAGCTCCTTCGT | 68 |
| mB,-actin_R | CGTCATCCATGGCGAACTG | |
| mCCL20_F | TTTTGGGATGGAATTGGACAC | 69 |
| mCCL20_R | TGCAGGTGAAGCCTTCAACC | |
| mCXCL1_F | CTTGGTTCAGAAAATTGTCCAAAA | 84 |
| mCXCL1_R | ACGGTGCCATCAGAGCAGTCT | |
| mlL-6_F | GTTCTCTGGGAAATCGTGGAAA | 78 |
| mlL-6_R | AAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTCATACA | |
| mTNFalpha_F | CATCTTCTCAAAATTCGAGTGACAA | 63 |
| mTNFalpha_R | CCTCCACTTGGTGGTTTGCT | |
| mCxcl2_F | CCCTCAACGGAAGAACCAAA | 72 |
| mCxcl2_R | CACATCAGGTACGATCCAGGC |
Gerçek zamanlı PCR analizi için kullanılan astar listesi Tablo 1.. QPCR analizi için kullanılan özel astar dizilerini sıralamaktadır. İleri ve fare ACTB için primerler, ters Cccl20, CXCL1 Il6, TNFa ve CXCL1 5'-3 'sekansları gibi sunulmuştur ve beklenen ürün uzunluğu hem baz çiftlerinde (bp) olarak gösterilir.
Tartışmalar
Terapötik maddelerin maddelerinin sublingual yoldan verilmesi solunum yollarında immun cevabı modüle etme yararlı bir yöntem olduğu kanıtlanmıştır. Solunum koşullarının tedavisi için SLIT'in başlıca avantajı, burun içinden tatbikat 31 dayanan tedavilerle daha güvenli olan, akciğer veya burun içine bileşiklerinin doğrudan iletilmesini içerir etmemesidir.
Sublingual immünoterapi ya da alerjik iltihaplanma ve astımın 32 semptomlarını iyileştirmek veya burada gösterildiği gibi akut akciğer enfeksiyonlarının tedavisi için doğal bağışıklık mekanizmalarını geçici aktivasyonunu uyarmak için düzenleme tepkilerinin uyarılması için, farklı şekillerde immun cevabı modüle etmek üzere kullanılabilir.
Bu video sunulan fare modeli SLĐT'in için terapötik maddeler olarak farklı bileşiklerin taranması için uygun bir yöntemdir.
Bu hayvan modeli etkisini belirlemek için kullanışlı bir araç sunmaktadırAkci¤erlere immün tepkisi, hem de diğer organları (örneğin,., lenf düğümleri veya uzak mukozal the drenaj), in vitro modellerinin kullanımı ile taklit edilemeyen SLIT'in. Dilaltı immünoterapi kullanılarak elde edilen sonuçları tanımlamak birçok makale olmasına rağmen, dilaltı uygulama prosedürleri için ayrıntılı yöntemleri henüz mevcut yapılmamıştır. Buna ek olarak, bu model solunum yolu sistemik hem de lokal koruma sağlamak amacıyla dil altı aşıların değerlendirilmesi için de kullanılabilir.
Eşlik eden video gösterildiği gibi, bileşiklerin sublingual yolla kolaylıkla geniş eğitim gerek duyulmadan basit bir işlemdir. Tipik olarak, hayvan kullanımı konusunda uzman bir kişi bu protokolde tarif edildiği gibi, enjekte edilebilir anestetikler ile 10 fareden oluşan bir grup SLĐT'i gerçekleştirmek için 1 saat gerektirir. Pnömokokal hücuma de gerçekleştirilirse, ilave 90 dakika hazırlamak için gerekli olacakBakteri süspansiyonu ve hayvanların burun içi bulaştırma gerçekleştirin.
Burada sunulan FACS protokolleri Akci¤erlere hücre dinamikleri üzerinde lenf düğümleri yanı sıra etkilerini drenaj, uygulama yerel yerinde SLIT'in etkisinin uygun karakterizasyonu izin verir.
Bronkoalveoler içeriği ve akciğer dokusu ayrı ayrı analizi hava yolu bağışıklık yerleşik ve doku içinde kalır bu hücre tiplerini sızmakta ayırt etmek önemlidir. BAL içeriğinin analizi alveoler makrofaj ciro çalışma yanı sıra farklı tedaviler ile neden olunan alveolar boşluk, örneğin., PMN, eozinofiller, monositler içine hücrelerin işe dinamiklerini sağlar. BAL için enzim bağlantılı immünosorbent deneyi (ELISA) ya da dil altı aşılamanın ardından ortaya salgılanan IgA antikorlarının tespiti tarafından salgılanan sitokinler ve kemokinlerin varlığını saptamak için kullanılabilir. Akci¤erlere doku Çalışmasıdiğer hücre türleri, klasik dendritik hücreleri, T hücreleri ve B hücreleri karakterizasyonu sağlayacaktır.
FACS analizi için BAL örnekleri ve lenf düğümleri hazırlanması basittir. Numune toplama sonra, normalde 60 dakika 10-20 örnekler için boyama protokolü tamamlamak için gereklidir. Hücre-dışı matrisin sindirim gerekli değildir ve bu Bunun aksine, akciğer veya dil altı doku hücrelerinin elde edilmesi daha fazla zaman gerekir. Dil altı yolu ile verilen terapötik maddenin emilimi vivo görüntüleme sistemleri kullanılarak, floresan veya radyoaktif işaretli moleküllerin takibi ile sağlanabilir.
Sublingual immunoterapinin bağışıklık solunum yollarında tepkileri vermenin yanı sıra tedavi etmek ya da önlemek için, solunum koşulları kullanılabilir sistemik olarak uyarılması için çekici bir yöntemdir. SLIT'in i sonra solunum yollarında bağışıklık tepkisinin aktivasyonunun belirlenmesi karşı tolerans mekanizmalarını aydınlatılmasıFarklı solunum koşullarına karşı mevcut tedaviler ile birlikte, tek başına veya kombinasyon halinde kullanılabilecek, yeni tedavi stratejileri rasyonel tasarım sağlamak çok önemlidir s.
Açıklamalar
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Teşekkürler
We acknowledge Dr. Jean-Claude Sirard from the Center for Infection and Immunity of Lille, Institute Pasteur de Lille-France, for kindly providing the purified flagellin and Dr. Teresa Camou, Director of the National Reference Laboratory, Ministry of Health of Uruguay for kindly providing the pneumococcal strain.
The authors would like to express their acknowledgement to Mr. Diego Acosta and Mr. Ignacio Turel form BichoFeo Producciones-Uruguay for their commitment and hard work during the entire video production and edition.
This work was supported by the grants PR_FCE_2009_1_2783 and BE_POS_2010_1_2544 from the National Agency of Research and Innovation, ANII from Uruguay, the Program for Development of Basic Sciences, PEDECIBA of Uruguay and Sectoral Commission of Scientific research, CSIC-Universidad de la República, Uruguay.
Malzemeler
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Ketamine solution (50 mg/ml) | Pharma Service, Uruguay | ||
| Xilacine solution (2 %) | Portinco S.A., Uruguay | ||
| Sterile 1 ml syringe | Modern, Uruguay | ||
| Sterile 27 G needle | Modern, Uruguay | ||
| RPMI 1640 | General Electric Health Care | E15885 | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | ATCC | 302020 | |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin Solution | SIGMA | P4333 | |
| Sterile PBS without Ca2+/Mg2+ | PAA | H21002 | |
| Type-I Collagenase | Life Technologies/Gibco | 17100017 | |
| Deoxyribonuclease I (DNAse-I) | SIGMA | D4513 | |
| Dispase | Life Technologies/Gibco | 17105041 | |
| PerCP-Cy5.5 conjugated rat anti mouse IgG2b anti CD11b | BD | 550993 | Clone M1/70 |
| APC conjugated hamster anti mouse IgG1 anti CD11c | BD | 550261 | Clone HL3 |
| APC-Cy7 conjugated rat anti mouse IgG2a anti Ly6G | BD | 560600 | Clone 1A8 |
| Sterile Saline Solution | Laboratorio Farmaco Uruguayo, Uruguay | ||
| Tryptic Soy Agar | BD Difco, France | 236950 | |
| Defibrinated Sheep Blood | Biokey, Uruguay | ||
| Sterile Petri Dishes | Greiner | 633180 | |
| p10 Pipette | Gilson | F144802 | |
| p20 Pipette | Eppendorf | 3120000097 | |
| p200 Pipette | Gilson | F123601 | |
| p200 Pipette | Capp | C200 | |
| p200 Pipette | Eppendorf | 3120000054 | |
| p1000 Pipette | Eppendorf | 3120000062 | |
| Sterile Filter Tips p10 | Greiner | 771288 | |
| Sterile Filter Tips p200 | Greiner | 739288 | |
| Sterile Filter Tips p1000 | Greiner | 750288 | |
| Vortex | BIOSAN | V1-plus | |
| Stainless steel fine tip forceps | SIGMA | Z168785/Z168777 | Curved and straight |
| Dressing tissue forceps | SIGMA | F4392 | Length 8 inches |
| Micro-dissecting forceps | SIGMA | F4017 | Straight |
| Micro-dissecting forceps | SIGMA | F4142 | Curved |
| Mayo Scissors | SIGMA | Z265993 | |
| Scalpel | SAKIRA MEDICAL | ||
| Sterile Biopsy Punch Ø 3mm | Stiefel Laboratories Ltd. | 2079D | 5 mm diameter can also be used |
| Sterile 1.5 ml Tubes | Deltalab | 200400P | |
| Sterile 15 ml Tubes | Greiner | 188271 | |
| Sterile 50 ml Tubes | Greiner | 227261 | |
| Sterile serological pipettes 5 ml | Greiner | 606160 | |
| Sterile serological pipettes 10 ml | Greiner | 607160 | |
| Sterile serological pipettes 25 ml | Greiner | 760180 | |
| Biological safety cabinet, class II | Thermo Scientific | 1300 series, type A2 | |
| Micro-Isolator Rack | RAIR IsoSystem | 76144W | Super Mouse 1800 AllerZone |
| Refrigerated Microcentrifuge | Eppendorf | Legend Micro 21R | |
| Microcentrifuge | Heraeus | Biofuge-pico | |
| Centrifuge | Thermo Scientific | Sorval ST40R | |
| CO2 Incubator | Thermo Scientific | Model 3111 | |
| Sterile Thin-tip pasteur pipettes | Deltalab | D210022 | |
| Sterile pasteur pipettes | Deltalab | 200007 | |
| Sterile 24-well plate | Greiner | 662160 | |
| Trypan Blue Solution | Life Technologies | T10282 | |
| Automatic Cell Counter - Countess | Life Technologies | C10227 | |
| Countess Cell Counting Chamber Slides | Life Technologies | C10312 | |
| Flow Cytometry Tubes | BD | 343675 | |
| Flow Cytometer - FACS Canto-II | BD | ||
| Real Time PCR Instrument - Rotor Gene Q or ABI 7900 | Qiagen / Applied Biosystems | ||
| Trizol Reagent | Life Technologies | 15596-026 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| DNAse-I | Life Technologies | 18068-015 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| DNAse-I Buffer 10X | Life Technologies | 18068015 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| EDTA 25 mM | Life Technologies | 18068015 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| Ultra-Pure Water | Life Technologies | 10977 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| RNAse Out | Life Technologies | 100000840 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| Random Hexamer Primers | Life Technologies | N8080127 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| M-MLV-RT buffer | Life Technologies | 18057-018 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| M-MLV-RT enzime | Life Technologies | 28025-021 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| QuantiTect Syber Green PCR Kit | Qiagen | 204143 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| Specific primers | Life Technologies | Molecular Biology Grade |
Referanslar
- . Pneumococcal vaccines WHO position paper--2012. Weekly Epidemiological Record. 14, 129-144 (2012).
- Appelbaum, P. C., et al. Carriage of antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae by children in eastern and central Europe-a multicenter study with use of standardized methods. Clin Infect Dis. 23, 712-717 (1996).
- Ramirez, J. A., Anzueto, A. R. Changing needs of community-acquired pneumonia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 66, 3-9 (2011).
- Cuburu, N., et al. Sublingual immunization induces broad-based systemic and mucosal immune responses in mice. Vaccine. 25, 8598-8610 (2007).
- Pedersen, G. K., et al. Evaluation of the sublingual route for administration of influenza H5N1 virosomes in combination with the bacterial second messenger c-di-GMP. PLoS One. 25, 1-12 (2011).
- Song, J. H., et al. Sublingual vaccination with influenza virus protects mice against lethal viral infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105, 1644-1649 (2008).
- Cogo, R., Ramponi, A., Scivoletto, G., Rippoli, R. Prophylaxis for acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis using an antibacterial sublingual vaccine obtained through mechanical lysis: a clinical and pharmacoeconomic study. Acta Biomed. 74, 76-87 (2003).
- Rosaschino, F., Cattaneo, L. Strategies for optimizing compliance of paediatric patients for seasonal antibacterial vaccination with sublingually administered Polyvalent Mechanical Bacterial Lysates (PMBL). Acta Biomed. 75, 171-178 (2004).
- Senna, G., Caminati, M., Canonica, G. W. Safety and tolerability of sublingual immunotherapy in clinical trials and real life. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 13, 656-662 (2013).
- Mascarell, L., et al. Oral dendritic cells mediate antigen-specific tolerance by stimulating TH1 and regulatory CD4+ T cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 122, 603-609 (2008).
- Mascarell, L., et al. Mapping of the lingual immune system reveals the presence of both regulatory and effector CD4+ T cells. Clin Exp Allergy. 39, 1910-1919 (2009).
- Mascarell, L., et al. Oral macrophage-like cells play a key role in tolerance induction following sublingual immunotherapy of asthmatic mice. Mucosal Immunology. 4, 638-647 (2011).
- Hervouet, C., et al. Antigen-bearing dendritic cells from the sublingual mucosa recirculate to distant systemic lymphoid organs to prime mucosal CD8 T cells. Mucosal Immunology. 7, 280-291 (2014).
- Munoz, N., et al. Mucosal administration of flagellin protects mice from Streptococcus pneumoniae lung infection. Infect Immun. 78, 4226-4233 (2010).
- Hayashi, F., et al. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature. 410, 1099-1103 (2001).
- Lightfield, K. L., et al. Critical function for Naip5 in inflammasome activation by a conserved carboxy-terminal domain of flagellin. Nature Immunology. 9, 1171-1178 (2008).
- Lightfield, K. L., et al. Differential requirements for NAIP5 in activation of the NLRC4 inflammasome. Infect Immun. 79, 1606-1614 (2011).
- Honko, A. N., Mizel, S. B. Mucosal administration of flagellin induces innate immunity in the mouse lung. Infect Immun. 72, 6676-6679 (2004).
- Janot, L., et al. Radioresistant cells expressing TLR5 control the respiratory epithelium's innate immune responses to flagellin. Eur J Immunol. 39 (6), 1587-1596 (2009).
- Van Maele, L., et al. TLR5 signaling stimulates the innate production of IL-17 and IL-22 by CD3(neg)CD127+ immune cells in spleen and mucosa. J Immunol. 185, 1177-1185 (2010).
- Lee, S. J., et al. Neurologic adverse events following influenza A (H1N1) vaccinations in children. Pediatrics international: official journal of the Japan Pediatric Society. 54, 325-330 (2012).
- Lewis, D. J., et al. Transient facial nerve paralysis (Bell's palsy) following intranasal delivery of a genetically detoxified mutant of Escherichia coli heat labile toxin. PLoS One. 4, e6999 (2009).
- Mutsch, M., et al. Use of the inactivated intranasal influenza vaccine and the risk of Bell's palsy in Switzerland. N Engl J Med. 350, 896-903 (2004).
- Kuo, C. H., Wang, W. L., Chu, Y. T., Lee, M. S., Hung, C. H. Sublingual immunotherapy in children: an updated review. Pediatr Neonatol. 50, 44-49 (2009).
- Nempont, C., Cavet, D., Rumbo, M., Bompard, C., Villeret, V., Sirard, J. C. Deletion of flagellin's hypervariable region abrogates antibody-mediated neutralization and systemic activation of TLR5-dependent immunity. J. Immunol. 181, 2036-2043 (2008).
- Marques, J. M., et al. Protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 1 acute infection shows a signature of Th17- and IFN-gamma-mediated immunity. Immunobiology. 217, 420-429 (2012).
- Stewart, C. C., Stewart, S. J., et al. Titering antibodies. Current Protocols in Cytometry. 4, Unit 4.1 (2001).
- Kubista, M., et al. The real-time polymerase chain reaction. Molecular Aspects of Medicine. 27, 95-125 (2006).
- Pedersen, G., Cox, R. The mucosal vaccine quandary: intranasal vs. sublingual immunization against influenza. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 8, 689-693 (2012).
- Vitaliti, G., et al. Mucosal immunity and sublingual immunotherapy in respiratory disorders. Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents. 26, S85-S93 (2012).
Yeniden Basımlar ve İzinler
Bu JoVE makalesinin metnini veya resimlerini yeniden kullanma izni talebi
Izin talebiDaha Fazla Makale Keşfet
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
JoVE Hakkında
Telif Hakkı © 2020 MyJove Corporation. Tüm hakları saklıdır