Method Article
Computer-based Multitaper Spectrogram Program for Electroencephalographic Data
In This Article
Summary
This protocol provides an open source, compiled MATLAB program that generates multitaper spectrograms for electroencephalographic data.
Abstract
Current web resources provide limited, user friendly tools to compute spectrograms for visualizing and quantifying electroencephalographic (EEG) data. This paper describes a Windows-based, open source code for creating EEG multitaper spectrograms. The compiled program is accessible to Windows users without software licensing. For Macintosh users, the program is limited to those with a MATLAB software license. The program is illustrated via EEG spectrograms that vary as a function of states of sleep and wakefulness, and opiate-induced alterations in those states. The EEGs of C57BL/6J mice were wirelessly recorded for 4 h after intraperitoneal injection of saline (vehicle control) and antinociceptive doses of morphine, buprenorphine, and fentanyl. Spectrograms showed that buprenorphine and morphine caused similar changes in EEG power at 1−3 Hz and 8−9 Hz. Spectrograms after administration of fentanyl revealed maximal average power bands at 3 Hz and 7 Hz. The spectrograms unmasked differential opiate effects on EEG frequency and power. These computer-based methods are generalizable across drug classes and can be readily modified to quantify and display a wide range of rhythmic biological signals.
Introduction
EEG data can be productively analyzed in the frequency domain to characterize levels of behavioral and neurophysiological arousal1. Multitaper spectrograms transform the EEG waveform into time and frequency domains, resulting in the visualization of the dynamic signal power at different frequencies across time. The multitaper spectrogram uses Fourier analysis to produce spectral density estimations. Spectral density estimation separates a waveform into the pure sinusoidal waves comprising the signal and is analogous to the diffraction of white light through a prism to see the entire spectrum of colors2. The multitaper spectrogram of the EEG represents the combined activity of multiple networks of neurons with discharge patterns that oscillate at different frequencies2. Due to its time shift invariant, the Fourier transform is considered the best transformation between time and frequency domains3. Fourier analysis also has a number of limitations. EEG signals are nonstationary. Therefore, small changes may not be perceived under Fourier methods and the analysis may change depending on the size of the data set. However, windowing is used when applying a Fourier transform to a nonstationary signal. This assumes that the spectrum of the signal changes only marginally over short periods of time. An alternate method for spectral analysis is wavelet transform which may be more appropriate for detecting brain disease3.
From a functional perspective, the different oscillations comprising an EEG signal are lower-level, trait phenotypes characteristic of higher-level, state phenotypes such as sleep and wakefulness2, or the loss of wakefulness caused by general anesthetics4,5,6. Regarding states of sleep and wakefulness, the spectrogram clearly illustrates that endogenously generated rhythms of sleep are continuous and dynamic7. Quantitative descriptions of states of sleep and wakefulness have traditionally involved a binning process that assigns a sleep or wake classification to each specifically defined epoch (e.g., 10 s) of EEG recording. These state bins are then plotted as a function of time. Time course data plots, often referred to as hypnograms, are used to differentiate normal sleep from sleep that is disrupted by disease, drug administration, changes in circadian rhythms, shift work, etc. A limitation of hypnogram plots is that they misrepresent EEG signals by expressing arousal states as square waveforms. Hypnogram plotting involves a discretization of arousal states2 and does not permit a finely grained display of intermediate or transition stages. Furthermore, 10 s scoring epochs produce a discretization of time by imposing a lower limit on the time scale. The result of the discretization of both state and time is the loss of neurophysiological information regarding the dynamic interplay between states of consciousness2 and drug-induced disruption of these states4. For example, different anesthetic agents act on different molecular targets and neural networks. Pharmacological manipulation of these neural networks reliably produces spectrograms unique to the drug, dose, and route of administration4.
The present protocol was developed to facilitate research regarding the mechanisms by which opioids alter sleep8, breathing9, nociception10, and brain neurochemistry11. This protocol describes the steps required to create a multitapered spectrogram for EEG analyses that can be completed using proprietary software or a system that does not have MATLAB licensing. C57BL/6J (B6) mice were used to validate the ability of this computer-based method to create novel EEG spectrograms during normal, undisturbed states of sleep and wakefulness and after systemic administration of opiates. The reliability and validity of the analyses were confirmed by systematic comparisons of differences between EEG spectrograms after B6 mice received intraperitoneal injections of saline (vehicle control) and antinociceptive doses of morphine, buprenorphine, and fentanyl.
Quantitative studies of neonatal mouse EEG dynamics have translational relevance by providing a model for studies aiming to achieve a better understanding of neonatal human EEG12. Quantifying EEG dynamics is not merely descriptive and can contribute to machine learning approaches that can predict arousal based in part on EEG data13. The goal of the present report is to promote translational science by providing a widely accessible, user friendly code for computing multitaper spectrograms that characterize drug-induced changes in mouse EEG.
Protocol
All procedures involving mice adhered to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (8th edition, National Academies Press, Washington DC, 2011) and were reviewed and approved by the University of Tennessee Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
1. Implantation of Recording Electrodes and Initial Data Collection
- Purchase mice and keep them in a humidity- and temperature-controlled room with ad libitum access to food and water. Allow mice to adapt to their new environment for one week before surgical implantation of recording electrodes. The implantation procedure has been described in detail1,14.
- Sterilize all surgical equipment.
- Anesthetize mice with isoflurane at 2.5%−3% delivered in 100% oxygen.
- Following the loss of the righting reflex, remove the mouse from the anesthesia induction chamber and transfer it to a stereotaxic frame.
- Apply an ophthalmic ointment to both eyes.
- Reduce the isoflurane to 1.7%, continuously delivered via a mask.
- Make a midline scalp incision to expose the skull.
- Drill two craniotomies above the left and right cortex (each at stereotaxic coordinates anterior = 1.0 and lateral = 3.0 relative to the bregma15).
- Insert the EEG electrodes into each craniotomy and secure with dental acrylic.
- Implant bipolar electrodes in the dorsal trapezius muscle for recording the electromyogram (EMG).
NOTE: The four electrodes are led to a wireless telemeter implanted subcutaneously above the lower right body quadrant. These surgical techniques can be viewed here (https://www.datasci.com/services/dsi-surgical-services/surgical-videos). - After the surgery, administer analgesic carprofen and place the mouse in a warm recovery cage. Observe the mouse until it is ambulatory. House implanted mice individually.
- Upon full recovery from the surgery, handle mice daily and evaluate the quality of the EEG and EMG recordings.
- Configure the data acquisition system to record all signals ± 1,000 mV.
- Obtain EEG and EMG recordings for the duration needed.
- Score each 10 s bin of the digital EEG and EMG recordings as wakefulness, rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, or non-REM (NREM) sleep using sleep scoring software.
NOTE: Among mouse strains there are genotype- and state-specific differences in EEG power expressed as a percentage of the total power16. In B6 mice, states of wakefulness are characterized by a 75−100 mV, mixed frequency EEG, and by EMG signals showing prominent muscle tone with large increases in amplitude during movement. Criteria for scoring NREM sleep include a reduction in EMG amplitude relative to the EMG amplitude of wakefulness. The NREM sleep EEG has a slower frequency and increased amplitude (100−150 mV) compared to wakefulness. REM sleep is characterized by muscle atonia and an EEG signal that is similar to the EEG of wakefulness. - Instruct two individuals to independently score the same record. At least one individual should be blinded to the treatment condition. Concordance values between the two sleep scorers should be greater than 90%.
2. Facilities and Equipment
- Amplify and digitize unfiltered EEG and EMG signals using data acquisition instrumentation and software.
NOTE: The Chronux Spectral Analysis Toolbox developed in the Mitra Laboratory at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory is used to express EEG signals as power in relation to time and frequency domains.
3. Spectrogram Computation
- If a Windows user, use the compiled program.
- If a Macintosh user, run the raw code file.
- Obtain raw, unprocessed EEG data in either EDF or CSV file format and place it in the same location as the compiled program file.
- Name the data files using the following constraints: names must consist of only letters, numbers, underscores, or dashes.
- Name the data files using the following constraints: filenames must not contain periods, commas, spaces, or any other symbols.
- Download the compiled Multitaper Spectrogram Program (https://drive.google.com/ or contact C. O'Brien at cobrien8@vols.utk.edu).
- Launch the spectrogram program and follow the pop-up prompts. Choose file type: *.CSV or *.EDF.
NOTE: Further program installation details are located in the readme.txt file. - Type the entire EEG file name (e.g., 419eeg.edf or 419.eeg.csv).
- Select parameters for spectrogram calculation: Default or New. This step requires the longest processing time as the spectrogram is being computed. The mathematical windowing function (taper) provides statistically-independent estimates of the underlying spectrum. The longer the recording duration, the longer this step will take. On a PC platform running Windows 10 this required a maximum of about 3−4 min for a 4 h recording.
- Use the following default spectrogram parameters:
Sampling frequency = 500 Hz. This represents the number of samples per second.
fpass = 0.3 Hz and 30 Hz. Fpass defines the frequencies of input and controls the range of frequencies supplied in the output.
Padding = 2. Padding works to finely interpolate the output without affecting the result calculation in any way. This may assist with visualization and the precise identification of spectral lines. The field is any integer from -1 and up.
Time-bandwidth product (NW) = 15. The product of the signal temporal duration and spectral width.
Number of tapers = 29. When choosing number of tapers, it is essential to use 2NW-1. There is no limit on the number of tapers used. The more tapers used will result in the inclusion of tapers with poor concentration in the specified frequency bandwidth.
Trial average = 1. This parameter governs whether or not trial or channel averaging is performed. If this parameter is set to 0, there is no channel averaging and the function will output independent results for each trial or channel passed as input data. However, if the trial average is set to 1, the results output to the user are averaged over trials or channels.
Time to compute FFT ~30 s. Used to follow the evolution of the spectrum by calculating the spectrum over many small windows.
Step size of window for FFT computation = 5. The amount the sliding time window advances after each spectrum calculation is performed.
NOTE: The default spectrogram parameters stated in step 3.7.1 can be changed as needed.
- Use the following default spectrogram parameters:
- Enter titles for both the spectrogram and EEG.
- Save the resulting spectrogram and EEG.
- Save figures by clicking File | Save in the figure window.
NOTE: The figures will provide program users with summaries that can be developed into publication-quality figures.
- Save figures by clicking File | Save in the figure window.
4. Troubleshooting
- Download the sample mouse sleep EEG data for sample spectrogram computation.
- Run program with the sample data to ensure the user is correctly using the program. Find the figures for these sample data in the appendix to ensure that the figures created from the sample data are accurate.
NOTE: All equipment and materials used have been provided in the Table of Materials.
Results
The following figures illustrate the type of novel insights into EEG indices of brain excitability that are provided by spectrograms.
Figure 1A illustrates similarities and differences in the cortical EEG during wakefulness, NREM sleep, and REM sleep. Many investigators use these kinds of traces, along with EMG recordings (not shown), to quantify sleep and wakefulness. Figure 1B uses a hypnogram plot to convey the temporal organization of states of sleep and wakefulness based on assessments of EEG and EMG recordings. States were scored in 10 s epochs and these epochs were plotted as the hypnogram during the 14,400 s comprising the 4 h recording. Hypnogram plots do not illustrate the fact that transitions between states are continuous and nonlinear. In contrast to a hypnogram plot, the spectrogram (Figure 1C) illustrates highly dynamic changes in EEG frequency and power as a function of time. The spectrogram also highlights the similarities between the cortical EEG signal during wakefulness and during REM sleep. The three boxes superimposed on the spectrogram (Figure 1C) mark states identified as wakefulness (WAKE), NREM sleep, and REM sleep in the hypnogram above (Figure 1B) and are provided to assist with visualizing the detailed changes in EEG frequency and power. The spectrogram for the entire recording provides a nuanced appreciation of the EEG as a continuous process.
Figure 2 provides four multitaper spectrograms, each summarizing 4 h of EEG recordings after intraperitoneal administration of saline, morphine, buprenorphine, and fentanyl. All four recordings are from the same mouse and were begun 2 h after light onset. The opiates, but not saline, inhibited NREM and REM sleep, and increased the amount of wakefulness. A number of novel features are visualized by the spectrograms. The detection of novel EEG features suggests the potential application for opiate differentiation in a chemical threat environment. After the saline injection (Figure 2A) the greatest amount of power resided in the 2−4 Hz range, indicating NREM sleep. Note that the EEG spectrograms were fundamentally altered by opiate administration, and that each opiate caused unique spectral changes.
Figure 3 demonstrates that EEG changes illustrated by the spectrograms can be quantified and expressed as average dominate spectral power of each half frequency (Figure 3A) and as the average spectral power within specific EEG frequency bands (Figure 3B). The greatest differences from saline were caused by buprenorphine and occurred in the delta and theta ranges.
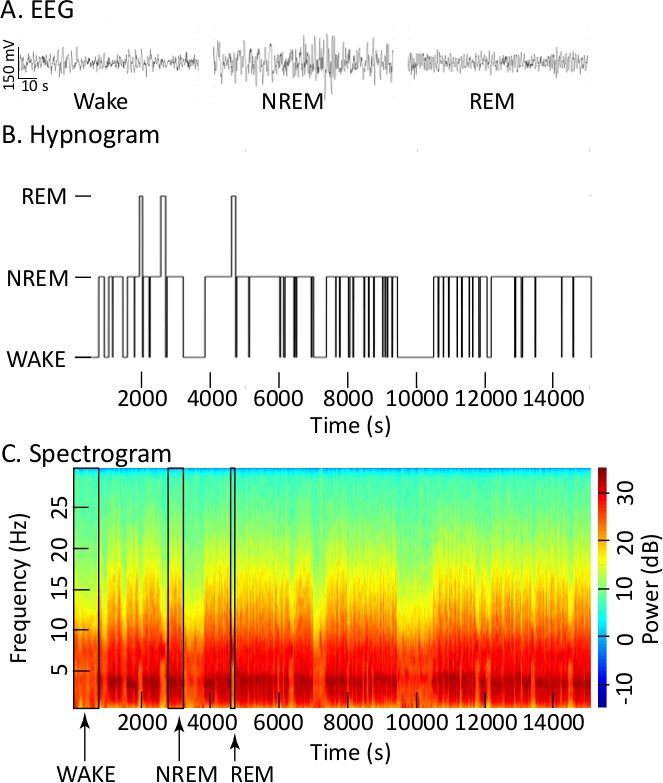
Figure 1: Cortical EEG recordings used to create hypnograms and spectrograms. (A) EEG waveforms recorded during wakefulness, NREM sleep, and REM sleep during a baseline (no injection) recording. Each trace shows 90 s of recording. (B) The hypnogram uses the height of the bars to convey state of consciousness (ordinate) versus 4 h of recording (abscissa). (C) Tapered spectrogram using a color bar to convey EEG power in decibels (dB, right ordinate) or spectral power density at different EEG frequencies in Hertz (Hz, left ordinate) as a function of 4 h recording time (abscissa). Black vertical lines have been added to the spectrogram to delineate one episode each of wakefulness, NREM sleep, and REM sleep. (Spectrogram parameters: sampling frequency = 500 Hz, fpass = 0.3 Hz and 30 Hz, padding = 2, time-bandwidth = 15, number of tapers 29, trial average = 1, duration of time to compute FFT ~30 s, step size of window for FFT computation = 5). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
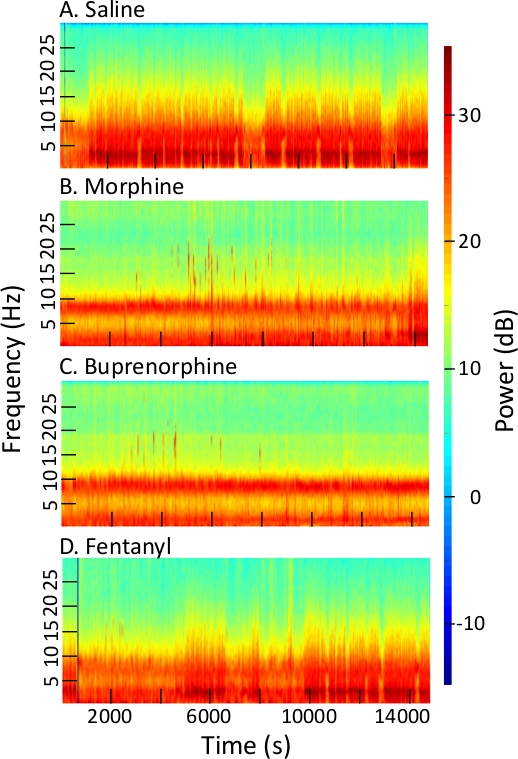
Figure 2: Spectrograms illustrating changes in EEG power and frequency caused by opiate administration. Each spectrogram plots EEG frequency in Hertz (Hz, left ordinate) and decibels (dB) of EEG power using a color bar (right ordinate) for 4 h (abscissa) after administration of (A) saline, (B) morphine, (C) buprenorphine, and (D) fentanyl. (Spectrogram parameters: sampling frequency = 500 Hz, fpass = 0.3 Hz and 30 Hz, padding = 2, time-bandwidth = 15, number of tapers 29, trial average = 1, time to compute FFT ~30 s, step size of window for FFT computation = 5). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
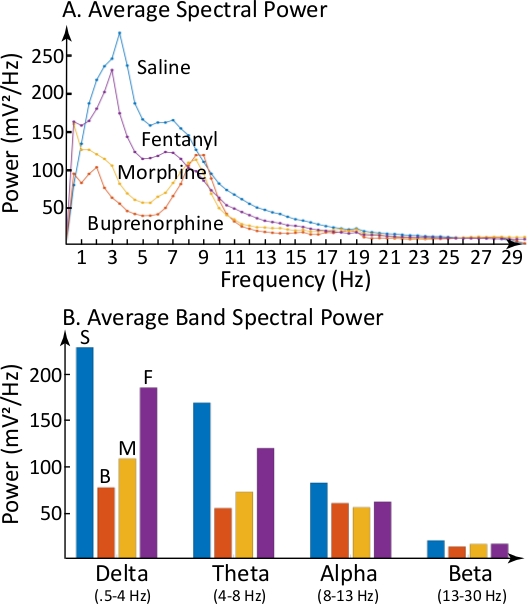
Figure 3: Opiates differentially altered the average EEG power within the delta and theta EEG frequency bands. (A) Summarizes the average EEG power during each 4 h recording shown in Figure 2. Ordinate plots average EEG power at each half frequency (abscissa). Relative to the saline control, each of the other three functions show opiate-specific alterations in average EEG power. (B) Illustrates the average EEG power in four EEG frequency bands (delta, theta, alpha, and beta) after administration of saline (S), buprenorphine (B), morphine (M), and fentanyl (F). Color coding is the same for power functions in A and average power bands in B. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
The program described here was developed to create a spectrogram using the nine steps outlined in protocol section 3, Spectrogram Computation. These steps involve acquiring the spectrogram program, ensuring the correct file format, and altering the computational parameters for the generation of unique user spectrograms. Users can create spectrograms that are tailored to a range of conceptual questions and experimental designs. In order to enhance the ease and efficiency of this development process, it is essential to provide the raw EEG data in the correct file format, named according to the constraints described above. Although example signals have been provided for mouse EEG data, the spectrogram program is readily applicable to human and non-human EEG data that are free of signal processing limitations.
The recommended approach for troubleshooting and method modification is to begin by analyzing a small data set. The major program outputs to consider include plots of the filtered EEG as well as the spectrogram. An appealing aspect of the tapered spectrogram is that it can be applied to a wide variety of periodic, biological signals. The variety ranges from long duration circadian (24 h) rhythms17 to very fast rhythms such as 1,000 Hz discharge rates of a Renshaw cell18.
Data formatting is a constraint of this spectrogram protocol. European data format (EDF) is widely used with EEG data. However, there are many other formatting options. For this reason, the raw code file has been included (see 3.2 above) in case the user would like to alter the file format. With regard to the raw program file, another limitation is the need for experience with the computer programming language in order to alter the file format. Not all investigators have access to the proprietary software and the full array of plug-ins. This protocol was developed to circumvent this issue by providing a compiled program that runs on a WINDOWS-based device without software licensing. This is achieved through the RUNTIME plugin which is included in the compiled program and does not require any software registration by the user.
This EEG spectrogram routine is a novel, open source, computer-based program that allows users to create personalized, multitaper spectrograms from a wide range of data. The user has complete control over all computational aspects of spectrogram generation. Without prior signal processing and computer programing knowledge, spectrograms can be difficult to generate. The protocol described here will facilitate spectrogram generation. Please see the supplemental material section for further signal processing readings and multitaper spectrogram guidance.
Supplemental Material
http://chronux.org
http://www-users.med.cornell.edu/~jdvicto/pdfs/pubo08.pdf
http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/tutorial/timefrequencyanalysis/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4502759/#SD3-data
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
This work supported in part by a NIH grant HL-65272. The authors thank Zachary T. Glovak and Clarence E. Locklear for their contributions to this project.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Dental acrylic | Lang Dental Manufacturing Co | Jet powder and liquid | |
| EEG/EMG Amplifier | Data Science International | model MX2 | |
| macOS Mojave | Apple | v10.14.4 | |
| MATLAB | Mathworks | v9.4.0.813654 | software for spectrogram comp. |
| Mouse anesthesia mask | David Kopf Instruments | model 907 | |
| Neuroscore | Data Science International | v3.3.9317-1 | software for scoring sleep and wakefulness |
| Ponemah | Data Science International | v5.32 | software for EEG/EMG Data Acquisition |
| Stereotaxic frame | David Kopf Instruments | model 962 | |
| Stereotaxic frame, mouse adapter | David Kopf Instruments | model 921 | |
| Windows 10 | Microsoft | v10.0.17763.503 | |
| Wireless Telemeter | Data Science International | model HD-X02 |
References
- Wasilczuk, A. Z., Proekt, A., Kelz, M. B., McKinstry-Wu, A. R. High-density electroencephalographic acquisition in a rodent model using low-cost and open source resources. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 117, 10 (2016).
- Prerau, M. J., Brown, R. E., Bianchi, M. T., Ellenbogen, J. M., Purdon, P. L. Sleep neurophysiological dynamics through the lens of multitaper spectral analysis. Physiology. 32, 60-92 (2017).
- Akin, M. Comparison of wavelet transform and FFT methods in the analysis of EEG signals. Journal of Medical Systems. 26 (3), 241-247 (2002).
- Purdon, P. L., Sampson, A., Pavone, A., Brown, E. N. Clinical electroencephalography for anesthesiologists Part 1: Background and basic signatures. Anesthesiology. 123 (4), 937-960 (2015).
- Liu, Q., et al. Frontal EEG temporal and spectral dynamics similarity analysis between propofol and desflurane induced anesthesia using Hilbert-Huang Transform. BioMed Research International. 2018, 4939480 (2018).
- Akeju, O., et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of dexmedetomidine-induced electroencephalogram oscillations. PLoS One. 11 (10), (2016).
- Ogilvie, R. D. The process of falling asleep. Sleep Medicine Reviews. 5 (3), 247-270 (2001).
- Baghdoyan, H. A., Lydic, R., Brady, S. T., Albers, R. W., Price, D. L., Siegel, G. J. . Basic Neurochemistry. , 982-999 (2012).
- Angel, C., et al. Buprenorphine depresses respiratory variablity in obese mice with altered leptin signaling. Anesthesiology. 128 (5), 984-991 (2018).
- Glovak, Z. T., Mihalko, S., Baghdoyan, H. A., Lydic, R. Leptin status alters buprenorphine-induced antinociception in obese mice with dysfunctional leptin receptors. Neuroscience Letters. 660, 29-33 (2017).
- Zhang, X., et al. Morphine and fentanyl delivered to prefrontal cortex of behaving mice depress breathing and alter neurotransmitter concentrations. Anesthesia & Analgesia. , (2019).
- Cornelissen, L., Kim, S. E., Purdon, P. L., Brown, E. N., Berde, C. B. Age-dependent electroencephalogram (EEG) patterns during sevoflurane general anesthesia in infants. eLIFE. 4, e06513 (2015).
- Chini, M., et al. Neural correlates of anesthesia in newborn mice and humans. Front Neural Circuits. 13 (Article 38), 1-13 (2019).
- Flint, R. R., Chang, T., Lydic, R., Baghdoyan, H. A. GABA-A receptors in the pontine reticular formation of C57BL/6J mouse modulate neurochemical, electrographic, and behavioral phenotypes of wakefulness. Journal of Neuroscience. 30 (37), 12301-12309 (2010).
- Paxinos, G., Franklin, K. B. J. . The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. , (2018).
- Franken, P., Malafosse, A., Tafti, M. Genetic variation in EEG activity during sleep in inbred mice. American Journal of Physiology. 257 (4), (1998).
- Ko, C. H., et al. Emergence of noise-induced oscillations in the central circadian pacemaker. PLoS Biol. 8 (10), e1000513 (2010).
- Steriade, M., Curró Dossi, R., Conteras, D. Electrophysiological properties of intralaminar thalamocortical cells discharging rhythmic (40 Hz) spike-bursts at 1000 Hz during waking and rapid eye movement sleep. Neuroscience. 56, 1-9 (1993).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved