Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Primary Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Grown from Explants
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
Here we describe a detailed method for growing primary human bronchial epithelial cells from explants of human bronchial airway tissue including differentiated growth on an air-liquid interface. This method provides an abundant source of primary cells for investigating the role of the airway epithelium in human lung health and disease.
Streszczenie
Protokół
Human Bronchial segments provide an abundant source of primary bronchial epithelial cells. In this article we describe a protocol for growth and expansion of Human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells from freshly isolated human bronchial segments. This protocol consists of five sections:
- Coating and Scratching 100mm Culture Plates
- Preparing Bronchial Tissue Explants
- Bronchial Tissue Transplants
- Passage of HBE Cells
- Growing Ciliated HBE Cells on Transwells
Before you begin Note that ALL STEPS ARE DONE IN THE BIOLOGICAL SAFETY CABINET (BSC) UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. Please make sure you have all the materials needed for this procedure. Please read the Materials, Reagents and Preparation section and make sure that you have aseptically (i.e. in a Biological Safety Cabinet or BSC) prepared the following:
Coating stock solution: fibronectin (10 μg/ml), BSA (10 μg/ml) and collagen (30 μg/ml) in Earle s Balanced Salt Solution (EBSS, sterile).
Culture Medium: DMEM/Ham F-12 with additives, antibiotic-antimycotic(1%) and FBS (1%)
Dissociation solutions: Trypsin/EDTA stock solution and DMEM/F-12 with FBS (10%)
1. Coating and Scratching 100mm Culture Plates: Explants will be plated in 100mm culture plates. Start by coating 100mm culture plates with coating solution. This should be done in the BSC, keep everything sterile.
- Place sterile 100mm culture plates and coating solution (collagen/fibronectin/BSA) in the BSC.
- Pipette 2.0 ml of coating solution in a 100mm plate.
- Swirl around to coat the base of the plate. Make sure the coating solution covers the base of the plate evenly.
- Pipette the leftover solution out and use it to coat a second 100mm plate. Repeat for as many plates as needed. The number of plates needed varies with the number of tissue explants.
- Make sure the coating solution covers the bases of the plates evenly as demonstrated.
- Cover the plates with their covers. Allow the plates to dry in the incubator for 1-2 hours and aspirate excess solution before use for bronchial tissue explants. Unused coated culture plates can be placed in a sterile bag; sealed and stored at 4°C for later use (can be stored up to a month in the fridge). Bring to room temperature before use.
- Spray clean small sharp scissors, scalpel, and forceps with 70% ethanol and bring into BSC. Scratch coated plates by pressing firmly with scalpel to form deep small X s (at least 4). If the scratch is not deep enough, tissue pieces will not settle into ridges and will float.
2. Preparing Bronchial Tissue Explants
Use bronchial tissue obtained within 24-36 hours after surgery. Keep tissue on ice in EBSS until ready for use.
- Outside the BSC: Place tissue in a Petri dish. Rinse the isolated human bronchial tissue specimens thoroughly in EBSS.
- Dissect out excess surrounding tissue.
- Cut open the bronchial pieces.
- Bring tissue into the BSC and transfer into a sterile 100mm tissue culture plate with cold DMEM/HamF12 + 1% antibiotic/antimycotic.
- Use the sharp small scissors to cut the tissue into 2-3 mm3 pieces.
- Place one piece of cut tissue in the center of each X with forceps and press gently.
- Let the tissue pieces (explants) adhere to the plate for a few seconds, and then gently add 10ml of complete media (DMEM/HamF12 + additives +1% antibiotic/antimycotic + 1%FBS). If the tissue floats after adding media, use forceps to push the tissue into the ridges of the X or make a new X. It may be necessary to make new X s if the ridges are not deep enough.
- Place plates in incubator and change media every 3-4 days.
- Tissues are ready to transplant when sufficient epithelial cells have grown around tissue explants to cover 1-2cm areas. This takes approximately 4 weeks.
3. Bronchial Tissue Transplants
- Use 100mm coated and scratched plates. Since some tissue explants might not be successful, the number of plates depends on how many pieces of tissue you are transplanting. If you are using plates that have previously been coated and stored at 4°C, bring to room temperature before use.
- Using forceps, carefully pick up tissue from the original plate and place in the centre of X s in the new plate, and press gently. Tissues with no outgrowth should be discarded.
- Let tissue adhere to plate for a few seconds, add media and incubate as described earlier for explants (2.7-2.9).
4. Passage of human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells
- Thaw 2ml of Trypsin/EDTA stock solution for each 100mm tissue culture plate. Dilute stock with 6ml of sterile 0.01M PBS (i.e. add 2 ml stock solution to 6 ml PBS (final concentration of trypsin is 250 μg/ml and for EDTA is 100 μg/ml).
- After moving explants to a new plate, aspirate media from plates with 1-2cm rings of cells.
- Add 8ml of warmed diluted Trypsin/EDTA solution to each 100mm plate and place in incubator (37°C) for 3-15 minutes. Check frequently, leaving trypsin on too long will damage the cells.
- Check plates under a microscope to be sure most of the cells have been lifted. Cells will round up and detach as shown.
- Add 8ml of warmed 10% FBS in media per plate to inactivate the trypsin/EDTA solution.
- Combine volumes of all plates into one tube (or separate tubes if different tissues). Count cells using a hemacytometer.
- Centrifuge at 100g for 5 minutes. A cell pellet will form at the base of the tube.
- Re-suspend cell pellet in complete media (DMEM/Ham F12 + all additives + 1% antibiotic-antimycotic+ 1% FBS) to the desired cell concentration.
- Place each 2-3 million cells per T75 flask and add complete media as required. Incubate and change media every 3-4 weeks. Cells grow to sub-confluence (80-90%) in T75 flasks in about 4 weeks. The cells should be lifted and expanded or used at sub-confluence to prevent senescence.
5. Growing Ciliated Human Bronchial Epithelial (HBE) cells on Transwells.
Primary epithelial cells grown from tissue explants/transplants, can be expanded up to three times, and then used. A seeding density of 50,000 to 100,000 cells per cm2 is recommended 1,2. Higher density promotes faster differentiation.
Note: Prepare a suspension of cells and measure their numbers. Re-suspend in culture medium at 1 million cells per 2ml.
- Start with preparing the permeable membranes of the transwells by pre-incubating the cell culture inserts with medium (DMEM/Ham F12) prior to use. This step is necessary with these sensitive cells and will help cell attachment.
- Use the 6.5 mm inserts that fit into the 24 well multiple well plates.
- Add medium to both sides of the membrane (for 6.5 mm inserts use 0.6ml on bottom, 0.1ml on top). Incubate 1 hour in cell culture incubator.
- Carefully remove (aspirate) the medium from both sides of the membrane starting with the basal volume first.
Carefully means: the membrane can be easily damaged, so pipette the medium down the side of the culture insert, use the volume recommended. Not doing so will result in leaking over of media to other wells.
- Seed Cells after Pre-incubation of Permeable Support
- Pipette carefully your cell suspension into the apical side of the membrane: for 6.5mm wells add 0.1 ml of cell suspension (i.e. 50,000 cells) to the apical side of the membrane.
- Pipette 0.6ml medium on the basal side of the membrane.
- Feed the cells from the apical and basal sides for 10 days to establish a well differentiated culture: exchange medium twice a week using the demonstrated method:
- Remove basal volume first
- Replace apical volume (0.1ml medium)
- Add 0.6 ml of medium to the basal side of the membrane.
This method promotes cell attachment to membrane and prevents cells from being exposed to air for long periods of time (exchange media quickly and put back in incubator). - Create an Air-Liquid interface (ALI) on day 10 by removing the apical medium, then replacing the 0.6 ml of medium on the basal side of the membrane.
- Maintain cells in ALI for 6 weeks, change media twice a week. Ciliated cells will start appearing 4 weeks after creation of the ALI. Cells will achieve uniform differentiation into ciliated cells 6 weeks after creation of the ALI.
Materials Preparation:
1. Preparation of Coating Stock Solution (do this in the BSC):
Primary Human bronchial epithelial cells grow well on surfaces coated with fibronectin/BSA/collagen 3. The coating stock solution is used for 100 mm tissue culture plates for explant and transplant cultures as described above. Also the coating solution can be used to coat coverslips to speed up cell attachment, the coverslips can then be utilized for immunostaining experiments.
- Fibronectin (1mg/ml stock solution): Use F2006-2mg from Sigma. Dissolve 2mg in 2mls of sterile Earle s Balanced Salt Solution (EBSS, Sigma 28888), filter with 0.2 μm syringe filter in the Biological Safety Cabinet (BSC). Store 1ml in the -20°C freezer for later use, and use 1 ml for preparing a 100 mls of coating solution.
- BSA (1mg/ml stock solution): Use Sigma A4919-1g. Weigh 20 mg BSA and dissolve in 20 mls sterile EBSS, filter with 0.2 μm syringe filter in the BSC. Aliquot into 1ml vials and store in the -20°C freezer until needed. Use 1ml of stock to make 100mls of coating solution.
- Collagen stock solution (provided as 0.1% or 1mg/ml from Sigma C8919). Note: open only in the BSC and seal tight before returning to fridge. Use 3 ml of stock to make 100 ml of coating solution.
- Coating stock solution: In the BSC: add 3mls collagen (1mg/ml) to 1ml Fibronectin (1mg/ml) and 1ml BSA (1mg/ml), plus 95 mls EBSS (sterile). Mix well and aliquot into 2 ml vials and store in the -20°C freezer until needed. Final concentrations in coating stock solution: fibronectin (10 μg/ml), BSA (10 μg/ml) and collagen (30 μg/ml) in EBSS.
2. Preparation of Culture Medium (prepare in the BSC): Medium consists of DMEM/Ham F-12 from Sigma with bovine pituitary extract (15 μg/ml) and epidermal growth factor (10 ng/ml) with other additives as indicated below. Antibiotic/antimycotic (1%) and FBS (1%) are added freshly every time the culture medium is changed. This medium was compiled by reviewing multiple methods that described airway epithelial cell cultures 3-9. Our medium is intended for optimal growth of human bronchial epithelial cells.
- Bovine pituitary extract (BPE 1mg/ml stock solution): Sigma P1476 (2.5 ml BPE at 14mg/ml sterile and filtered solution): Dilute 2.5 mls of stock (14mg/ml) to a final concentration Of 1mg/ml. i.e. add 2.5 ml BPE stock to 32.5 ml of sterile EBSS for a stock of 1mg/ml. Divide into 7.5 ml aliquots (4 tubes of 7.5 ml aliquots and one tube of 5 ml aliquot). After dilution, store aliquots at -20°C until needed. Prolonged storage of reconstituted product and repeated freezing and thawing are not recommended.
- Epidermal growth factor (EGF 10 μg/ml stock solution): Sigma E9644-0.2mg. Reconstitute the contents (0.2mg) in 20 ms of 0.2 mm filtered 10 mM acetic acid containing 0.1% BSA (i.e. dissolve 20 mg BSA in 20 ml of 10 mM acetic acid and filter then use to reconstitute EGF). Aliquot into 0.5 ml aliquots and store in the -20 freezer. Use 100μl for 100 ml media.
- Epinephrine (5mg/ml stock solution): Sigma E1635. Dissolve 10mg in 2ml OF 1M filtered hydrochloric acid (HCl), aliquot into 50 μl vials and freeze (-20°C).
- Insulin (2mg/ml stock solution): Sigma I6634 50mg. Dissolve 50mg in 25ml filtered (0.2μm filter) diluted HCl (1mM). Aliquot into 1.25ml vials.
- Tranferrin Human (50 mg/ml stock solution): Sigma T8158 100mg. Dissolve 100mg in 2ml DH20 (filtered with 0.2 μm filter). Aliquot to 100μl each (in 0.5ml vials).
- Triiodo-L-thyronine (1mg/ml stock solution): Sigma T6397 100mg. Dissolve 100mg in 100ml 1M filtered HCl. Aliquot into 1ml aliquots. Aliquot 0.5ml into 10μl aliquots.
- Hydorcortisone (5mg/ml stock solution): Sigma H0888. Weigh out 100mg and dissolve in 20ml filtered ethanol for 5mg/ml stock. Aliquot to 1ml vials. Divide a 1ml (5mg/ml) to 50μl aliquots (0.5ml vials).
- Retinoic Acid (1mg/ml stock solution, diluted to 0.01mg/ml when used): Sigma R2625 100mg). Dissolve 100mg in 10ml of ethanol. Divide to 1.0ml aliquots. Divide (1ml) vial to 50 tubes of 20μl each. Freeze at -20°C. Take one 20μl vial and dilute to 2000μl with media for a stock of 0.01mg/ml when needed.
- Albumin solution from bovine serum, sterile-filtered, cell culture tested: Sigma A8412. Store solution in the cold (4°C) until needed. Open only in the BSC.
- Antibiotic-Antimycotic, Sigma A5955: aliquot to 1ml volumes and freeze at -20°C until needed. Use at 1% final concentration in medium.
- FBS, Sigma F1015: Inactivate FBS at 50°C for 30 minutes. Allow to cool in the BSC. Aliquot into 1ml and 10 ml sterile vials. Use at 1% final concentration in culture medium and at 10% final concentration in media to neutralize Trypsin/EDTA solution.
- Constitution of culture medium:
For 500 ml of medium DMEM/HamF12 use:- 1 tube of BPE (each 7.5ml of 1mg/ml) for a final concentration of 15μg/ml.
- 1 tube of EGF (0.5ml of 10μg/ml) for a final concentration of 10ng/ml.
- 1 tube of Epinephrine (50μl of 5mg/ml) for a final concentration of 0.5μg/ml.
- 1 vial of Insulin (1.25ml of 2mg/ml) for a final concentration of 5μg/ml.
- 1 vial of Transferin (100μl of 50mg/ml) for a final concentration of 10μg/ml.
- 5 μl of Triiodo-L-thyronine (at 1mg/ml) for a final concentration of 10ng/ml.
- 1 vial of Hydrocortisone (50μl of 5mg/ml) for a final concentration of 0.5μg/ml.
- 5 μl of Retinoic Acid diluted to 0.01mg/ml for a final concentration of 0.1ng/ml.
- 10 μl albumin solution from bovine serum for a final concentration of 1.5μg/ml
3. Preparation of Dissociation Solutions:
- Preparation of Trypsin/EDTA stock solution: dissolve 100mg trypsin (Sigma T9935-100mg) and 40mg EDTA (Sigma E6758) in 500 ml 0.01M PBS (Sigma E6758). Aliquot into 2ml vials and store in the -20°C freezer. Dilute stock solution: add 2 ml stock solution to 6 ml PBS (final concentration of trypsin is 250 μg/ml and for EDTA is 100 μg/ml).
- Solution for stopping enzymatic reactions: Prepare fresh 10% FBS in media in the BSC: add 1 ml FBS to 9 ml media (DMEM/Ham F-12). For each 100mm plate use 8 ml of warmed 10% FBS to neutralize 8 ml of the dissociation solution.
4. Special Requirements:
- When culturing epithelial cells, you need to keep everything clean and disinfected. All reagents used for cell culture should be sterile or filtered with 0.2μm filter. Preparation of materials and additives should be done in a Biological Safety Cabinet (BSC). Media addition or changing of media should be done in a BSC.
- Tie hair away, wear a disposable cap if available, and wear a laboratory coat and gloves.
- Keep all work surfaces free from clutter. Clean the work surfaces with 70% ethanol between operations and allow a minimum of 15 minutes between handling different cultures.
- Label all reagents and bottles of media, include date received and date prepared.
- Examine cultures and media regularly for evidence of gross bacterial or fungal contamination.
- Test regularly for mycoplasma (if needed)
- Warm up culture medium to 37°C before changing media on the cells.
- Antibiotics/antimycotics and FBS should be freshly added to medium.
- Change medium at least every 3-4 days. Do not let the cells sit at room temperature for a long time. Change media and promptly return to incubator.
Representative Results:
Culture characteristics and morphology of human bronchial epithelial cells
Microscopy of human bronchial epithelial cells brushed from the bronchial segments used for culture, prior to culturing, demonstrated strips of both ciliated and non-ciliated epithelial cells indicating a normal epithelium (Figure 1, Supplement 1). Immunostaining of cytospin preparations of cells from explants and cells seeded on coverslips revealed that all cells were positive for the epithelium-specific cytokeratins (Figure 3). Successful cultures from explants of the bronchial tissue occurred in 8 out of 9 tissues, as one of the explant cultures got infected. The rings of epithelial cells reached 1-2 cm radius in 3-4 weeks (Figure 2a). Successful explants were cultured again up to 6 times. In all successful cultures, there was evidence of cell migration within 48 hours of starting the transplants (Figure 2b). Cells had a cobblestone appearance that is distinct for these epithelial cells as shown in Figures 2, 4, 5 and 6. Sub-cultured bronchial cells showed uniform positive immunostaining for cytokeratin and E-cadherin. Immunostaining with specific antibodies against other cell types did not show any indication of contamination of cultures by fibroblasts, mesenchymal, or endothelial cells (α-SMA, vimentin and CD31: PECAM-1 stains respectively) (Figure 5). Cells cultured on permeable polyester membranes (transwells) with Air-Liquid Interface differentiated into ciliated epithelium as demonstrated in Figure 6. Representative video recordings of the bronchial epithelial cells grown on transwells demonstrate a differentiated epithelium with beating cilia (Supplement 2).
Characteristics of the human bronchial epithelial cell cultures tested are shown in Table 1. The median time to first passage (P1) was 4 weeks, and the mean yield was 15.1±2.75 million cells (n=9 tissues). The viability of cells from explants and at P1 was assessed by trypan blue exclusion, and was consistently high (99%) in these bronchial cultures. Sub-cultured cells from the explant cultures from each tissue were pooled after first passage for subsequent use. The mean cell number recovered from explants was significantly higher than the subsequent Passage culture (every 2 million cells from P1 yielded P2: 6.75±2.4 million cells, n=5 tissues). One P2 culture was discarded as the morphology was not typical of epithelial cells (Figure 7a). Similarly, two other passages (P2 and P3) of different tissues (Figure 7b) were discarded.
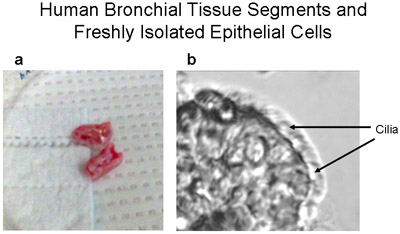
Figure 1 Human bronchial tissue segments and a freshly isolated epithelial strip of ciliated and non-ciliated cells. (a) Representative picture of human bronchial tissue segments -~1-2cm long and <1cm diameter- used for primary cultures of human bronchial epithelial cells. (b) A strip of human bronchial epithelial cells brushed from the bronchial segment demonstrates both ciliated and non-ciliated epithelial cells, magnification 320X. Video of cells with beating cilia is provided as Supplement 1.
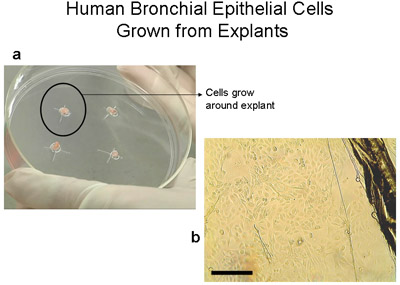
Figure 2 Human bronchial epithelial Cells grown from explants on 100mm tissue culture plates. a) 100mm plate with 2-3mm3 tissue. Note the ring of cells of about 1-2cm which becomes visible to the naked eye after 3-4 weeks. b) Image of edge of explant tissue and epithelial cells as they migrate from the explant, bar=100μm. Explants transferred to a new plate become transplants. Explants can be transplanted up to 6 times.
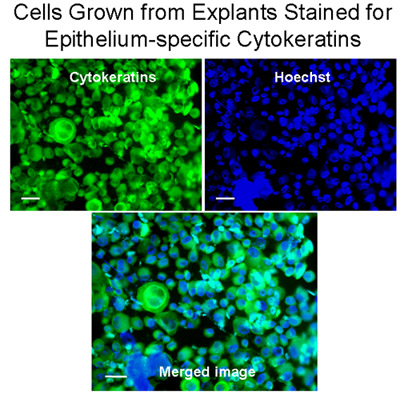
Figure 3 Cells grown from explants stained for epithelium-specific cytokeratins. Cytospins of Cells from explants were stained for cytokeratins (green) with the Monoclonal anti-Pan Cytokeratin-FITC (mixture) which recognizes human cytokeratins 1, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 13, 18, and 19. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst stain (blue). The merged image demonstrates that bronchial cells grown from explants were mainly epithelial cells, Bar=20μm.
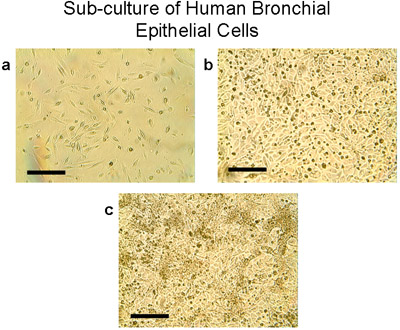
Figure 4 Sub-culture of human bronchial epithelial cells. a) Using trypsin/EDTA, cells from explants and transplants are lifted from the 100mm plates, counted and seeded at 2-3 million cells per T75 flask. Cells grow to sub-confluence (80-90%) in T75 flasks in 28-30 days (b, c). Note the typical cobblestone morphology of epithelial cells, Bar=100μm.
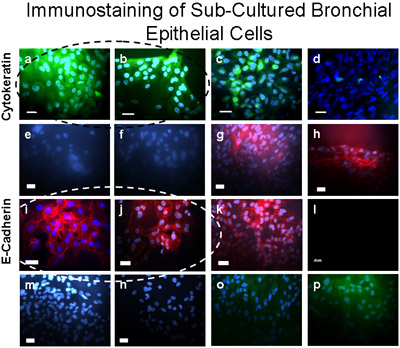
Figure 5 Sub-Cultured bronchial cells were verified as epithelial using immunostaining. These cells stained positive (green) for Cytokeratin-FITC (a,b), a positive control for cytokeratin-FITC is shown in A549 epithelial cells (c) and a negative control is demonstrated in fibroblasts (d). Cultured Bronchial cells stained positive (dark red) for E-Cadherin/Alexa Fluor 594 (i,j), and did not stain for α-SMA-cy3 (e,f), Vimentin/TRITC (m), nor CD31 (PECAM-1/FITC) (o) indicating no contamination of the primary cultured bronchial epithelial cells with smooth muscle, mesenchymal, or endothelial cells respectively. Positive (dark red) control for E-Cadherin/Alexa Fluor 594 is demonstrated on A549 epithelial cells (k). Positive control for α-SMA-cy3 (red) is demonstrated in fibroblasts (g,h). Secondary antibody controls are shown in bronchial epithelial cells for Alexa Fluor 594 (l); rabbit anti-mouse TRITC (n) and Donkey anti-goat FITC (p). Bar=20μm.
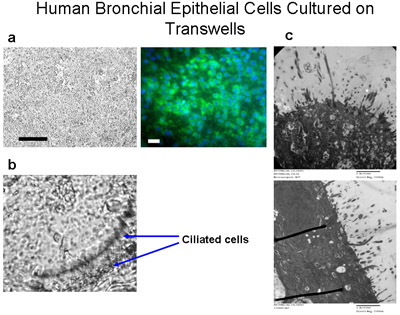
Figure 6 Human bronchial epithelial cells cultured on transwells. Ciliated cells are cultured on permeable polyester membranes (6.5mm diameter) at a seeding density of 50,000 cells per well (a) Bar=100μm. Immunostaining of the cells cultured on transwells with cytokeratin-FITC (green) and DAPI (blue) demonstrates that these cells are mainly epithelial cells, Bar=20μm. Cells are cultured submerged in media for 10 days, then fed media from the bottom only for another 4-6 weeks to create an ALI until cilia are grown as shown in (b), magnification 160x. See Supplement 2 for videos of beating cilia. (c) TEM images demonstrate cilia growth of ALI cultures at 6 weeks, magnification=150000x.
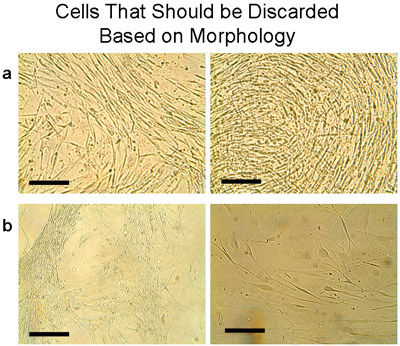
Figure 7 Example of cells that should be discarded based on morphology. These cells usually appear when the tissue has been transplanted many times. Note that both cells and transplant should be discarded. a) Cells were collected from one plate with transplants that were cultured 6 times and plated in a T75 flask. Within 1 week the cells showed a distinct morphology that did not represent the cobblestone appearance of epithelial cells. Instead, thin elongated cells were growing densely. b) More examples of cells that should not be pooled with the typical epithelial cells, but should be discarded. Bar=100μm.
Table 1: Characteristics of human bronchial epithelial cell cultures
| Success rate (# of tissues) | 8/9 (88.8%) |
| Median time (range) to P1 (weeks) | 4 (3-5) |
| Mean (SEM) cell no. at P1 | 15.1 (2.75) x 106 |
| Mean (SEM) viability at P1 | 99% (2%) |
| (P1 = first passage) | |
Supplement 1 shows a strip of ciliated and non-ciliated bronchial epithelial cells brushed from a human bronchial segment used for transplants, magnification 320X. Click Here for the Supplement 1 Video.
Supplement 2 Differentiated bronchial epithelial cells grown on an air-liquid interface. Videos (2a and 2b) show beating cilia, magnification 160X and 320X respectively. Click Here for the Supplement 2A Video. Click Here for the Supplement 2B Video.
Dyskusje
In this study we presented detailed methods for culture and expansion of primary human bronchial epithelial cells. We demonstrated how explants and transplants of bronchial tissue, cultured in media which promote epithelial cell growth, can provide a continuous source of human airway epithelial cells for studies of non-differentiated (submerged) and differentiated (grown on air-liquid interface) cell models. These cells can be utilized in drug testing systems that more closely resemble the cells in their real physiologic...
Podziękowania
The authors are very thankful to Dr. Richard Inculet for providing the bronchial tissues. Research Ethics Board approvals were obtained from St. Joseph's Healthcare Hamilton and The University of Western Ontario/London Health Sciences Centre (Dr. David McCormack), Tissue and Archives Committee, Department of Pathology. We also thank Ernie Spitzer (Electron Microscopy, McMaster University) for providing TEMs of our ALI cultures, and Daniela Farkas for providing some of the materials needed for immunostaining. This work was funded by a Block term grant from the Ontario Thoracic Society; Dr. Asma Yaghi was supported by an FSORC scholarship, St. Joseph's Healthcare, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Albumin from bovine serum, powder | Sigma-Aldrich | A4919 | Use for coating solution |
| COLLAGEN TYPE I 0.1% Solution Sterile-filtered | Sigma-Aldrich | C8919 | Use for coating solution |
| Fibronectin from human plasma | Sigma-Aldrich | F2006 | Use for coating solution |
| Earle’s Balanced Salt Solution (EBSS, sterile) | Sigma-Aldrich | 28888 | Use for rinsing tissue and for coating solution |
| DMEM/Ham F-12 | Sigma-Aldrich | D8437 | |
| FBS | Sigma-Aldrich | F1015 | Inactivate, then aliquot and freeze (-20°C); use fresh when needed |
| Antibiotic-Antimycotic Stabilized | Sigma-Aldrich | A5955 | Aliquot into 2 ml vials and freeze (-20°C); use fresh when needed |
| Albumin solution from bovine serum | Sigma-Aldrich | A8412 | BSA |
| Pituitary Extract Bovine | Sigma-Aldrich | P1476 | BPE |
| Epidermal growth factor | Sigma-Aldrich | E9644 | EGF |
| (±)-Epinephrine | Sigma-Aldrich | E1635 | |
| Insulin | Sigma-Aldrich | I6634 | |
| Tranferrin Human | Sigma-Aldrich | T8158 | |
| Triiodo-L-thyronine | Sigma-Aldrich | T6397 | |
| Hydorcortisone | Sigma-Aldrich | H0888 | |
| Retinoic Acid | Sigma-Aldrich | R2625 | |
| Trypsin | Sigma-Aldrich | T9935 | |
| EDTA | Sigma-Aldrich | E6758 | EDTA |
| Phosphate buffered saline | Sigma-Aldrich | P5368 | PBS |
| 70% ethanol | Use for disinfecting and cleaning | ||
| 24 well Transwells | Corning | 3470 | |
| Cell Culture Flasks (T75) CLLBND from Corning | Fisher Scientific | 05-539-104 | These flasks have a Cell Bind coating which promotes cell attachment and growth |
| Monoclonal Anti-Cytokeratin, pan-FITC antibody | Sigma-Aldrich | F3418 | Permeabilization: 0.2% TRITON X-100/PBS; Use 1:250 dilution |
| Antibody: E-Cadherin (H108) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. | sc-7870 | Do not permeabilize; Use 1:250 dilution and A21207 (Invitrogen) as secondary antibody |
| Alexa Fluor 594 donkey anti-rabbit IgG | Invitrogen | A21207 | Use 1:400 dilution |
| Antibody: Monoclonal mouse Anti- α-Smooth Muscle Actin-Cy3 | Sigma-Aldrich | C6198 | Permeabilization: 0.2% TRITON X-100/PBS; Use 1:100 dilution |
| Antibody: Vimentin (RV202) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. | Sc-32322 | Permeabilization: 0.2% TRITON X-100/PBS; Use 1:100 dilution and T2402 (Sigma- Aldrich) as secondary antibody |
| Rabbit anti-mouse TRITC | Sigma-Aldrich | T2402 | Use 1:400 dilution |
| Antibody: CD31 or PECAM-1 (M-20) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. | Sc-1506 | Do not permeabilize; Use 1:200 dilution and Donkey anti-goat IgG-FITC as secondary antibody |
| Donkey anti-goat IgG-FITC | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. | Use 1:100 dilution | |
| Vectashield Mounting medium with DAPI | Vector Laboratories | H-1200 | Refrigerate in the dark; stains nuclei and retains fluorescence duringprolonged storage |
| Vectashield Mounting medium | Vector Laboratories | H-1000 | Refrigerate in the dark; retains fluorescence during prolonged storage |
| H–chst Stain solution | Sigma-Aldrich | H6024 | Stains nuclei; use 1:10 dilution and Vectashield H-1000 |
Other requirements: incubator, biological safety cabinet (BSC), centrifuge, 100mm culture plates, sterile tubes (15 ml, 50 ml, and 2 ml), sterile pipette tips, scalpel handle and blades, small sharp scissors, lab coats and gloves. These can be obtained from your preferred suppliers. | |||
Odniesienia
- Phillips, J. Growing Cells on Transwell Inserts - Tips and Techniques [Internet]. Corning Life Sciences, Technical Resources, Online Training. , (2008).
- Turi, J. L. Oxidative stress activates anion exchange protein 2 and AP-1 in airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 283, L791-L798 (2002).
- Lechner, J. F., Haugen, A., McClendon, I. A., Pettis, E. W. Clonal growth of normal adult human bronchial epithelial cells in a serum-free medium. In Vitro. 18, 633-642 (1982).
- Yoshisue, H. Characterization of ciliated bronchial epithelium 1, a ciliated cell-associated gene induced during mucociliary differentiation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 31, 491-500 (2004).
- Wetering, S. v. a. n. Regulation of secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor (SLPI) production by human bronchial epithelial cells: increase of cell-associated SLPI by neutrophil elastase. J. Investig. Med. 48, 359-366 (2000).
- Tristram, D. A., Hicks, W., Hard, R. Respiratory syncytial virus and human bronchial epithelium. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 124, 777-783 (1998).
- Mattinger, C., Nyugen, T., Schafer, D., Hormann, K. Evaluation of serum-free culture conditions for primary human nasal epithelial cells. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health. 205, 235-238 (2002).
- Freshney, R. I., Freshney, R. I. . Culture of epithelial cells. , 1-23 (1992).
- Freshney, R. I., Freshney, R. I. Normal human bronchial epithelial cell cultures in Culture of specialized cells series. Culture of epithelial cells. , 181-196 (1992).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone