29.14 : Magnetic Vector Potential
In electrostatics, the electric field can be written as the negative gradient of the potential. In magnetostatics, the zero divergence of the magnetic field ensures that the magnetic field can be expressed as the curl of a vector potential. This potential is known as the magnetic vector potential.
Consider an ideal solenoid with n turns per unit length and radius R. If I is the current through the solenoid, the magnetic field inside the solenoid is expressed as the product of vacuum permeability, the number of turns per unit length, and the current. Conversely, the magnetic field outside the solenoid is zero. Considering this, what is the vector potential for an ideal solenoid?
The magnetic flux through the solenoid is given by
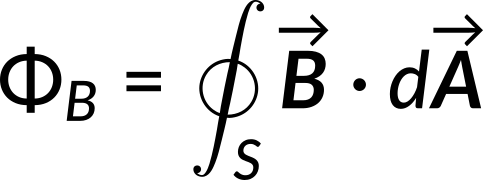
Since the magnetic field equals the curl of the vector potential, the magnetic flux can be rewritten in terms of the vector potential.
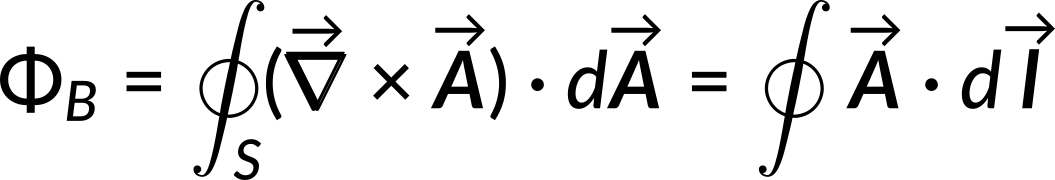
Thus, the line integral of the magnetic vector potential equals the surface integral of the magnetic field.
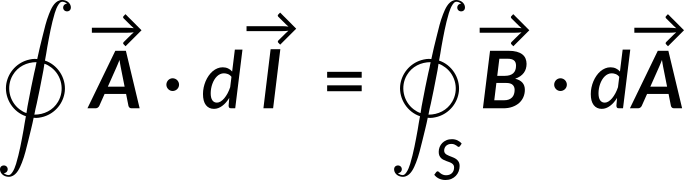
Now consider a circular Amperian loop of radius r inside the solenoid. The magnetic flux through this loop is given by
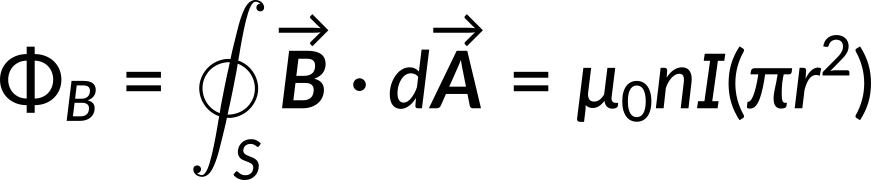
Equating the magnetic flux to the line integral of the magnetic vector potential, the expression for the vector potential can be obtained.
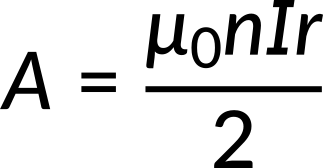
The vector potential mimics the magnetic field and acts along the circumference.
Dal capitolo 29:

Now Playing
29.14 : Magnetic Vector Potential
Sources of Magnetic Fields
553 Visualizzazioni

29.1 : Campo magnetico dovuto a cariche in movimento
Sources of Magnetic Fields
8.4K Visualizzazioni

29.2 : Legge di Biot-Savart
Sources of Magnetic Fields
5.9K Visualizzazioni

29.3 : Legge di Biot-Savart: risoluzione dei problemi
Sources of Magnetic Fields
2.5K Visualizzazioni

29.4 : Campo magnetico dovuto a un sottile filo dritto
Sources of Magnetic Fields
4.8K Visualizzazioni

29.5 : Campo magnetico dovuto a due fili dritti
Sources of Magnetic Fields
2.4K Visualizzazioni

29.6 : Forza magnetica tra due correnti parallele
Sources of Magnetic Fields
3.5K Visualizzazioni

29.7 : Campo magnetico di un circuito di corrente
Sources of Magnetic Fields
4.4K Visualizzazioni

29.8 : Divergenza e arricciatura del campo magnetico
Sources of Magnetic Fields
2.8K Visualizzazioni

29.9 : Legge di Ampere
Sources of Magnetic Fields
3.7K Visualizzazioni

29.10 : Legge di Ampere: risoluzione dei problemi
Sources of Magnetic Fields
3.5K Visualizzazioni

29.11 : Solenoidi
Sources of Magnetic Fields
2.5K Visualizzazioni

29.12 : Campo magnetico di un solenoide
Sources of Magnetic Fields
3.8K Visualizzazioni

29.13 : Toroidi
Sources of Magnetic Fields
2.9K Visualizzazioni

29.15 : Potenziale dovuto a un oggetto magnetizzato
Sources of Magnetic Fields
262 Visualizzazioni
See More