A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
ارتفاع الإنتاجية وحيدة الخلية ومتعددة الخلية الصغيرة التغليف
In This Article
Summary
الجمع بين monodisperse جيل قطرة مع ترتيب بالقصور الذاتي من الخلايا والجزيئات، ونحن تصف طريقة لتغليف العدد المطلوب من الخلايا أو الجزيئات في قطرة واحدة في معدلات كيلوهرتز. علينا أن نبرهن الكفاءات يتجاوز ضعف تلك التي التغليف غير مرتبة لقطرات واحد ومزدوجة الجسيمات.
Abstract
Microfluidic encapsulation methods have been previously utilized to capture cells in picoliter-scale aqueous, monodisperse drops, providing confinement from a bulk fluid environment with applications in high throughput screening, cytometry, and mass spectrometry. We describe a method to not only encapsulate single cells, but to repeatedly capture a set number of cells (here we demonstrate one- and two-cell encapsulation) to study both isolation and the interactions between cells in groups of controlled sizes. By combining drop generation techniques with cell and particle ordering, we demonstrate controlled encapsulation of cell-sized particles for efficient, continuous encapsulation. Using an aqueous particle suspension and immiscible fluorocarbon oil, we generate aqueous drops in oil with a flow focusing nozzle. The aqueous flow rate is sufficiently high to create ordering of particles which reach the nozzle at integer multiple frequencies of the drop generation frequency, encapsulating a controlled number of cells in each drop. For representative results, 9.9 μm polystyrene particles are used as cell surrogates. This study shows a single-particle encapsulation efficiency Pk=1 of 83.7% and a double-particle encapsulation efficiency Pk=2 of 79.5% as compared to their respective Poisson efficiencies of 39.3% and 33.3%, respectively. The effect of consistent cell and particle concentration is demonstrated to be of major importance for efficient encapsulation, and dripping to jetting transitions are also addressed.
Introduction
Continuous media aqueous cell suspensions share a common fluid environment which allows cells to interact in parallel and also homogenizes the effects of specific cells in measurements from the media. High-throughput encapsulation of cells into picoliter-scale drops confines the samples to protect drops from cross-contamination, enable a measure of cellular diversity within samples, prevent dilution of reagents and expressed biomarkers, and amplify signals from bioreactor products. Drops also provide the ability to re-merge drops into larger aqueous samples or with other drops for intercellular signaling studies.1,2 The reduction in dilution implies stronger detection signals for higher accuracy measurements as well as the ability to reduce potentially costly sample and reagent volumes.3 Encapsulation of cells in drops has been utilized to improve detection of protein expression,4 antibodies,5,6 enzymes,7 and metabolic activity8 for high throughput screening, and could be used to improve high throughput cytometry.9 Additional studies present applications in bio-electrospraying of cell containing drops for mass spectrometry10 and targeted surface cell coatings.11 Some applications, however, have been limited by the lack of ability to control the number of cells encapsulated in drops. Here we present a method of ordered encapsulation12 which increases the demonstrated encapsulation efficiencies for one and two cells and may be extrapolated for encapsulation of a larger number of cells.
To achieve monodisperse drop generation, microfluidic "flow focusing" enables the creation of controllable-size drops of one fluid (an aqueous cell mixture) within another (a continuous oil phase) by using a nozzle at which the streams converge.13 For a given nozzle geometry, the drop generation frequency f and drop size can be altered by adjusting oil and aqueous flow rates Qoil and Qaq. As the flow rates increase, the flows may transition from drop generation to unstable jetting of aqueous fluid from the nozzle.14
When the aqueous solution contains suspended particles, particles become encapsulated and isolated from one another at the nozzle. For drop generation using a randomly distributed aqueous cell suspension, the average fraction of drops Dk containing k cells is dictated by Poisson statistics, where Dk = λk exp(-λ)/(k!) and λ is the average number of cells per drop. The fraction of cells which end up in the "correctly" encapsulated drops is calculated using Pk = (k x Dk)/Σ(k' x Dk'). The subtle difference between the two metrics is that Dk relates to the utilization of aqueous fluid and the amount of drop sorting that must be completed following encapsulation, and Pk relates to the utilization of the cell sample. As an example, one could use a dilute cell suspension (low λ) to encapsulate drops where most drops containing cells would contain just one cell. While the efficiency metric Pk would be high, the majority of drops would be empty (low Dk), thus requiring a sorting mechanism to remove empty drops, also reducing throughput.15
Combining drop generation with inertial ordering provides the ability to encapsulate drops with more predictable numbers of cells per drop and higher throughputs than random encapsulation. Inertial focusing was first discovered by Segre and Silberberg16 and refers to the tendency of finite-sized particles to migrate to lateral equilibrium positions in channel flow. Inertial ordering refers to the tendency of the particles and cells to passively organize into equally spaced, staggered, constant velocity trains. Both focusing and ordering require sufficiently high flow rates (high Reynolds number) and particle sizes (high Particle Reynolds number).17,18 Here, the Reynolds number Re =uDh/ν and particle Reynolds number Rep =Re(a/Dh)2, where u is a characteristic flow velocity, Dh [=2wh/(w+h)] is the hydraulic diameter, ν is the kinematic viscosity, a is the particle diameter, w is the channel width, and h is the channel height. Empirically, the length required to achieve fully ordered trains decreases as Re and Rep increase. Note that the high Re and Rep requirements (for this study on the order of 5 and 0.5, respectively) may conflict with the need to keep aqueous flow rates low to avoid jetting at the drop generation nozzle. Additionally, high flow rates lead to higher shear stresses on cells, which are not addressed in this protocol. The previous ordered encapsulation study demonstrated that over 90% of singly encapsulated HL60 cells under similar flow conditions to those in this study maintained cell membrane integrity.12 However, the effect of the magnitude and time scales of shear stresses will need to be carefully considered when extrapolating to different cell types and flow parameters. The overlapping of the cell ordering, drop generation, and cell viability aqueous flow rate constraints provides an ideal operational regime for controlled encapsulation of single and multiple cells.
Because very few studies address inter-particle train spacing,19,20 determining the spacing is most easily done empirically and will depend on channel geometry, flow rate, particle size, and particle concentration. Nonetheless, the equal lateral spacing between trains implies that cells arrive at predictable, consistent time intervals. When drop generation occurs at the same rate at which ordered cells arrive at the nozzle, the cells become encapsulated within the drop in a controlled manner. This technique has been utilized to encapsulate single cells with throughputs on the order of 15 kHz,12 a significant improvement over previous studies reporting encapsulation rates on the order of 60-160 Hz.4,15 In the controlled encapsulation work, over 80% of drops contained one and only one cell, a significant efficiency improvement over Poisson (random) statistics, which predicts less than 40% efficiency on average.12
In previous controlled encapsulation work,12 the average number of particles per drop λ was tuned to provide single-cell encapsulation. We hypothesize that through tuning of flow rates, we can efficiently encapsulate any number of cells per drop when λ is equal or close to the number of desired cells per drop. While single-cell encapsulation is valuable in determining individual cell responses from stimuli, multiple-cell encapsulation provides information relating to the interaction of controlled numbers and types of cells. Here we present a protocol, representative results using polystyrene microspheres, and discussion for controlled encapsulation of multiple cells using a passive inertial ordering channel and drop generation nozzle.
Protocol
البروتوكولات في هذا القسم وصف المواد والمعدات التي تستخدم خصيصا للحصول على النتائج التجريبية المقدمة. لاحظ أن يمكن استخدام الموردين بديل للكيماويات ومعدات.
1. تصنيع الجهاز، والطباعة الحجرية الناعمة
معيار تقنيات الطباعة الحجرية الناعمة، و 21 عددا منها قد وردت في مقالات سابقة [جوف]، وقد استخدمت (22) لخلق polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) شبكات متناهية المستعبدين من ركائز الزجاج. وبصرف النظر عن سيد تلفيق قالب طبق الأصل من قبل SU-8 ضوئيه، قد يتم تنفيذ عمليات خارج غرفة نظيفة أو غطاء محرك السيارة نظيفة، وينبغي مع ذلك لا يزال، والغبار والجسيمات أن يكون الحد الأدنى لتحقيق نتائج متسقة.
- تصميم نمط الدقيقة قناة كما هو موضح في الشكل رقم 1 في أوتوكاد (اوتوديسك شركة). استخدام منتج طرف ثالث (شركة Fineline التصوير) لطباعة عالية الدقة (50،000 نقطة في البوصة) العابرةقناع parency على الفيلم مايلر أو الكوارتز حيث قنوات شفافة على خلفية داكنة.
- إنشاء السيليكون وSU-8 سيد مقاومة للضوء لصب طبق الاصل. لفترة وجيزة، وتدور SU-8 2050 (MicroChem) مقاومة للضوء سلبي مع دورة في الدقيقة وأوصت الشركة المصنعة على المغطي الجانبية لخلق طبقة سميكة ميكرومتر 52 على 7.5 سم نظيفة أو 10 سم رقاقة السيليكون. بعد لينة خبز، حافة حبة إزالة، والتعرض للأشعة فوق البنفسجية من خلال قناع الاتصال، وخبز بعد التعرض، والتنمية، والتعرض للفيضانات، وقياس سماكة الفعلي للطبقة SU-8 باستخدام profilometer Dektak (Veeco). شريط القالب الرئيسي على الجزء السفلي من صحن 4 "أو 5" بيتري للتحضير لصب طبق الاصل PDMS.
- مزيج قاعدة الاستومر PDMS مع وكيل المعالجة الاستومر (داو كورنينج) في قاعدة 10:01 ث / ث نسبة إلى وكيل المعالجة. صب الجيدة الخلط PDMS السلائف على سيد السيليكون لخلق 2-3 مم سماكة طبقة النهائية. خليط من 20 قاعدة الاستومر مع 2 ز ز وكيل المعالجة غير كافية لتغطية سطح بقطر 4 ".
- وضع masteص العفن وPDMS في مجفف فراغ (Jencons) لPDMS دي الغاز uncured. استخدام منظم ضغط (كول Parmer)، وانخفاض الضغط ببطء سعة غرفة من 0 "الزئبق إلى -27" الزئبق أكثر من 20 دقيقة لتجنب الإفراط في الرغوة. ترك الجهاز في فراغ الغرفة على الزئبق "-27 لمدة 30 دقيقة أو حتى تختفي فقاعات الهواء.
- الافراج عن فراغ ونقل القالب الرئيسي وPDMS إلى 65 درجة مئوية فرن (الحرارية العلمية) للحصول على الحد الأدنى من أربع ساعات. يمكن ترك الجهاز في فرن بين عشية وضحاها لتحسين علاج.
- إزالة الجهاز من الفرن والسماح لتبرد. قطع بعناية PDMS حول رقاقة دائري باستخدام سكين الدقة وقشر خارج PDMS. قطع مخطط جهاز كما هو موضح في الشكل رقم 1 مع مشرط.
- لكمة الموانئ fluidic (ثلاثة في كل جهاز) في المناطق الثلاث جولة هو مبين في الشكل 1 باستخدام لكمة خزعة. لهذا الجهاز، واستخدام 0.75 مم القطر الخارجي لكمة (هاريس).
- تلتزم الاسكتلندي إلى جانب نمط من PDMS وقشر لإزالة أيةغبار. كبديل لتوفير التكاليف ولكن قابلة للحياة إلى الأجهزة التقليدية بلازما الأوكسجين، 21،22 بلازما معالجة الجانب منقوشة من PDMS و 3 نظيفة "س 1" شريحة زجاجية تستخدم باليد مختبر الاكليل المفاوض (الكهربائية ومنتجات شركة تكنيك ). يجب أن تبقى 23 لاحظ أنه ينبغي أن يستخدم هذا الجهاز في غطاء الدخان أو جيد التهوية المنطقة بسبب التفريغ الأوزون، وجميع الساعات والهواتف المحمولة لا يقل عن عشرة أمتار. ضبط كورونا التفريغ للوصول الى الاكليل مستقر مع الحد الأدنى من اثار. موجة ببطء القطب حوالي 1/4 "فوق كل سطح لحوالي 20 ثانية ومن ثم جلب على الفور الأسطح المعالجة في اتصال لتشكيل رابطة قوية دائمة قبل السطوح PDMS العودة إلى حالتها الأصلية.
- وضع الجهاز على لوحة معدنية، مكان في فرن بارد، وضبط الفرن إلى 120 درجة مئوية، وتخبز لاستكمال الربط بين عشية وضحاها وإعادة PDMS إلى حالته الأصلية مسعور (24). وخلال هذا الخبز ارتفاع في درجة الحرارة، تيوقال انه أيضا السطح الزجاجي لقناة ستقدم مسعور بسبب ترسب طبقة رقيقة مسعور على الزجاج. بدلا من ذلك، قد يتم حقنها الطلاء مسعور مثل Aquapel (اندستريز) في الموانئ fluidic باستخدام حقنة 1 مل و إبرة الحقن. 12 بعناية ولكن حقن بقوة Aquapel تليها تطهير الهواء في المنافذ fluidic دون كسر زجاج PDMS على السندات . كرر بقوة على تطهير الهواء في كل المنافذ على مدخل ومخرج في حين محو أي Aquapel الزائدة من أجل تجنب أي الودائع التي قد تسد القنوات على تجفيف.
2. عينة تحضير
- تعد زراعة الخلايا وفقا للإجراءات المتبعة لنوع الخلية الذي تم اختياره. للجهاز خاص المستخدمة في هذه الدراسة، وينبغي أن الجسيمات 8-15 ميكرون أو تأمر الخلايا على نحو كاف لتغليف. قد أنواع الخلايا أصغر أو أكبر يتطلب تغيير أبعاد قناة تركز على تحقيق كاف ف رد. للاطلاع على البياناتنتائج مظاهرة ثود هو مبين في هذه الورقة، وتستخدم 9.9 ميكرون المجهرية البوليسترين (G1000، الحرارية العلمية) كبديل الخلية.
- إعداد جسيم مائي أو تعليق الخلية من خلال خلط لطيف. عند استخدام خلايا أو جزيئات البوليستيرين، ومراقبة تركيز أساسي (انظر الشكل 4) لتحقيق المثل الأعلى التغليف أمر. باستخدام البيانات السابقة 12 مرشدا، وحساب الخلية المطلوبة أو تركيز الجسيمات على أساس تباعد قطار أمرت والصغرى قناة الحجم على النحو التالي: خلية واحدة أو الجسيمات في المتوقعة طولية مرات المباعدة بين قطار وتركز قناة مستعرضة المنطقة. إذا كان تركيز الأوراق المالية (1٪ وزن / وزن) غير كافية، وزيادة تركيز (هنا إلى 1.5٪ وزن / وزن) بواسطة الطرد المركزي بلطف العينة الأوراق المالية، وإزالة السائل طاف، وإعادة تعليق، والجزيئات التي دوامة الاختلاط، أو ألطف الاختلاط عند استخدام الخلايا. يعد حجم كاف لحساب حجم المطلوب، وجمع لوقت التشغيل المرتبطة فلوريداآه ضبط.
- كل من الخلايا والجزيئات البوليسترين لها الثقل النوعي أكبر من واحد. وإن لم يكن هو موضح في هذا البروتوكول، على المدى الطويل التجارب دائم على النظام من عدة دقائق إلى ساعات، الطفو تتطابق مع حل عن طريق إضافة المذاب مثل CaCl 2 للجسيمات أو OptiPrep (سيغما الدريخ) للخلايا.
- إعداد عينة 10 مل من المرحلة الفلوروكربونية النفط مستمر عن طريق خلط زيت الفلوروكربونية FC-40 (3M) و PFPE PEG-بالسطح كتلة كوبوليمر 25 (2.5٪ وزن / وزن) (رايندانس تكنولوجيز) في أنبوب الطرد المركزي 15 مليلتر. بدلا من ذلك، يمكن أن تستخدم ضوء الزيوت المعدنية (مواد كيميائية عملية كونا) مع أبي بالسطح 90-EM (2.5٪ وزن / وزن) (Evonik غولدشميت شركة).
3. إعداد التجريبية
- السلطة في المجهر الضوئي المقلوب (محوري المراقب، زييس) وكاميرا عالية السرعة (فانتوم V310، الرؤية للبحوث). التركيز وتفقد قنوات للالسدادات والحطام من قبل أي تحرك يدويا أو جهازباستخدام مجهر مرحلة الآلية. قد تكون دفعت بعض الحطام صغيرة من السائل عندما يتدفق عبر. للحطام كبير أو السدادات واضح، حدد قناة أخرى على الجهاز والحطام في القناة مع التركيز يمكن أن تتحلل يأمر الجودة بشكل ملحوظ. لاحظ أن في كثير من الأحيان، قباقيب يمكن إزالتها تحت تدفق بالضغط بقوة على سطح PDMS فوق المنطقة المنكوبة مع ملاقط غير حادة.
- قطع ثلاثة أطوال من الأنابيب البلاستيكية (0.01 "ID/0.03" التطوير التنظيمي، Tygon) لمدخل مائي، مدخل النفط، ومنفذ مستحلب. للتقليل من حجم القتلى، وقطع ما يكفي للوصول إلى أنابيب من مضخات المحاقن الى المرحلة المجهر. قطع نهايات الأنابيب بزاوية 45 درجة لتسهيل الإدراج في الموانئ fluidic.
- استخدام ملاقط للضغط على احتواء أنبوب ينتهي في الموانئ fluidic لكمات في الخطوة 1 ثم اضغط على احتواء كل منهما 30 مقياس صريحا معلومات سرية حقنة من الصلب غير القابل للصدأ الإبر (SmallParts) في نهايات خالية من كل مائي وأنابيب النفط مدخل (لا يلزم لاصق) . وضع أنبوب منفذ إلى R النفاياتeservoir. وسوف يتم في وقت لاحق هذا الأنبوب انتقلت الى خزان جمع.
- نقل الجهاز وأنابيب المرفقة إلى مرحلة المجهر، ومواءمة، والتركيز على فوهة الجهاز باستخدام هدفا المتاحة (20x وكانت تستخدم لهذه التجربة). ضبط K hler الإضاءة وإعدادات المجهر الأخرى على النحو المطلوب لتسجيل الأمثل.
- شغل حقنة 1 مل (دينار بحريني) مع المرحلة الجيدة الخلط المائي وحقنة مل 3 (دينار بحريني) مع زيت حل مرحلة إعداد في الخطوة 2. لاحظ التي يمكن أن تستخدم أي محاقن من أي حجم، وينبغي اختيارها بعناية وفقا لمرات المدى المطلوب، والتقليل من أي pulsatility. إمالة 1 حقنة عموديا، ونفض الغبار لتحريك فقاعات الهواء إلى منفذ حقنة. خفض ببطء الغطاس بما فيه الكفاية لدفع الهواء إلى طرف الحقنة. عقد المحقنة عموديا، ربط المحاقن إلى إبرة حقنة كل منها مرفقة بالفعل إلى الجهاز في الخطوة 3.3. خفض الغطاس لإجبار الهواء من خلال حقنة حجم إبرة القتلى حتى السائل صushed من خلال الأنبوب تقريبا للجهاز. جبل آمن المحقنة إلى مضخة محقنة (نيكزس 3000، Chemyx) وإشراك كتلة الغطاس. كرر اتصالات للحقنة الثانية وجبل لمضخة الحقنة الثانية.
- القوة في كل مضخة محقنة والبرنامج باستخدام البروتوكولات لصناعة المضخات و. ضبط معدلات تدفق النفط الأولية إلى س = 50 ميكروليتر / دقيقة، وعبد القدير س = 5 ميكرولتر / دقيقة للمرحلة النفط والمرحلة المائية، على التوالي. بدء تشغيل المضخات.
- انتظر كل السوائل من دخول الجهاز وملء القنوات، مما دفع الهواء خارج ميت المتبقية. وهذا قد يستغرق عدة دقائق. إذا كان هناك كمية كبيرة من الهواء في أنابيب مدخل، وزيادة معدل تدفق كل مؤقتا حتى يتم طرد الهواء. لا زيادة معدلات تدفق عالية جدا لدرجة أن الضغوط كبيرة تحدث في القناة، مما قد يؤدي إلى فشل السندات PDMS إلى زجاج.
- باستخدام معدلات تدفق الأولي، ومراقبة تشكيل قطرات في فوهة (النتائج هو موضح هنا: 20X magnificatioن، والإطار معدل 21005 إطارا في الثانية، تعرض 3 ميكرو ثانية). الحد من مجال رؤية الكاميرا إلى فوهة الوحيد لتحقيق أقصى معدل الإطار وتقليل متطلبات الذاكرة إذا كان ذلك ممكنا. التقاط الفيديو عينة وثبت أن نسبة العينات غير كافية لتجنب التعرج.
- لتجنب النفث (انظر الشكل 2)، وتبدأ مع انخفاض معدلات تدفق مائي. زيادة ببطء معدل تدفق مائي لمراقبة ترتيب الجزيئات في قناة محلول مائي طويل كما يزيد معدل التدفق.
- إذا كان تركيز الجسيمات منخفضة للغاية لتوفير القطارات مع عدد قليل نسبيا من الجزيئات "المفقود" وكان لا تطابق عينة الطفو، إمالة بدنيا ضخ حقنة في اتجاه منفذ حقنة لتوفير حل تدريجي من الجسيمات في اتجاه منفذ حقنة. ويتجلى هذا الأسلوب في بروتوكول الفيديو. قد دوريا بالتناوب الحقنة على طول محور يخفض أيضا تصفية غير المرغوب فيها.
- مرة واحدة كافية ترتيب يحدث، وضبط معدل تدفق النفط لضبط وتيرة توليد وحجم قطرات. ويمكن حساب حجم الانخفاض يعني استخدام معدل تدفق مائي مقسوما على انخفاض وتيرة توليد مقاسا التقاط الفيديو. ضبط تكراري معدلات التدفق على حد سواء لتحقيق معدلات التغليف المطلوب وحجم الانخفاض.
- ويؤكد مرة التغليف أمر مستقر، نقل منفذ أنابيب من الخزان النفايات إلى خزان جمع أو إطعام في جهاز آخر للاختبار لاحق.
- تحديد الوقت على أساس جمع العدد المطلوب من قطرات، وتردد جيل محسوب.
- تسجيل جزء من قطرات تحتوي على 0، 1، 2، ...، N الجسيمات لقياس كفاءة باستخدام نتائج الفيديو قطرة جيل أو بواسطة pipetting عينة من مستحلب تجمع للتفتيش.
4. ممثل النتائج
وتعرض النتائج التي تحقق على حد سواء للرقابة واحد جسيم وجسيم للرقابة مزدوجة التغليف (الشكل 3). عن طريق خفض معدل تدفق FC-40 النفط إلى النصف، واحد جسيم التغليف يصبح اثنين من الجسيمات التغليف. وعلى العكس، كان من الممكن أن رفعنا معدل تدفق مائي لتقديم الجسيمات إلى فوهة بسرعة أكبر، ولكن نحن أيضا ما قد زادت من مخاطر النفث من تيار مائي. رسوم بيانية في الشكل (3) تقديم عدد كسري من جسيمات من كل قطرة ماء لالحالتين، جنبا إلى جنب مع مقارنات للاحصاءات بويسون. ويلاحظ هبوط في بعض الأحيان مع جزيئات الصفر هي في المقام الأول بسبب الجسيمات "المفقودين" في القطارات وأمر، في حين أن الحالات التي توجد فيها جزيئات أكثر مغلفة من النتيجة المرجوة من المحلية تركيزات الجسيمات العالية والجزيئات التي تهاجر في بعض الأحيان في اتجاه واحد من المواقف العمودية 2 التركيز. لاحظ لم يستخدم هذا الطفو مطابقة كما هو موضح في القسم 2. بدلا من ذلك، وكان يميل بدنيا ضخ حقنة للسماح للتسوية من الجسيمات في اتجاه منفذ حقنة، مما يؤدي إلى تركيز عال من الجسيمات خلال الفترة السابقة.
فئة يظهر = "jove_content"> على تشغيل تجريبي يدل على الحاجة إلى الجسيمات السليم وتركيزات الخلية في الشكل 4. بدون ترتيب كامل، يتم تغليف الجماعات المحلية من أجل الجسيمات، ولكن العديد من قطرات دون الجزيئات. رسم بياني يبين كفاءة التغليف انخفض لتغليف المطلوب اثنين من الجسيمات.
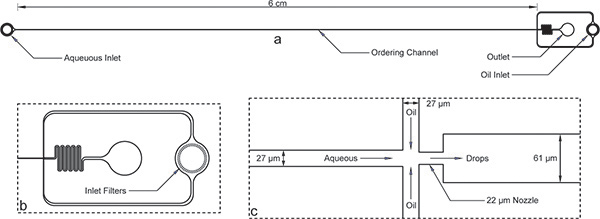
الشكل 1. جهاز تغليف. أ) الجهاز بشكل عام مع مداخل، مخرج، وطويلة قناة يأمر. ارتفاع الجهاز هو 52 ميكرون، وعرض القناة يأمر هو 27 ميكرون. ب) كلاهما مائي ومداخل النفط لديها مرشحات الحطام كبير مع وجود ثغرات في النظام من عرض القناة طلب للرأي الموسع لمدخل النفط. ج) وجهة نظر فوهة الموسع تظهر الاعراض على قدم المساواة قناة من 27 ميكرون للقنوات المائية والنفطية، تليها انكماش فوهة من 22 ميكرون، وتوسع مفاجئ لقناة ميكرومتر أوسع 61.لاحظ أن تم التحقق من أبعاد الجهاز هو موضح هنا باستخدام profilometer بعد الدقيقة وتختلف قليلا من أبعاد رمزية على القناع. الصورة الحقيقية للقناة بسهولة وفوهة متاحة على الانترنت و الرقم الإضافي 1 . في ملف أوتوكاد قناع كما أدرجت على الانترنت كملحق لهذا المخطوط.
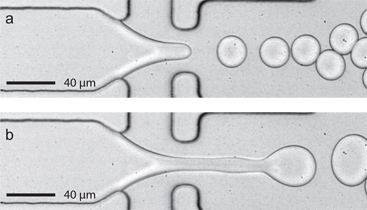
الشكل 2. التخلفية ليقطر على انتقال النفث باستخدام أوسع جهاز (80 ميكرومتر واسعة × 22 ميكرون عالية). أ) على معدل ثابت FC-40 التدفق (Q النفط = 45 ميكروليتر / دقيقة)، ثابت تشكيل انخفاض يحدث في 10 كيلوهرتز باستخدام معدل تدفق مائي عبد القدير س = 8 ميكروليتر / دقيقة. كما يزداد ببطء في معدل تدفق مائي إلى 10 & Mيتم تشغيل لتر / دقيقة، النفث من تيار مائي سائل، ش. ب) عندما يتم إرجاع معدل التدفق إلى 8 ميكروليتر / دقيقة النفث لا يزال مستمرا. لاحظ أنه يمكن تشكيل ثابت انخفاض إعادة تأسيس من قبل التوقف لفترة وجيزة مضخة تدفق مائي (وقفة 1 الثاني هو نموذجي).
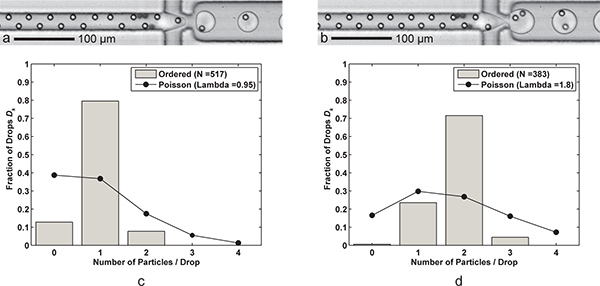
الشكل 3. التغليف واحدة، وضعف الجسيمات. تشكيل قطرة) مع خلية واحدة من كل قطرة ماء (س زيت = 60 ميكروليتر / دقيقة، عبد القدير س = 9 ميكرولتر / دقيقة) مع انخفاض معدل جيل من 6،1 كيلو هرتز، ومتوسط حجم قطرة 24.4 PL، والكفاءات القبض على وحيد الخلية D ك = 79.5٪ و ك ف = 83.7٪ (λ = 0.95) للحصول على حجم العينة ن د = 517 قطرات و ن ع = 491 جزيئات تشكيل قطرة. ب) مع اثنين من الخلايا كل قطرة ماء يتم تحقيق ذلك ببساطة عن طريق خفض معدل تدفق FC-40 س النفط إلى 30 μ لتر / دقيقة. وتشكل أكبر (39.8 PL) قطرات بمعدل 3.8 كيلو هرتز مع كفاءة القبض على اثنين من خلية D ك = 71.5٪ و ك ف = 79.5٪ (λ = 1.80) للحصول على حجم العينة ن د = 383 قطرات و n ع = 689 الجسيمات. CD) اثنين من رسوم بيانية مقارنة الكفاءة الجسيمات انخفاض التغليف D ك من أمر واحد والتغليف المزدوج الجسيمات مع إحصاءات بواسون (التغليف عشوائي). لاحظ أن لكلتا الحالتين، والمباعدة بين الجسيمات في اتجاه تدفق حوالي 17-18 ميكرومتر للجسيمات، أمرت تماما بالتناوب. أشرطة الفيديو تظهر تكميلية على حد سواء التغليف واحد ومزدوجة الجسيمات على شبكة الإنترنت. انقر هنا لعرض الفيلم 3A إضافي . انقر هنا لعرض الفيلم 3B إضافي .
الحمار = "jove_content"> 
الشكل 4. التركيز تؤثر بشكل كبير في كفاءة التغليف. أ) وبما أن انخفاض تركيز، وطلب كامل لا يحدث، وبالتالي "ثغرات" في قطارات في الظهور، وترك بعض قطرات مع عدد أقل من جزيئات المتوقعة. ب) رسم بياني يبين تناقص كفاءة ( D ك = 55.9٪، ف ك = 70.9٪) لمدة الجسيمات التغليف نتيجة لانخفاض قيمة λ = 1.57 حيث هناك ما يقرب من العديد من الجسيمات واحد كما ان هناك قطرات المزدوج الجسيمات قطرات. هذه النتائج شخصية من النفط س = 30 ميكروليتر / دقيقة، وعبد القدير س = 9 ميكرولتر / دقيقة، والظروف تدفق بنفس الشكل ل3B. فيديو ممثل إضافي على شبكة الإنترنت. انقر هنا لعرض إضافي 4 الفيلم .
Discussion
على الرغم من درجات عالية نسبيا من الطلب، وليس كل قطرات تحتوي على عدد مناسب من الجزيئات أو الخلايا. ويمكن احتساب كفاءة التغليف وعدد الخلايا أو الجزيئات التي أصبحت مغلفة في قطرات مع الاشغال المطلوبة مقسوما عددهم الإجمالي. ويمكن الحصول على هذه البيانات الخام إما من آلي?...
Disclosures
JE هو المخترع على براءة اختراع في انتظار بناء على التكنولوجيا المستخدمة في هذه المخطوطة.
Acknowledgements
نشكر تقنيات رايندانس لعينة من PFPE PEG-السطحي المستخدمة في هذه الدراسة، ونحن نشكر الموارد BioMEMS مركز (محمد الحبر، مدير) للرقاقة السيليكون قالب يستخدم لإنشاء قناة PDMS المقلدة.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| اسم كاشف | شركة | فهرس العدد | تعليقات |
| أوتوكاد | اوتوديسك | ||
| قناع الشفافية | Fineline التصوير المؤتمر الوطني العراقي. | ||
| SU-8 الواقي الضوئي | MicroChem | 2050 | |
| Dektak Profilometer | Veeco | ||
| طبق بتري | دينار بحريني الصقر | 351058 | |
| PDMS كيت سيليكون إلاستومر | شركة داو كورنينج | Sylgard 184، عدد المواد (240) 4019862 | |
| فراغ المجفف | Jencons | 250-030 | |
| فراغ مضخة | الكاتيل فراغ التكنولوجيا | 2010 C2 | |
| فراغ منظم | كول، Parmer | EW-00910-10 | |
| فرن | الحرارية العلمية | ليندبرج الأزرق M، OV800F | |
| خزعة لكمة، 0.75 ملم | هاريس | أحادي النواة 15072 | |
| مختبر كورونا المفاوض | الكهربائية ومنتجات شركة تكنيك | BD-20AC، SKU 12051A | |
| زجاج الشرائح | الذهب الختم | 3010 | |
| Aquapel | اندستريز | استراتيجية بديلة | |
| المجهرية البوليسترين، 9.9 ميكرون | الحرارية | G1000 | |
| OptiPrep | سيغما الدريخ | D1556 | لم يثبت |
| Luer لوك الحقن | دينار بحريني | 1 مل: 309628 3 مل: 309585 | |
| FC-40 النفط الفلوروكاربون | شركة 3M | سيجما ألدريتش، F9755 | |
| PFPE PEG-Fluorosurfactant | رايندانس تقنيات | ||
| ضوء المعدنية النفط | كيماويات برس تراست أوف إنديا عملية | 08042-47-5 | استراتيجية بديلة |
| الزيوت المعدنية للتوتر السطحي | Evonik غولدشميت شركة | أبي EM 90 | استراتيجية بديلة |
| Tygon الأنابيب البلاستيكية | SmallParts | TGY-010 | |
| 30 المقياس Luer لوك الحقنة إبرة، 1/2 " | SmallParts | NE-301PL-C | |
| مجهر مقلوب | كارل زايس التصوير | محوري Observer.Z1 | |
| ارتفاع سرعة الكاميرا | رؤية بحوث | شبح V310 | |
| مضخات المحاقن (2) | Chemyx المؤتمر الوطني العراقي. | رابطة 3000 | |
| سيليكون النفط | داو كورنينج | 200 السوائل، 10 سنتيستوك | اختياري للتخزين مستحلب |
References
- Zagnoni, M., Lain, G. L. e., Cooper, J. M. Electrocoalescence mechanisms of microdroplets using localized electric fields in microfluidic channels. Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids. 26, 14443-14449 (2010).
- Niu, X. Z., Gielen, F., Edel, J. B., deMello, A. J. A microdroplet dilutor for high-throughput screening. Nat. Chem. 3, 437-442 (2011).
- Vincent, M. E., Liu, W., Haney, E. B., Ismagilov, R. F. Microfluidic stochastic confinement enhances analysis of rare cells by isolating cells and creating high density environments for control of diffusible signals. Chemical Society reviews. 39, 974-984 (2010).
- Huebner, A. Quantitative detection of protein expression in single cells using droplet microfluidics. Chemical communications. , 1218-1220 (2007).
- Love, J. C., Ronan, J. L., Grotenbreg, G. M., van der Veen, A. G., Ploegh, H. L. A microengraving method for rapid selection of single cells producing antigen-specific antibodies. Nature biotechnology. 24, 703-707 (2006).
- Bradshaw, E. M. Concurrent detection of secreted products from human lymphocytes by microengraving: Cytokines and antigen-reactive antibodies. Clin. Immunol. 129, 10-18 (2008).
- Liu, W. S., Kim, H. J., Lucchetta, E. M., Du, W. B., Ismagilov, R. F. Isolation, incubation, and parallel functional testing and identification by FISH of rare microbial single-copy cells from multi-species mixtures using the combination of chemistrode and stochastic confinement. Lab on a chip. 9, 2153-2162 (2009).
- Boedicker, J. Q., Li, L., Kline, T. R., Ismagilov, R. F. Detecting bacteria and determining their susceptibility to antibiotics by stochastic confinement in nanoliter droplets using plug-based microfluidics. Lab on a chip. 8, 1265-1272 (2008).
- Koster, S. Drop-based microfluidic devices for encapsulation of single cells. Lab on a chip. 8, 1110-1115 (2008).
- Kelly, R. T., Page, J. S., Marginean, I., Tang, K., Smith, R. D. Dilution-free analysis from picoliter droplets by nano-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 48, 6832-6835 (2009).
- Hong, J., deMello, A. J., Jayasinghe, S. N. Bio-electrospraying and droplet-based microfluidics: control of cell numbers within living residues. Biomedical materials. 5, 21001 (2010).
- Edd, J. F. Controlled encapsulation of single-cells into monodisperse picolitre drops. Lab on a chip. 8, 1262-1264 (2008).
- Anna, S. L., Bontoux, N., Stone, H. A. Formation of dispersions using "flow focusing" in microchannels. Applied Physics Letters. 82, 364 (2003).
- Utada, A., Fernandez-Nieves, A., Stone, H., Weitz, D. Dripping to Jetting Transitions in Coflowing Liquid Streams. Physical Review Letters. 99, (2007).
- Chabert, M., Viovy, J. L. Microfluidic high-throughput encapsulation and hydrodynamic self-sorting of single cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 105, 3191-3196 (2008).
- Segrí, G., Silberberg, A. Radial Particle Displacements in Poiseuille Flow of Suspensions. Nature. 189, 209-210 (1961).
- Carlo, D. D. i. Inertial microfluidics. Lab on a chip. 9, 3038-3046 (2009).
- Carlo, D. D. i., Edd, J., Humphry, K., Stone, H., Toner, M. Particle Segregation and Dynamics in Confined Flows. Physical Review Letters. 102, (2009).
- Humphry, K. J., Kulkarni, P. M., Weitz, D. A., Morris, J. F., Stone, H. A. Axial and lateral particle ordering in finite Reynolds number channel flows. Physics of Fluids. 22, 081703 (2010).
- Lee, W., Amini, H., Stone, H. A., Carlo, D. D. i. Dynamic self-assembly and control of microfluidic particle crystals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107, 22413 (2010).
- Duffy, D. C., McDonald, J. C., Schueller, O. J. A., Whitesides, G. M. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane. Anal. Chem. 70, 4974-4984 (1998).
- Kotz, K., Cheng, X., Toner, M. PDMS Device Fabrication and Surface Modification. J. Vis. Exp. (8), e319 (2007).
- Haubert, K., Drier, T., Beebe, D. PDMS bonding by means of a portable, low-cost corona system. Lab on a chip. 6, 1548-1549 (2006).
- Hatch, A. C. 1-Million droplet array with wide-field fluorescence imaging for digital PCR. Lab on a chip. , 3838-3845 (2011).
- Holtze, C. Biocompatible surfactants for water-in-fluorocarbon emulsions. Lab on a chip. 8, 1632-1639 (2008).
- Garstecki, P., Stone, H., Whitesides, G. Mechanism for Flow-Rate Controlled Breakup in Confined Geometries: A Route to Monodisperse Emulsions. Physical Review Letters. 94, (2005).
- Garstecki, P., Fuerstman, M. J., Stone, H. A., Whitesides, G. M. Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction-scaling and mechanism of break-up. Lab on a chip. 6, 437-446 (2006).
- Nie, Z. Emulsification in a microfluidic flow-focusing device: effect of the viscosities of the liquids. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics. , (2008).
- Holt, D. J., Payne, R. J., Chow, W. Y., Abell, C. Fluorosurfactants for microdroplets: interfacial tension analysis. Journal of colloid and interface science. 350, 205-211 (2010).
- Holt, D. J., Payne, R. J., Abell, C. Synthesis of novel fluorous surfactants for microdroplet stabilisation in fluorous oil streams. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 131, 398-407 (2010).
- Hatch, A. C., Fisher, J. S., Pentoney, S. L., Yang, D. L., Lee, A. P. Tunable 3D droplet self-assembly for ultra-high-density digital micro-reactor arrays. Lab on a chip. 11, 2509-2517 (2011).
- Baret, J. C. Surfactants in droplet-based microfluidics. Lab on a chip. 12, 422-433 (2012).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved