A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Mitochondrial Isolation from Skeletal Muscle
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes a procedure to study the respiration of mitochondria isolated from skeletal muscles. This method was adapted from Scorrano et al. (2007). The mitochondrial isolation procedure requires about 2 hours. The mitochondrial respiration can be completed in about 1 hour.
Abstract
Mitochondria are organelles controlling the life and death of the cell. They participate in key metabolic reactions, synthesize most of the ATP, and regulate a number of signaling cascades2,3. Past and current researchers have isolated mitochondria from rat and mice tissues such as liver, brain and heart4,5. In recent years, many researchers have focused on studying mitochondrial function from skeletal muscles.
Here, we describe a method that we have used successfully for the isolation of mitochondria from skeletal muscles 6. Our procedure requires that all buffers and reagents are made fresh and need about 250-500 mg of skeletal muscle. We studied mitochondria isolated from rat and mouse gastrocnemius and diaphragm, and rat extraocular muscles. Mitochondrial protein concentration is measured with the Bradford assay. It is important that mitochondrial samples be kept ice-cold during preparation and that functional studies be performed within a relatively short time (~1 hr). Mitochondrial respiration is measured using polarography with a Clark-type electrode (Oxygraph system) at 37°C7. Calibration of the oxygen electrode is a key step in this protocol and it must be performed daily. Isolated mitochondria (150 μg) are added to 0.5 ml of experimental buffer (EB). State 2 respiration starts with addition of glutamate (5mM) and malate (2.5 mM). Then, adenosine diphosphate (ADP) (150 μM) is added to start state 3. Oligomycin (1 μM), an ATPase synthase blocker, is used to estimate state 4. Lastly, carbonyl cyanide p-[trifluoromethoxy]-phenyl-hydrazone (FCCP, 0.2 μM) is added to measurestate 5, or uncoupled respiration 6. The respiratory control ratio (RCR), the ratio of state 3 to state 4, is calculated after each experiment. An RCR ≥4 is considered as evidence of a viable mitochondria preparation.
In summary, we present a method for the isolation of viable mitochondria from skeletal muscles that can be used in biochemical (e.g., enzyme activity, immunodetection, proteomics) and functional studies (mitochondrial respiration).
Protocol
1. Preparation of Buffers
- Turn on centrifuge 5804R and set to 4°C. Turn on Isotemp 3006D water bath and set to 37°C.
- Prepare the following solutions before muscle isolation:
- PBS: Dissolve phosphate buffered saline (PBS) tablets in distilled water (5 tablets/liter). Mix well.
- PBS plus 10 mM EDTA: To prepare a 100 ml solution, add 2 ml of 500 mM EDTA to 98 ml of PBS.
- 8X Mitochondria buffer: 10.28 g of sucrose for a final concentration of 0.6 M, 400 mg of free-fatty acid bovine serum albumin (BSA) for a final concentration of 0.8%, 2.08 g of HEPES for a final concentration of 160 mM, pH to 7.4 and QS to 50 ml with distilled water.
- Isolation Buffer 1 (IB1): Add 200 μl of 500 mM EDTA for a final concentration of 10 mM, 0.392 g of D-mannitol for a final concentration of 215 mM, 1.25 ml of 8X mitochondria buffer, pH to 7.4 and QS to 10 ml with distilled water.
- Isolation Buffer 2 (IB2): Add 60 μl of 500 mM EGTA for a final concentration of 3 mM, 0.392 g of D-mannitol for a final concentration of 215 mM, 1.25 ml of 8X mitochondria buffer, pH to 7.4 and QS to 10 ml with distilled water.
- Experimental Buffer (EB): Add 100 μl of 500 mM MgCl2 for a final concentration of 5 mM, 0.392 g of D-mannitol for a final concentration of 215 mM, 25 μl of 2.5 mM KH2PO4 for a final concentration of 6.25 μM, 2 μl of 100 mM EGTA for a final concentration of 20 μM, 1.25 ml of mitochondrial buffer, pH to 7.4 and QS to 10 ml with distilled water.
2. Muscle Isolation
- In an ice bucket, put three 10 ml beakers, Potter-Elvehjem tissue grinders and all other necessary instruments/supplies on ice. Everything must stay ice-cold throughout the experiment.
- Place IB1 and IB2 in ice bucket and EB in warm water bath when done.
- In the three 10 ml beakers, the following solutions should be added:
- Beaker 1: 10 ml of PBS
- Beaker 2: 10 ml of PBS/EDTA
- Beaker 3: 3 ml of IB1
- Kill a rat humanely as approved by your local Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
- Rapidly isolate 250-500 mg of skeletal muscle, rinse in Beaker 1, then transfer to Beaker 2.
3. Homogenization/Mitochondrial Isolation
- Transfer muscle to Beaker 3 and finely mince the muscle with scissors.
- Transfer the solution to the Potter-Elvehjem homogenizer. Homogenize the muscle using a motorized pestle (a drill press will do the job) 10 times keeping the tube in ice at all times.
- Transfer homogenate to pre-chilled 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes and centrifuge at 700 g for 10 minutes at 4° C.
- Transfer supernatant to a new pre-chilled microcentrifuge tube. Discard pellet.
- Centrifuge supernatant at 10,500 g for 10 minutes at 4° C.
- Transfer supernatant to a new pre-chilled microcentrifuge tube and label SN1 (supernatant number 1) and muscle type.
- Re-suspend pellet in 500 μl of IB2.
- Centrifuge at 10,500 g for 10 minutes at 4° C.
- Transfer supernatant to a new pre-chilled microcentrifuge tube and label SN2 (supernatant number 2) and muscle type.
- Suspend final mitochondrial pellet in 100 μl of IB2.
- Re-spin final mitochondrial suspension in minifuge for a few seconds. If there is a pellet, transfer supernatant to a new pre-chilled microcentrifuge tube and discard the pellet.
- Determine protein concentration using the Bradford assay 8.
4. Electrode Calibration
NOTE: Complete electrode calibration during mitochondrial isolation.
- Add 100 ml of distilled water to 250 ml flask. Stir vigorously for 20 minutes to equilibrate the water with atmospheric gas.
- Add a few drops of 50% KCl to the Oxygraph electrode.
- Place a small piece of Blue Rizla rolling paper on top of electrode.
- Place a piece of PTFE membrane on top of the rolling paper.
- Apply the inner ring using the ring applicator and then place the outer ring in the electrode groove.
- Connect electrodes and assemble the rest of the equipment: bigger plastic ring base, mitochondrial chamber, and water hoses.
- Turn on Oxygraph boxes and start Oxygraph software.
- Add the equilibrated water to mitochondrial chamber.
- Add stir bar and turn on to a speed of 60.
- Begin a new experiment.
- Click on calibrate and then liquid phase calibration for Box 1. Change temperature to 37° C and click "OK" twice.
- When "Override" changes to "OK" click it and open the nitrogen gas tank.
- Place tip connected to nitrogen tank into chamber and establish zero oxygen. Click "OK" when it switches from "Override."
- Aspirate water and add 500 μl of EB buffer to mitochondrial chambers.
- Seal chamber with plunger.
- If using multiple boxes, repeat steps 11-15 for calibration of Box 2.
5. Mitochondrial Respiration
- Start a new experiment; let it run for about 1 minute to stabilize signal.
- Add necessary volume of the mitochondrial suspension (step 3.11) for 150 μg in each chamber, mark event, and let it run for 1 minute.
- Add 10 μl of warm 250 mM/125 mM glutamate/malate for a final concentration of 5 mM/2.5 mM. Mark and let run for 1 minute. This is defined as State 2.
- Add 7.5 μl of 10 mM ADP for a final concentration of 150 μM, mark, and let run for 30 seconds. This is defined as State 3.
- Add another 7.5 μl of 10 mM ADP, mark, and let run for 1.5 minutes.
- Add 0.5 μl of cold 10 mM oligomycin for a final concentration of 1 μM, mark, and let run for 3 minutes. This is defined as State 4.
- Add 1 μl of cold 0.1 mM FCCP for a final concentration of 0.2 μM, mark, and let run for 3 minutes. This is defined as State 5.
- When finished, end experiment and save.
- Acquire respiration rates using Oxygraph software.
- Enter normalization factor: if adding 150 μg of mitochondrial protein, the normalization factor will be 0.15.
- Calculate normalized respiration rates for the different respiration states.
- Calculate the Respiratory Control Ratio (RCR) by dividing State 3 by State 4.
6. Representative Results:
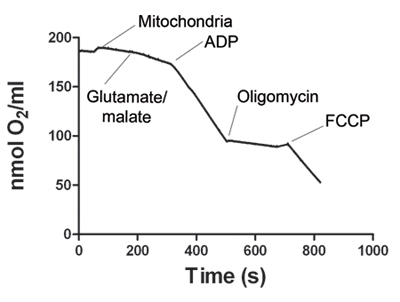
Figure 1. shows a representative tracing of oxygen consumption by skeletal muscle mitochondria. After the electrode signal is stabilized, the mitochondria sample is added to the Oxygraph chamber. State 2 respiration starts with addition of glutamate and malate. Addition of ADP increases oxygen consumption, defining state 3 respiration. ATP synthase is blocked by addition of oligomycin to obtain state 4 respiration. Finally, FCCP is added to uncouple mitochondrial respiration (state 5). Table 1 shows representative oxygen consumption rates for states 2, 3, 4 and 5. The respiratory control ratio (RCR) is calculated for each experiment. RCR ≥4 is considered as evidence of a viable mitochondria preparation.
| States | Normalized Rates |
| State 2 | 34.74 |
| State 3 | 153.40 |
| State 4 | 16.49 |
| State 5 | 143.70 |
| RCR | 9.30 |
Table 1. Mitochondrial respiration rates. Representativeoxygen consumption rates from skeletal muscle mitochondria. Values are normalized to the amount of mitochondria added to the chamber. The respiratory control ratio (RCR) is determined by dividing state 3 by state 4. An RCR≥4 represents a viable mitochondria preparation.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
We present a protocol to isolate viable mitochondria from skeletal muscles. If yield is a problem, the protocol can be modified by incubating the isolated muscle in 5 ml of PBS/10mM EDTA/0.01% trypsin for 30 minutes in ice. To assure complete muscle digestion with trypsin, the muscle needs to be fully minced. After the 30-minute incubation, the PBS/10mM EDTA/0.01% trypsin solution must be completely replaced with 3 ml of isolation buffer 1 (IB1). In addition, the use of trypsin may interfere with some mitochondrial subst...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest declared.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Eye Institute (R01 EY12998) to F.H. Andrade.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 95% CO2 / 5% O2 mix | Local Gas Supplier | ||
| Adenosine 5′-diphosphate sodium salt | Sigma-Aldrich | A2754 | |
| Blue Rizla Paper | Hansatech | 890101 | |
| Bradford protein assay | Bio-Rad | 500-0006 | |
| Carbonylcyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone (FCCP) | Sigma-Aldrich | C2920 | |
| Centrifuge 5804R | Eppendorf | ||
| Compressed nitrogen | Local Gas Supplier | ||
| D-mannitol | Sigma-Aldrich | M9647 | |
| Ethlyene-glycol-bis-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) | Sigma-Aldrich | E3889 | |
| Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) | Bio-Rad | 161-0728 | |
| Free fatty acid bovine serum albumin | Sigma-Aldrich | A8806 | |
| Glutamic acid | Sigma-Aldrich | G5889 | |
| HEPES sodium salt | Sigma-Aldrich | H7006 | |
| Isotemp 3006D | Fisher Scientific | ||
| Magnesium chloride | Sigma-Aldrich | M8266 | |
| Male Sprague Dawley Rats | Harlan Laboratories | 300-500g | |
| Malic acid | Sigma-Aldrich | M9138 | |
| Minifuge | ISC Bioexpress | C1301P | |
| Oligomycin | Sigma-Aldrich | O4876 | |
| Oxygen electrode disc | Hansatech | S1 | |
| Oxygraph | Hansatech | ||
| Oxygraph Plus V1.01 Software | Hansatech | ||
| pH-meter | Mettler Toledo | 1225506149 | |
| Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | Sigma-Aldrich | P4417 | |
| Potassium chloride | Sigma-Aldrich | P3911 | |
| Potassium phosphate | Sigma-Aldrich | P8416 | |
| Potter-Elvehjem homogenizers | Fisher Scientific | 08-414-14A | |
| PTFE (0.0125mm × 25mm) membrane | Hansatech | S4 | |
| SKIL 3320 drill press | Hardware store | ||
| Sucrose | Sigma-Aldrich | S5016 |
References
- Frezza, C., Cipolat, S., Scorrano, L. Organelle isolation: functional mitochondria from mouse liver, muscle and cultured fibroblasts. Nat Protoc. 2, 287-295 (2007).
- Duchen, M. R. Roles of mitochondria in health and disease. Diabetes. 53, Suppl 1. S96-S102 (2004).
- Johannsen, D. L., Ravussin, E. The role of mitochondria in health and disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol. , (2009).
- Pallotti, F., Lenaz, G. Isolation and subfractionation of mitochondria from animal cells and tissue culture lines. Methods Cell Biol. 80, 3-44 (2007).
- Pallotti, F., Lenaz, G. Isolation and subfractionation of mitochondria from animal cells and tissue culture lines. Methods Cell Biol. 65, 1-35 (2001).
- Gamboa, J. L., Andrade, F. H. Mitochondrial content and distribution changes specific to mouse diaphragm after chronic normobaric hypoxia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. , (2009).
- Patel, S. P., Gamboa, J. L., McMullen, C. A., Rabchevsky, A., Andrade, F. H. Lower respiratory capacity in extraocular muscle mitochondria: evidence for intrinsic differences in mitochondrial composition and function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50, 180-186 (2009).
- Bradford, M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72, 248-254 (1976).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved