A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Agrobacterium rhizogenes-Mediated Transformation of Potato and the Promoter Activity of a Suberin Gene by GUS Staining
In This Article
Summary
Here, we present two protocols to transform potato plants. The Agrobacterium tumefaciens transformation leads to a complete transgenic plant while the Agrobacterium rhizogenes produces transgenic hairy roots in a wild type shoot that can be self-propagated. We then detect promoter activity by GUS staining in the transformed roots.
Abstract
Agrobacterium sp. is one of the most widely used methods to obtain transgenic plants as it has the ability to transfer and integrate its own T-DNA into the plant's genome. Here, we present two transformation systems to genetically modify potato (Solanum tuberosum) plants. In A. tumefaciens transformation, leaves are infected, the transformed cells are selected and a new complete transformed plant is regenerated using phytohormones in 18 weeks. In A. rhizogenes transformation, stems are infected by injecting the bacteria with a needle, the new emerged transformed hairy roots are detected using a red fluorescent marker and the non-transformed roots are removed. In 5-6 weeks, the resulting plant is a composite of a wild type shoot with fully developed transformed hairy roots. To increase the biomass, the transformed hairy roots can be excised and self-propagated. We applied both Agrobacterium-mediated transformation methods to obtain roots expressing the GUS reporter gene driven by a suberin biosynthetic gene promoter. The GUS staining procedure is provided and allows the cell localization of the promoter induction. In both methods, the transformed potato roots showed GUS staining in the suberized endodermis and exodermis, and additionally, in A. rhizogenes transformed roots the GUS activity was also detected in the emergence of lateral roots. These results suggest that A. rhizogenes can be a fast alternative tool to study the genes that are expressed in roots.
Introduction
Aside from economic interest, the generation of transgenic plants has its own relevance in research to demonstrate the ultimate function of genes and to better understand plant physiology and development. The most widely used method for plant DNA insertion is Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is able to generate crown galls in the infected tissue of many plant species by the action of its tumour-inducing (Ti) plasmid. The plasmid contains a T-DNA region with a set of genes that will be integrated in the plant genome and induce tissue dedifferentiation1,2. The exchange of these genes within the T-DNA by the transgene has allowed the generation of specific plant modifications avoiding phenotypic effects3. To facilitate the transgene cloning into the T-DNA, the T-DNA region has been excised in an independent plasmid called a binary plasmid, while the rest of the genes of the Ti plasmid (the virulence genes that allow the T-DNA transfer and insertion mechanisms) have been placed in a helper plasmid. For plant biotechnology research, transformation by A. tumefaciens has several advantages: it does not need expensive devices, is able to generate both stable and transient plant transformation, and low numbers of gene copies are integrated into the chromosome4. However, for most plants, but not Arabidopsis, the generation of stable transformants requires plant regeneration from a single or a few cells using exogenous phytohormones, making this process laborious and time consuming. A. rhizogenes is also able to modify the plant genome, producing hairy roots or adventitious roots at the infection sites due to the expression of rol (root loci) genes encoded in the root-inducing (Ri) plasmid5. Although less studied than A. tumefaciens, A. rhizogenes is also used for obtaining transgenic roots. In this case, the A. rhizogenes contains the original T-DNA in the Ri plasmid and a binary plasmid with a second T-DNA carrying the transgene. When the infection site is in stems or hypocotyls, a composite plant can be obtained, with new hairy transgenic roots emerging from wild type shoots. Alternatively, hairy transformed roots can grow autonomously in vitro in media with carbon source inputs. The use of A. rhizogenes instead of A. tumefaciens to produce transgenic tissue is gaining relevance when the root is the target organ, because plant regeneration is not required and hence it is faster and less costly. Previous studies have demonstrated this methodology appropriated for the phenotypic characterization of root specific genes6,7,8,9.
The potato (Solanum tuberosum) is the fourth most important crop in the world according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) since the tuber has nutritional relevance for human consumption for being a good source of vitamins and minerals. For that reason, potato has been placed in the spotlight of agricultural biotechnology and also is considered as a good biological model for genetic and developmental studies10,11. Potato transformation significantly contributed to the understanding of molecular mechanisms underlying suberized tissues through the characterization of genes involved in suberin and wax biosynthesis12,13,14,15,16,17, suberin monomer transport18 and transcription regulation19. The suberin feruloyl transferase gene, FHT, is one of these characterized biosynthetic genes; its downregulation gives rise to a strong impairment of the periderm protection, which is correlated with a strong decrease in ferulate esters of suberin and waxes in potato tubers14. Concomitantly, in roots and seeds of Arabidopsis, the knockout of its putative orthologue (ASFT/RWP1) also demonstrated its role in producing alkyl ferulates in suberin20,21. In potato, the FHT transcriptional reporter line and the FHT antibody showed respectively that the promoter activity and the protein are located in the exodermis, the endodermis, the phellogen-derivatives and in wounded tissues15.
In this work, we detail a protocol using A. rhizogenes to produce transgenic hairy roots that are maintained in a wild type shoot, generating composite potato plants, or excised to grow autonomously in vitro. We also provide the protocol using A. tumefaciens to obtain complete transgenic potato plants. As a case study, A. rhizogenes and A. tumefaciens transformed with the same binary vector are used to obtain roots with the FHT promoter driving GUS reporter gene expression. The results are reported and compared.
Protocol
The A. rhizogenes transformation protocol was adapted and modified from Horn et al.7 and the genotype tested was S. tuberosum ssp. tuberosum (cv. Désirée). The A. tumefaciens transformation protocol was adapted and modified from Banerjee et al.22 and the genotypes tested were S. tuberosum ssp. tuberosum (cv. Désirée) and S. tuberosum ssp. andigena. The main steps of both procedures are summarized in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively.
NOTE: In all the steps of the procedure performing in vitro transfers, do so rapidly, and when possible, maintain the plates or pots closed, thus minimizing plant exposure to the air to avoid wilting and contamination. Otherwise stated, all the plant incubations were done in cabinets under the conditions of 12 h of 24 °C light/12 h of 20 °C dark and 67 µmol m-1 s-1. Otherwise stated, perform all the bacteria manipulation and in vitro plant transfers in aseptic conditions in a laminar flow hood. All the media recipes for Agrobacterium and in vitro plant cultures are provided in Table S1.
CAUTION: Deposit all the genetically modified bacteria and plants to the appropriated waste container.
1. Agrobacterium cultures used for transformation
NOTE: The strain used for A. rhizogenes transformation was the C58C1:Pri15837 (kindly provided by Dr. Inge Broer) and that for the A. tumefaciens was the GV2260 (kindly provided by Dr. Salomé Prat). A. rhizogenes was transformed with the binary vector PK7GWIWG2_II-RedRoot (VIB-Department of Plant Systems Biology at Universiteit Gent; http://gateway.psb.ugent.be) that contains a T-DNA carrying a transformation marker to monitor the hairy root formation. To compare the transformed roots generated by A. rhizogenes and A. tumefaciens, both were transformed with the binary vector pKGWFS7 which contains a T-DNA carrying the FHT promoter driving the β-glucoronidase (GUS) reporter gene and the Kanamycin resistance gene as a selectable marker15.
- Pick a colony of Agrobacterium and grow it overnight (O/N) in 5 mL of YEB medium supplemented with antibiotics (Table S1) in a 50 mL centrifuge tube at 28 °C with shaking at 200 rpm.
- For A. tumefaciens transformation, measure the optical density, which must be OD600 = 0.6-1.0.
- If the optical density is higher, make a subculture lowering it to OD600 = 0.3 with fresh media and wait until the culture reaches OD600 = 0.6-1.
- Centrifuge 1 mL of Agrobacterium culture at 3,000 x g in a bench-top centrifuge for 10 min at room temperature.
- Remove the supernatant by pipetting, and resuspend cells in 1 mL of fresh YEB medium without antibiotics. Repeat this step to ensure the complete removal of antibiotics.
- For A. tumefaciens transformation, in the last resuspension add the appropriate YEB volume to obtain a final optical density of OD600 = 0.8.
- Keep cells on ice while preparing the plants to be infected.
2. Plant material for transformation
- Make one or two node stem cuttings either containing the apical or the auxiliary buds from sterile in vitro potato plants (donor plants); grow them in solid 2MS medium in pots for 3 to 4 weeks (Figure 1A and Figure 2A).
3. Plant transformation using A. rhizogenes (Figure 1)
NOTE: This procedure allows the obtaining of transformed hairy roots. To evaluate the transgene expression, a negative control is needed. To prepare the negative control, follow the procedure using an A. rhizogenes strain either untransformed or transformed with the empty vector that includes the transformation marker gene.
- Use fresh media plates; alternatively, the plates can be kept at 4 °C with the lid side up, tightly sealed with transparent film to avoid media dehydration. To prepare the square media plates, incline them ~15°, fill with 40 mL of MS, and let them solidify. This will minimize the contact of the aerial part of the plant with the medium.
- Transfer very carefully a donor plant from the 2MS medium to a 120 mm x 120 mm square plate.
- Inject to one stem internode 3 μL of the A. rhizogenes culture using a surgical needle and repeat it twice per plant in different internodes when possible.
NOTE: Consider each injection as an independent transformation event (Figure 1B). - Transfer immediately the entire plant to a square plate with solid MS medium supplemented with 0.1 mM acetosyringone. Accommodate 2 plants per plate.
NOTE: The 1 M acetosyringone stock solution is prepared in DMSO and can be stored at -20 °C. - Seal the plate using surgical tape and arrange it vertically inside a growth cabinet for 4 days.
- Transfer the plant to a new square plate with MS medium supplemented with cefotaxime sodium [500 µg/mL] to kill A. rhizogenes.
- After 10-12 days, hairy roots will start to appear (Figure 1C,1D). Then, excise the native roots of the plant, and transfer the plant to a new square plate with MS medium supplemented with cefotaxime sodium [500 µg/mL].
NOTE: Transformed hairy roots can be checked by red fluorescence when using a DsRed transformation marker (Figure 3D). - To obtain a composite plant (Figure 1E), let the transgenic hairy roots grow for 3-4 weeks in MS medium supplemented with cefotaxime sodium [500 μg/mL] (change the medium every week).
- Depending on the purpose, propagate the transgenic hairy roots and the negative controls as follow.
- Transfer the whole composite plant to a hydroponic (Table S2) or soil medium to allow for massive development.
- To individually propagate the transformed hairy roots, using a scalpel cut the roots expressing the red fluorescent transformation marker (DsRed protein) when they are 4-8 cm long (Figure 1E) and transfer them into a Petri dish with Gamborg B5 solid medium supplemented with 2% sucrose and cefotaxime sodium [500 μg/mL]. Seal the plates with plastic laboratory film and grow them in the dark at 20 °C.
NOTE: The roots can be manipulated under a stereomicroscope equipped to detect the fluorescence under sterile conditions (see Table of Materials). - For biomass production (i.e., gene expression analysis), cut a 5 cm long hairy root and propagate it in a 150 mL Erlenmeyer flask with 20 mL of Gamborg B5 liquid medium supplemented with 2% sucrose and cefotaxime sodium [500 µg/mL]. Grow it for 6 weeks in the dark at 20 °C and 60 rpm.
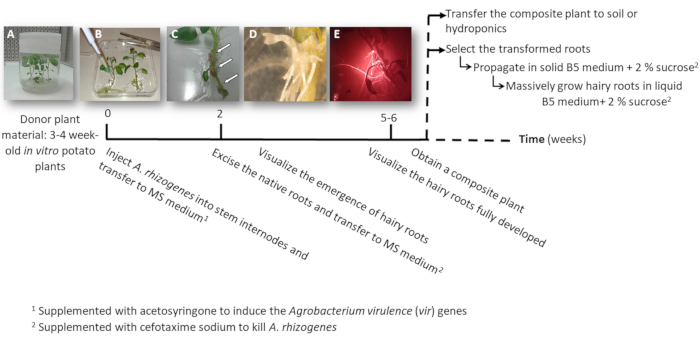
Figure 1: Timeline to obtain potato transgenic hairy roots using A. rhizogenes. The cumulative weeks to reach each stage of the transformation process and the subsequent steps to grow the hairy roots are shown. Representative images of different stages are depicted: the initiation of the process using 3-week-old in vitro plants (A), then infection of the plants by injecting A. rhizogenes (B), the formation of the proliferative tissue (C, arrows) with emerging hairy roots (D), and the developed hairy roots expressing the red fluorescent transformation marker DsRed (E). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Plant transformation using A. tumefaciens (Figure 2)
NOTE: This procedure allows the obtaining of transformed plants. To evaluate the transgene’s effect, a negative control is needed. One option is to follow the procedure using an A. tumefaciens transformed with the empty vector. Alternatively, wild type plants can be used.
- Cut and place a leaf from the 3-4-week-old plants (Figure 2A) in a Petri dish. Using a scalpel exclude the petiole and make transverse cuts (1-3 depending on the leaf size) from the center of the leaf to the edges avoiding cutting them off (Figure 2B).
- Immediately place the leaf floating on 10 mL of fresh 2MS liquid media in a Petri dish with the abaxial side up and close the plate. Repeat the step accommodating up to 15 leaves for cv. Désirée and 25 leaves for ssp. andigena (depending on the leaf size).
- Immediately add 80 µL of A. tumefaciens culture at OD600 = 0.8 in the liquid media and homogenize the plate manually for 1 min to distribute the bacterial solution.
- Carefully seal with sealing film, cover with aluminum foil and incubate for 2 days in a chamber at 24 °C to let the transformation occur.
- Transfer the leaves keeping abaxial side up to CIM medium (Figure 2B) and incubate them for one week in a growth cabinet.
- Scrape the CIM medium with the tweezers so that the leaves can be better accommodated on the media.
- Transfer the leaves keeping abaxial side up to SIM medium (Figure 2C) and incubate them in a growth cabinet, refreshing the medium every 7-10 days, until the shoots are about 2 cm tall.
- Scrape the SIM medium with the tweezers so that the leaves can be fully surrounded by the media. When the emerged shoots reach the lid, work with tall Petri dishes (100 x 20 mm, height x diameter).
NOTE: The callus will form after 2-3 weeks in SIM medium (Figure 2D) and the shoots after 6-7 weeks (Figure 2E). The shoots will be considered as independent transformation events when they emerge from callus formed from independent wounds.
- Scrape the SIM medium with the tweezers so that the leaves can be fully surrounded by the media. When the emerged shoots reach the lid, work with tall Petri dishes (100 x 20 mm, height x diameter).
- Cut three shoots emerged from each callus (considered the same transformation event) (Figure 2E), transfer them to culture flasks with MG medium supplemented with cefotaxime sodium [250 mg/L] to allow rooting, label the subset with a number and incubate in a growth cabinet for 3-4 weeks or until the shoots are vigorous (Figure 2F).
NOTE: When cutting the shoots, remove well the callus otherwise the root will not form.- Repeat the step as many times as independent lines are needed. Up to 5 different transformation events can be placed in a culture flask with a diameter of 8 cm to work in full confidence that the plants from different events are not mixed.
- Select the most vigorous plant of each event, cut the apical segment of the shoot with 3-4 internodes and place it in a new culture flask with 2MS medium supplemented with cefotaxime sodium [250 mg/L].
NOTE: In 3-6 weeks the plant will grow efficiently, developing a vigorous shoot and roots.- Bring back to the chamber the non-selected shoots until the plant selected has fully developed.
- Cut stem segments from the plant with at least one internode or with the apical bud and transfer them to new 2MS medium supplemented with cefotaxime [250 mg/L]. Incubate them in the growth cabinet.
- Replicate every 3-4 weeks to establish the in vitro transformed lines.
NOTE: The cefotaxime sodium is needed in at least three subsequent transfers to 2MS medium to be sure to kill the A. tumefaciens; afterwards, if A. tumefaciens overgrowth is observed, transfer the plants again to 2MS media supplemented with cefotaxime sodium.
- Replicate every 3-4 weeks to establish the in vitro transformed lines.
- To characterize the plant phenotype, transfer plants to soil for their full characterization or to hydroponics culture for root inspection.
- Keep the tubers produced in soil to propagate and maintain the established lines.

Figure 2: Timeline to obtain potato transformed plants using A. tumefaciens. The cumulative weeks to reach each stage of the transformation process and the subsequent steps to grow the plants are shown. Representative images of different stages are depicted: the initiation of the process using leaves from 3-week old in vitro plants (A), the transfer of the wounded and infected leaves to the CIM media (B), the leaves when transferred to SIM media (C), the visualization of the callus around the wounded areas after 2-3 weeks in SIM media (D), the shoot formation after 9-11 weeks in SIM media (E), and the shoots after being transferred to MG media (F). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. Hydroponic culture
- Prepare the Hoagland’s solution to a half strength (0.5x) (Table S2) in a 10 L bucket.
- Immerse an aquarium pump to maintain homogeneity and proper oxygen conditions.
- Cover the walls of the bucket with aluminum foil to grow roots in dark conditions.
- Avoiding root damage, transfer in vitro plants to hydroponic culture.
NOTE: Remove any remaining in vitro medium from roots to avoid microorganism proliferation during incubation by shaking carefully the roots immersed in water. - Cover the plants with transparent film like a glasshouse to allow adequate acclimatization and incubate in the growing chamber.
- Make holes in the film after 3 days and remove it completely one week after.
- Replace with fresh media every 10 days.
6. GUS histochemical reporter gene assay
NOTE: In our case the GUS analysis was performed with roots of 2-3 weeks grown in hydroponics or in vitro.
- Fix the roots with 90% chilled acetone (v/v) and incubate it for 20 minutes on ice.
- Perform two washings with distilled water.
- Add fresh GUS staining solution (Table 1) and apply vacuum (-70 Pa) for 20 min.
- Incubate at 37 °C in dark to protect the photosensitive GUS for 4 h or until a blue color is visible.
NOTE: The presence of ferri- and ferrocyanide in GUS solution minimize the diffusion of reaction products and provide more precise localization.
CAUTION: Use a fume hood and wear protective clothing when handling the toxic cyanide derivatives in GUS solution (the potassium ferricyanide and potassium ferrocyanide). The GUS substrate and the disposal material should be disposed safely. - Remove GUS staining solution and discard it in appropriate containers.
- Perform two washings with ethanol 70% (v/v).
- Observe under a bright field microscope.
NOTE: GUS staining is stable for a few weeks; however, during the first week, the GUS signal is clear and diffuses less into neighboring cells. For longer storage, seal the tube and store it at 4 °C.
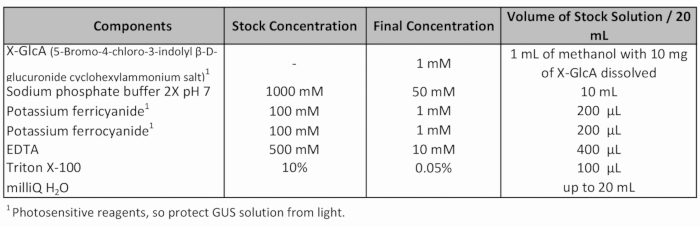
Table 1: GUS staining solution recipe.
Results
Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated potato transformation
In this manuscript, the step-by-step procedure set up to obtain transformed root with A. rhizogenes is presented. Figure 1 presents an overview of the procedure, which altogether takes around 5-6 weeks (from injection of A. rhizogenes to obtaining fully developed hairy roots). Then, ...
Discussion
In potato, the most common system to obtain stable complete transgenic plants uses the transformation by Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains that require organogenesis using exogenous phytohormones. Although the Agrobacterium based protocols has the potential to integrate non-T-DNA vector sequence25, this methodology is still the easiest and less expensive available to transform potato plants. During last years, the interest in A. rhizogenes-mediated transformation has got...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministerio de Innovación y Ciencia (AGL2009-13745, FPI grant to PB), the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad and FEDER funding (AGL2012-36725, AGL2015-67495-C2-1-R), and the University of Girona (PhD grant to SF, and grant SING11/1). The authors are grateful to Dr. Inge Broer (Institute for Land Use, University of Rostock, Rostock, Germany) and Dr. Salomé Prat (Centro Nacional de Biotecnología, Madrid, Spain) for providing the A. rhizogenes and the A. tumefaciens strain, respectively, and Dr. Marçal Soler and Dr. Anna Plasencia for the help and support received in initiating the A. rhizogenes transformation experiments (Toulouse III Paul Sabatier University—CNRS, Plant Research Laboratory (LRSV), Castanet Tolosan, France). The authors thank Sara Gómez (Departament de Biologia, UdG, Girona) for her valuable assistance in carrying out the laboratory work and taking care of plants, and Ferran Fontdecaba and Carla Sánchez who assisted with some of the experiments while they were doing their final degree projects.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acetone | Panreac | 1.310.071.21 | |
| Acetosyringone | Acros | 115540050 | |
| Aquarium pump | Prodac | MP350 | |
| Autoclave | Ragpa Strelimatic | ||
| Bacteriological agar | Lab Conda | 1800 | |
| BAP | Duchefa | B0904 | |
| Beef extract | Lab Conda | 1700 | |
| Plant growing cabinet | Nuaire | ||
| Carbenicillin | Duchefa | C0109 | |
| Cefotaxime sodium | Duchefa | C0111 | |
| DMSO | Merck | 1029310161 | |
| Ecotron infors | HT | 29378 | |
| Ethanol | Merck | 1,009,831,011 | |
| Falcon tube | Control tecnica | CFT011500 | |
| Ferricyanate | Sigma | 101001081 | |
| Ferrocyanate | Sigma | 100979088 | |
| Flask (8.06 cm diameter and 11.3 cm height) and plastic lid for in vitro culture | Apiglass | ref16 | |
| GA3 | Sigma | G7645 | |
| Gamborg B5 media | Duchefa | G0210 | |
| Gelrite | Duchefa | G1101 | |
| Glucosa | Sigma | G5767 | |
| Kanamycin | Sigma | K1377 | |
| Leukopor tape | BSN Leukopor | BDF47467 | |
| Lupe | Wild-Heerbrugg | M420 | |
| Magnetic shaker | Agimatic | 7000243 | |
| MES hydrate | Sigma | M2933-25G | |
MgSO4 | Panreac | 131404 | |
| Microscope | Olympus | ||
| Minufugue centrifugue 5415R | Eppendorf | ||
| Murashige and Skoog media | Duchefa | M0254.0050 | |
Na2HPO4 | Panreac | 131679 | |
| NAA | Duchefa | N0903 | |
| NaCl | Panreac | 131659 | |
NaH2PO4 | Sigma | 58282 | |
| NightSea Stereo | SFA Moonting Adapter | ||
| Parafilm | Anorsa | PRFL-001-001 | |
| Peptone | Lab Conda | 1616 | |
| Petri dishes (90 x 14) | Anorsa | 200200 | |
| pHmetre | Crison | ||
| Phytotron | Inkoa | RFTI-R5485 | |
| Plant Agar | Duchefa | P1001 | |
| Refrigeratot | Liebherr Medline | ||
| Rifampicin | Duchefa | R0146 | |
| Spectinomycin | Sigma | 59007 | |
| Spectrophotometer | Shimadzu | ||
| Square plates (120 x 120) | Deltalab | 200204 | |
| Streptomycin | Sigma | S6501 | |
| Sucrose | Panreac | 131621 | |
| Surgical blades | Swann-Morton | 201 | |
| Surgical needle | NIPRO | 015/0204 | |
| Triptone | Lab Conda | 1612 | |
| Triton | Serva | 37240 | |
| Unimax 1010 shaker | Heidolph | ||
| Vacuum | Dinko | ||
| x-GlcA (5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indoxyl-beta-D-glucuronic acid, sodium salt anhydrous) | Biosynth | B-7398 | |
| Yeast extract | Lab Conda | 1702.00 | |
| Zeatin riboside | Sigma | 1001042850 |
References
- Gelvin, S. B. Traversing the Cell: Agrobacterium T-DNA's journey to the host genome. Frontiers in Plant Science. 3, 1-11 (2012).
- Lacroix, B., Citovsky, V. The roles of bacterial and host plant factors in Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation. The International Journal of Developmental Biology. 57 (6-8), 467-481 (2013).
- Lee, L. Y., Gelvin, S. B. T-DNA binary vectors and systems. Plant Physiology. 146 (2), 325-332 (2008).
- Ishida, Y., et al. High efficiency transformation of maize (Zea mays L.) mediated by Agrobacteriumtumefaciens. Nature Biotechnology. 14 (6), 745-750 (1996).
- White, F. F., Taylor, B. H., Huffman, G. A., Gordon, M. P., Nester, E. W. Molecular and genetic analysis of the transferred DNA regions of the root-inducing plasmid of Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Journal of Bacteriology. 164 (1), 33-44 (1985).
- Dinh, P. T. Y., Brown, C. R., Elling, A. A. RNA Interference of effector gene Mc16D10L confers resistance against Meloidogyne chitwoodi in Arabidopsis and Potato. Phytopathology. 104 (10), 1098-1106 (2014).
- Horn, P., et al. Composite potato plants with transgenic roots on non-transgenic shoots: a model system for studying gene silencing in roots. Plant Cell Reports. 33 (12), 1977-1992 (2014).
- Plasencia, A., et al. Eucalyptus hairy roots, a fast, efficient and versatile tool to explore function and expression of genes involved in wood formation. Plant Biotechnology Journal. 14 (6), 1381-1393 (2015).
- Ron, M., et al. Hairy root transformation using Agrobacteriumrhizogenes as a tool for exploring cell type-specific gene expression and function using tomato as a model. Plant Physiology. 166 (2), 455-469 (2014).
- Zhang, W., et al. Development and application of a universal and simplified multiplex RT-PCR assay to detect five potato viruses. Journal of General Plant Pathology. 83 (1), 33-45 (2017).
- Almasia, N. I., et al. Successful production of the potato antimicrobial peptide Snakin-1 in baculovirus-infected insect cells and development of specific antibodies. BMC Biotechnology. 17 (1), 1-11 (2017).
- Serra, O., et al. Silencing of StKCS6 in potato periderm leads to reduced chain lengths of suberin and wax compounds and increased peridermal transpiration. Journal of Experimental Botany. 60 (2), 697-707 (2009).
- Serra, O., et al. CYP86A33-Targeted gene silencing in potato tuber alters suberin composition, distorts suberin lamellae, and impairs the periderm's water barrier function. Plant Physiology. 149 (2), 1050-1060 (2008).
- Serra, O., et al. A feruloyl transferase involved in the biosynthesis of suberin and suberin-associated wax is required for maturation and sealing properties of potato periderm. The Plant Journal. 62 (2), 277-290 (2010).
- Boher, P., Serra, O., Soler, M., Molinas, M., Figueras, M. The potato suberin feruloyl transferase FHT which accumulates in the phellogen is induced by wounding and regulated by abscisic and salicylic acids. Journal of Experimental Botany. 64 (11), 3225-3236 (2013).
- Serra, O., Chatterjee, S., Figueras, M., Molinas, M., Stark, R. E. Deconstructing a plant macromolecular assembly: chemical architecture, molecular flexibility, and mechanical performance of natural and engineered potato suberins. Biomacromolecules. 15 (3), 799-811 (2014).
- Vulavala, V. K. R., et al. Identification of genes related to skin development in potato. Plant Molecular Biology. 94 (4-5), 481-494 (2017).
- Landgraf, R., et al. The ABC transporter ABCG1 is required for suberin formation in potato tuber periderm. The Plant Cell. 26 (8), 3403-3415 (2014).
- Verdaguer, R., et al. Silencing of the potato StNAC103 gene enhances the accumulation of suberin polyester and associated wax in tuber skin. Journal of Experimental Botany. 67 (18), 5415-5427 (2016).
- Molina, I., Li-Beisson, Y., Beisson, F., Ohlrogge, J. B., Pollard, M. Identification of an Arabidopsis feruloyl-coenzyme A transferase required for suberin synthesis. Plant Physiology. 151 (3), 1317-1328 (2009).
- Gou, J. Y., Yu, X. -. H., Liu, C. J. A hydroxycinnamoyltransferase responsible for synthesizing suberin aromatics in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (44), 18855-18860 (2009).
- Banerjee, A. K., Prat, S., Hannapel, D. J. Efficient production of transgenic potato (S. tuberosum L. ssp. andigena) plants via Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Plant Science. 170 (4), 732-738 (2006).
- Sunil Kumar, G. B., Ganapathi, T. R., Srinivas, L., Revathi, C. J., Bapat, V. a. Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in potato hairy roots. Plant Science. 170 (5), 918-925 (2006).
- Schmidt, J. F., Moore, M. D., Pelcher, L. E., Covello, P. S. High efficiency Agrobacteriumrhizogenes-mediated transformation of Saponariavaccaria L. (Caryophyllaceae) using fluorescence selection. Plant Cell Reports. 26 (9), 1547-1554 (2007).
- Petti, C., Wendt, T., Meade, C., Mullins, E. Evidence of genotype dependency within Agrobacteriumtumefaciens in relation to the integration of vector backbone sequence in transgenic Phytophthorainfestans-tolerant potato. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 107 (3), 301-306 (2009).
- Gaudin, V., Vrain, T., Jouanin, L. Bacterial genes modifying hormonal balances in plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. 32 (1), 11-29 (1994).
- Nemoto, K., et al. Function of the aux and rol genes of the Ri plasmid in plant cell division in vitro. Plant Signaling &. Behavior. 4 (12), 1145-1147 (2009).
- Visser, R. G. F., et al. Expression and inheritance of inserted markers in binary vector carrying Agrobacteriumrhizogenes-transformed potato (Solanumtuberosum L.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics. 78 (5), 705-714 (1989).
- Guillon, S., Trémouillaux-Guiller, J., Pati, P. K., Rideau, M., Gantet, P. Hairy root research: recent scenario and exciting prospects. Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 9 (3), 341-346 (2006).
- Georgiev, M. I., Agostini, E., Ludwig-Müller, J., Xu, J. Genetically transformed roots: from plant disease to biotechnological resource. Trends in Biotechnology. 30 (10), 528-537 (2012).
- Ooms, G., Lenton, J. R. T-DNA genes to study plant development: precocious tuberisation and enhanced cytokinins in A. tumefaciens transformed potato. Plant Molecular Biology. 5 (4), 205-212 (1985).
- de Vries-Uijtewaal, E., et al. Fate of introduced genetic markers in transformed root clones and regenerated plants of monohaploid and diploid potato genotypes. TAG. Theoretical and applied genetics. 78 (2), 185-193 (1989).
- Bird, D., et al. Characterization of Arabidopsis ABCG11/WBC11, an ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter that is required for cuticular lipid secretion. The Plant Journal: For Cell and Molecular Biology. 52 (3), 485-498 (2007).
- Luo, B., Xue, X. Y., Hu, W. L., Wang, L. J., Chen, X. Y. An ABC transporter gene of Arabidopsis thaliana, AtWBC11, is involved in cuticle development and prevention of organ fusion. Plant and Cell Physiology. 48 (12), 1780-1802 (2007).
- Panikashvili, D., et al. The Arabidopsis DESPERADO/AtWBC11 transporter is required for cutin and wax secretion. Plant Physiology. 145 (4), 1345-1360 (2007).
- Panikashvili, D., et al. The Arabidopsis DSO/ABCG11 transporter affects cutin metabolism in reproductive organs and suberin in roots. Molecular Plant. 3 (3), 563-575 (2010).
- Bjelica, A., et al. Fatty acid ω-hydroxylases from Solanum tuberosum. Plant Cell Reports. 35 (12), 2435-2448 (2016).
- Ding, Y., et al. Abscisic acid coordinates nod factor and cytokinin signaling during the regulation of nodulation in Medicago truncatula. The Plant Cell. 20 (10), 2681-2695 (2008).
- Isayenkov, S., Mrosk, C., Stenzel, I., Strack, D., Hause, B. Suppression of allene oxide cyclase in hairy roots of Medicagotruncatula reduces jasmonate levels and the degree of mycorrhization with glomus intraradices 1[w]. Plant Physiology. 139 (3), 1401-1410 (2005).
- Dalton, D. A., et al. Physiological roles of glutathione S-Transferases in soybean root Nodules 1[C][W][OA]. Plant Physiology. 150 (1), 521-530 (2009).
- Limpens, E., et al. RNA interference in Agrobacteriumrhizogenes-transformed roots of Arabidopsis and Medicago truncatula. Journal of Experimental Botany. 55 (399), 983-992 (2004).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved