A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
نهج السريع إلى التصوير الإسفار عالية الدقة في الدماغ شرائح شبه سميكة
In This Article
Summary
نحن هنا وصفا لطريقة سريعة وبسيطة لصورة fluorescently المسمى الخلايا في الدماغ شبه شرائح سميكة. عن طريق تحديد ، تشريح ، وإزالة أنسجة الدماغ بصريا وصفنا كيف يمكن استخدام معيار التصوير epifluorescent مبائر أو لتصور الخلايا الفردية والشبكات العصبية داخل الأنسجة العصبية سليمة.
Abstract
A fundamental goal to both basic and clinical neuroscience is to better understand the identities, molecular makeup, and patterns of connectivity that are characteristic to neurons in both normal and diseased brain. Towards this, a great deal of effort has been placed on building high-resolution neuroanatomical maps1-3. With the expansion of molecular genetics and advances in light microscopy has come the ability to query not only neuronal morphologies, but also the molecular and cellular makeup of individual neurons and their associated networks4. Major advances in the ability to mark and manipulate neurons through transgenic and gene targeting technologies in the rodent now allow investigators to 'program' neuronal subsets at will5-6. Arguably, one of the most influential contributions to contemporary neuroscience has been the discovery and cloning of genes encoding fluorescent proteins (FPs) in marine invertebrates7-8, alongside their subsequent engineering to yield an ever-expanding toolbox of vital reporters9. Exploiting cell type-specific promoter activity to drive targeted FP expression in discrete neuronal populations now affords neuroanatomical investigation with genetic precision.
Engineering FP expression in neurons has vastly improved our understanding of brain structure and function. However, imaging individual neurons and their associated networks in deep brain tissues, or in three dimensions, has remained a challenge. Due to high lipid content, nervous tissue is rather opaque and exhibits auto fluorescence. These inherent biophysical properties make it difficult to visualize and image fluorescently labelled neurons at high resolution using standard epifluorescent or confocal microscopy beyond depths of tens of microns. To circumvent this challenge investigators often employ serial thin-section imaging and reconstruction methods10, or 2-photon laser scanning microscopy11. Current drawbacks to these approaches are the associated labor-intensive tissue preparation, or cost-prohibitive instrumentation respectively.
Here, we present a relatively rapid and simple method to visualize fluorescently labelled cells in fixed semi-thick mouse brain slices by optical clearing and imaging. In the attached protocol we describe the methods of: 1) fixing brain tissue in situ via intracardial perfusion, 2) dissection and removal of whole brain, 3) stationary brain embedding in agarose, 4) precision semi-thick slice preparation using new vibratome instrumentation, 5) clearing brain tissue through a glycerol gradient, and 6) mounting on glass slides for light microscopy and z-stack reconstruction (Figure 1).
For preparing brain slices we implemented a relatively new piece of instrumentation called the 'Compresstome' VF-200 (http://www.precisionary.com/products_vf200.html). This instrument is a semi-automated microtome equipped with a motorized advance and blade vibration system with features similar in function to other vibratomes. Unlike other vibratomes, the tissue to be sliced is mounted in an agarose plug within a stainless steel cylinder. The tissue is extruded at desired thicknesses from the cylinder, and cut by the forward advancing vibrating blade. The agarose plug/cylinder system allows for reproducible tissue mounting, alignment, and precision cutting. In our hands, the 'Compresstome' yields high quality tissue slices for electrophysiology, immunohistochemistry, and direct fixed-tissue mounting and imaging. Combined with optical clearing, here we demonstrate the preparation of semi-thick fixed brain slices for high-resolution fluorescent imaging.
Protocol
1. الدماغ في تثبيت الوضع الطبيعي
* تحضير حقنة 10 مل (28 إبرة قياس) مليئة الفوسفات مخزنة المالحة (PBS).
* تحضير حقنة 10 مل (28 إبرة قياس) مليئة بارافورمالدهيد 4 ٪ (PFA) في برنامج تلفزيوني. الاحتياطي إلى ترخيص إضافي 5-10 PFA / لتثبيت برنامج تلفزيوني آخر.
- ضخ تجريبي intraperitoneally الفأر مع جرعة قاتلة من آفيرتين أو Nembutal.
- بمجرد مخدرا الماوس ، والرطب في البطن مع الإيثانول وتأمين الماوس إلى أسفل الدرج الطبقات مع الفلين والشمع ، أو الاستومر سيليكون باستخدام دبابيس تشريح. البطن مع مواجهة وتأمين الكفوف أربعة إلى السطح -- نشرها على أوسع نطاق ممكن.
- الاستيلاء على الجلد مع ملقط على مستوى القص ، وقطع بالعرض لفضح الكبد. قطع أفقيا ثم ارتفعت خلال الضلوع والحجاب الحاجز. إزالة الأنسجة رفرف الصدري وتستمر حتى قطع القلب للوصول.
- بيرس أو قص الأذين الأيمن لاستنزاف الدم تعميمها.
- تدفق الدم المتبقية من الدورة الدموية التي نضح من خلال برنامج تلفزيوني البطين الأيسر.
- الوصول إلى ثقب الإبرة نفسها ، إصلاح الماوس كله عن طريق نضح اللاحقة PBS / منهاج العمل من خلال البطين الأيسر.
2. تشريح الدماغ واستخراج
- إزالة الجلد من الرأس والعنق والجمجمة عن طريق خفض حول قناة الأذن والعين المدارات ، يليها سحب الجلد الأمامية لفضح الجمجمة.
* انظر الشكل رقم 2 لتوضيح الخطوات 2.2) إلى 2.5) - باستخدام مقص العظام ، وقطع بالعرض من العين عن طريق مأخذ عظام المحارة الأنفية. للقيام بذلك كل جانب. ينبغي أن يكون إقطع الأمامي للعين وبصيلات الشم.
- قطع بالطول من كل قناة الأذن إلى تجويف العين.
- باستخدام مقص تشريح الصغيرة ، وقطع لوحة العظم القذالي تغمر المخيخ من قناة الأذن واحدة إلى أخرى.
- مع مقص تشريح نفسه ، خفضت الأمامية على طول خط الوسط على مستوى البصيلات الشمية.
- باستخدام الملقط ، وإزالة كل لوحة العظام من الدماغ ، مع الحرص على إزالة أي نوع من الأنسجة الضامة بحيث أن الدماغ لا يزال سليما عندما رفع قبالة العظام.
- قص قطع الأعصاب البصرية والجمجمة والفقرات العنقية العليا ، وإزالة تثبيتي في الدماغ.
- في مرحلة ما بعد الإصلاح لمدة 1-2 ساعات في 4 درجات مئوية. اغسل 3 مرات كل 15 دقيقة في برنامج تلفزيوني.
3. Agarose التضمين
- تذوب 2 ٪ عالية القوة ، وانخفاض نقطة agarose هلام نوع IB (سيغما رقم الكتالوج : A0576) في برنامج تلفزيوني مع المالحة فرن الميكروويف.
- نقل agarose المنصهر إلى أنبوب اختبار. مكان أنبوب الاختبار في حمام ماء دافئ أو الحاضنة (40 ° -41 درجة مئوية) حتى موازنة درجة الحرارة.
- الغراء أنسجة المخ ثابتة على المكبس من المحاقن مع عينة cyanoacrylate الغراء (3A الشكل). فرشاة طبقة رقيقة من محلول السكروز ، PBS المشبعة على سطح أنسجة المخ لتسهيل الافراج في وقت لاحق من الحلبة agarose من شرائح الدماغ.
- سحب المكبس مع أنسجة المخ في السكن المكبس (الشكل 3B).
- ماصة أو صب agarose الدافئة في السكن المكبس ، الذي يغطي أنسجة المخ. تجنب احتباس فقاعات الهواء في agarose. وفقاعات الهواء في agarose تؤثر سلبا على جودة شريحة.
- المشبك المحقنة مع العينة (° 0 إلى -25 درجة مئوية) الباردة كتلة تقشعر لها الأبدان لمدة 1 دقيقة لضبط agarose (الشكل 3C).
4. Sectioning شريحة الدماغ مع Compresstome
- تجميع العينات حقنة تحتوي على أنسجة المخ في Compresstome (الشكل 3D).
- محاذاة حافة شفرة الحلاقة بشكل وثيق مع مخرج المحقنة العينة (الشكل 3E).
- تعبئة خزان العازلة مع الحل برنامج تلفزيوني.
- تدوير شريحة سمك ميكرومتر الى الأمام لبثق كتلة أنسجة الدماغ agarose من حقنة العينة.
- اضغط على زر "ابدأ" في وحدة التحكم من Compresstome للشروع في عملية sectioning.
- كرر الخطوات من 4.4) إلى 4.5) حتى يتم الحصول على المطلوب في تحديد شرائح سمك.
- شرائح الدماغ الحصاد مع فرشاة أو ماصة للقوارير أو الآبار مملوءة PBS تلوين الشكل (3F).
5. تبادل البصرية
- إعداد المجلد 75 ٪ : المجلد حل الجلسرين : برنامج تلفزيوني.
- صب (أو ماصة) قبالة حجم نصف PBS غسل الدماغ من الشرائح التي تم جمعها.
- إضافة مرة أخرى حجم إزالة مع الجلسرين / برنامج تلفزيوني.
- السماح للتوازن مع مزج لطيف في 4 درجات مئوية حتى تغرق شرائح.
- كرر الخطوات من 6.2) إلى 6.4) حتى تصل إلى تركيز الجلسرين النهائية 75 ٪.
- استبدال حل مع الجلسرين 90 ٪ في برنامج تلفزيوني ، والسماح للتوازن.
* ملاحظة : احرص على عدم إدخال فقاعات الهواء في حين اضاف حلول الجلسرين. صب المزيج ببطء وحلول بلطف ، منذ فقاعات الهواء سوف تتداخل مع equilibra موحدةوسيتم تنفيذ نشوئها والى شريحة متزايدة.
6. شريحة متزايدة للتصوير
- قطع لاصقة على الوجهين الختم (SA - S - 1L ، غريس بيو مختبرات) في مستطيل مفتوح لتناسب مساحة للعرض شريحة متناهية الصغر (Superfrost زائد ، 25 X 75 X 1 ملم ، والقط. # 48311-703 ، VWR ) مع الجانبين 2-3 مم واسعة.
- مكان شرائح الدماغ داخل مركز للمستطيل باستخدام شريط لاصق ماصة أو فرشاة الرسم. إزالة الزائدة الجلسرين مع التطلع لطيف.
- ترتيب شرائح الدماغ على الشريحة في الترتيب المطلوب مع فرشاة الرسم.
- انخفاض الغطاء برفق زجاج (24 X 60 مم ، القط. # 48383-139 ، VWR) على شريط لاصق ، مع الحرص على عدم إدخال فقاعات الهواء. بلطف تطبيق الضغط على الزجاج غطاء لضمان الاتصال مع شريط لاصق.
- نضح الجلسرين الزائد من الحواف بين الشرائح وساترة.
- وختم الشريحة ساترة باستخدام طلاء الأظافر واضحة.
- السماح ليجف قبل التصوير ، أو تخزين طويل الأجل في صناديق الشريحة في 4 درجات مئوية.
7. ممثل النتائج :
وقد أصبحت معالجة ، والتصوير ، وتحليل fluorescently المسمى أنسجة المخ التي لا غنى عنها لدراسة البيولوجيا العصبية. كثير من هذه التحقيقات تتطلب التلاعب الجيني متطورة للحصول على التعبير مراسل فرعية في الخلايا العصبية المستهدفة ، تليها كل من يحلل صورة منخفضة وعالية الدقة. في كثير من الأحيان قيود التجريبية والتقنية تجعل من المستحيل الحصول على هذه الأنواع من البيانات من نفس الحيوان ، أو بطريقة سريعة. إعداد مسح بصريا ، والمقاطع الدماغ شبه سميكة لمكافحة الإيدز التصوير فلوري في هذا التحدي. مثال على شريحة سميكة الدماغ سليمة المسمى مع فيروس داء الكلب المعدلة وراثيا هندسيا لEGFP التعبير ، والتقط باستخدام المجهر epifluorescent ومبائر هو مبين في الشكل (4) والشكل (5) على التوالي. التصوير epifluorescent استخدمنا M205 ايكا اتحاد كرة القدم ، والحصول على الصور مبائر استخدمنا LSM زايس 510. بسبب البساطة النسبية للبروتوكول المرفق ، وهذه الطريقة هي قادرة على إنتاج بيانات الصور مفيدة من نسيج التعبير عن صحفيين الفلورسنت مع فترة زمنية أقل من يوم واحد ، ومتوافق مع كل من المجهري الإضاءة الخافتة والعالية الدقة.
إذا كان محقق تختار إدماج أساليب إضافية الوسم بعد الوفاة ، وتلطيخ المناعى ، أو جعل أرق المقاطع ، وبروتوكول يطول تبعا لذلك. ومع ذلك ، فإن الطريقة الموصوفة أعلاه يمثل طريقة بسيطة والإنتاجية العالية نسبيا من أجل فحص أنماط التعبير مراسل حيوية في الدماغ سليمة.
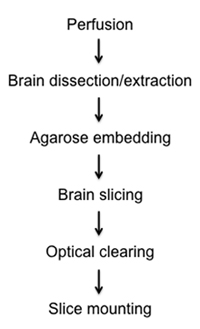
الشكل 1. مخطط تدفق diagraming التثبيت ، تشريح ، تشريح ، تبادل المعلومات ، وإجراءات متزايدة من شرائح الدماغ شبه سميكة.
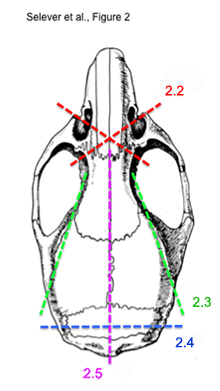
الشكل 2. مخطط لقطع خطوات متتابعة لاستخراج مخ الفأر سليمة.
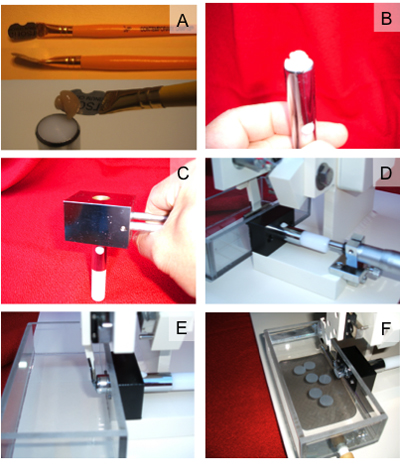
الشكل 3 خطوات لتحميل وشريحة أنسجة المخ باستخدام Compresstome. أ) الموضع من أنسجة المخ على خفض استخدام superglue المكبس. ب) رسم أسفل أنسجة المخ التي شنت في المكبس لتضمين agarose. C) التقوية القابس الدماغ agarose باستخدام كتلة ضغط مبردة. D) الإدراج من المكونات الدماغ والمكبس agarose في غرفة قطع Compresstome. E) محاذاة razorblade إلى الجهاز المكبس. F) ، وجمع قطع من شرائح الدماغ في غرفة عازلة Compresstome.
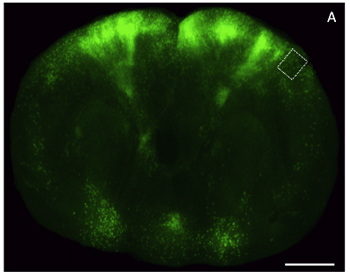
الشكل 4. الصور المجهري الضوء على شريحة سميكة من الجلسرين تطهيرها أنسجة المخ من خلال التعبير عن القشرة الخارجية الخضراء المعززة بروتين فلوري (EGFP). شريحة) الاكليل من خلال مخ الفأر (200 ميكرون سميكة) المسمى مع EGFP ناقلات فيروسية في التعبير عن وتصويرها باستخدام دقة منخفضة المجسام epifluorescent. مقياس شريط ، 2 ملم.

الشكل 5. صورة عالية التكبير طبقة fluorescently المسمى 06/05 العصبونات القشرية في الدماغ شريحة سميكة تطهيرها. أ) صورة عالية الدقة مبائر لإسقاط الحد الأقصى Z - المكدس (150 ميكرون سميكة) من خلال تسليط الضوء على المنطقة في (الشكل 4). مقياس بار ، و 25 ميكرون.
Discussion
نظرا للتطبيق على نطاق واسع من استخدام البروتينات الفلورية لاستهداف الخلايا العصبية فرعية للتحقيق عبر المجهر الضوئي ، والحاجة إلى سرعة الشاشة والصورة وتحليل الشبكات العصبية داخل أنسجة الدماغ سليمة أصبحت لا تقدر بثمن.
التقدم الت...
Disclosures
جيان تشيانغ كونغ موظف في شركة Precisionary ، والصكوك ، التي تقوم بتصنيع منتج المستخدمة في هذه المقالة.
Acknowledgements
وقد تم تمويل هذا العمل عن طريق الدعم من خلال مؤسسة ماكنير ، NARSAD ، ومنح NINDS R00NS064171 - 03.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| اسم البند | الشركة | فهرس العدد | تعليقات (اختياري) |
|---|---|---|---|
| مقص العظام | FST | 16044-10 | أو ما يعادلها |
| FST | 14084-08 | أو ما يعادلها | |
| نوع IB agarose | سيغما | A0576 | |
| Compresstome | آلات Precisionary | VF - 200 | - vibratomes أخرى متوافقة |
| لاصقة مزدوجة من جانب | جريس بيو مختبرات | SA - S - 1L | |
| Superfrost بلس الشرائح | VWR | 48311-703 | |
| غطاء من الزجاج | VWR | 48383-139 | |
| الجلسرين | EMD شركة الكيماويات | GX0185 - 6 | أو ما يعادلها |
References
- Pfister, H., Lichtman, J., Reid, C. . The Connectome Project. , (2009).
- Briggman, K. L., Denk, W. Towards neural circuit reconstruction with volume electron microscopy techniques. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 16, 562-570 (2006).
- Micheva, K. D., Smith, S. J. Array tomography: a new tool for imaging the molecular architecture and ultrastructure of neural circuits. Neuron. 55, 25-36 (2007).
- Arenkiel, B. R., Ehlers, . Molecular genetic and imaging technologies for circuit based neuroanatomy. Nature. 461, 900-907 (2009).
- Capecchi, M. R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 244, 1288-1292 (1989).
- Luo, L., Callaway, E. M., Svoboda, K. Genetic dissection of neural circuits. Neuron. 57, 634-660 (2008).
- Shimomura, O., Johnson, F., Saiga, Y. Extraction, purification, and properties of aequorin, a bioluminescent protein from the luminous hydromedusan, Aequorea. J. Cell Comp Physiol. 59, 223-239 (1962).
- Chalfie, M., Tu, Y., Euskirchen, G., Ward, W., Prasher, D. Gene fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science. 263, 802-805 (1994).
- Giepmans, B. N., Adams, S. R., Ellisman, M. H., Tsien, R. Y. The fluorescent toolbox for assessing protein location and function. Science. 312, 217-224 (2006).
- Micheva, K. D., Smith, S. J. Array tomography: a new tool for imaging the molecular architecture and ultrastructure of neural circuits. Neuron. 55, 25-36 (2007).
- Svoboda, K., Yasuda, R. Principles of two-photon excitation microscopy and its applications to neuroscience. Neuron. 50, 823-839 (2006).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved