14.4 : Gravedad entre cuerpos esféricos
Newton's law of gravitation describes the gravitational force between any two point masses. However, for extended spherical objects like the Earth, the Moon, and other planets, the law holds with an assumption that masses of spherical objects are concentrated at their respective centers.
This assumption can be proved easily by showing that the expression for gravitational potential energy between a hollow sphere of mass (M) and a point mass (m) is the same as it would be for a pair of extended spherical solid objects.
Consider a tiny ring of width Rdϕ and mass dM on the surface of a spherical hollow sphere at a distance s from the point mass as shown in Figure 1(a).
The gravitational potential energy between the ring and the point mass (m) is expressed as:
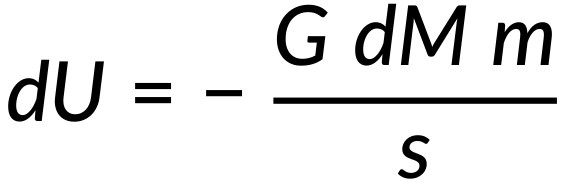
The ratio of the ring's mass to the entire shell's mass is equal to the ratio of the ring's area to the shell's area. Therefore, on simplification, the ring's mass can be expressed as:
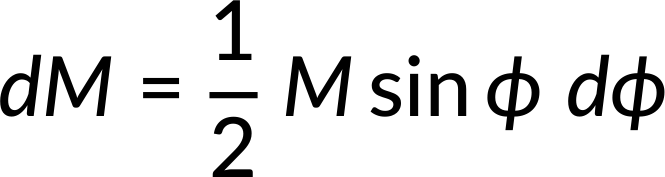
Now, the square of distance (s) can be expressed as the sum of squares of the triangle's other two sides, as seen in Figure 1(b).
Simplifying further and taking differentials on either side,
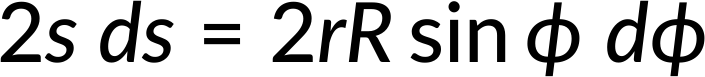
Considering the entire shell, s can vary between r − R and r + R, as seen in Figure 1(c).
Therefore, substituting dM and s in the potential energy equation and integrating within the limits of r − R to r + R, the relation obtained is the potential energy between point masses m and M at a distance r.
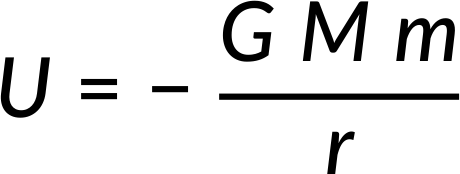
Therefore, the assumption is proven.
Since force is a derivative of potential energy, the assumption holds for gravitational forces between two spherically solid objects like the Earth and the Moon. Therefore, Newton's law of gravitation can be used to determine the gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon, and the Earth and the Sun.
Del capítulo 14:

Now Playing
14.4 : Gravedad entre cuerpos esféricos
Gravitación
8.1K Vistas

14.1 : Gravitación
Gravitación
6.0K Vistas

14.2 : Ley de la gravitación de Newton
Gravitación
12.2K Vistas

14.3 : Gravitación entre masas esféricamente simétricas
Gravitación
816 Vistas

14.5 : Coordenadas de masa reducida: problema aislado de dos cuerpos
Gravitación
1.2K Vistas

14.6 : Aceleración debida a la gravedad en la Tierra
Gravitación
10.4K Vistas

14.7 : Aceleración debida a la gravedad en otros planetas
Gravitación
4.0K Vistas

14.8 : Peso aparente y la rotación de la Tierra
Gravitación
3.5K Vistas

14.9 : Variación en la aceleración debida a la gravedad cerca de la superficie terrestre
Gravitación
2.3K Vistas

14.10 : Energía potencial debida a la gravitación
Gravitación
5.4K Vistas

14.11 : El principio de superposición y el campo gravitatorio
Gravitación
1.3K Vistas

14.12 : Velocidad de escape
Gravitación
5.5K Vistas

14.13 : Órbitas circulares y velocidad crítica para satélites
Gravitación
2.8K Vistas

14.14 : Energía de un satélite en una órbita circular
Gravitación
2.1K Vistas

14.15 : Primera ley de Kepler sobre el movimiento planetario
Gravitación
3.8K Vistas
See More
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados