14.4 : Gravity between Spherical Bodies
Newton's law of gravitation describes the gravitational force between any two point masses. However, for extended spherical objects like the Earth, the Moon, and other planets, the law holds with an assumption that masses of spherical objects are concentrated at their respective centers.
This assumption can be proved easily by showing that the expression for gravitational potential energy between a hollow sphere of mass (M) and a point mass (m) is the same as it would be for a pair of extended spherical solid objects.
Consider a tiny ring of width Rdϕ and mass dM on the surface of a spherical hollow sphere at a distance s from the point mass as shown in Figure 1(a).
The gravitational potential energy between the ring and the point mass (m) is expressed as:
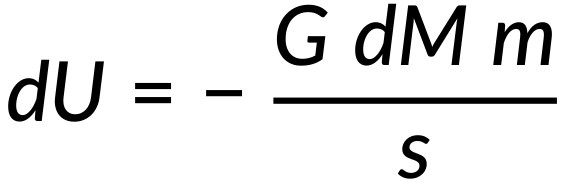
The ratio of the ring's mass to the entire shell's mass is equal to the ratio of the ring's area to the shell's area. Therefore, on simplification, the ring's mass can be expressed as:
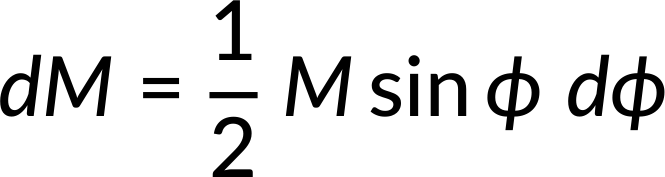
Now, the square of distance (s) can be expressed as the sum of squares of the triangle's other two sides, as seen in Figure 1(b).
Simplifying further and taking differentials on either side,
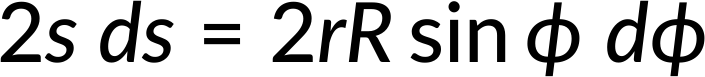
Considering the entire shell, s can vary between r − R and r + R, as seen in Figure 1(c).
Therefore, substituting dM and s in the potential energy equation and integrating within the limits of r − R to r + R, the relation obtained is the potential energy between point masses m and M at a distance r.
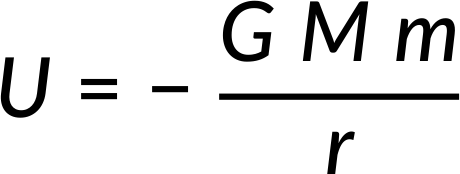
Therefore, the assumption is proven.
Since force is a derivative of potential energy, the assumption holds for gravitational forces between two spherically solid objects like the Earth and the Moon. Therefore, Newton's law of gravitation can be used to determine the gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon, and the Earth and the Sun.
Из главы 14:

Now Playing
14.4 : Gravity between Spherical Bodies
Gravitation
8.3K Просмотры

14.1 : Тяготение
Gravitation
6.2K Просмотры

14.2 : Закон всемирного тяготения Ньютона
Gravitation
12.4K Просмотры

14.3 : Гравитация между сферически симметричными массами
Gravitation
846 Просмотры

14.5 : Координаты приведенной массы: изолированная задача двух тел
Gravitation
1.2K Просмотры

14.6 : Ускорение под действием силы тяжести на Земле
Gravitation
10.5K Просмотры

14.7 : Ускорение из-за гравитации на других планетах
Gravitation
4.1K Просмотры

14.8 : Кажущийся вес и вращение Земли
Gravitation
3.5K Просмотры

14.9 : Изменение ускорения из-за гравитации у поверхности Земли
Gravitation
2.4K Просмотры

14.10 : Потенциальная энергия под действием гравитации
Gravitation
5.4K Просмотры

14.11 : Принцип суперпозиции и гравитационное поле
Gravitation
1.3K Просмотры

14.12 : Вторая космическая скорость
Gravitation
5.6K Просмотры

14.13 : Круговые орбиты и критическая скорость для спутников
Gravitation
2.9K Просмотры

14.14 : Энергия спутника на круговой орбите
Gravitation
2.2K Просмотры

14.15 : Первый закон движения планет Кеплера
Gravitation
3.9K Просмотры
See More
Авторские права © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Все права защищены