Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Two Methods of Heterokaryon Formation to Discover HCV Restriction Factors
* Wspomniani autorzy wnieśli do projektu równy wkład.
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
We describe two methods for conditional trans-complementation of hepatitis C virus (HCV) assembly and the completion of the full viral life cycle, which rely on heterokaryon formation. These techniques are suitable to screen for cell lines that express dominant restriction factors, which preclude production of infectious HCV progeny.
Streszczenie
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a hepatotropic virus with a host-range restricted to humans and chimpanzees. Although HCV RNA replication has been observed in human non-hepatic and murine cell lines, the efficiency was very low and required long-term selection procedures using HCV replicon constructs expressing dominant antibiotic-selectable markers1-5. HCV in vitro research is therefore limited to human hepatoma cell lines permissive for virus entry and completion of the viral life cycle. Due to HCVs narrow species tropism, there is no immunocompetent small animal model available that sustains the complete HCV replication cycle 6-8. Inefficient replication of HCV in non-human cells e.g. of mouse origin is likely due to lack of genetic incompatibility of essential host dependency factors and/or expression of restriction factors.
We investigated whether HCV propagation is suppressed by dominant restriction factors in either human cell lines derived from non-hepatic tissues or in mouse liver cell lines. To this end, we developed two independent conditional trans-complementation methods relying on somatic cell fusion. In both cases, completion of the viral replication cycle is only possible in the heterokaryons. Consequently, successful trans-complementation, which is determined by measuring de novo production of infectious viral progeny, indicates absence of dominant restrictions.
Specifically, subgenomic HCV replicons carrying a luciferase transgene were transfected into highly permissive human hepatoma cells (Huh-7.5 cells). Subsequently, these cells were co-cultured and fused to various human and murine cells expressing HCV structural proteins core, envelope 1 and 2 (E1, E2) and accessory proteins p7 and NS2. Provided that cell fusion was initiated by treatment with polyethylene-glycol (PEG), the culture released infectious viral particles which infected naïve cells in a receptor-dependent fashion.
To assess the influence of dominant restrictions on the complete viral life cycle including cell entry, RNA translation, replication and virus assembly, we took advantage of a human liver cell line (Huh-7 Lunet N cells 9) which lacks endogenous expression of CD81, an essential entry factor of HCV. In the absence of ectopically expressed CD81, these cells are essentially refractory to HCV infection 10 . Importantly, when co-cultured and fused with cells that express human CD81 but lack at least another crucial cell entry factor (i.e. SR-BI, CLDN1, OCLN), only the resulting heterokaryons display the complete set of HCV entry factors requisite for infection. Therefore, to analyze if dominant restriction factors suppress completion of the HCV replication cycle, we fused Lunet N cells with various cells from human and mouse origin which fulfill the above mentioned criteria. When co-cultured cells were transfected with a highly fusogenic viral envelope protein mutant of the prototype foamy virus (PFV11) and subsequently challenged with infectious HCV particles (HCVcc), de novo production of infectious virus was observed. This indicates that HCV successfully completed its replication cycle in heterokaryons thus ruling out expression of dominant restriction factors in these cell lines. These novel conditional trans-complementation methods will be useful to screen a large panel of cell lines and primary cells for expression of HCV-specific dominant restriction factors.
Protokół
Cell Fusion by PEG
1. Cell Culture
- Culture Huh-7.5, HeLa and Hep56.1D naïve or packaging cell lines 12 on 15 cm cell culture dishes in DMEM complete (DMEM cplt) medium, DMEM supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine, 1x non-essential amino acids, 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 10% fetal calf serum. Apply appropriate selection to stable cell lines as indicated in Table 1.
2. Transfection of HCV RNA
- Wash Huh-7.5 cells (one confluent 15 cm dish) twice with Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS), trypsinize, and resuspend at a concentration of 1.5x107 cells/mL in Cytomix (120 mM KCl, 0.15 mM CaCl2, 10 mM K2HPO4 [pH 7.6], 25 mM HEPES, 2 mM EGTA, 5 mM MgCl2, adjusted to pH 7.6 with KOH and sterilized by filtration) containing 2 mM ATP and 5 mM glutathione.
- Transfect via electroporation 400 μL of the cell suspension (6x106 cells) with 10 μg HCV RNA (pFKi389Luc-EI/NS3-3'_JFH1_dg 13) using cuvettes with a gap width of 0.4 cm and a Gene pulser Xcell system (Biorad) set to 975 μF and 270 V as described previously 14.
- Immediately transfer transfected Huh-7.5 cells to 10 mL of DMEM cplt medium and seed the entire suspension into a single culture dish of 10 cm diameter. Culture cells for 24 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
3. Induction of Fusion by PEG
- Harvest cells as described in 2.1, resuspend in DMEM cplt medium and dilute to 5x105 cells/mL.
- Generate single-cell suspensions of Huh-7.5, HeLa, and Hep56.1D packaging cells, and dilute to 5x105 cells/mL, 2x105 cells/mL, and 2x105 cells/mL, respectively. Note that packaging cells ectopically express HCV proteins core, E1, E2, p7 and NS2 after transduction with two independent lentiviral vectors transducing a C-E1 and E2-p7-NS2 expression cassette, respectively 13, 15.
- Prepare 6-well culture plates with 2-3 sterile glass cover slips per well for further analysis of fusion efficiency.
- Combine 1 mL of transfected Huh-7.5 cells harboring the subgenomic replicon with 1 mL of packaging cells, seed into one well of a 6-well plate, and incubate for 24 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- At this time point, cell density should range between 60-80% confluency before induction of cell fusion in order to allow cells to be in close proximity for cell membranes to fuse.
- Aspirate medium from co-cultured cells and wash once with 1 mL PBS, then carefully add 500 μL of pre-warmed 40% PEG-1500 or PBS as control and incubate for 5 min at 37 °C to induce heterokaryon formation.
- Aspirate PEG and carefully wash 3-5 times for 1 minute (min) per wash with 2 mL PBS to remove excess PEG and finally add 2 mL of DMEM cplt medium to each well and incubate at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Forty-eight hours post fusion, collect each supernatant and filter through a 0.45 μm filter.
- Measure production of infectious particles in fused heterokaryons by inoculation of naïve Huh-7.5 cells (8x104 cells/well seeded in a 12-well plate, 24 h prior to inoculation) with 500 μL of cell-free culture fluid and subsequent determination of luciferase activity 14 .
4. Immunofluorescence to Determine Fusion Efficiency
- After collecting cell culture supernatants (section 3.8), wash wells containing glass cover slips once with 1 mL of PBS for 1 min. All following steps should be performed at room temperature (RT) and washing should be done with 1 mL PBS for 1 min per wash.
- Fix cells with 600 μL of 3% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in PBS for 15 min and then wash 3x with PBS. Carefully transfer cover slips into a 24-well plate using forceps.
- Permeabilize cells with 500 μL of 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS for 5 min and subsequently wash 3x with PBS.
- Prepare primary antibody solution in PBS supplemented with 5% goat serum. Use anti-NS5A antibody (9E10) at a concentration of 0.5 μg/mL and human monoclonal anti-E2 antibody (CBH-23) at a concentration of 6.4 ng/mL. Apply 250 μL to each well and incubate at RT for 45 min.
- Wash 3x with PBS and detect bound primary antibodies with 250 μL secondary goat anti-mouse or goat anti-human IgG-specific antibodies conjugated to Alexa-Fluor 546 or Alexa-Fluor 488, at a concentration of 2 μg/mL in PBS supplemented with 5% goat serum. Incubate for 30 min at RT in the dark.
- Then, wash 1x with PBS and subsequently stain cell nuclei with 250 μL DAPI (4',6'- diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride) diluted 1:3,000 in PBS, incubate for 1 min at RT in the dark.
- Wash 4x with PBS and 1x with H2O, then mount cover slips upside down onto a drop of Fluoromount on a microscope slide, let it dry in the dark and evaluate sample by indirect fluorescence microscopy.
Fusion by transient transfection of prototype foamy virus (PFV) glycoprotein
5. Preparation of Viral Inoculum
- Produce a high titer virus stock by transfecting in vitro transcribed HCV RNA into Huh-7.5 cells and harvesting cell culture supernatant after 48 h and 72 h as described previously 14. Determine viral titer by limiting dilution assay (TCID50) 13.
6. Cell Culture, Cell Fusion by Transfection of a Fusogenic PFV Glycoprotein
- Culture Lunet N, HeLa, and Hep56.1D hCD81 cells according to the instructions in Table 1 in DMEM cplt medium containing appropriate selections.
- Detach cells as described in 2.1, prepare single cell suspensions in DMEM cplt medium, and co-cultivate Lunet N cells with HeLa or Hep56.1D hCD81 cell lines at appropriate ratios (e.g. 1:2 for Hep56.1D hCD81 or 1:1 for HeLa cells) yielding a total cell density of 1.5x105 cells per 12-well and incubate for 24 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- The next day, transiently transfect cells with the highly fusogenic PFV envelope protein (pczHFVenvEM066 16) by using Lipofectamine 2000 according to the manufacturer's instructions.
7. Infection Assay
- Inoculate heterokaryons 30 h after transfection with 350 μL of virus stock (MOI of ~2.3) for 12 h overnight, wash once with PBS and add 1 mL of DMEM cplt medium per well. Incubate for 48 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Harvest supernatant of heterokaryon culture, filter through a 0.45 μm filter and inoculate Huh-7.5 cells, seeded in 96-well plates (1x104 cells/well) the day before, in a limiting dilution assay 13.
- After 72 h, stain infected Huh-7.5 cells with an HCV-specific antibody (NS5A; 9E10) to quantify production of infectious progeny particles.
8. Visualization of Cell Fusion
- To visualize fusion events, prepare 5 to 10 μM solutions of CellTracker dyes in DMEM medium without additives and complete the steps below 6 h before co-culture (described in sections 6.2 and 6.3).
- Wash adherent cells once with 5 mL of PBS and then incubate cells with 4 mL of staining solution per 10 cm dish for 45 min at 37 °C and 5% CO2 (stain Lunet N cells with CellTracker Orange CMTMR and HeLa or Hep56.1D hCD81 cells with CellTracker Green CMFDA, separately).
- Wash cells once with 5 mL of PBS for 1 min and add DMEM cplt medium, incubate for 6 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Prepare seeding and transfection of stained cells as described above in sections 6.2 and However, add a cover slip to the cell culture dish before seeding.
- 30 h post transfection, wash cells carefully with 1 mL of PBS for 1 min and then fix cells with 250 μL of 3% PFA for 15 min at RT. Wash cells once with 1 mL PBS for 1 min, stain with DAPI for 1 min as described in section 4.6, wash once with 1 mL PBS for 1 min, repeat wash with H2O and mount cover slips on glass slides (see section 4.7). Analyze cells with a fluorescence microscope.
| Species | Cell line | Origin | Growth medium & selection |
| Human | Huh-7.5 | Subclone of Huh-7 hepatoma cell line 17 | DMEM cplt |
| Huh-7.5 [CE1][E2p7NS2] | Stably expressing viral proteins core, E1, E2, p7, and NS2, transduced by lentiviral gene transfer of two independent gene cassettes | DMEM cplt + Blasticidin 5 μg/mL | |
| Huh-7 Lunet N | Subclone of Huh-7 hepatoma cell line 9 | DMEM cplt | |
| HeLa | Cervical adenocarcinoma cell line (ATCC number: CCL-2) | DMEM cplt | |
| HeLa [CE1][E2p7NS2] | Stably expressing viral proteins core, E1, E2, p7, and NS2, transduced by lentiviral gene transfer of two independent gene cassettes | DMEM cplt + G418 750 μg/mL; Blasticidin 5 μg/mL | |
| Mouse | Hep56.1D | Primary hepatocellular carcinoma (kind gift of J. Encke) Adult C57BL/6J mice | DMEM cplt |
| Hep56.1D [CE1][E2p7NS2] | Stably expressing viral proteins core, E1, E2, p7, and NS2, transduced by lentiviral gene transfer of two independent gene cassettes | DMEM cplt + G418 750 μg/mL; Blasticidin 5 μg/mL | |
| Hep56.1D hCD81 | Stably expressing human CD81 transduced by lentiviral gene transfer | DMEM cplt + Blasticidin 5 μg/mL |
Table 1. Specifications about origin and culture condition of used cell lines Cplt: complete, G418: geneticin, h: human.
9. Representative Results
In this study, we applied two different methods of somatic cell fusion that allow us to specifically investigate the impact of restriction factors on completion of the HCV replication cycle in heterokaryons. Of note, the conditional design of trans-complementation upon fusion of the two different cell types assures that only in true heterokaryons between human liver cells and non-permissive cell lines, virus assembly (approach 1) or virus entry and the full HCV replication cycle (approach 2) are accomplished.
In the first approach Huh-7.5 cells, highly permissive for HCV, were transiently transfected with a subgenomic replicon expressing a luciferase transgene and HCV non-structural proteins supporting subgenomic HCV RNA replication (Huh-7.5 replicon cells). These cells were co-cultured and fused to cell lines expressing HCV structural proteins core, E1, E2, as well as accessory proteins p7, and NS2. Figure1A shows an overview of the experimental procedure. Importantly, following PEG fusion, all proteins required for particle assembly should be present in the formed heterokaryon which can be confirmed by immunofluorescence against individual viral proteins. Figure 1B depicts an exemplary fusion event in which signals for both NS5A expressed in Huh-7.5 replicon cells and E2 expressed in Huh-7.5[CE1][E2p7NS2] packaging cells were detected in the same cytoplasm upon PEG-induced heterokaryon formation. When co-cultured cells were instead treated with PBS, no fusion was induced thus only single-positive cells and no co-localization of signals was observed. Furthermore, to control transgene expression, we performed ELISAs specific for core and E2 (previously reported in detail 15). In addition to the control packaging cell line Huh 7.5[CE1][E2p7NS2], we generated HeLa and Hep56.1D packaging cells as representatives for human non-liver and mouse liver cells, respectively. HCV RNA replication efficiency in these latter cells is low and HCV assembly and release has not been shown. Figure 1C illustrates the results of the fusion assay. Supernatants were collected from the co-culture at 48 h post fusion induction and used to inoculate naïve Huh-7.5 cells for subsequent luciferase assays. Notably, when Huh-7.5 replicon cells were fused with either naïve cell lines or treated with PBS as control, no infectivity was detected in the culture fluids. However, when cell fusion between Huh-7.5 replicon and packaging cell lines was induced by PEG, trans-complementation between replicon and constitutively expressed structural proteins rescued virus production in the resulting heterokaryons and infectious viral particles were released into the culture fluids. We therefore concluded that virus production required cell fusion and expression of viral proteins in the packaging cell lines. Strikingly, not only the heterokaryons of Huh-7.5 human hepatoma cells, but also heterokaryons with human non-liver (HeLa[CE1][E2p7NS2]) and mouse liver (Hep56.1D[CE1][E2p7NS2]) cells allowed virus release, indicating that assembly and release are not dominantly inhibited by possible restriction factors in these cell types. Expression of structural proteins in packaging cell lines and authentic entry into target cells was shown in Frentzen et al. 15.
An alternative method of cell fusion was utilized to analyze possible restrictions affecting cell entry, RNA translation and RNA replication stages of the replication cycle and to exclude that a high viral burden in transfected Huh 7.5 replicon cells would preclude detection of restriction factors by saturation. To this end, we developed an independent assay based on inoculation of heterokaryons with HCVcc and detection of de novo virus production in these cells. As outlined in Figure 2A, somatic cell fusion was induced by the expression of a fusogenic glycoprotein after co-cultivation of the cells. This method was chosen because sensitivity was increased likely due to increased fusion efficiency. Heterokaryons were visualized by staining separate cell lines with CellTracker dyes prior to co-cultivation. A heterokaryon with homogenously distributed dyes within the cytoplasm indicates fusion of two cell types as indicated in Figure 2B. Only in heterokaryons of Lunet N cells with HeLa cells or Hep56.1D hCD81 cells are all HCV entry factors expressed thus selectively rendering heterokaryons susceptible to HCV cell entry. Challenge with HCVcc resulted in complete replication of HCV in heterokaryons which is evident from de novo production of infectious viral progeny approximately 10-fold above the background of the assay (Figure 2C). As a control, Lunet N cells were fused with Lunet N cells. Importantly only very low levels of infectious HCV close to the detection limit were observed. Similar results were obtained when Lunet N cells were fused with naïve Hep56.1D cells. In both cases, human CD81 was absent so that HCV could not productively infect the heterokaryons. This very low infectivity detected in these two latter cases is likely attributable to low level of infection of Lunet N cells and/or low levels of residual infectious virus input from the inoculum. In contrast HeLa cells and Hep56.1D hCD81 cells express human CD81, thus complementing the lacking cell entry factor in the heterokaryons and permitting HCV cell entry. The 10-fold increased level of infectious HCV detected in the medium of heterokaryons involving these two cell lines therefore likely reflects de novo production of infectious particles in heterokaryons. Thus, we concluded that completion of the HCV replication cycle is not restricted excluding the expression of dominant HCV restriction factors in these cell lines.
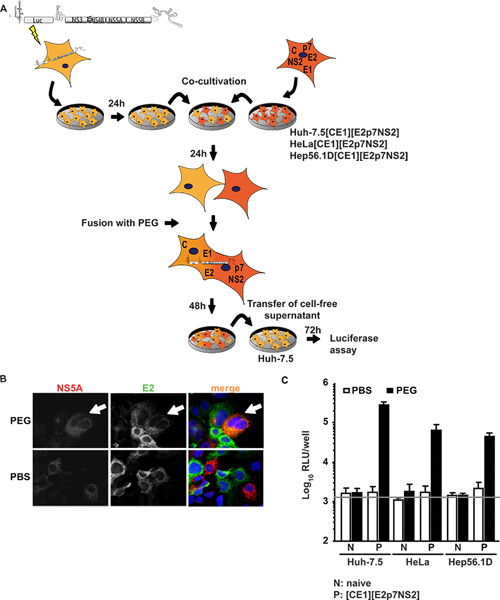
Figure 1. Trans-complementation of HCV assembly and release in heterokaryons. (A) Schematic outline of the experimental procedure of PEG-mediated cell fusion. The JFH1 luciferase reporter replicon Luc-NS3-5B was transfected into naïve Huh-7.5 cells by electroporation. The next day, cells were detached and co-cultured with naïve cells or packaging cells constitutively expressing HCV core, E1, E2, p7 and NS2. 24 h post co-cultivation, heterokaryon formation was induced by treatment with 40% PEG using PBS as negative control. After 48 h, cell-free supernatant was harvested to inoculate naïve Huh-7.5 cells. Infectivity was determined by luciferase activity. (B) For detection of heterokaryons, cells were immunostained using monoclonal antibodies against E2 and NS5A. Simultaneous expression of both proteins within cells is indicative of cell fusion. (C) Luciferase measurements were performed to quantify viral infectivity produced from heterokaryons. Mean values of three independent experiments and the standard deviations of the means are given. The horizontal bar represents the background RLU determined in uninfected Huh-7.5 cells. Click here to view larger figure.
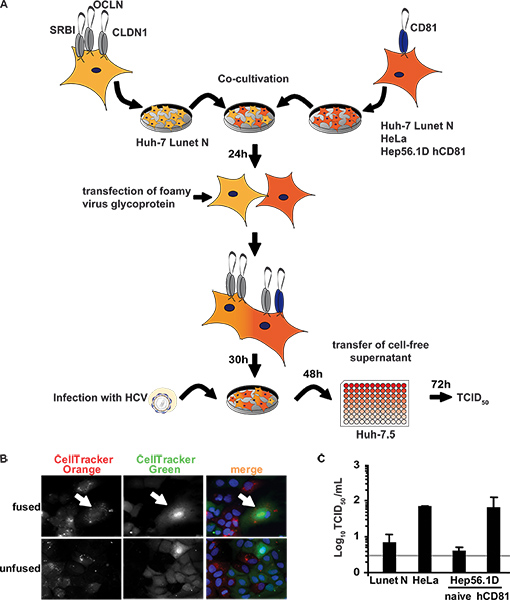
Figure 2. Completion of HCV replication cycle after inoculation of heterokaryons. (A) Schematic overview of the experimental procedure. Huh-7 Lunet N cells lacking CD81 were co-cultured with the indicated cell lines lacking or expressing human CD81. Importantly, these latter cells lack at least one HCV entry factor and therefore cannot be productively infected. The next day, fusion was initiated by transfection of a fusogenic viral envelope protein from PFV. Thirty hours later, cells were challenged with infectious HCV particles. To measure cell entry, RNA replication and virus production sustained by these heterokaryons, released infectivity in the cell-free culture fluids was determined 48 h post inoculation. To this end, naïve Huh-7.5 cells were used as target cells in a limiting dilution assay (TCID50). (B) For detection of heterokaryons, cells were stained with CellTracker Green or CellTracker Orange 6 h prior to co-cultivation and transfection. Thirty hours later, cells were fixed and stained with DAPI. (C) Lunet N cells were fused to HeLa cells, naïve Hep56.1D or Hep56.1D cells expressing human CD81. These cultures were inoculated with HCVcc (MOI of 2.3). Culture fluids were collected 48 h later and de novo particle release from heterokaryons was determined by TCID50 using naïve Huh-7.5 target cells. Mean values of three independent experiments are given. The horizontal bar represents the detection limit of the assay. Click here to view larger figure.
Dyskusje
We present two methods to induce heterokaryon formation in cultured cells for the analysis of dominant negative restrictions that preclude HCV replication. Using these procedures we excluded the presence of a dominant constitutively expressed or virus-induced factor in various human non-liver and in murine liver cell lines. The first assay primarily analyzes if restriction factors prevent HCV assembly and release of infectious progeny. Since in this case the packaging cells are fused to HCV replicon cells, possible restr...
Ujawnienia
TP received consulting fees from Biotest.
Podziękowania
We are grateful to Takaji Wakita and Jens Bukh for JFH1 and J6CF isolates, respectively. Furthermore we thank Charles Rice for Huh-7.5 cells and the 9E10 antibody, Steven Foung for the E2-specific antibody CBH-23, and all members of the Department of Experimental Virology, Twincore for helpful suggestions and discussions.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| DMEM | Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany | 41965-039 | |
| L-glutamine | Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany | 25030-024 | |
| Non-essential amino acids | Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany | 11140-035 | |
| Penicillin/ streptomycin | Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany | 15140-122 | |
| Fetal calf serum | PAA, Cölbe, Germany | A15151 | |
| α-E2 (CBH23) | kindly provided by Steven Foung 10 | ||
| ATP | Sigma, Steinheim, Germany | A2833-106 | |
| Glutathione | Sigma, Steinheim, Germany | G4251-1G | |
| Blasticidin | Invivo Gen, San Diego, USA | Ant-bl-1 | |
| G418 (geneticin) | Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany | 11811-064 | |
| Polyethylene-glycol-1500 | Roche, Mannheim, Germany | 10783641001 | |
| Paraformaldehyde | Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany | 0335.3 | |
| Triton X-100 | Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany | 3051.2 | |
| Goat serum | Sigma, Steinheim, Germany | G9023-5mL | |
| α-NS5A (9E10) | Kindly provided by Charles Rice 7 | ||
| DAPI (4',6'- diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride) | Invitrogen | D1306 | |
| Alexa-Fluor 546 - goat anti-human IgG | Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany | A21089 | |
| Alexa-Fluor 488 - goat anti-mouse IgG | Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany | A10680 | |
| Lipofectamine 2000 | Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany | 11668-019 | |
| CellTracker CMTMR | Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany | C2927 | |
| CellTracker CMFDA | Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany | C2925 | |
| Fluoromount | Sigma, Steinheim, Germany | F4680-25ML | |
| All other chemicals | Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany | ||
| Cell culture materials | Sarstedt, Nümbrecht, Germany |
Odniesienia
- Zhu, Q., Guo, J. T., Seeger, C. Replication of hepatitis C virus subgenomes in nonhepatic epithelial and mouse hepatoma cells. J. Virol. 77, 9204-9210 (2003).
- Kato, T. Nonhepatic cell lines HeLa and 293 support efficient replication of the hepatitis C virus genotype 2a subgenomic replicon. J. Virol. 79, 592-596 (2005).
- Ali, S., Pellerin, C., Lamarre, D., Kukolj, G. Hepatitis C virus subgenomic replicons in the human embryonic kidney 293 cell line. J. Virol. 78, 491-501 (2004).
- Date, T. Genotype 2a hepatitis C virus subgenomic replicon can replicate in HepG2 and IMY-N9 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 22371-22376 (2004).
- Chang, K. S. Replication of hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA in mouse embryonic fibroblasts: protein kinase R (PKR)-dependent and PKR-independent mechanisms for controlling HCV RNA replication and mediating interferon activities. J. Virol. 80, 7364-7374 (2006).
- Zhong, J. Robust hepatitis C virus infection in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 9294-9299 (2005).
- Lindenbach, B. D. Complete replication of hepatitis C virus in cell culture. Science. 309, 623-626 (2005).
- Wakita, T. Production of infectious hepatitis C virus in tissue culture from a cloned viral genome. Nat. Med. 11, 791-796 (2005).
- Witteveldt, J. CD81 is dispensable for hepatitis C virus cell-to-cell transmission in hepatoma cells. J. Gen. Virol. 90, 48-58 (2009).
- Bitzegeio, J. Adaptation of hepatitis C virus to mouse CD81 permits infection of mouse cells in the absence of human entry factors. PLoS Pathog. 6, e1000978 (2010).
- Lindemann, D., Goepfert, P. A. The foamy virus envelope glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 277, 111-129 (2003).
- Brohm, C. Characterization of determinants important for hepatitis C virus p7 function in morphogenesis by using trans-complementation. J. Virol. 83, 11682-11693 (2009).
- Steinmann, E., Brohm, C., Kallis, S., Bartenschlager, R., Pietschmann, T. Efficient trans-encapsidation of hepatitis C virus RNAs into infectious virus-like particles. J. Virol. 82, 7034-7046 (2008).
- Koutsoudakis, G. Characterization of the early steps of hepatitis C virus infection by using luciferase reporter viruses. J. Virol. 80, 5308-5320 (2006).
- Frentzen, A. Completion of hepatitis C virus replication cycle in heterokaryons excludes dominant restrictions in human non-liver and mouse liver cell lines. PLoS Pathog. 7, e1002029 (2011).
- Lindemann, D. A particle-associated glycoprotein signal peptide essential for virus maturation and infectivity. J. Virol. 75, 5762-5771 (2001).
- Blight, K. J., McKeating, J. A., Rice, C. M. Highly permissive cell lines for subgenomic and genomic hepatitis C virus RNA replication. J. Virol. 76, 13001-13014 (2002).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone