Visualizing Soil Microorganisms via the Contact Slide Assay and Microscopy
Overview
Source: Laboratories of Dr. Ian Pepper and Dr. Charles Gerba - The University of Arizona
Demonstrating Author: Bradley Schmitz
Soil comprises the thin layer at the earth’s surface, containing biotic and abiotic factors that contribute to life. The abiotic portion includes inorganic particles ranging in size and shape that determine the soil’s texture. The biotic portion incorporates plant residues, roots, organic matter, and microorganisms. Soil microbe abundance and diversity is expansive, as one gram of soil contains 107-8 bacteria, 106-8 actinomycetes, 105-6 fungi, 103 yeast, 104-6 protozoa, 103-4 algae, and 53 nematodes. Together, the biotic and abiotic factors form architectures around plant roots, known as the rhizosphere, that provide favorable conditions for soil microorganisms.
Biotic and abiotic factors promote life in soils. However, they also contribute stressful dynamics that limit microbes. Biotic stress involves competition amongst life to adapt and survive in environmental conditions. For example, microbes can secrete inhibitory or toxic substances to harm neighboring microorganisms. Penicillium notatum is a notorious fungus, as it reduces competition for nutrients by producing an antimicrobial, which humans harvest to create the pharmaceutical penicillin. Abiotic stresses arise from physical or chemical properties limiting microbial survival, such as light, moisture, temperature, pH, nutrients, and texture.
Principles
Directly observing the interrelationships between soil organisms, particles, and behaviors within varying soil environments is difficult, but the contact slide assay, also known as the buried-slide technique, developed by Rossi et al. (1936) provides a snapshot viewpoint into soil microbiology. This method is useful for observing soil fungi, actinomycetes, and bacteria via microscopy. Although, it is not intended for microbial quantifications, as it only implies one small portion of a larger heterogeneous environment.
This method is easily performed by burying a glass slide into soil for several days, then fixing the microorganisms on the slide with acetic acid. The microbes are stained with Rose Bengal dye and observed via microscopy using oil immersion on the 100X objective. Three microbial groups can be distinguished, as bacteria appear as small rounded shapes, actinomycetes filaments as thin strings, and fungal hyphae as thick threads. In soil, almost all bacteria are smaller and rounder than those in pure culture due to nutritional stress, which causes shrinking and rounding for a more favorable surface: volume ratio. The irregular dark shapes not stained are soil particles. Different nutrient amendments can be added to the soil to provide carbon and glucose sources that promote microbial growth and interactions. This technique allows for easy observation of soil microbiology and helps to identify several organisms present in the environment.
Procedure
1. Soil Slide Microcosm Preparation
- Collect garden soil from the surface (0-6” depth), and weigh 150 g soil into two separate cups.
- If soil has high density of organic matter, weigh 100 g.
- Label one cup “Treatment” and the other “Control.”
- Calculate amount of water needed to alter moisture content.
- Moisture content is often close to field capacity.

- Moisture content is often close to field capacity.
- Measure amount of distilled water with a graduated cylinder.
- Pour amount of distilled water into two vials.
- Label one vial “Treatment” and the other “Control.”
- Amend the water in the “Treatment” vial with enough glucose for a final soil glucose concentration of 1%, according to a dry weight basis in the “Treatment” soil.
- Add 200 mg NH4NO3 into the “Treatment” vial and stir to dissolve the amendments. The nitrate serves as a nitrogen source of nutrients for the soil microbes.
- Do not amend the “Control” vial.
- In small aliquots of approximately 50 mg, mix the contents of the “Treatment” vial into the “Treatment” cup. Stir with a spatula after each aliquot addition.
- In small aliquots, mix the contents of the “Control” vial into the “Control” cup. Stir with a spatula after each aliquot addition.
- Label four clean microscope slides: two “Treatment” and two “Control” slides.
- Insert the two “Treatment” slides into the “Treatment” soil cup, and insert the two “Control” slides into the “Control” soil cup. Leave 2 cm of each slide projecting above the soil surface, and be sure to leave a gap between the two slides.
- Cover the cups with plastic wrap and secure it with a rubber band.
- Puncture the wrap several times to allow air, but still prevent excessive evaporation.
- Record the weight of both cups.
- Incubate the soil-filled cups at room temperature in a designated area/incubator for 7 days.
2. Slide Staining and Microscopy
- Record the weight of both cups.
- Calculate the soil moisture at the time of slide removal.
- Remove the two slides from each cup by pressing each slide to an inclined position and withdrawing so the upper face of the slide is not disturbed.
- Identify and mark the side of the slide to be stained and observed.
- Gently tap the slides on the bench top to remove large soil particles.
- Using a damp paper towel, clean the lower face of the slides. Dry the slides at room temperature.
- Wearing protective goggles and holding each slide with forceps, immerse the slides into 40% (v/v) acetic acid for 1-3 min under a fume hood.
- Wash off the excess acid under a gentle stream of water.
- Using a dropper bottle, cover the surface of the slides with phenolic Rose Bengal. Support the slide on a staining rack over a container to catch the excess stain. Be careful, do not wash with force that may remove microorganisms from the surface of the slides.
- Stain the slides for 5-10 min. Do not let the slide become dry. Add more stain as needed.
- Gently wash the slides to remove excess stain.
- Let the slides dry at room temperature.
- Using the oil immersion objective, observe the slide using a microscope (Figure 1).
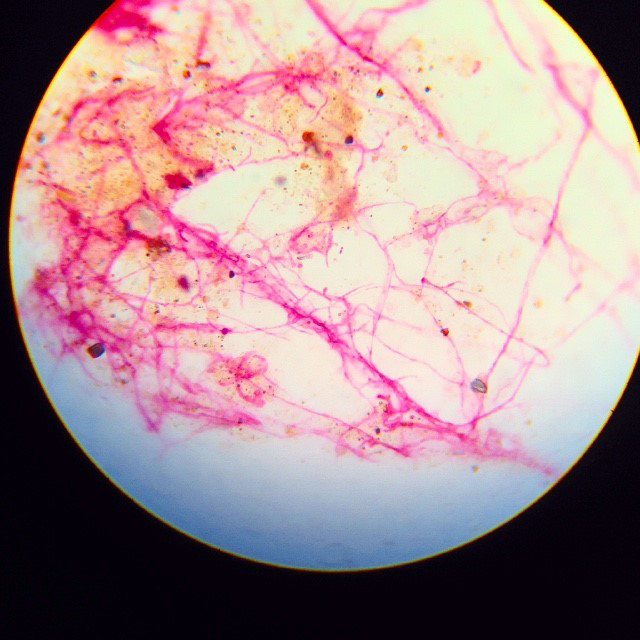
Figure 1. A slide under a microscope.
Results
Fungi display thick, filamentous hyphae (Figure 2). Actinomycetes display thin, filamentous hyphae. Bacteria display small cocci or rod shapes. They’re often found in clumps, on soil particles, or lining fungal hyphae. Soil particles display irregular, dark shapes (Figure 3).

Figure 2. Contact slide image using 100X objective lens.
Photo courtesy W.H. Fuller.

Figure 3. Contact slide image using 100X objective lens.
Photo courtesy W.H. Fuller.
Application and Summary
The contact slide assay, also referred to as the buried-slide, is a simple technique utilized to qualitatively observe soil biota. This assay qualitatively shows the spatial interactions between fungal hyphae, actinomycete filaments, bacteria, and soil particles. Individuals or industry can employ this assay to gather knowledge on a particular soil’s health in regards to agriculture, gardening, composting, teaching, and studying. However, this technique does not quantify soil micro biota, as it only encompasses a small portrait of a larger heterogeneous environment.
Soil organism relationships can be observed by performing the contact slide assay and viewing the results through 100X oil immersion microscopy (Figures 2 and 3). The simplicity and ease to performing this assay makes it a great starting technique for those who have never been exposed to microbiology and may be viewing microorganisms through a microscope for the first time.
References
- Pepper, I. L., & Gerba, C P. 'Contact Slide Assay.' Environmental Microbiology A Laboratory Manual. 2nd ed. Elsevier 19-25 (2004).
- Pepper, I. L., Gerba, C. P., & Gentry, T. J. 'Earth Environments.' Environmental Microbiology. 3rd ed. Elsevier 59-88 (2014).
- Rossi, G., Ricardo, S., Gesue, G., Stanganelli, M., and Want, T.K. Direct Microscopic and bacteriological investigations of the soil. Soil Science. 41, 52 – 66 (1936).
Skip to...
Videos from this collection:

Now Playing
Visualizing Soil Microorganisms via the Contact Slide Assay and Microscopy
Environmental Microbiology
42.4K Views

Determination of Moisture Content in Soil
Environmental Microbiology
359.8K Views

Aseptic Technique in Environmental Science
Environmental Microbiology
126.5K Views

Gram Staining of Bacteria from Environmental Sources
Environmental Microbiology
100.5K Views

Filamentous Fungi
Environmental Microbiology
57.6K Views

Community DNA Extraction from Bacterial Colonies
Environmental Microbiology
28.9K Views

Detecting Environmental Microorganisms with the Polymerase Chain Reaction and Gel Electrophoresis
Environmental Microbiology
44.6K Views

RNA Analysis of Environmental Samples Using RT-PCR
Environmental Microbiology
40.6K Views

Quantifying Environmental Microorganisms and Viruses Using qPCR
Environmental Microbiology
47.9K Views

Water Quality Analysis via Indicator Organisms
Environmental Microbiology
29.6K Views

Isolation of Fecal Bacteria from Water Samples by Filtration
Environmental Microbiology
39.4K Views

Detection of Bacteriophages in Environmental Samples
Environmental Microbiology
40.9K Views

Culturing and Enumerating Bacteria from Soil Samples
Environmental Microbiology
184.9K Views

Bacterial Growth Curve Analysis and its Environmental Applications
Environmental Microbiology
296.3K Views

Algae Enumeration via Culturable Methodology
Environmental Microbiology
13.8K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved