È necessario avere un abbonamento a JoVE per visualizzare questo. Accedi o inizia la tua prova gratuita.
Method Article
Microscopia elettronica a scansione (SEM) Protocolli per problematico Plant, oomicete, e campioni fungine
In questo articolo
Riepilogo
Problems in the processing of biological samples for scanning electron microscopy observation include cell collapse, treatment of samples from wet microenvironments and cell destruction. Low-cost and relatively rapid protocols suited for preparing challenging samples such as floral meristems, oomycete cysts, and fungi (Agaricales) are compiled and detailed here.
Abstract
I problemi più comuni nel trattamento dei campioni biologici per le osservazioni con il microscopio elettronico a scansione (SEM) includono il collasso delle cellule, il trattamento di campioni provenienti da microambienti umidi e la distruzione delle cellule. Utilizzando i giovani tessuti floreali, cisti oomiceti e spore di funghi (Agaricales) come esempi, i protocolli specifici per trattare i campioni delicati sono descritte qui che superano alcune delle principali sfide nel trattamento del campione per l'acquisizione di immagini sotto il SEM.
meristemi floreali fissate con FAA (formalina-acetico-alcol) ed elaborate con la Critical Point Dryer (CPD) non veniva visualizzato crollati pareti cellulari o organi distorti. Questi risultati sono cruciali per la ricostruzione dello sviluppo floreale. Un simile trattamento CPD-based dei campioni microambienti umidi, come le cisti oomiceti glutaraldeide fisso, è ottimale per testare la crescita differenziale di caratteristiche diagnostiche (ad esempio, le spine cisti) su diversi tipi di dobstrates. La distruzione delle cellule nutrici collegati a spore di funghi è stato evitato dopo la reidratazione, la disidratazione, e il trattamento CPD, un passo importante per ulteriori studi funzionali di queste cellule.
I protocolli descritti qui rappresentano a basso costo e le alternative rapide per l'acquisizione di immagini di buona qualità per ricostruire i processi di crescita e di studiare le caratteristiche diagnostiche.
Introduzione
In biologia, l'uso di microscopia elettronica a scansione (SEM) è stato esteso a studi di evoluzione strutturale, morfologia comparativa sviluppo degli organi, e la caratterizzazione di popolazioni o specie 1. Con la sua vista bidimensionale di strutture microscopiche, aree come micromorfologia e sistematica beneficiato dal SEM tecnica progressi a partire dalla seconda metà del 20 ° secolo. Ad esempio, l'introduzione della metodologia di rivestimento sputtering nel 1970 resa possibile osservazioni di materiali delicati quali apici dei germogli e fiori migliorando l'imaging del tessuto non conduttivi 2, 3. SEM utilizza elettroni emessi dalla superficie del campione per riprodurre la topografia in un ambiente ad alto vuoto 4.
Gli studi che coinvolgono SEM sono focalizzati sia l'inferenza di caratteri strutturali e la ricostruzione di growtprocessi h. Nuovi personaggi strutturali rilevanti per la tassonomia e sistematica di una vasta gamma di organismi sono stati scoperti da osservazioni SEM. Ad esempio, i tratti vegetali utilizzati per la diagnosi specie o di classificazioni supraspecific, come ad esempio i pozzi vestured di legno 5, la stigmatizzazione della diversità 6, nettario e floreale morfologia 7, 8, dettagli tricomi 9, e grani di polline 10, 11, non può essere visualizzato correttamente senza SEM. Osservazioni di successo con SEM convenzionale sono stati raggiunti anche per lungo tempo gli organismi fissati in formalina 12 e vegetale erbario esemplari 13.
D'altra parte, studi di ricostruzione dei processi di crescita mediante SEM coinvolgono un'ampia gamma di argomenti, quali lo sviluppo dell'organo 14, infeZIONI indotte da batteri 15, pianta radice fisiologia 16, meccanismi di attacco del parassita-ospite 17, 18, gli effetti della droga sui parassiti 19, mycoparasitism e antibiosi 20, 21, la crescita malformazioni 22, sviluppo comparativa di individui selvatici e mutanti 23, e interi cicli di vita 24. Sebbene microscopi a scansione ambientale elettroni (ESEM) 25 possono avere importanti vantaggi per l'osservazione di campioni biologici umidi nei processi di crescita, materiale delicato può ancora essere compromessa anche in condizioni di basso vuoto della ESEM), e devono essere trattati adeguatamente per evitare perdite di pregevole osservazione morfologica.
In questo lavoro, una revisione dei protocolli specifici per SEM osservazione di tre difftipi diversi di campioni è presentato: meristemi floreali, oomiceti (Saprolegnia), e materiale fungino. Questi protocolli compilare l'esperienza dei nostri studi precedenti SEM-base 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, dove sono stati trovati difficoltà specifiche e soluzioni alternative. Nel caso di impianti di sviluppo comparativo e studi strutturali, l'uso di SEM ha iniziato nel 1970 34, 35, e da allora, i ricercatori hanno scoperto che certe caratteristiche floreali sono più labili di quanto si pensasse 36. Ricostruzione di sviluppo floreale comporta la cattura di tutte le fasi tra giovani meristemi floreali e antesi. Per raggiungere questo obiettivo, è essential che la topografia del campione e l'integrità parete cellulare non sono compromesse dopo la fissazione e successiva disidratazione. I giovani meristemi floreali sono particolarmente vulnerabili al collasso della parete cellulare (figure 1a, 1b). Allo stesso modo, le strutture delicate come nettarii, petali, stimmi e sporangi richiedono protocolli efficaci e undamaging. Questa review riassume un protocollo ottimale per mantenere giovani e delicati tessuti intatti per l'imaging SEM.
Nel caso dei oomiceti (Stramenopiles), uno dei gruppi più diversi e diffusi di parassiti, con padroni di casa che vanno dai microbi e piante per invertebrati e vertebrati 37 - ci sono spore che crescono e si sviluppano in un ambiente umido. Questa condizione rappresenta una sfida per l'osservazione SEM perché le spore hanno bisogno di un supporto adeguato non è adatto per protocolli standard SEM. Tra le oomiceti, specie di Saprolegnia sono di particolare interesse perché can causare gravi riduzioni di acquacoltura, la pesca, e le popolazioni di anfibi 38. Caratteristiche micromorfologici, come ad esempio le spine uncinate di cisti, sono stati trovati per essere utile per identificare le specie di Saprolegnia, che è fondamentale per stabilire i controlli di infezione e potenziali trattamenti 39. Qui, vi è un protocollo sperimentale di confrontare i modelli di crescita colonna di cisti su diversi substrati e per manipolare il campione per la preparazione critica punto asciugatrice (CPD) e successiva osservazione SEM.
In un terzo caso, ci sono risultati interessanti, che salgono dopo un controllo delle spore dei funghi Phellorinia Herculanea f. f stellata. nova (Agaricales) 31. Insieme con le spore, un gruppo di celle di vivai inaspettati stato identificato sotto la SEM. Con i protocolli tradizionali precedenti e materiale non trattato, le cellule venivano infermiere out completamente crollato (Figura 1c). Ulteriori inferenze su particolari tessuti associati alle spore possono essere realizzati con semplici ma cruciali modifiche agli approcci standard qui descritti (Figura 1d).
In questa recensione, ci sono protocolli dettagliati SEM che possono essere utilizzati per affrontare diversi problemi associati con l'osservazione SEM negli angiosperme, oomiceti, e Agaricales, come ad esempio il collasso delle cellule e restringimento dei tessuti meristematico, la crescita non ottimale di spine cisti, e la distruzione di tessuti effimere, rispettivamente.
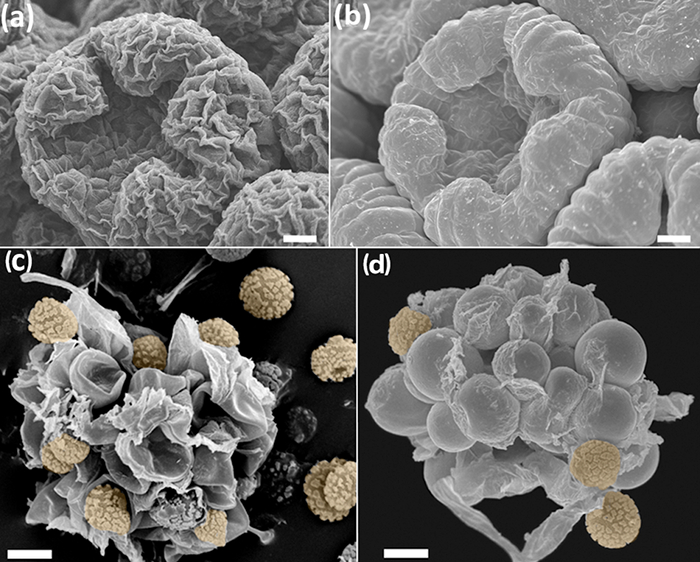

Figura 1: Confronto tra campioni trattati, senza (a, c) e (b, d) il protocollo FAA-etanolo-CPD. (A - b) gemme floreali di Anacyclus clavatus, a metà dello sviluppo. Bud trattato con tetrossido di osmio 46 </ sup> (a) e Bud trattati con il protocollo FAA-CPD (b). (C - d) le cellule infermiera con spore di Phellorinia Herculanea f. Stellata. Campioni essiccati senza alcun trattamento (c) e con il protocollo qui descritto per Agaricales (d). Le spore in arancione. Bilancia: (ab) 100 micron, (cd) 50 micron. Le foto sono state scattate da Y. Ruiz-León. Clicca qui per vedere una versione più grande di questa figura.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocollo
NOTA: Questo protocollo comprende sei sezioni principali, tre dedicati ad organismi specifici (sezioni 1-3), e tre descrivono le procedure comuni a tutti (4-6). Asterischi (*) indicano passi modificati dagli sperimentatori.
1. Studi di sviluppo e di strutture vegetali completamente formati
- Raccolta e la fissazione
- Se il materiale vegetale viene raccolto in un luogo senza accesso ad una cappa, introdurre e immergere il materiale in 70% di etanolo in provette da centrifuga. Idealmente, immergere il materiale dopo 48 ore in FAA (passi 1.1.1-1.1.3) per evitare la disidratazione eccessivo nel etanolo. Se una cappa è accessibile al materiale vegetale, ignorare questo passo e continuare con 1.1.1.
- Preparare il fissativo formalina acetica-alcol (FAA) in una cappa dotato di un filtro di aldeide. Aggiungere 85 parti di etanolo al 70% denaturato, 10 parti di soluzione di formaldeide al 60%, e 5 parti di acido acetico glaciale. Preparare la FAAappena prima di fissare il materiale, come la sua conservazione a lungo termine non è raccomandato 40.
- Sotto la cappa, versare il brodo di FAA in singoli bocca larga e bottiglie di plastica a perfetta tenuta. Utilizzare come molte bottiglie in quanto vi sono campioni disponibili, e creare etichette per l'identificazione dei campioni.
- Selezionare i meristemi floreali o vegetative per risolvere, in modo che essi non vengano danneggiati da insetti, funghi o da condizioni atmosferiche estreme. Tagliare i rami, rimuovendo materiale indesiderato, e depositare il campione immediatamente nella soluzione FAA.
- Dopo 72-96 h, versare la FAA in un contenitore di plastica per lo smaltimento chimico. Immediatamente, lavare i campioni tre volte con fresco 70% etanolo per rimuovere ogni residuo FAA. materiale fisso può essere conservato a tempo indeterminato nel 70% di etanolo.
- Dissection e disidratazione
- Sezionare il materiale fissato in etanolo al 70% con lo stereomicroscopio con una pinzetta ultra fine, needles, pinze, spazzole, e micro-bisturi (la dimensione massima del tessuto dovrebbe essere di circa 1 cm 3, o 2 cm per materiale piatto). Sezionare i campioni in una piastra di Petri rivestito con etanolo per evitare che i tessuti di essiccazione. Utilizzare una capsula di Petri con la base ricoperta di silicone nero asciutto per vedere meglio i tessuti bianchi a contrasto.
- Mettere il materiale sezionato in contenitori dei campioni per l'essiccatore punto critico (CPD, Figura 2a). A questo punto, immergere i contenitori nella capsula di Petri con 70% di etanolo, e comprendono le etichette di identificazione del campione (realizzato con carta e matita). Per un'asciugatura più efficace per ulteriori manipolazioni, evitare di mescolare i campioni giovani e mature nello stesso contenitore. *
- Mettere i coperchi sui contenitori e depositarli in provette da centrifuga di plastica con un sacco di etanolo al 70%. Conservare le provette durante la notte se il materiale non viene elaborato immediatamente.
- Trasferire il materiale sezionato con la seguente serie di etanolos in barattoli ermetici o tubi da centrifuga: 70%, 90%, 100% e 100%. Lasciare i campioni in ciascuna soluzione per 1 h almeno. Mantenere i campioni notte in una soluzione di etanolo al 100%.
- Trasferire i contenitori con il materiale CPD (sezione 4).
- Montaggio e preparazione tessuti vegetali per l'osservazione SEM
- Scrivere il numero di identificazione del campione sotto i titolari del campione SEM (ad esempio, stub alluminio). Coprire la parte superiore del stub con nastro biadesivo. Posizionare gli stub in un portacampioni (Figura 2b).
- Sotto uno stereomicroscopio, aprire con cautela i contenitori di campioni giovani e delicati già essiccati al CPD. Tenete a mente che dopo il trattamento CPD, i campioni diventano più leggeri e sensibili alle elettrostatica. Chiudere i contenitori una volta che i campioni sono stati accesi per evitare che polvere o impurità.
- Mettere i campioni sulla superficie adesiva del stub, la pianificazione per il futuro desideratoposizione (una volta che i campioni toccano la superficie, è molto difficile da rimuovere). Non cercare di portare un importante dissezione, a questo punto; basta rimuovere il tessuto indesiderato che è facile da raccogliere. Per gli studi palinologici, sezionare le antere e aprirli per esporre il polline sul stub.
- Campioni lunghi Put (ad esempio, 2 cm) come infiorescenze in posizione orizzontale. Quando possibile, i campioni orientare della stessa struttura per polare, laterale e viste basso. Lasciare spazio sufficiente tra i campioni sulla matrice.
- Se i campioni non possono essere elaborati immediatamente, tenerli protetti durante la notte in un contenitore ermetico con gel di silice per evitare reidratazione (figura 2c) *. Coat i campioni utilizzando il dispositivo a induzione polverizzazione e trasferirli al SEM (sezioni 5 e 6).
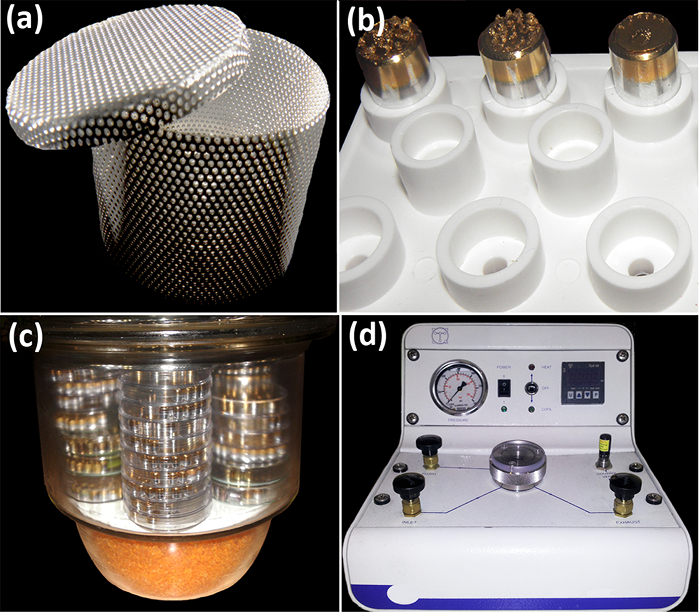
Figura 2: Strumenti per manipulati campionesu e elaborazione prima osservazione SEM. (A) container esemplare acciaio da pareti forate per lo scambio etanolo / CO 2 nella camera CPD. (B) stub acciaio all'interno di un supporto del campione di plastica. Contenitore (c) vetro utilizzato per mantenere i campioni al riparo da umidità e polvere. Alla base, vi è un vano per il gel di silice. (D) dei punti critici di Dryer. Nella parte anteriore, ci sono (da sinistra a destra) il manometro, l'interruttore di alimentazione, il sistema di controllo della temperatura, e la visualizzazione della temperatura. Pressione di esercizio normale per CO 2 -etanolo interscambio è di 60 bar (800 psi). In cima, ci sono quattro valvole (controlli aspirazione, di scarico, di ventilazione e scarico) che fiancheggiano la camera campione centrale. Le foto sono state scattate da Y. Ruiz-León e MA Bello. Clicca qui per vedere una versione più grande di questa figura.
- Crescere e fissa le cisti
- Preparare peptone e glucosio (PG-l) supporto 41 mediante D - (+) - glucosio (6 g) e peptone mycological (3 g) *. Aggiungere fino a 900 ml di acqua di rubinetto e autoclave 40 min a 121 ° C. Versare 50 mL della soluzione precedentemente autoclavato A (NaH 2 PO 4, 0,13 M) e 50 ml di soluzione B (Na 2 HPO 4, 0,13 M).
- Provenienti da colture di ceppi di Saprolegnia parasitica mantenuto il peptone, il glucosio, i media agar (PGA, che viene preparato come PG-L ma aggiungendo 10 g di agar batteriologico europea al glucosio e il peptone prima autoclave), crescono colonie miceli in 0,5 ml di PG-l goccioline per 24-48 ore a 20 ° C in piastre di Petri. Indurre sporulazione lavando il micelio con acqua di rubinetto in autoclave per tre volte e incubando per 15 ore a 20 ° C= "xref"> 42, 43.
- Raccogliere le zoospore secondari rilasciati pipettando delicatamente la parte superiore della sospensione e piscina in 1 porzioni mL. Agitare vigorosamente le zoospore per 30 s con il vortex per produrre cisti secondarie 44.
- Per verificare la crescita differenziale delle spine delle cisti, in separata Petri piatti (p60), mettere 0,5 mL della sospensione cisti secondario su superfici diverse (ad esempio, carbone, griglie d'oro, e TEM rame, salmone e pesce di nasello scale (in precedenza sbiancati), e copertura in vetro scivola) *. Incubare le cisti a 20 ° C per 70 min, che favorisce il fissaggio delle cisti alla superficie.
- Rimuovere il liquido e aggiungere 0,5 ml di 2% glutaraldeide per ogni superficie per il fissaggio delle cisti. Mantenere i campioni a temperatura ambiente sotto una cappa per 1 ora.
- Rimuovere la glutaraldeide e disidratare il campione attraverso una serie di etanolo (30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 100% e 100%), aggiungendo 5 ml di ciascuna soluzione di etanolo per 15 min. Una volta in ultima soluzione di etanolo al 100%, il campione può essere conservato fino ad un mese in una capsula di Petri sigillata. In questa fase, i campioni sono pronti per essere essiccato in CPD.
- Trasferire accuratamente le griglie e le scale dalla piastra di Petri di un supporto adatto per la CPD (sezione 4). Per questo passaggio, utilizzare un supporto griglia CPD o un portacampioni impilabili, che mantengono campioni separati l'uno dall'altro. Prendere le griglie e le scale con le pinzette, tenendo presente che le cisti devono essere rivolte verso l'alto sulle griglie per tutto il tempo. *
- Montaggio e preparazione dei campioni cisti per l'osservazione SEM
- Montare le griglie e le scale sui stub in alluminio che in precedenza erano coperte con nastro biadesivo carbonio ed etichettati sotto.
- Trasferire i campioni al verniciatore polverizzazione (sezione 5).
- Osservare i campioni sotto il SEM (sezione 6).
3. Studio di Erbario fungine spore di Phellorinia Herculanea sotto SEM
- La reidratazione e disidratazione delle spore
- Avvolgere ogni campione accuratamente con carta da filtro, la formazione di buste matita marcata ~ 0,5-1 cm 2, facendo attenzione a non schiacciarli. Sigillare la carta da filtro con graffette. Trasferire i campioni confezionati ad una capsula di Petri e immergerli in 10 ml di acqua per reidratare i tessuti intorno alle spore.
- Subito mettere i campioni in un forno a microonde (600 W per circa 20 s). Rimuovere il materiale una volta che l'acqua inizia ad evaporare, e lasciarlo raffreddare a temperatura ambiente.
- Passare i campioni attraverso la seguente serie di etanolo: 30%, 50%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 95%, 100% e 100%. A seconda della quantità di campioni, utilizzare un becher o centrifuga per questo passo. Lasciare i campioni per 15 min in ciascuna soluzione.
- Posizionare i campioni al CPD (sezione 4).
- Montaggio e preparing spore per l'osservazione SEM
- Aprire le buste. Versare le spore su uno stub precedentemente preparata con nastro biadesivo. In alternativa, raccogliere le spore con la superficie adesiva del stub, facendo attenzione a non schiacciarli *.
- Se i campioni contengono poche spore, oltre al passaggio precedente, tagliare un piccolo pezzo della busta (~ 1 mm 2) e posizionarla su un nuovo stub *.
- Posizionare i tessuti nel verniciatore polverizzazione (sezione 5).
- Osservare sotto il SEM (sezione 6).
4. essiccazione di materiale utilizzando un dei punti critici di Dryer (CPD, Figura 2d)
- Utilizzare il CPD in una zona ventilata e verificare che tutte le valvole della macchina sono chiuse. Controllare se la camera del campione è vuoto e pulito.
- Accendere la macchina e verificare che il test del sistema di controllo della temperatura avviene automaticamente. Se il CPD ha un sistema di refrigerazione vasca esterna, controllare i livelli di acqua prima di passare itonnellata.
- Seguire le istruzioni del CPD specifico utilizzato per l'etanolo e CO 2 interscambio del produttore. Per sicurezza, continuare questo passaggio sotto la supervisione di una persona qualificata per l'utilizzo della macchina. Ricordate che è esposto a variazioni di pressione rapidi, potrebbe soffiare violentemente.
- Estrarre i campioni e continuare con il passo 1.3 se si lavora con tessuti vegetali, passo 2.2 se si lavora con oomiceti cisti, e passi 3.2 se si lavora con spore di funghi.
5. Rivestimento i campioni con oro Utilizzando la polverizzazione catodica Coater (Figura 3a)
- Controllare il dispositivo a induzione polverizzazione. Verificare che il bersaglio oro catodo è in buone condizioni. Usare un panno privo di lanugine intriso con il 90% di etanolo per pulire le pareti della camera a vuoto e il coperchio della camera, se necessario.
- Segnare il supporto polverizzazione con i numeri accanto a ogni foro stub per l'ulteriore identificazione dei campioni al microscopio. Con cautela, inserire il stub caricato con la samplES e fissarli. Utilizzare un rotativo fase campione planetario per garantire un rivestimento uniforme su campioni con superfici irregolari.
- Seguire le istruzioni del produttore per regolare le impostazioni come ad esempio la distanza di lavoro, pressione del gas di funzionamento (ad esempio, 5 x 10 -1 - 7 x 10 -1 mbar) (ad esempio, 30 mm.), Il tempo di sputtering (ad esempio, 50 s), spessore dello strato di oro (ad esempio, 12 nm) la corrente (ad esempio, 15 mA) e la tensione di alimentazione (ad esempio, 600 V) 45.
- Rimuovere gli stub e portarli al SEM (sezione 6). In alternativa, posizionare gli stub in un contenitore sigillato con gel di silice (figura 2c).
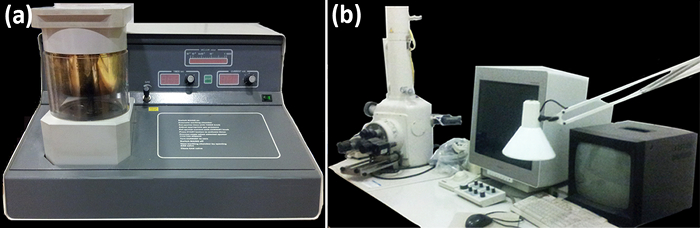
Figura 3: polverizzazione catodica coater (a) e microscopio elettronico a scansione (b). (A) Vista frontale della camera a vuoto (a sinistra), VALV gase, timer, vuoto e controlli attuali. (B) Vista laterale dei componenti principali SEM (da sinistra a destra): la colonna sotto vuoto con la camera del campione, lo schermo del computer con i controlli, e il monitor della Camera. Le foto sono state scattate da Y. Ruiz-León. Clicca qui per vedere una versione più grande di questa figura.
6. l'osservazione al microscopio elettronico a scansione (SEM, figura 3b)
- SEM start up
- Seguire le istruzioni del produttore per avviare e impostare il SEM, regolando l'altezza del campione del diametro di apertura dell'obiettivo (ad esempio, per gli impianti di 2 micron e per i funghi e oomiceti 4 micron), la tensione di funzionamento (ad esempio, 15 kV).
- Controllare il corretto allineamento del sistema fascio elettronico e impostare l'allineamento assiale e le stigmators secondo i costruttori indicazioni. regolare tha distanza di lavoro al fine di ottenere un'adeguata profondità di campo.
- acquisizione di immagini
- Ottenere una immagine focalizzata del campione e usarlo come punto di partenza. Aumentare l'ingrandimento vicino al livello massimo e concentrare nuovamente l'immagine. Scegli aree con irregolarità superficiali come i buchi. astigmatismo corretta e regolare il contrasto e la luminosità ottimale.
- Catturare l'immagine SEM con l'alta risoluzione. Utilizzare il rilevatore di BSE se l'immagine mostra che i campioni pagano. In caso contrario, impostare il rivelatore SE. Modificare i rivelatori di seguito le istruzioni del produttore.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Risultati
Sviluppo floreale e la fissazione di sviluppo e strutture vegetali completamente formato
Utilizzando il protocollo FAA-CPD descritto qui, giovani e mature tessuti vegetali sono perfettamente fissati e disidratati per l'imaging SEM. Processi come lo sviluppo floreale possono essere ricostruiti, perché la topografia e la forma delle gemme non sia falsata da cellule restringimento (Figure 1b, 1d, 4a-f). Le str...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussione
Per quanto riguarda i protocolli standard SEM, le procedure qui presentati sono relativamente rapido, facile da seguire, e le metodologie a basso costo. A seconda della quantità di campioni e sulla facilità di lavorazione, ci vogliono quattro o cinque giorni per acquisire immagini di buona qualità. Compreso adeguate misure di sicurezza per la CPD e il funzionamento SEM, le procedure sono facili da gestire. Particolare cautela deve essere assunto con formalina e la glutaraldeide (vedere i passaggi da 1.1.1 a 1.1.3 e 2...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Divulgazioni
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Riconoscimenti
Questo progetto ha ricevuto un finanziamento dal programma di ricerca e innovazione Orizzonte 2020 dell'Unione Europea con convenzione di sovvenzione n ° 634429. Questa pubblicazione riflette il punto di vista degli autori, e la Commissione Europea non può essere ritenuta responsabile per qualsiasi uso che possa essere fatto delle informazioni esso contenute. Abbiamo anche riconoscere il contributo finanziario da parte del Jardin Botanico, CSIC. SR è grata per l'Unione europea [ITN-SAPRO-238550] per il sostegno della sua ricerca in Saprolegnia. Vogliamo anche ringraziare Francisco Calonge per gentilmente fornire le immagini Herculanea Phellorinia e B. Pueyo per l'elaborazione di campioni (Figura 5). Tutte le immagini sono state scattate dal servizio SEM al Jardin Botanico-CSIC di Madrid.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materiali
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acetic acid | No specific supplier | Skin irritation, eye irritation | |
| aluminium stubs | Ted Pella, Inc. | 16221 | www.tedpella.com |
| Centrifuge tubes | No specific supplier | ||
| Critical Point Dryer | Polaron Quatum Technologies | CPD7501 | |
| D-(+)-Glucose | Merck | 1,083,421,000 | |
| Double sided sellotape | No specific supplier | ||
| Ethanol absolute | No specific supplier | Flammable | |
| European bacteriological agar | Conda | 1800.00 | www.condalab.com |
| Filter paper | No specific supplier | ||
| Forceps | No specific supplier | ||
| Formalin 4% | No specific supplier | Harmful, acute toxicity, skin sensitisation, carcinogenicity. Flammable | |
| Glass cover slips | No specific supplier | ||
| Glass hermetic container | No specific supplier | ||
| Glutaraldehyde 25% DC 253857.1611 (L) | Dismadel S.L. | 3336 | www.dismadel.com |
| Mycological peptone | Conda | 1922.00 | www.condalab.com |
| needles | No specific supplier | ||
| Petri dishes | No specific supplier | ||
| Plastic containers | No specific supplier | ||
| Sample holder with lid for the critical point dryer | Ted Pella, Inc. | 4591 | www.tedpella.com |
| scalpels | No specific supplier | ||
| Scanning Electron Microscope | Hitachi | S3000N | |
| Software for SEM | |||
| Solution A: NaH2PO4 | |||
| Solution B: Na2HPO4 | |||
| Specimen holders | No specific supplier | ||
| Sputter coater | Balzers | SCD 004 | |
| Stereomicroscope | No specific supplier | ||
| Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) grids | Electron Microscopy Sciences | G200 (Square Mesh) | www.emsdiassum.com |
| Tweezers | No specific supplier |
Riferimenti
- Endress, P. K., Baas, P., Gregory, M. Systematic plant morphology and anatomy: 50 years of progress. Taxon. 49 (3), 401-434 (2000).
- Falk, R. H., Gifford, E. M., Cutter, E. G. Scanning electron microscopy of developing plant organs. Science. 168 (3938), 1471-1474 (1970).
- Damblon, F. Sputtering, a new method of coating pollen grains in scanning electron microscopy. Grana. 15 (3), 137-144 (1975).
- Everhart, T. E., Thornley, R. F. M. Wide-band detector for micro-microampere low-energy electron currents. J. Sci. Instrum. 37 (7), 37246-37248 (1960).
- Collins, S. P., et al. Advantages of environmental scanning electron microscopy in studies of microorganisms. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 25 (5-6), 398-405 (1993).
- Fannes, W., Vanhove, M. P. M., Huyse, T., Paladini, G. A scanning electron microscope technique for studying the sclerites of Cichlidogyrus. Parasitol. Res. 114 (5), 2031-2034 (2015).
- Erbar, C., Leins, P. Portioned pollen release and the syndromes of secondary pollen presentation in the Campanulales-Asterales complex. Flora. 190 (4), 323-338 (1995).
- Jansen, S., Smets, E., Baas, P. Vestures in woody plants: a review. IAWA Journal. 19 (4), 347-382 (1998).
- Bortolin Costa, M. F., et al. Stigma diversity in tropical legumes with considerations on stigma classification. Bot. Rev. 80 (1), 1-29 (2014).
- Almeida, O. J. G., Cota-Sánchez, J. H., Paoli, A. A. S. The systematic significance of floral morphology, nectaries, and nectar concentration in epiphytic cacti of tribes Hylocereeae and Rhipsalideae (Cactaceae). Perspect. Plant Ecol. 15 (5), 255-268 (2013).
- Konarska, A. Comparison of the structure of floral nectaries in two Euonymus L. species (Celastraceae). Protoplasma. 252 (3), 901-910 (2015).
- Giuliani, C., Maleci Bini, L. Insight into the structure and chemistry of glandular trichomes of Labiatae, with emphasis on subfamily Lamioideae. Plant Syst. Evol. 276 (3-4), 199-208 (2008).
- Li, K., Zheng, B., Wang, Y., Zhou, L. L.Breeding system and pollination biology of Paeonia delavayi (Paeoniaceae), an endangered plant in the Southwest of China. Pak. J. Bot. 46 (5), 1631-1642 (2014).
- García, L., Rivero, M., Droppelmann, F. Descripción morfológica y viabilidad del polen de Nothofagus nervosa (Nothofagaceae). Bosque. 36 (3), 487-496 (2015).
- Prenner, G., Klitgaard, B. B. Towards unlocking the deep nodes of Leguminosae: floral development and morphology of the enigmatic Duparquetia orchidacea (Leguminosae, Caesalpinioideae). Am. J. Bot. 95 (11), 1349-1365 (2008).
- Ratnayake, K., Joyce, D. C., Webb, R. I. A convenient sample preparation protocol for scanning electron microscope examination of xylem-occluding bacterial biofilm on cut flowers and foliage. Sci. Hortic-Amsterdam. 140 (1), 12-18 (2012).
- Çolak, G., Celalettin Baykul, M., Gürler, R., Çatak, E., Caner, N. Investigation of the effects of aluminium stress on some macro and micro-nutrient contents of the seedlings of Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. by using scanning electron microscope. Pak. J. Bot. 46 (1), 147-160 (2014).
- Arafa, S. Z. Scanning electron microscope observations on the monogenean parasite Paraquadriacanthus nasalis from the nasal cavities of the freshwater fish Clarias gariepinus in Egypt with a note on some surface features of its microhabitat. Parasitol. Res. 110 (5), 1687-1693 (2012).
- Uppalapatia, S. R., Kerwinb, J. L., Fujitac, Y. Epifluorescence and scanning electron microscopy of host-pathogen interactions between Pythium porphyrae (Peronosporales, Oomycota)and Porphyra yezoensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). Bot. Mar. 44 (2), 139-145 (2001).
- Meaney, M., Haughey, S., Brennan, G. P., Fairweather, I. A scanning electron microscope study on the route of entry of clorsulon into the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol. Res. 95 (2), 117-128 (2005).
- Sundarasekar, J., Sahgal, G., Subramaniam, S. Anti-candida activity by Hymenocallis littoralis extracts for opportunistic oral and genital infection Candida albicans. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 7 (3), 211-216 (2012).
- Benhamou, N., Rey, P., Picard, K., Tirilly, Y. Ultrastructural and cytochemical aspects of the interaction between the mycoparasite Pythium oligandrum and soilborne plant pathogens. Phytopathology. 89 (6), 506-517 (1999).
- Singh, A., et al. First evidence of putrescine involvement in mitigating the floral malformation in mangoes: A scanning electron microscope study. Protoplasma. 251 (5), 1255-1261 (2014).
- Xiang, C., et al. Fine mapping of a palea defective 1 (pd1), a locus associated with palea and stamen development in rice. Plant Cell Rep. 34 (12), 2151-2159 (2015).
- Mendoza, L., Hernandez, F., Ajello, L. Life cycle of the human and animal oomycete pathogen Pythium insidiosum. J. Clin. Microbiol. 31 (11), 2967-2973 (1993).
- Bello, M. A., Rudall, P. J., González, F., Fernández, J. L. Floral morphology and development in Aragoa (Plantaginaceae) andrelated members of the order Lamiales. Int. J. Plant Sci. 165 (5), 723-738 (2004).
- Bello, M. A., Hawkins, J. A., Rudall, P. J. Floral morphology and development in Quillajaceae and Surianaceae (Fabales), the species-poor relatives of Leguminosae and Polygalaceae. Ann. Bot. 100 (4), 1491-1505 (2007).
- Bello, M. A., Hawkins, J. A., Rudall, P. J. Floral ontogeny in Polygalaceae and its bearing on the homologies of keeled flowers in Fabales. Int. J. Plant Sci. 171 (5), 482-498 (2010).
- Bello, M. A., Alvarez, I., Torices, R., Fuertes-Aguilar, J. Floral development and evolution of capitulum structure in Anacyclus (Anthemideae, Asteraceae). Ann. Bot. 112 (8), 1597-1612 (2013).
- Bello, M. A., Martínez-Asperilla, A., Fuertes-Aguilar, J. Floral development of Lavatera trimestris and Malva hispanica reveals the nature of the epicalyx in the Malva generic alliance. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 181 (1), 84-98 (2016).
- Calonge, F. D., Martínez, A. J., Falcó, I., Samper, L. E. Phellorinia herculanea f. stellata f. nova encontrada en España. Bol. Soc. Micol.Madrid. 35 (1), 65-70 (2011).
- Liu, Y., et al. Deciphering microbial landscapes of fish eggs to mitigate emerging diseases. ISME J. 8 (10), 2002-2014 (2014).
- Sandoval-Sierra, J. V., Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. A comprehensive protocol for improving the description of Saprolegniales (Oomycota): two practical examples (Saprolegnia aenigmatica sp. nov. and Saprolegnia racemosa sp. nov.). PLOS one. , (2015).
- Endress, P. K. Zur vergleichenden Entwicklungsmorphologie, Embryologie und Systematik bei Laurales. Bot. Jahrb. Syst. 92 (2), 331-428 (1972).
- Tucker, S. Floral development in Saururus cernuus (Saururaceae):1. Floral initiation and stamen development. Am. J. Bot. 62 (3), 993-1005 (1975).
- Endress, P. K., Matthews, M. L. Progress and problems in the assessment of flower morphology in higher-level systematics. Plant Syst. Evol. 298 (2), 257-276 (2012).
- Beakes, G. W., Glockling, S. L., Sekimoto, S. The evolutionary phylogeny of the oomycete "fungi". Protoplasma. 249 (1), 3-19 (2012).
- Romansic, J. M., et al. Effects of the pathogenic water mold Saprolegnia ferax on survival of amphibian larvae. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 83 (3), 187-193 (2009).
- van West, P. Saprolegnia parasitica, an oomycete pathogen with a fishy appetite: new challengues for an old problem. Mycologist. 20 (3), 99-104 (2006).
- Johansen, D. A. Plant microtechnique. , McGrow-Hill. New York. (1940).
- Unestam, T. Studies on the crayfish plague fungus Aphanomyces astaci. Some factors affecting growth in vitro. Physiol. Plantarum. 18 (2), 483-505 (1965).
- Cerenius, L., Söderhäll, K. Repeated zoospore emergence from isolated spore cysts of Aphanomyces astaci. Exp. Mycol. 8 (4), 370-377 (1984).
- Diéguez-Uribeondo, J., Cerenius, L., Söderhäll, K. Repeated zoospore emergence in Saprolegnia parasitica. Mycol. Res. 98 (7), 810-815 (1994).
- Söderhäll, K., Svensson, E., Unestam, T. Chitinase and protease activities in germinating zoospore cysts of a parasitic fungus, Aphanomyces astaci, Oomycetes. Mycopathologia. 64 (1), 9-11 (1978).
- Echlin, P. Handbook of sample preparation for scanning electron microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis. , Springer Science + Business Media, LLC. NY. (2009).
- Osumi, M., et al. Preparation for observation of fine structure of biological specimens by high-resolution SEM. Microscopy. 32 (4), 321-330 (1983).
- Rezinciuc, S. The Saprolegniales morpho-molecular puzzle: an insight into markers identifying specific and subspecific levels in main parasites. , Universidad Internacional Menéndez Pelayo. Doctoral Thesis (2013).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Ristampe e Autorizzazioni
Richiedi autorizzazione per utilizzare il testo o le figure di questo articolo JoVE
Richiedi AutorizzazioneThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon