需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Method Article
一种制备浸渍接枝胺基二氧化硅复合材料的合成方法
摘要
这项工作旨在促进将胺化化合物浸渍或接枝到二氧化硅基质上的标准化技术的发展,这些技术通常在文献中被广泛描述。将详细讨论溶剂、底物、胺的具体用量以及其他重要实验参数的值。
摘要
最近,通过使用碳捕获材料作为点源或直接空气捕获 (DAC) 方法,在减少或减轻 CO2 排放方面做出了重大努力。这项工作的重点是用于DAC的胺官能团化CO2 吸附剂。这些材料具有低再生能耗和高吸附能力,因此具有去除 CO2 的前景。将胺类掺入多孔基材中结合了胺类对 CO2 的亲和力以及多孔基材的大孔体积和表面积的优点。胺基CO2 吸附剂的制备常用方法有三种,具体取决于胺种类、材料载体和制备方法的选择。这些方法是浸渍、接枝或化学合成。二氧化硅是基板材料的普遍选择,因为它具有可调节的孔径、耐湿性、温度稳定性以及在 DAC 应用中吸附低浓度 CO2 的能力。本文描述了浸渍和接枝胺-二氧化硅复合材料的典型合成方法和主要属性。
引言
过去几十年来,人为的二氧化碳排放被广泛认为是驱动温室气体效应的主要因素,因此也是相关的气候变化1,2,3,4。CO2 捕获有两种通用方法,点源和直接空气捕获。50 多年来,湿法洗涤 CO 2 捕集技术一直被用于行业内的点源捕集,以减少 CO2 排放 5,6。这些技术基于液相胺,液相胺在干燥条件下与 CO2 反应形成氨基甲酸酯,在水存在下形成碳酸氢盐7,8,见图 1。在大点(工业)源利用碳捕获和封存的主要原因是为了防止大量 CO2 的进一步释放,从而对大气中 CO2 的总浓度产生中性影响。然而,点源碳捕集系统存在一些缺点,例如设备腐蚀、溶剂降解和再生的高能源需求9.直接空气捕获 (DAC) 不仅能减少排放,还有助于从大气中去除 CO2。去除现有的二氧化碳对于限制持续的气候变化是必要的。 DAC 是一种新兴方法,必须解决在大气条件(400 至 420 ppm)中去除低浓度 CO 2 的困难,在各种不同的环境条件下运行,并满足对可多次重复使用的具有成本效益的材料的需求 1,2,3 .需要大量工作来确定满足这些要求的材料,这将加速DAC的采用并提高其经济可行性。最重要的是,需要就测量的关键参数建立社区共识,这对于开发基准材料至关重要。
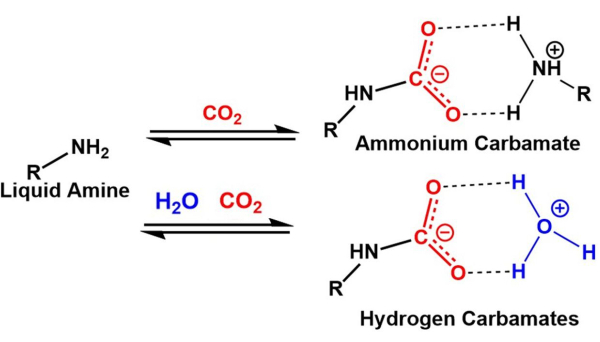
图 1:预期的液胺吸附剂 CO2 捕获机理示意图。 顶部反应在干燥条件下,底部反应在水分存在下。 请点击这里查看此图的较大版本.
为了弥补这些缺点,对新型多孔材料技术的大量研究和开发产生了一系列有前途的材料,这些材料有可能被用作DAC的捕获材料或基板。此类材料的一些实例包括介孔二氧化硅物种 10、11、12、13、沸石 14、15、活性炭 16、17 和金属有机框架 18。许多固体负载的胺吸附剂还显示出更高的耐水性,这是通过DAC方法去除CO2的重要考虑因素。对于 DAC 应用,研究人员必须考虑潮湿/干燥的环境条件、热/冷温度以及大气中整体稀薄的 CO2 浓度。在各种基材中,二氧化硅因其孔径可调、表面功能化能力和大表面积而被普遍使用1,2,3。本文描述了浸渍和接枝胺-二氧化硅复合材料的典型合成程序和主要特征(图2)。直接合成,即材料由基质和胺两种成分原位制成,是另一种常用的方法2.
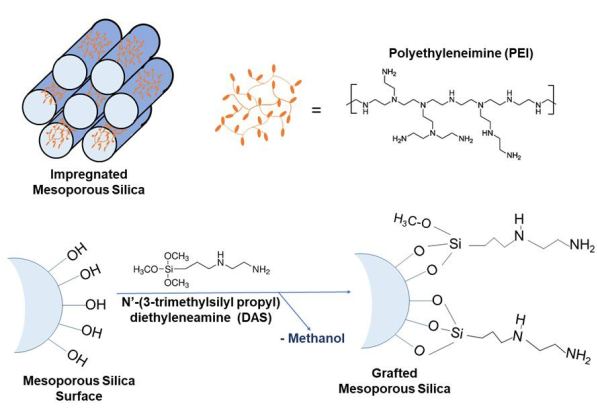
图 2:浸渍示意图。 PEI和二氧化硅基质通过扩散在甲醇中的混合(上图)和通过共价系留法接枝的胺-二氧化硅复合材料(下图)。 请点击这里查看此图的较大版本.
浸渍是一种通过范德华力和胺与二氧化硅表面之间的氢键将胺物理吸附到表面(在本例中为多孔二氧化硅介质)上的方法,见 图2。通常使用乙醇和甲醇等溶剂来促进分子扩散到基材的多孔结构中。还可以加热溶液以增加高摩尔质量多胺的溶解度,从而增加胺在孔内渗透的均匀性。在浸渍材料的情况下,引入二氧化硅基材的胺量由胺的初始量和基材的表面积决定。如果引入的胺量超过二氧化硅基材的可用表面积,则胺类将在其表面团聚。这种团聚是显而易见的,因为浸渍材料看起来具有凝胶状涂层,通常是黄色的,而不是预期的白色和粉末状外观1。在众多类型的胺基固体吸附剂中,聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)和四乙烯五胺(TEPA)因其高稳定性和高氮含量而应用最广泛20。对于物理浸渍体系,胺的理论负载量可以根据基材的预加权量和胺的密度计算得出。物理浸渍的明显优势在于制备它的合成程序简单明了,并且由于二氧化硅基底的高孔隙率,有可能产生大量胺含量。相反,胺在二氧化硅中的稳定性是有限的,因为胺和二氧化硅载体之间没有共价键。因此,经过多次循环的CO2 吸收和通过加热或蒸汽再生后,胺可以从孔隙中浸出。尽管存在这些缺点,但用于DAC的这种材料的实施对于从大气中去除CO2 具有很大的希望。
制备DAC材料的另一种选择是接枝。接枝是一种通过化学反应将胺固定在多孔二氧化硅基底上的方法,如图2所示。该反应通过氨基硅烷与表面的硅醇官能团反应进行,从而产生共价键。因此,二氧化硅基底表面官能团的数量影响接枝胺密度21,22。与胺浸渍吸附剂相比,化学接枝方法具有较低的CO2吸附能力,这主要是由于胺负载量低21。相反,化学接枝胺由于其共价结合结构而具有更高的热稳定性。这种稳定性可用于材料的再生,因为吸附剂(如接枝二氧化硅)被加热和加压以去除捕获的 CO2 以供重复使用,从而节省材料和成本。在典型的合成过程中,将介孔二氧化硅底物分散在溶剂(例如无水甲苯)中,然后加入氨基硅烷。然后洗涤所得样品以除去未反应的氨基硅烷。据报道,氨基硅烷密度的改善是通过加水实现的,特别是用SBA-15,以扩大孔径23。本文将要描述的嫁接程序使用湿敏技术。因此,不会使用额外的水。接枝氨基硅烷材料在DAC中的应用前景广阔,因为它们在CO2吸附和解吸过程中具有预期的稳定性。然而,这种方法的主要缺点包括这些材料的反应/制备复杂,导致成本增加,以及它们的整体 CO2 吸附能力较低,这意味着需要更大的数量。
总体而言,许多先前研究的结果表明,底物的结构和胺相关的修饰对吸附性能有重大影响,具体研究利用透射电子显微镜 (TEM) 和准弹性中子散射 (QENS) 等技术来充分表征这些材料24,25.换句话说,基材的结构特性(例如孔隙率和表面积)决定了胺负载量,因此增加这些参数可以提高 CO2 容量24,25。对衬底材料和制备工艺的优化和设计的持续研究对于开发高性能DAC吸附剂至关重要。这项工作的目的是为浸渍和接枝胺合成提供指导,以期促进合成技术的透明度。在文献中,并不总是描述溶剂、底物和胺含量的具体细节,因此很难理解实验负载量与胺-二氧化硅复合材料定量测量之间的相关性。本文将提供确切的加载量和实验程序的详细描述,以更好地促进这些类型的比较。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
研究方案
注意: 与本节中使用的设备、仪器和化学品相关的详细信息可在 材料表中找到。
1. 用摩尔质量为 800 g/mol 的聚乙烯亚胺浸渍二氧化硅 (PEI 800)
- 反应的制备
- 在该反应中使用无水甲醇作为溶剂。它的沸点低;因此,它的挥发性有利于以后在较低温度下去除。
注:无水溶剂很重要,因为水可以防止PEI 800进入二氧化硅载体的孔隙。另一种常用的溶剂是乙醇,其沸点较高,需要更长的干燥时间和更高的干燥温度。 - 使用公式 1 计算胺的质量分数 (%),其中 m 胺 =胺 的质量,m 二氧化硅 = 所用二氧化硅 的质量。
公式 1: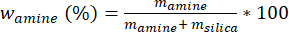
- MCM-41 二氧化硅中胺(w胺)的质量分数为 59.9%(750 毫克胺和 500 毫克二氧化硅)。每 1 g 胺,使用 10 mL 无水甲醇。这样做是为了让整体混合物成为稀浆料。这些计算量将被归类为实验量(w amine_exp),并针对每种合成方法(例如,w amine_exp_imp(浸渍)和 w amine_exp_graft(嫁接))进一步分类。
- 为确保所有玻璃器皿没有水分,请在使用前将它们放入 140 °C 的烤箱中至少 1 小时。
- 在该反应中使用无水甲醇作为溶剂。它的沸点低;因此,它的挥发性有利于以后在较低温度下去除。
- 二氧化硅载体的制备
注:MCM-41二氧化硅是该工艺中使用的固体基质。由于MCM-41是吸附剂二氧化硅,因此有望从大气中或制造过程中吸附水。- 干燥 MCM-41 二氧化硅,以确保没有水吸附到其孔隙中。将所需量的二氧化硅放入玻璃培养皿中,用刺破的铝箔覆盖,然后将其放入真空烘箱中。
- 首先,施加真空(通常小于 3 kPa,根据每个单独的真空系统而变化),然后将烤箱设置为约 110 °C 的温度以确保除水。在进行合成之前,执行此步骤至少2小时。
- 浸渍方法
- 使用干净、干燥的实验室刮刀,将所需量(750mg)的聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)转移到反应容器中(在这种情况下,为35mL干燥小瓶)。运输时盖上反应容器的盖子。
- 将反应容器转移到化学通风橱中,将其夹紧或固定在通风橱内,然后将其放在搅拌板上。取下反应容器的盖子。
- 将干净、干燥的搅拌棒放入反应容器中。
注意:使用搅拌棒将确保均匀混合,可以使溶液搅拌更长时间,促进更好的分散,并且可以在不需要手动混合的情况下安全加热反应。 - 使用移液管,从量筒中加入 7.5 mL 无水甲醇(每 1 g 胺使用 10 mL 甲醇)。打开搅拌板。让溶液混合15分钟,以确保PEI完全溶解并均匀分散在溶剂中。
注意:混合后,溶液将呈现清澈/透明,表示聚合物完全溶解。 - 使用干净、干燥的实验室刮刀将所需量(500 mg)的预干燥二氧化硅(在本例中为 MCM-41)转移到称量纸上。将二氧化硅转移到通风橱内的反应容器中。
注意:该实验负载量的胺将与热重分析(TGA)的实际测量量相匹配。
注意:吸入二氧化硅粉尘会损害肺组织。建议在使用二氧化硅基材时佩戴 N95 呼吸器(有关个别实验室的适当选择,请参阅当地安全指南)并在化学排气罩中工作。这些二氧化硅材料通常表现出"静态粘附"特性,并且很容易分散在通风橱内。快速执行此步骤,以避免水分从空气中吸附到二氧化硅上。 - 如果需要,添加额外的甲醇以将二氧化硅冲洗到容器中,以确保完全暴露于溶液中的PEI。混合物将以浆状形式出现;请参阅 图 3。
- 将容器置于 40 °C 至 50 °C 的硅油浴、加热块或加热罩中,以确保 PEI 的完全溶解度、均匀混合,并促进胺负载到多孔二氧化硅中。
注意:在浸渍过程中并不总是使用高温,文献表明其他温度在室温 (RT)1,2,3 下混合。在该协议中,加热用于促进均匀混合。 - 确保搅拌棒均匀混合溶液。让溶液在加热下搅拌约1小时。
注:根据反应大小和个人偏好,反应容器的选择可能会有所不同。因此,反应的加热方式(油浴、加热块或加热罩)可能会有所不同,以最好地适应反应容器的选择。 - 将反应容器从热源中取出,使其冷却至室温,同时仍在搅拌。完全冷却后,停止搅拌并取下搅拌棒。
- 将装有样品的容器置于舒伦克管路上的真空下(通常为 <3 kPa,缓慢降低压力以避免碰撞)。
- 让反应容器保持在舒伦克管路上,直到所有溶剂明显去除。然后,将样品转移到不同的储存容器中,例如玻璃培养皿。
- 然后将样品放入真空烘箱中,打开真空(通常为<1.3 kPa),然后将烘箱设置为约70°C。 让样品在真空下干燥至少18小时,以确保已除去足够量的甲醇。
注意:在将所选容器放入真空烘箱之前,请考虑溶剂的液位,因为样品和溶液可能会因真空而不规则地离开容器。通常,在将样品/容器放入真空烘箱之前,样品/容器中残留的溶剂不超过 1 mL。 - 干燥后,物料呈白色粉末状。将其存放在无湿气、无空气的环境中,直到需要进一步使用。
注意: 此步骤可以在真空干燥器或手套箱中进行,该干燥器或手套箱是在无空气和无湿气的环境中制备的。有关预期的最终产品外观,请参见 图 4 。
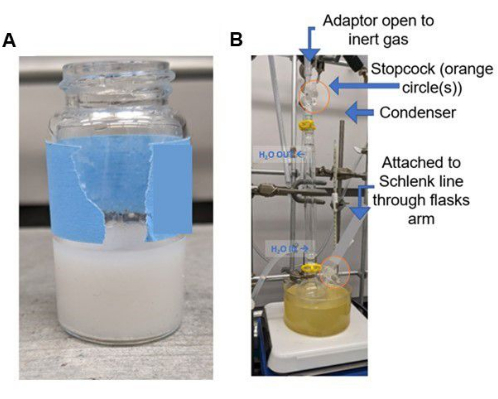
图3:反应的代表性图像。 (A) PEI 浸渍期间 PEI 二氧化硅浆料(在甲醇中)的照片,然后转移到加热块中,以及 (B) 加热 6 小时后 DAS 接枝装置完成。 请点击这里查看此图的较大版本.
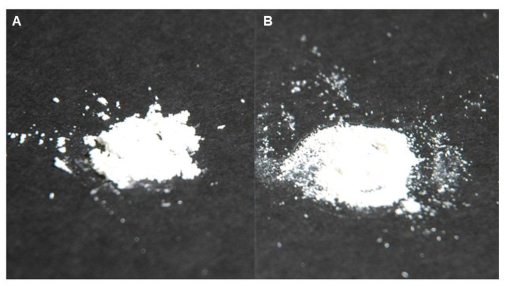
图4:干燥后最终产品的代表性外观。 (A) PEI浸渍在wamine_exp_imp = 59.9 %。(B) 接枝 DAS 的 wamine_exp_das = 90.0 %。 请点击这里查看此图的较大版本.
2.N'-(3-三甲基硅丙基)二乙烯胺(DAS)湿法接枝二氧化硅的制备
- 溶液的制备
- 在该反应中使用无水甲苯。它具有高沸点(110°C),因此可以进行高温混合。氨基硅烷(N'-(3-三甲基硅丙基)二乙烯胺(DAS)在这种介质中极易溶解。
注:在无水条件下进行该反应很重要,因为水可以与氨基硅烷相互作用,从而改变其与二氧化硅表面键合的性质。使用的无水甲苯带有隔膜盖。因此,将使用气密注射器将溶剂转移到反应容器中。每 1 g DAS,使用 5 mL 甲苯。因此,对于 5 mL DAS (1.028 g/mL),使用 25 mL 溶剂。
- 在该反应中使用无水甲苯。它具有高沸点(110°C),因此可以进行高温混合。氨基硅烷(N'-(3-三甲基硅丙基)二乙烯胺(DAS)在这种介质中极易溶解。
- 二氧化硅载体的制备
- 使用上述步骤1.2中的程序干燥二氧化硅。
- 硅氧烷的制备
- 氨基硅烷对水分敏感,因为水的存在会导致聚合。因此,将反应作为无水分反应处理。将 DAS 储存在带隔盖的瓶中,并使用气密注射器进行转移。
注意:氨基硅烷存在许多健康风险和危害。在开始实验之前,请重新view 安全数据表,并遵守所有推荐的安全预防措施。
- 氨基硅烷对水分敏感,因为水的存在会导致聚合。因此,将反应作为无水分反应处理。将 DAS 储存在带隔盖的瓶中,并使用气密注射器进行转移。
- 接枝二氧化硅方法
- 需要注意的是,与浸渍方法不同,氨基硅烷在二氧化硅基底上的接枝氮含量预计较低。因此,在该反应中,通过实验将 wamine_exp_graft = DAS 的 90.0% 负载量增加氨基硅烷在二氧化硅载体上定位硅醇基团并成功共价键合的概率。
- 使用前在烤箱中干燥所有玻璃器皿至少 2 小时,以确保表面无潮。
- 用所需量(500mg)的二氧化硅支持物(MCM-41)填充装有磁力搅拌棒的圆底舒伦克烧瓶。
- 将橡胶隔膜插入反应容器中,并在舒伦克管路上循环反应容器三次,以去除空气和水分。为此,将反应容器的旋塞阀打开至真空约 30 秒,关闭旋塞阀,切换到惰性气体(N 2 或 Ar2)约 30 秒,然后重新打开旋塞阀。反应容器循环后,保持惰性气体环境以进行以下程序步骤。
- 将一行惰性气体插入隔膜盖(确保密封)瓶中,然后使用气密注射器并用惰性气体吹扫注射器,然后除去所需量的无水甲苯(在这种情况下,25 mL)。
注: 有关带有惰性气体入口和气密注射器的密封容器的图像,请参见 图 5 。在转移之前将弯头(蓝色箭头)放入管中以防止任何滴落。这种技术适用于任何需要气密注射液体时。溶剂的用量由氨基硅烷的添加量决定。每1 mL氨基硅烷,使用5 mL无水甲苯,以保证溶解度。重要的是用 25 mL 甲苯填充注射器,然后将针头抬高到瓶内的溶液水平以上。然后从甲苯上方的顶部空间抽出一些惰性气体,然后再从甲苯容器中取出注射器。 - 在开始此步骤之前,确保反应容器内的磁力搅拌棒搅拌平稳。通过刺穿反应容器上的隔膜并将甲苯释放到容器中,转移气密注射器中所含的无水甲苯。
- 用惰性气体取下针头。
- 用氨基硅烷(4.8mL DAS)重复相同的步骤(2.4.6至2.4.8)。
- 使用适配器将舒伦克管线的管线连接到使用真空润滑脂的冷凝器。用聚四氟乙烯 (PTFE) 胶带包裹冷凝器设备的底部(此步骤确保不会被油脂污染)。然后将冷凝器装置连接到圆底舒伦克烧瓶上,以准备玻璃器皿设置;请参阅 图 3。
- 将"冷"水管连接到冷凝器并打开它。
注意: "冷"水(低于 23 °C)将进入冷凝器底部,然后从顶部进入水槽。管子将被固定(用电线、扎带或钢制软管夹),以避免连接点漏水。 - 将反应容器放入硅油浴或加热块中,或将其置于80°C至100°C之间的加热罩中。 选择此温度有助于促进氨基硅烷 (DAS) 的接枝、均匀混合并促进胺负载。
- 关闭旋塞阀,关闭圆底舒伦克烧瓶上的惰性气体,并使冷凝器上的旋塞阀保持打开状态;参见 图 3B。
注意:执行此步骤是为了防止甲苯上升到靠近设备(舒伦克烧瓶侧臂)的管中,同时由于冷凝器顶部的入口而将反应保持在惰性气氛下;有关此设置,请参见 图 3 。 - 确保搅拌棒均匀混合溶液。加热6小时时搅拌。
- 使用真空过滤捕获滤纸上的固体接枝胺二氧化硅,并用大量无水甲苯冲洗(10 mL 冲洗 3 次)。
- 要进行真空过滤,请为锥形过滤器烧瓶配备臂,以通过软管进行真空抽真空。在开口处放置一个橡胶塞,将 Buchner 漏斗放在橡胶塞的顶部,最后在 Buchner 漏斗中放置一张滤纸。用无水甲苯润湿滤纸。
- 打开真空吸尘器,快速将溶液分配到滤纸上。它有助于在洗涤过程中将无水甲苯倒入滤纸上之前用无水甲苯冲洗反应容器。
- 最终材料在滤纸上显示为白色。使用干净干燥的实验室刮刀从滤纸上去除接枝的硅烷材料,并将其放入小瓶中。
- 用刺破的铝箔盖住小瓶,然后将其放入真空烘箱中。打开真空吸尘器。将烤箱设置为约100°C,并干燥约18小时以除去多余的甲苯。
注意: 材料干燥后呈白色粉末状,并储存在无湿气、无空气的环境中。这可以放在真空干燥器或手套箱中,该干燥器或手套箱是在无空气和无湿气的环境中制备的。最终产品外观见 图 4 。 - 此过程再重复两次(总共 3 次,步骤 2.4.1 - 2.4.16)。
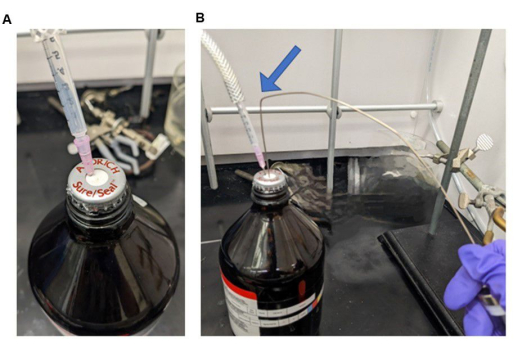
图 5:密封容器的照片。 (A) 带有连接到惰性气体(N 2 或 Ar2)的针头的容器,以及 (B) 连接惰性气体并连接气密注射器的容器,带有"弯曲"针头(蓝色箭头),用于转移而不会泄漏。请点击这里查看此图的较大版本.
3. TGA对二氧化硅复合材料的分析
注:与此测量相关的标准不确定度约为质量± 0.01±%,温度约为 1 °C。
- 利用仪器的 TGA 应用软件,去皮一个空锅。
- 从样品装载区域取出去皮的平底锅,然后将样品添加到平底锅中。将标本放在烤盘中央,至少使用2mg,以确保质量损失的充分解决。将装有试样的平底锅放回装载区域。
- 使用仪器软件,定制程序运行,首先在100%N2环境中在约50°C下平衡5分钟,气体流速为60 mL/min。然后将斜坡设置为2°C/min至5°C/min至1000°C。 标记循环的结束。这些测量值表示为 wamine_TGA,因为它们使用 TGA 评估材料中的真实胺含量。这进一步分类为每种合成方法(例如,w amine_TGA_imp(浸渍法)和wamine_TGA_graft(接枝法))。
注意:对于单个 TGA,流速的具体建议可能有所不同。在为单个实验选择合适的流速之前,请咨询制造商的规格。 - 重复步骤 3.1-3.3 进行任何其他实验运行。
- 将步骤3.1应用于CO2 吸附实验设置。
- 使用仪器软件,自定义程序运行,首先在 100 °C 下平衡 5 分钟,然后以 20 °C/min 的速率升温至 40 °C。 然后,在40°C下等温保持10分钟,然后在N 2中引入5%CO2的混合气体,流速为60mL / min。
- 在这种气体混合物条件下将样品保持在40°C下100分钟。执行此程序以通过重量增加来测量 CO2 吸附。这些测量值表示为 wCO2,因为它们评估材料内的 CO2 吸附。这进一步分类为每种合成方法(例如,w CO2_imp(浸渍法)和wCO2_graft(接枝法))。
- 对于循环研究,使用仪器软件,自定义程序运行,首先打开至 100% N2 气体,等温保持 5 分钟,然后以 20 °C/min 升温至 105 °C,等温线保持 5 分钟。
- 接下来,以10°C / min的速度下降到40°C,等温线保持1分钟,然后释放N 2中5%CO2的混合物,等温线保持35分钟。重复程序步骤 10 次。
- 在软件中,根据需要多次附加此运行以添加额外的循环步骤。确保不要更改平移数,也不要在第一次运行后删除附加运行的重量稳定步骤。这允许用户将多个 10 个周期的运行放在一个方法中。
4. 使用衰减全反射 (ATR) 附件通过傅里叶变换红外光谱 (FTIR) 分析二氧化硅复合材料
注:与该仪器相关的标准不确定度在峰值强度± 1%,波数± 4 cm−1 ,因此,使用不确定度的线性传播,报告曲线中的强度不确定度± 1.4%。
- 用低绒湿巾和甲醇清洁 FTIR-ATR 附件上的窗口(金刚石)。
- 使用软件的基本测量窗口收集背景光谱。
- 使用干净干燥的刮刀,将样品放在FTIR-ATR窗口上。使用ATR压缩探头将样品推入窗口接触。
- 通过按基本测量窗口中的"收集样品"按钮 收集样品 光谱,然后从步骤 4.2 中获得的文件中加载相关的背景。
- 对所有样品重复步骤 4.1 到 4.4。
5. 通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)分析胺浸渍和接枝前后的二氧化硅复合材料
- 小心地将样品铺在碳导电双面胶带上,将粉末状样品安装在铝桩上。体视显微镜通过增加样品扩散的可见性来帮助完成此过程。
- 溅射涂覆每个样品的 5 nm 金钯 (Au-Pd) 导电涂层,以获得最佳成像条件。
- 在高真空(即小于 0.4 mPa,3 x 10−6 torr)下,在双光束场发射 SEM 上浸渍或接枝前后对基底二氧化硅材料的表面形态进行成像。
注:所选的光束能量 (1 keV) 和探头电流(6.3 pA 和 25 pA)参数经过优化,图像清晰,充电、伪影和漂移最小。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
结果
TGA通常用于量化这些材料在二氧化硅表面负载或接枝的胺量。得到的TGA曲线显示,在60 °C至100 °C之间,残留溶剂和水的损失,在衍生物重量(重量%/°C)曲线中显示为第一个峰,胺的损失在衍生物重量曲线(重量%/°C)中显示为第二个峰。对于PEI浸渍的二氧化硅,胺的损失预计将出现在200°C至300°C左右,这是衍生物重量曲线中的第二个峰,而对于DAS接枝二氧化硅,胺的损失预计将出现在350°C至550°...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
讨论
本文中描述的方法旨在提供制备浸渍和接枝胺二氧化硅复合吸附剂的方案。我们记录的程序是基于对文献中报道的技术和我们实验室中改进的技术的回顾。1,2,3.这些材料的制备在二氧化碳去除研究领域中很有用,可以开发或基准测试可用于降低大气(直接空气捕获)或工业过程中(点源捕获)中二氧化碳排放的其他材?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
披露声明
所有作者均未披露任何竞争性利益冲突。本文中使用的程序的完整描述需要识别某些商业产品及其供应商。包含此类信息绝不应被解释为表明此类产品或供应商已获得NIST的认可,或由NIST推荐,或者它们一定是所述目的的最佳材料、仪器、软件或供应商。
致谢
Charlotte M. Wentz 感谢通过 NIST 奖 # 70NANB8H165 获得的资金。Zois Tsinas 希望通过 NIST 奖 # 70NANB22H140 获得资助。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Anhydrous methanol | Sigma-Aldrich | 322415 | Does not come with sure-seal |
| Anhydrous toluene | Sigma-Aldrich | 244511 | Comes with sure-seal |
| Ceramic Stirring Hot Plate | NA | NA | The size, watage, and thermal capabilities of the stirr plate will differ depending on individual lab facilities. |
| Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) | Nicolet i550 series spectrometer | NA | Run on OMNIC standard software |
| Gastight syringe | NA | NA | As long as the gas tight syringe has a PTFE plunger and luer tip, is suited for air sensitive technique and can be used in this protocol. |
| Glass vial | NA | NA | As long as the vial is made if borosilicate glass and has a screw based cap the brand name, size, or general shape does not matter for the protocol. |
| MCM-41 silica | ACS Material | MSM41A01 | Cas no. 7631-86-9 |
| Metal needle | NA | NA | Syringe needles need to be stainless steel. It is recommended to determine length and outerdiameter of needle by what will be transferred using the gas tight syringe. For large quantities of liquid a larger outer diameter will improve transfer rates. |
| N’-(3-trimethylsilyl propyl) diethyleneamine (DAS) | Sigma-Aldrich | 104884 | Comes with sure-seal |
| Polyethyleneimine (PEI) | Sigma-Aldrich | 408719 | Does not come with sure-seal |
| Schlenk round bottom flask | ChemGlass AirFree | NA | As long as the flask is suited for high pressure and temperture but the brand name, size, or general shape does not matter for the protocol |
| Thermogravemetric Anlysis (TGA) | TA Advantage | NA | 550 series from Waters and TA Instruments |
参考文献
- Zhu, X., et al. Recent advances in direct air capture by adsorption. Chemical Society Reviews. 51 (15), 6574-6651 (2022).
- Zhao, P., Zhang, G., Yan, H., Zhao, Y. The latest development on amine functionalized solid adsorbents for post-combustion CO2 Capture: Analysis review. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering. 35 (8), 17-43 (2021).
- Chen, D., Zhang, S., Row, K. H., Ahn, W. -S. Amine-silica composites for CO2 capture: A short review. Journal of Energy Chemistry. 26 (5), 868-880 (2017).
- Nie, L., Mu, Y., Jin, J., Chen, J., Mi, J. Recent developments and considerations issues in solid adsorbents for CO2 capture from flue gas. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering. 26 (11), 2303-2317 (2018).
- Nithyashree, N., Manohara, G. V., Maroto-Valer, M. M., Garcia, S. Advanced high-temperature CO2 sorbents with improved long-term cycling stability. American Chemical Society Applied Material Interfaces. 12 (30), 33765-33774 (2020).
- Song, C., et al. Alternative pathways for efficient CO2 capture by hybrid processes-A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Review. 82, 215-231 (2018).
- Rochelle, G. T. Amine scrubbing for CO2 capture. Science. 325 (5948), 1625-1654 (2009).
- Vaidye, P. D., Kenig, E. Y. CO2-alkanolamine reaction kinetics: A review of recent studies. Chemical Engineering & Technology. 30 (11), 1467-1474 (2007).
- Veawab, A., Tontiwachwuthikul, P., Chakma, A. Corrosion behavior of carbon steel in the CO2 adsorption process using aqueous amine solutions. Industrial & Engineering Chemical Research. 38 (10), 3917-3924 (1999).
- Chen, S., Bhattacharjee, S. Trimodal nanoporous silica as a support for amine-based CO2 adsorbents: Improvement in adsorption capacity and kinetics. Applied Surface Science. 396, 1515-1519 (2017).
- Jiao, J., Cao, J., Xia, Y., Zhao, L. Improvement of adsorbent materials for CO2 capture by amine functionalized mesoporous silica with worm-hole framework structure. Chemical Engineering Journal. 306, 9-16 (2016).
- Guo, X., Ding, L., Kanamori, K., Nakanishi, K., Yang, H. Functionalization of hierarchically porous silica monoliths with polyethyleneimine (PEI) for CO2 adsorption. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials. 245, 51-57 (2017).
- Fatima, S. S., Borhan, A., Ayoub, M., Ghani, N. A. Development and progress of functionalized silica-based adsorbents for CO2 capture. Journal of Molecular Liquids. 338, 116913(2021).
- Cheng, J., Liu, M., Hu, L., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Zhou, J. Polyethyleneimine entwine thermally-treated Zn/Co zeolitic imidazolate frameworks to enhance CO2 adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal. 364, 530-540 (2019).
- Zagho, M. M., Hassan, M. K., Khraisheh, M., Al-Maadeed, M. A. A., Nazarenko, S. A review on recent advances in CO2 separation using zeolite and zeolite-like materials as adsorbents and fillers in mixed matrix membranes (MMMs). Chemical Engineering Journal Advances. 6, 100091(2021).
- Wang, J., Wang, M., Zhao, B., Qiao, W., Long, D., Ling, L. Mesoporous carbon-supported solid amine sorbents for low-temperature carbon dioxide capture. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 52 (15), 5437-5444 (2013).
- Ünveren, E. E., Monkul, B. O., Sarioğlan, S., Karademir, N., Alper, E. Solid amine sorbents for CO2 capture by chemical adsorption: A review. Petroleum. 3 (1), 37-50 (2017).
- Demir, H., Aksu, G. O., Gulbalkan, H. C., Keskin, S. MOF membranes for CO2 capture: Past, present and future. Carbon Capture Science & Technology. 2, 100026(2022).
- Xu, X., Song, C., Andresen, J. M., Miller, B. G., Scaroni, A. W. Novel polyethylenimine-modified mesoporous molecular sieve of MCM-41 type as high-capacity adsorbent for CO2 capture. Energy & Fuels. 16 (6), 1463-1469 (2002).
- Gelles, T., Lawson, S., Rownaghi, A., Rezaei, F. Recent advances in development of amine functionalized adsorbents for CO2 capture. Adsorption. 26 (94), 5-50 (2020).
- Rao, N., Wang, M., Shang, Z., Hou, Y., Fan, G., Li, J. CO2 adsorption by amine-functionalized MCM-41: A comparison between impregnation and grafting modification methods. Energy Fuels. 32 (1), 670-677 (2018).
- Anyanwu, J. T., Wang, Y., Yang, R. T. Amine-grafted silica gels for CO2 capture including direct air capture. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 59 (15), 7072-7079 (2020).
- Anyanwu, J. -T., Wang, Y., Yang, R. T. CO2 capture (including direct air capture) and natural gas desulfurization of amine-grafted hierarchical bimodal silica. Chemical Engineering Journal. 427 (14), 131561(2022).
- Sanz, R., Calleja, G., Arencibia, A., Sanz-Pérez, E. S. Amino functionalized mesostructured SBA-15 silica for CO2 capture: Exploring the relation between the adsorption capacity and the distribution of amino groups by TEM. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials. 158, 309-317 (2012).
- Moon, H. J., et al. Understanding the impacts of support-polymer interactions on the dynamics of poly(ethyleneimine) confined in mesoporous SBA-15. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 144 (26), 11664-11675 (2022).
- Xu, X., Song, C., Andresen, J. M., Miller, B. G., Scaroni, A. W. Preparation and characterization of novel CO2 "molecular basket" absorbents based on polymer-modified mesoporous molecular sieve MCM-41. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials. 62 (1-2), 29-45 (2003).
- Sousa, J. A. R., et al. H2S and H2O combined effect on CO2 capture by amino functionalized hollow microsphere silicas. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 60 (28), 10139-10154 (2021).
- Rim, G., et al. Sub-ambient temperature direct air capture CO2 using amine-impregnated MIL-101(Cr) enables ambient temperature CO2. JACS Au. 2 (2), 380-393 (2022).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。