Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Combination of Adhesive-tape-based Sampling and Fluorescence in situ Hybridization for Rapid Detection of Salmonella on Fresh Produce
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
This protocol describes a simple adhesive-tape-based approach for sampling of tomato and other fresh produce surfaces, followed by rapid whole cell detection of Salmonella using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).
Streszczenie
This protocol describes a simple approach for adhesive-tape-based sampling of tomato and other fresh produce surfaces, followed by on-tape fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for rapid culture-independent detection of Salmonella spp. Cell-charged tapes can also be placed face-down on selective agar for solid-phase enrichment prior to detection. Alternatively, low-volume liquid enrichments (liquid surface miniculture) can be performed on the surface of the tape in non-selective broth, followed by FISH and analysis via flow cytometry. To begin, sterile adhesive tape is brought into contact with fresh produce, gentle pressure is applied, and the tape is removed, physically extracting microbes present on these surfaces. Tapes are mounted sticky-side up onto glass microscope slides and the sampled cells are fixed with 10% formalin (30 min) and dehydrated using a graded ethanol series (50, 80, and 95%; 3 min each concentration). Next, cell-charged tapes are spotted with buffer containing a Salmonella-targeted DNA probe cocktail and hybridized for 15 - 30 min at 55°C, followed by a brief rinse in a washing buffer to remove unbound probe. Adherent, FISH-labeled cells are then counterstained with the DNA dye 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) and results are viewed using fluorescence microscopy. For solid-phase enrichment, cell-charged tapes are placed face-down on a suitable selective agar surface and incubated to allow in situ growth of Salmonella microcolonies, followed by FISH and microscopy as described above. For liquid surface miniculture, cell-charged tapes are placed sticky side up and a silicone perfusion chamber is applied so that the tape and microscope slide form the bottom of a water-tight chamber into which a small volume (≤ 500 μL) of Trypticase Soy Broth (TSB) is introduced. The inlet ports are sealed and the chambers are incubated at 35 - 37°C, allowing growth-based amplification of tape-extracted microbes. Following incubation, inlet ports are unsealed, cells are detached and mixed with vigorous back and forth pipetting, harvested via centrifugation and fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin. Finally, samples are hybridized and examined via flow cytometry to reveal the presence of Salmonella spp. As described here, our "tape-FISH" approach can provide simple and rapid sampling and detection of Salmonella on tomato surfaces. We have also used this approach for sampling other types of fresh produce, including spinach and jalapeño peppers.
Protokół
1. Surface Sampling with Sterile Adhesive Tape
- Select a tape to use for sampling. The commercially available Fungi-Tape or Con-Tact-It sampling tapes are sterile and specially packaged for ease of use. However, we have found that transparent (optically clear) generic office tape can also be used.
- Use a permanent marker to draw 1 cm2 squares on the non-sticky side of a 10 cm piece of adhesive tape (a paper template can be used). This will serve as a visual guide for noting which portion of the tape has been used to sample the food or environmental surface.
- Form a "C"-shaped loop of tape, with the sticky side facing the surface to be sampled. To do this, hold the sticky ends with the thumb and middle finger and position the index finger against the drawn square on the back (non-sticky side) of the tape (Figure 1).
- Place the tape on the surface to be sampled and gently press the marked area against the surface. Without releasing the edges of the tape, use the index finger to ensure that the sticky side of the tape comes in full contact with the sample surface, avoiding bubbles.
- Using an even motion, slowly pull the tape away from the sample, physically extracting surface-bound microbes. Fasten the cell-charged tape, sticky side up, onto a glass microscope slide using generic transparent office tape. Ensure proper tension/stretching of the tape so that a flat, non-wrinkly surface is created. This will help minimize problems with deformation/curling of the tape during subsequent heating during hybridization.
2. Solid-phase Enrichment and Liquid Surface Miniculture
- Solid-phase enrichment is performed by placing the tape face-down on xylose-lysine-Tergitol 4 (XLT-4) agar plates so that the sampled cells are placed in direct contact with the agar surface. The templated/sample contact portion of the tape is placed flush with the agar surface and one end of the tape is loosely adhered to the side wall of the Petri dish to facilitate easy removal of the tape from the agar surface following enrichment.
- Plates are inverted (to avoid condensation) and incubated at 35 - 37°C to allow sufficient growth of Salmonella spp. The length of the incubation period needed to enrich the cells to a detectable level will depend on initial Salmonella contamination levels. We have observed excellent microcolony formation from low initial inocula after 8 h enrichment.
- After the desired enrichment period, open the agar plate. The tape will retain its tackiness during incubation. Gently press the tape against the agar using the index finger to ensure maximum recovery of microcolonies formed at the tape-agar interface. Grasp the tape from the edge attached to the wall of the Petri dish and remove it with a slow, even motion. Mount the cell-charged tape, sticky side up, onto a microscope slide as described in section 1.5 above. Proceed to "Fixation and Dehydration" step below.
- For liquid surface miniculture, begin by fastening the tape used for sampling onto a microscope slide as described in section 1.5 above. Next, cover the templated/sample contact portion of the tape with a non-sterile silicone perfusion chamber (Coverwell, Grace Bio-Labs, Inc.), forming a sealed chamber whose bottom is comprised of the cell-charged tape, facing upwards. Firmly, but gently press the chamber into place to ensure a watertight seal.
- Using a flexible gel loading pipette tip, transfer ≤ 500 μL Trypticase Soy Broth or other suitable enrichment medium through one of the chamber's small inlet ports. Seal both ports with transparent office tape to prevent evaporation and incubate slides at 35 -37°C as needed for sufficient enrichment. Although all operations should be performed according to good sampling and handling practices, sterility of port-sealing tape or perfusion chambers is not required during liquid surface miniculture. The combination of FISH and flow cytometry will enable clear discrimination of Salmonella spp. from non-target bacteria that may be present, with the largest contribution of non-target flora expected to come from the sample itself. Proceed to "Fixation and Dehydration" step below.
3. Fixation and Dehydration
- For direct surface sampling or for solid phase enrichment of Salmonella spp. on XLT-4 agar, perform on-tape cell fixation for 30 min at 25°C by covering the sample contact area with 500 μL 10% neutral buffered formalin.
- Discard fixative into a sealable container (under a chemical hood to minimize exposure to irritating/toxic vapor).
- Dehydrate in an ethanol series (50%, 80% and 95%; 300 μL/3 min each concentration). Proceed to "Hybridization" step below.
- For fixation of 500 μL liquid surface miniculture samples, perfusion chambers are unsealed, and a flexible gel-loading pipette tip is used to extract the enrichate. Rapid up and down pipetting is used to help ensure effective removal of any remaining tape-bound cells.
- Next, the entire 500 μL miniculture volume is transferred to a microcentrifuge tube and spun down at 2,000 x g (5 min). The supernatant is discarded, the pellet is vortexed vigorously for 30-60 s, then resuspended in an equal volume of 10% neutral buffered formalin. Cells are fixed for 30 min at 25°C.
- Next, fixative is removed and the sample is resuspended in cell storage buffer, as follows. The sample is spun down at 2,000 x g (5 min, 25°C) the supernatant is discarded, the pellet is vortexed vigorously for 30 - 60 s, the resuspended in an equal volume of 50% non-denatured ethanol-50% phosphate-buffered saline. Fixed cells can be stored indefinitely (years) at -20°C. Note: Whenever liquids are changed (for example, when introducing a fixative or different buffer), it is important to thoroughly resuspend (with vortexing) the cell pellet in a minimal portion (~10 - 20 μL) of the "outgoing" liquid system. This will help prevent clumping and ensure that even suspensions of individual cells are obtained. Proceed to "Hybridization" step below.
4. Hybridization
- Prepare hybridization/washing buffer using the commercial molecular biology-grade solutions noted in Materials Table. Final buffer component concentrations are 0.7 M NaCl, 0.1 M TRIS [pH 8.0], 10 mM EDTA, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, made up to the final desired volume with molecular-grade water and filtered using a 0.22 μm syringe or cup filter. The same buffer, without the addition of probes (see below) is used as a washing buffer. Preheat hybridization and washing buffers to 55°C.
- Add fluorescently-labeled Sal3 (Nordentoft et al., 1997; 5'- AAT CAC TTC ACC TAC GTG-3') and Salm-63 (Kutter et al., 2006; 5'-TCG ACT GAC TTC AGC TCC-3') oligonucleotide probes (Materials Table) to preheated hybridization buffer. A total probe concentration of 5 ng μL-1 is used (e.g. 2.5 ng μL-1 each probe; Bisha and Brehm-Stecher, 2009a).
- For direct-to-tape and solid phase enrichment samples, overlay the templated sample contact area of the tape with 300 μL of hybridization buffer containing the probe cocktail and hybridize tape-bound cells in a moist, sealed incubation chamber set to 55°C. If a direct-contact incubator such as the Slide Moat instrument (Materials Table) is used, samples are hybridized for 15 min and >20 slides can be processed simultaneously. If a rotary-style hybridization oven such as the Bambino instrument (Materials Table) is used, slides are placed in 50 mL polypropylene centrifuge tubes for hybridization, one slide per tube. Because heat transfer is not direct, these samples are hybridized for longer periods (up to 30 min).
- Following hybridization, the slides are removed and the probe-containing hybridization buffer overlay is discarded. Slides are then either briefly and gently rinsed with preheated washing buffer by pipetting a small volume of buffer over a tilted slide (3 rinses of 300 μL each), or formally washed (up to 30 min) with either an overlay of preheated washing buffer or immersion in a 50 mL polypropylene centrifuge tube containing preheated washing buffer. In our experience, although a formal wash will provide improved results (less haze from unbound probe), a simple rinse is adequate for unambiguous detection of Salmonella spp. Next, slides are air-dried before moving to the "Detection" step below.
- Hybridization of liquid surface miniculture samples is performed by spinning down samples (freshly-fixed or kept in storage buffer at -20°C) for 5 min at 2,000 x g, followed by vigorous vortexing of the pellet and resuspension in 100 μL preheated hybridization buffer containing the probe cocktail. Samples are hybridized at 55°C for 30 min on a heat block or other suitable incubation station (Materials Table), followed by addition of 500 μL preheated washing buffer. As with tape-bound samples, these samples may be formally washed for up to 30 min with further incubation at 55°C in this wash buffer, with intermittent vortexing. Alternatively, samples may be thoroughly vortexed after addition of 500 μL preheated washing buffer, followed by immediate harvesting for analysis (below).
- In preparation for detection of Salmonella spp. via flow cytometry, liquid surface miniculture samples are spun down at 2,000 x g for 5 min, the supernatant is discarded and the samples are resuspended in 300 μL room temperature (~25°C) PBS. If samples require transport to a distant facility, or if a delay is expected in between hybridization and analysis, samples may be refrigerated or held on ice prior to analysis. Alternatively, samples may be transferred to cell storage buffer (50:50 mixture of PBS and absolute ethanol) and held at -20°C for up to a week without appreciable losses in probe-conferred fluorescence (Bisha and Brehm-Stecher, 2009b).
5. Detection
- For on-tape detection of Salmonella spp. via fluorescence microscopy, direct-to-tape or solid phase enrichment samples are overlayed with ~10 μL Vectashield H-1200 mounting medium containing the nuclear counterstain 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), mounted with a cover slip, then incubated in the dark for 10 min.
- Immersion oil is placed on the cover slip, and samples are examined using a high-magnification oil objective (63x or 100x). The DAPI filter is used to bring the sample into focus, the microscope is then switched to the appropriate filter (green or red, depending on the dye used to end-label the probes) and Salmonella cells are scored visually according to their fluorescence (Figures 2 and 3).
- For cytometric detection of liquid surface miniculture samples, various instruments may be used, depending on local availability. In our lab, PBS-suspended samples are transferred to 5 mL round bottom sampling tubes (BD Falcon) and examined using a FACSCanto flow cytometer with excitation at 647 nm (Materials Table). For enriched samples containing high numbers of total bacteria, the "low flow rate" setting (10 μL min-1) is used and 5,000-50,000 events are collected. Data are analyzed using FlowJo software (version 8.8.6, Tree Star, Inc., Ashland, OR) or other suitable analysis software (Figure 4, panels A and B).
6. Representative Results
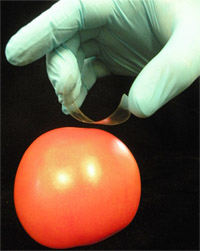
Figure 1. Use of adhesive tape for sampling of Salmonella spp. from the surface of an artificially contaminated tomato.

Figure 2. Typical results for direct-to-tape sampling and FISH detection of Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 14028 from the surface of a tomato (100 X oil objective). A two-probe cocktail of Texas Red-labeled probes (Sal3/Salm-63) was used to label these cells.

Figure 3. Microcolonies of Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 14028 formed on the surface of Xylose Lysine Tergitol-4 (XLT-4) agar after an 8 h on-tape enrichment at 37°C. The initial inoculum was sampled from the surface of an artificially contaminated tomato. Solid-phase enrichment increases the numbers of cells available for detection and also enhances cellular rRNA content.

Figure 4. Use of adhesive tape for sampling of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium from the surface of an artificially contaminated tomato, followed by direct analysis via FISH and flow cytometry (panel A) or after 5 h non-selective liquid surface miniculture enrichment in a perfusion chamber filled with 500 μL Trypticase Soy Broth (panel B).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Dyskusje
Simple and rapid methods for detection of pathogens on produce surfaces may help mitigate foodborne disease by providing timely and actionable data. Adhesive tape-based sampling methods have been used in environmental, clinical and food microbiology since the 1950's and involve pressing of "Scotch"-style tape to surfaces for removal of microorganisms, followed by direct microscopic examination or transfer of adherent microorganisms to solid media for growth (Barnetson & Milne, 1973; Edwards & Hartman, 1952; Evanc...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Ujawnienia
No conflicts of interest declared.
Podziękowania
Funding for this work was provided by a Grow Iowa Values Fund award to BFBS.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Fungi-Tape sampling tape | Scientific Device Laboratory | 745 | http://www.scientificdevice.com/ |
| Con-Tact-It sampling tape | Birko Corporation, Denver, CO | http://www.birkocorp.com/ | |
| Clear office tape, generic | Various | Should be optically clear, have low intrinsic fluorescence | |
| Food surface | Local Grocery Store | Tomat–s (red tomat–s on the vine, not waxed or oiled) used here | |
| Trypticase Soy Broth | Difco Laboratories | 211768 | For non-selective liquid surface miniculture enrichment |
| Xylose-lysine-Tergitol 4 agar base | Difco Laboratories | 223420 | For Salmonella-selective agar (XLT-4) |
| Xylose-lysine-Tergitol 4 agar supplement | Difco Laboratories | 235310 | For Salmonella-selective agar (XLT-4) |
| Formalin solution | Sigma-Aldrich | HT5011 | 10% solution, neutral, buffered (cell fixative) |
| Absolute ethanol | Sigma-Aldrich | E7023 | Molecular biology grade (pre-hybridization dehydration) |
| 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes | Various | RNase- and DNase-free | |
| Microscope slides and cover slips | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | ||
| NaCl solution | Sigma-Aldrich | S5150 | Molecular biology grade, 5M solution (hybridization buffer component) |
| Tris-EDTA buffer solution (100X concentrate) | Sigma-Aldrich | T9285 | 1M Tris [pH 8.0], 0.1M EDTA (hybridization buffer component) |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate solution | Sigma-Aldrich | L4522 | 10% solution in 18 megohm water (hybridization buffer component) |
| Sal3 and Salm-63 oligonucleotide probes | Integrated DNA Technologies | 5’-labeled with 6-carboxyfluorescein (FAM) or Texas Red (for microscopy) or Cy5 (for cytometry), HPLC-purified | |
| Variable speed microcentrifuge | Various | Use rotor diameter to calculate RPM needed for RCF values described in protocol | |
| CoverWell perfusion chamber | Grace Bio-Lab Inc. | PC1R-2.0 | Non-sterile |
| Gel loading pipette tips (FS MultiFlex) | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | 05-408-151 | Long, thin tips for easy access to small sampling ports and maneuverability within chamber |
| Aluminum heat block or precision-controlled heating station | Various | Eppendorf Thermomixer R dry block heating and cooling shaker used here | |
| Bambino mini hybridization oven | Boekel Scientific | Model 230300 | Slides are placed in 50 ml polypropylene centrifuge tubes for hybridization, heat transfer not direct |
| Slide Moat slide hybridizer | Boekel Scientific | Model 240000 | Provides rapid, direct transmission of heat through glass slide |
| Vectashield H-1200 mounting medium with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) | Vector Laboratories | H-1200 | Minimizes quenching of fluorescence during microscopy, provides DAPI counterstain |
| Fluorescence microscope | Various | Leitz Laborlux S used here | |
| Digital camera | Various | Canon PowerShot A640 camera used here | |
| Image acquisition software | Various | Axiovision software v. 4.6 (Carl Zeiss) used | |
| Adobe Photoshop | Adobe | For minimal processing of images (overlay of images taken in different channels) | |
| Flow cytometer | Various | FACSCanto flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) with red (647 nm) excitation used | |
| Flow cytometry analysis software | Various | FlowJo software v. 8.7.1 (Tree Star, Inc.) used |
Odniesienia
- Almeida, C., Azevedo, N. F., Fernandes, R. M., Keevil, C. W., Vieira, M. J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization method using a peptide nucleic acid probe for the identification of Salmonella spp. in a broad spectrum of samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76, 4476-4485 (2010).
- Barnetson, R. S., Milne, L. J. R. Skin sampling for Candida with adhesive tape. Br. J. Dermatol. 88, 487-491 (1973).
- Bisha, B., Brehm-Stecher, B. F. Simple adhesive-tape-based sampling of tomato surfaces combined with rapid fluorescence in situ hybridization for Salmonella detection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 1450-1455 Forthcoming.
- Bisha, B., Brehm-Stecher, B. F. Flow-through imaging cytometry for characterization of Salmonella subpopulations in alfalfa sprouts, a microbiologically complex food system. Biotechnol. J. 4, 880-887 (2009).
- Edwards, R. W., Hartman, E. A simple technique for collecting fungus specimens from infected surfaces. Lloydia. 15, 39-39 (1952).
- Evancho, G. M., Sveum, W. H., Moberg, L. J., Frank, J. F. Microbiological monitoring of the food processing environment. Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods. Pouch Downes, F., Ito, K. , 4th edition, American Public Health Association. Washington, D.C. (2001).
- Fung, D. Y. C., Lee, C. Y., Kastner, C. L. Adhesive tape method for estimating microbial load on meat surfaces. J. Food. Prot. 43, 295-297 (1980).
- Kutter, S., Hartmann, A., Schmid, M. Colonization of barley (Hordeum vulgare) with Salmonella enterica and Listeria spp. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 56, 262-271 (2006).
- La Cono, V., Urz, C. Fluorescent in situ hybridization applied on samples taken with adhesive tape strips. J. Microbiol. Meth. 55, 65-71 (2003).
- Lakshmanan, C., Schaffner, D. W. Understanding and controlling microbiological contamination of beverage dispensers in university foodservice operations. Food Prot. Trends. 26, 27-31 (2005).
- Langvad, F. A simple and rapid method for qualitative and quantitative study of the fungal flora of leaves. Can. J. Microbiol. 26, 666-670 (1980).
- Nordentoft, S., Christensen, H., Wegener, H. C. Evaluation of a fluorescence-labelled oligonucleotide probe targeting 23S rRNA for in situ detection of Salmonella serovars in paraffin-embedded tissue sections and their rapid identification in bacterial smears. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35, 2642-2648 (1997).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone