14.4 : Gravity between Spherical Bodies
Newton's law of gravitation describes the gravitational force between any two point masses. However, for extended spherical objects like the Earth, the Moon, and other planets, the law holds with an assumption that masses of spherical objects are concentrated at their respective centers.
This assumption can be proved easily by showing that the expression for gravitational potential energy between a hollow sphere of mass (M) and a point mass (m) is the same as it would be for a pair of extended spherical solid objects.
Consider a tiny ring of width Rdϕ and mass dM on the surface of a spherical hollow sphere at a distance s from the point mass as shown in Figure 1(a).
The gravitational potential energy between the ring and the point mass (m) is expressed as:
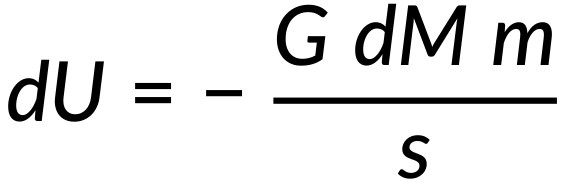
The ratio of the ring's mass to the entire shell's mass is equal to the ratio of the ring's area to the shell's area. Therefore, on simplification, the ring's mass can be expressed as:
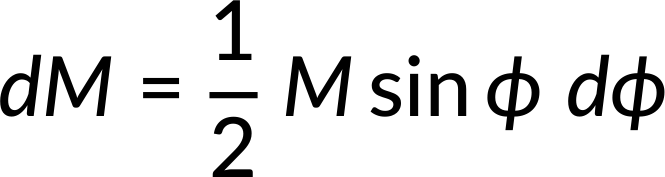
Now, the square of distance (s) can be expressed as the sum of squares of the triangle's other two sides, as seen in Figure 1(b).
Simplifying further and taking differentials on either side,
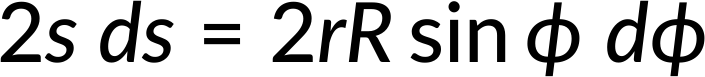
Considering the entire shell, s can vary between r − R and r + R, as seen in Figure 1(c).
Therefore, substituting dM and s in the potential energy equation and integrating within the limits of r − R to r + R, the relation obtained is the potential energy between point masses m and M at a distance r.
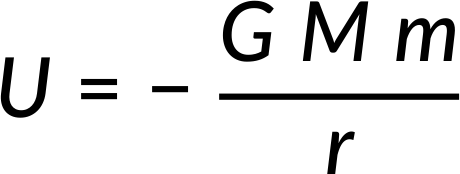
Therefore, the assumption is proven.
Since force is a derivative of potential energy, the assumption holds for gravitational forces between two spherically solid objects like the Earth and the Moon. Therefore, Newton's law of gravitation can be used to determine the gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon, and the Earth and the Sun.
Du chapitre 14:

Now Playing
14.4 : Gravity between Spherical Bodies
Gravitation
8.3K Vues

14.1 : Gravitation
Gravitation
6.3K Vues

14.2 : La loi universelle de la gravitation
Gravitation
12.5K Vues

14.3 : Gravitation entre des masses sphériquement symétriques
Gravitation
854 Vues

14.5 : Coordonnées de masse réduites : problème à deux corps isolés
Gravitation
1.2K Vues

14.6 : La pesanteur terrestre
Gravitation
10.6K Vues

14.7 : La pesanteur sur d'autres planètes
Gravitation
4.2K Vues

14.8 : Rotation de la Terre et poids apparent
Gravitation
3.5K Vues

14.9 : Variation de la pesanteur près de la surface de la terre
Gravitation
2.4K Vues

14.10 : Énergie potentielle gravitationnelle
Gravitation
5.5K Vues

14.11 : Le principe de superposition et le champ gravitationnel
Gravitation
1.3K Vues

14.12 : Vitesse de libération
Gravitation
5.6K Vues

14.13 : Orbites circulaires et vitesse critique des satellites
Gravitation
2.9K Vues

14.14 : Énergie d'un satellite en orbite circulaire
Gravitation
2.2K Vues

14.15 : La première loi de Kepler sur le mouvement des planètes
Gravitation
3.9K Vues
See More