A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Capillary Electrophoresis-based Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange for Conformational Characterization of Proteins with Top-down Mass Spectrometry
In This Article
Summary
Presented here is a protocol for a capillary electrophoresis-based hydrogen/deuterium exchange (HDX) approach coupled with top-down mass spectrometry. This approach characterizes the difference in higher-order structures between different protein species, including proteins in different states and different proteoforms, by conducting concurrent differential HDX and electrophoretic separation.
Abstract
Resolving conformational heterogeneity of multiple protein states that coexist in solution remains one of the main obstacles in the characterization of protein therapeutics and the determination of the conformational transition pathways critical for biological functions, ranging from molecular recognition to enzymatic catalysis. Hydrogen/deuterium exchange (HDX) reaction coupled with top-down mass spectrometric (MS) analysis provides a means to characterize protein higher-order structures and dynamics in a conformer-specific manner. The conformational resolving power of this technique is highly dependent on the efficiencies of separating protein states at the intact protein level and minimizing the residual non-deuterated protic content during the HDX reactions.
Here we describe a capillary electrophoresis (CE)-based variant of the HDX MS approach that aims to improve the conformational resolution. In this approach, proteins undergo HDX reactions while migrating through a deuterated background electrolyte solution (BGE) during the capillary electrophoretic separation. Different protein states or proteoforms that coexist in solution can be efficiently separated based on their differing charge-to-size ratios. The difference in electrophoretic mobility between proteins and protic solvent molecules minimizes the residual non-deuterated solvent, resulting in a nearly complete deuterating environment during the HDX process. The flow-through microvial CE-MS interface allows efficient electrospray ionization of the eluted protein species following a rapid mixing with the quenching and denaturing modifier solution at the outlet of the sprayer. The online top-down MS analysis measures the global deuteration level of the eluted intact protein species, and subsequently, the deuteration of their gas-phase fragments. This paper demonstrates this approach in differential HDX for systems, including the natural protein variants coexisting in milk.
Introduction
Distinguishing protein species in different conformational, binding, or modification states and characterizing their structural differences are important for monitoring the pathways of transitions between these species involved in biological events, ranging from molecular recognition to enzymatic catalysis, and understanding the mechanisms underlying these events. Conventional biophysical techniques do not provide a complete solution due to the limitations such as insufficient resolution and loss of dynamic information in solution. Hydrogen/deuterium exchange coupled with mass spectrometry (HDX MS) is a technique that labels the structural and conformational features of proteins with deuterium (2H) via the exchange between labile hydrogen atoms of proteins and 2H from the deliberately introduced 2H2O solution. Protons involved in hydrogen bonding or that are sequestered from the solvent in the protein interior do not exchange readily1. Thus, as the exchange rate at an exchangeable site is highly dependent on its involvement in higher-order structures, the protein structures can be revealed at high spatial resolution by MS that probes the extent and rate of 2H-uptake based on the differing atomic masses between 1H and 2H. Over the recent decades, HDX MS has become an outstandingly successful technique for studying protein conformations and dynamics2.
In the classical bottom-up approach of HDX MS, the ensemble of protein species in different conformational, binding, or modification states is proteolyzed without separation at the intact protein level, making it infeasible to characterize individual species by analyzing the resulting proteolytic fragments with convoluted deuterium contents. In contrast, in the top-down approach, different protein states or proteoforms that have incorporated different deuterium contents give rise to multiple distributions of intact protein masses in an MS scan. This allows individual species to be separated by mass-selection of ions corresponding to each mass distribution using a proper mass filter (such as a quadrupole) and the characterization of their conformational differences in the subsequent tandem MS analysis3,4,5,6. However, the efficiency of separating protein states or proteoforms in this strategy is limited by the extent of difference in their corresponding mass distributions.
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) provides a means to separate protein species based on their differing charges and hydrodynamic sizes in the solution phase with high efficiency7. Combining CE with HDX offers additional separation of protein states or proteoforms in the solution phase. In addition, the small volume of the CE capillary allows the utilization of a fully deuterated solution as the background electrolyte solution (BGE), i.e., the running buffer, rendering the capillary as an HDX reactor for protein samples. Due to the difference in electrophoretic mobility between proteins and protic reagents in the electrophoresis process, conducting HDX during CE results in a nearly complete deuterating environment for the protein analytes with minimal residual non-deuterated contents, thereby enhancing the sensitivity of the structural analysis using HDX data. As such, we developed a CE-based differential HDX approach coupled with top-down MS to characterize protein higher-order structures in a state- or proteoform-specific manner8.
This paper describes protocols for this approach by detailing the steps of material preparation, experimental procedure, and data analysis. Factors that may affect the method performance or data quality are listed in short notes. The representative results presented here include differential HDX data of mixtures of different proteins and natural variants of bovine β-lactoglobulin (β-lg), the major whey protein present in milk9. We demonstrate separation efficiency, reproducibility, and 2H-labeling performance of the two abundant variants of β-lg, i.e., A and B10,11 during the CE-based HDX and variant-specific characterization of their conformations.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
NOTE: Use high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) grade or MS grade reagents whenever possible to minimize the contaminants that may interfere with MS analysis. Do not touch the CE-MS interface with bare hands during the measurement to avoid the possibility of an electrical shock caused by either the electrophoretic voltage or electrospray voltage.
1. Material preparation
- Modification of fused silica capillary for CE
- Prepare a 5% (w/w) hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) solution by dissolving HPC powder (molecular weight [MW]: 100 kDa) in water with continuous stirring at room temperature on a magnetic stirrer for ~12 h or until complete disappearance of solid particles12. Remove any visible air bubbles with an ultrasonicator.
- Mount a fused silica glass capillary (inner diameter [ID]: 50 µm, outer diameter [OD]: 360 µm) of approximately 85 cm length into a CE instrument. Rinse the capillary by continuously infusing an organic solvent, such as acetone13, using the autosampler of CE at an infusion pressure of 40 psi for 10-15 min.
- Fill the cleaned capillary with HPC solution using the autosampler at an infusion pressure of 40 psi (which often takes ~40 min). Infuse air into the HPC-filled capillary at 40 psi to ensure free airflow in the capillary, indicated by the air bubbles ejected from the capillary upon immersion in water.
- Bake the HPC-coated capillary in a temperature-programmable oven (ideally the temperature-controlled column oven of a temperature-programmed gas chromatograph) with nitrogen gas (25 psi) flowing through the capillary, following the temperature program shown in Figure 1.
- Cool the oven to room temperature before taking the capillary out. Use this HPC-modified capillary for CE separation.
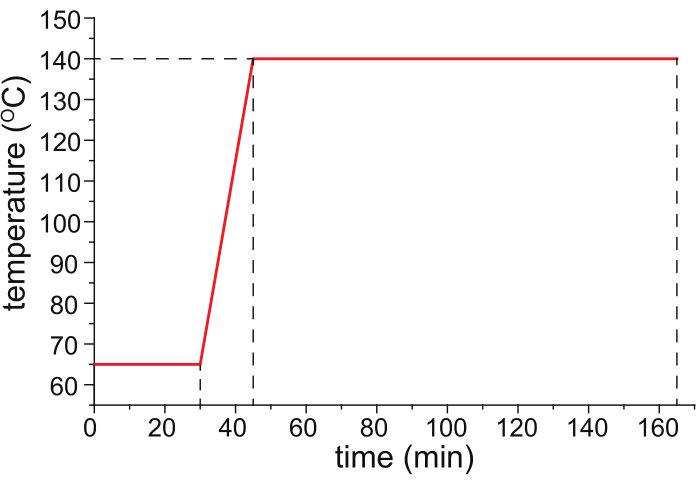
Figure 1: A recommended temperature program for capillary baking. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Background electrolyte (BGE) solution and modifier solution8
- Prepare 1-10 mL of BGE at the desired concentration (e.g., 10 mM) by dissolving the appropriate quantity of ammonium acetate in 2H2O. Place 200 µL-aliquots of BGE in separate BGE vials and seal the vials with parafilm to minimize the HDX reaction between BGE and water vapor in the air.
- Prepare 10 mL of a modifier solution with 75% (v/v) methanol and 25% (v/v) water, with pH adjusted to 2.5 using formic acid.
NOTE: Use 2H2O and deuterated methanol to prepare the modifier solution if the deuterium atoms in the side chains and unprotected backbone amides should be retained for detection by MS.
- Desalting of protein samples
- Prepare an ammonium acetate solution in non-deuterated water at the desired concentration.
NOTE: A concentration less than 100 mM is recommended to avoid a high electric current during electrophoresis and the resulting Joule heating effect. - When necessary, adjust the pH of the ammonium acetate solution to the desired level using formic acid (for pH < 6.8) or ammonium hydroxide (for pH > 6.8).
- Substitute the original buffers of the protein solution with an ammonium acetate solution (prepared in non-deuterated water at the desired concentration; pH adjusted to 7.5 with ammonium hydroxide) through at least five sequential concentrations and dilution steps at 4 °C using a centrifugal filter with a proper MW cutoff.
NOTE: The protein samples to be desalted may be either from prior production procedures (e.g., purification or formulation) or prepared by dissolving the lyophilized powder of protein. The "salts" to be removed from the sample solutions in this step refer in general to all small ions or molecules that are non-volatile. Although these species can be efficiently separated from proteins during the electrophoresis process, this step is recommended to avoid compromising the electrophoretic resolution and thus minimizing the contamination of the mass spectrometer. When protein analytes should be stabilized by specific salts or additives, include them in the BGE. - Determine the protein concentration using a microvolume UV-Vis spectrophotometer.
- Prepare an ammonium acetate solution in non-deuterated water at the desired concentration.
2. Operation of CE-based HDX MS analysis
NOTE: The mass spectrometer used in this approach should be equipped with a mass analyzer with ultra-high resolution, such as a Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance (FTICR) or orbitrap, a mass-filter, such as a quadrupole that allows mass-selection of precursor ions for fragmentation, and electron-transfer dissociation (ETD) or electron-capture dissociation (ECD) functions to perform top-down analysis with reliable tandem MS data (ideally isotopically resolved signals of fragment ions).
- Optimization of CE and MS settings
- Perform a pilot MS measurement using a standard electrospray ionization (ESI) source by spraying either the preloaded sample from a metal-coated borosilicate glass capillary (the "static" nanoESI scheme) or the continuously infused sample from a metal emitter to optimize the MS settings for measurement of intact proteins (MS1) and their gas-phase fragments (MS2). Fragment the protein species of interest by mass-selection of the ensemble of its ions in a single charge state, followed by ETD or ECD of the precursor ions.
NOTE: The essential settings include the parameters that affect desolvation, the mass-selection of precursor ions (to avoid interference from other species), and fragmentation efficiency. Both the center and width of the mass-selection window should be increased to match the resulting mass distribution of the analyte ions after HDX. Because the elution window of a protein species in CE typically ranges from 0.5 min to 2 min, assess the fragmentation efficiency based on MS2 scans accumulated over a comparable time window. The optimal values of these parameters are protein-specific; readers are referred to previously published reports for exemplary settings8,14. - Perform a pilot CE measurement using a CE instrument equipped with an optical detector, i.e., a photodiode array (PDA) detector or a UV detector to optimize the CE settings for the separation of the protein species and the migration times, which is equivalent to the HDX reaction times.
NOTE: This step is optional depending on the availability of the optical detector of CE. In the absence of an optical detector, the CE settings can be optimized using CE-MS upon completion of section 2.2, following the instructions described in section 2.3. The essential settings include parameters that affect separation efficiency, peak shapes shown in electropherograms, and elution times.
- Perform a pilot MS measurement using a standard electrospray ionization (ESI) source by spraying either the preloaded sample from a metal-coated borosilicate glass capillary (the "static" nanoESI scheme) or the continuously infused sample from a metal emitter to optimize the MS settings for measurement of intact proteins (MS1) and their gas-phase fragments (MS2). Fragment the protein species of interest by mass-selection of the ensemble of its ions in a single charge state, followed by ETD or ECD of the precursor ions.
- Pre-conditioning of the CE-HDX setup
- Clean the flow-through microvial CE-MS interface with a mixture of 50% methanol, 49% water, and 1% formic acid (v/v) using ultrasonication for at least 30 min at room temperature.
- Upon mounting of the HPC-modified capillary on a CE instrument, rinse the capillary with BGE using the autosampler for 10 min and leave the capillary filled with BGE.
- Obtain a proper length of unmodified fused silica capillary tubing (ID: 50 µm, OD: 360 µm) as the infusion tubing for the modifier solution. Connect the modifier tubing to a gas-tight glass syringe with a blunt tip using a union and proper sleeve, and rinse the tubing with the modifier solution using an infusion pump for at least 10 min.
- Insert the outlets of the HPC-coated CE capillary and modifier tubing, which have been loaded with corresponding solutions, into the cleaned CE-MS interface, as illustrated in Figure 2.
- Advance the syringe for the modifier infusion either manually or with the infusion pump to ensure that the modifier solution reaches the tip of the interface. Mount the assembled CE-MS interface on a nanoESI source housing of a mass spectrometer.
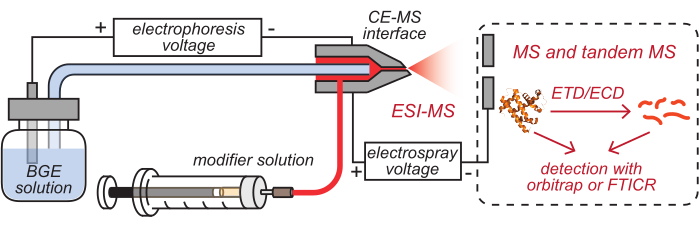
Figure 2: Schematic illustration of the CE-based HDX MS setup. This figure has been modified from8. Abbreviations: BGE = background electrolyte solution; CE = capillary electrophoresis; MS = mass spectrometry; HDX = hydrogen/deuterium exchange; ESI = electrospray ionization; FTICR = Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance; ETD = electron-transfer dissociation; ECD = electron-capture dissociation. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Simultaneous CE separation, HDX reaction, and MS analysis
NOTE: Deuterated BGE is recommended to be used within 1 day after unsealing.- Apply a spray voltage of 3-5 kV to the CE-MS interface.
- Start infusing the modifier solution with the infusion pump at a flow rate ranging from 0.1 to 10 µL/min, and ensure a stable electrospray at the tip of the CE-MS interface.
- Place the sample vial containing the BGE in the autosampler, and use it in step 2.3.4 to acquire blank electropherograms and blank mass spectra.
- Inject the sample solution using the autosampler at 2 psi and for a proper duration to allow the injection of a desired quantity of the sample. Estimate the injection volume using the relationship between injection volume and injection parameters15 defined by equation (1).
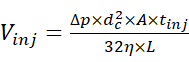 (1)
(1)
Where Vinj is the injection volume, Δp is the pressure of injection, dc is the inner diameter of the capillary, A is the cross-section of the capillary, tinj is the duration of injection, η is the viscosity of the liquid in the capillary, and L is the length of the capillary. - Start the CE separation by applying an electrophoretic voltage of 30 kV and infusion pressure ranging from 0 to 2 psi, and acquire the electropherogram. Meanwhile, start the acquisition of the MS data in the chromatographic mode where the ion current graph is acquired as a function of time, and the corresponding MS scans are not automatically combined into a single spectrum.
NOTE: Proteins undergo spontaneous HDX reaction at the point of contacting 2H2O molecules in BGE during their electrophoretic migration in this step. The optical detection for CE can be used in addition to the MS detection. As on-column detection requires the removal of a certain length of polyimide coating at the outlet end of the fused silica capillary, additional care should be taken to avoid capillary damage during the assembly of the CE-MS interface. - Save the blank electropherogram and mass spectra as references.
NOTE: Blank data are to be used for troubleshooting rather than baseline subtraction. - Place the sample vials containing the desired concentrations of the protein sample solutions in the autosampler. Acquire the electropherograms and mass spectra for the protein samples following steps 2.3.4-2.3.5. Collect an adequate number of MS scans to obtain MS1 spectra of the electrophoretically separated and 2H-labeled protein species.
- Perform tandem MS measurements for the species of interest either after acquiring the MS1 spectra within the same run or in a subsequent, separate run.
- When necessary, adjust the migration times/HDX reaction times by changing the infusion pressure or the length of the CE capillary. If the HDX reaction time must be shorter than the migration time, use the approach described previously8, which employs both deuterated and non-deuterated BGE in the capillary during the CE process.
- Flush the CE capillary with BGE at a pressure of 20 psi for at least 10 min after each measurement.
- Upon completion of the experiments, clean the CE-MS interface and all tubing for storage.
- Acquire a data set of the HDX "endpoint" sample (which can be prepared using approaches described previously6,16) with MS in direct infusion mode.
NOTE: This step is only required when a deuterated modifier solution is used for CE-based HDX.
3. Data analysis
- Analysis of CE data
- Use one of the following plots as the electropherogram to determine the electrophoretic characteristics, including the number of peaks, migration times, and separation efficiency: (a) UV absorbance vs. migration time, acquired by the optical detector of CE instrument (when available); (b) the total ion current (TIC) graph acquired by MS; (c) the extracted ion current (EIC/XIC) graph acquired by MS.
NOTE: EIC/XIC provides the optimal signal/noise ratio (S/N), in general, among the aforementioned formats of electropherograms. It is noteworthy that even in the absence of any instrumental biases, while UV absorbance is proportional to the mass concentration of protein, the MS signal is proportional to the molar concentration. Hence, it is reasonable to observe differences in peak patterns between CE- and MS-derived electropherograms. - Use the area under the curve (AUC) of the peaks shown in the electropherograms for semi-quantitation. For samples involving protein complexes, use the approach described previously17 to deduce the mass concentration data from the TIC/EIC electropherograms.
- Use one of the following plots as the electropherogram to determine the electrophoretic characteristics, including the number of peaks, migration times, and separation efficiency: (a) UV absorbance vs. migration time, acquired by the optical detector of CE instrument (when available); (b) the total ion current (TIC) graph acquired by MS; (c) the extracted ion current (EIC/XIC) graph acquired by MS.
- Analysis of MS data
- Obtain the MS1 and MS2 spectra by combining the MS1 and MS2 scans acquired within the corresponding elution windows, respectively.
- Determine the masses of the intact protein (M (intact protein)) and fragments by either of the following two methods.
- Calculate the average masses of the ions giving rise to the isotopically resolved signal clusters.
- Use the center of the Gaussian-like curves resulting from the fitting of the corresponding isotopic envelopes6.
- Use software such as Biopharma Finder, ProSight18, or MASH Suite19 to generate the mass list of the fragment ions and identify them.
- Analysis of HDX data
- Determine the overall deuteration level of an intact protein species using equation (2).
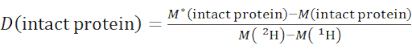 (2)
(2)
where M (2H) or M (1H) are atomic weights of 2H or 1H. The asterisk indicates data of the 2H-labeled sample. - Determine the cumulative protection or cumulative deuteration of backbone-amides of a specific segment.
- For data acquired with a deuterated modifier solution, use equations (3) and (4) to determine the cumulative protection level.
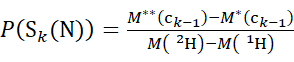 (3)
(3)
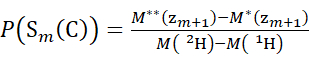 (4)
(4)
Where P(Sk(N)) is the total protection of the N-terminal segment spanning residues 1 through k, P(Sm(C)) is the total protection of the C-terminal segment comprising m residues, M (2H) or M (1H) are atomic weights of 2H or 1H, and M (ci) or M (zi) are the molecular weights of ci or zi ions.
NOTE: The double-asterisk indicates data of the HDX "endpoint" sample. - For data acquired with a non-deuterated modifier solution, use equations (5) and (6) to determine the cumulative deuteration level.
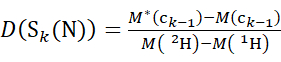 (5)
(5)
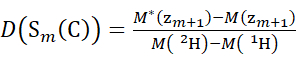 (6)
(6)
Where D(Sk(N)) is the cumulative deuterium uptake of the N-terminal segment spanning residues 1 through k; D(Sm(C)) is the cumulative deuterium uptake of the C-terminal segment comprising m residues.
- For data acquired with a deuterated modifier solution, use equations (3) and (4) to determine the cumulative protection level.
- Determine the deuteration level at a local backbone amide group
- For data acquired with a deuterated modifier solution, use equations (7), (8), (9), (10), and (11) to determine the local protection level.
for data deduced from c-ions
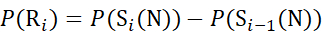 (7)
(7)
for data deduced from z-ions
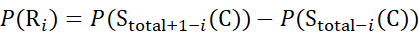 (8)
(8)
Where P(Ri) is the protection of a backbone amide at residue i, and the subscript "total" denotes the total residue number of the protein.
For residue sites where subsequent fragment ions were missing, assign P(Ri) using equations (9) and (10).
for data deduced from c-ions
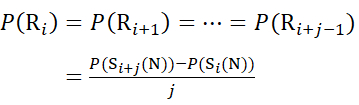 (9)
(9)
for data deduced from z-ions
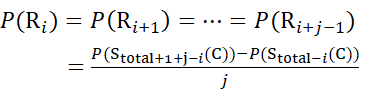 (10)
(10)
Then, determine the deuteration level D(Ri) at a local backbone amide group using equation (11).
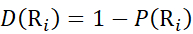 (11)
(11) - For data acquired with a non-deuterated modifier solution, use equations (12), (13), (14), and (15) to determine the local protection level.
for data deduced from c-ions
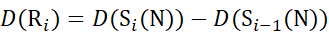 (12)
(12)
for data deduced from z-ions
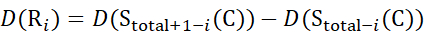 (13)
(13)
Where D(Ri) is the protection of a backbone amide at residue i, and the subscript "total" denotes the total residue number of the protein.
For residue sites where subsequent fragment ions were missing, assign D(Ri) using equations (14) and (15).
for data deduced from c-ions
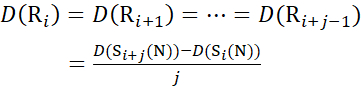 (14)
(14)
for data deduced from z-ions
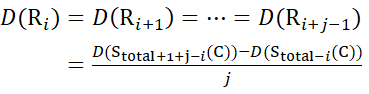 (15)
(15)
- For data acquired with a deuterated modifier solution, use equations (7), (8), (9), (10), and (11) to determine the local protection level.
- Determine the overall deuteration level of an intact protein species using equation (2).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Changing the infusion pressure of BGE allows the adjustment of both separation efficiency and migration time, which is equivalent to the HDX reaction time of the proteins to be separated (Figure 3). A lower infusion pressure results in better separation of CE peaks at the cost of the duration of the experiment (Figure 3A). A longer migration/HDX reaction time results in a higher level of deuteration of the protein analytes (Figure 3B
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
The objectives of coating the inner wall of the CE capillary include the minimization of the electroosmotic flow and protein absorption during the CE process13. Although electroosmotic flow is beneficial for conventional CE analysis of small molecules owing to its capability of driving neutral or oppositely charged species to the detector, it compromises the separation efficiency of protein species with similar sizes and net charges in solution. Coating the capillary with HPC minimizes the electro...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
D. D. Y. Chen is one of the founders of the Knowledge for Health Institute for Biomolecules, which is commercializing the flow-through microvial CE-MS interface. Other authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 21974069). The authors also received support from the Institute for Cell Analysis, Shenzhen Bay Laboratory, China; Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Biomedical Functional Materials; and Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Biomedical Materials at Nanjing Normal University, China.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| ammonium acetate | Fisher Chemical | A/3446/50 | ≥99% |
| CESI 8000 plus capillary electrophoresis system | Sciex, USA | ||
| centrifuge | Eppendorf | 5406000097 | |
| centrifugal filter | Merck | UFC201024 | 10 kDa cutoff |
| deuterium oxide | Energy Chemical | E090001 | 99.9 % D |
| formic acid | Acros Organics | 270480250 | |
| fused silica glass capillary | Polymicro Technologies | 1068150017 | ID 50μm, OD 360μm |
| gas chromatography | Agilent | GC6890N | |
| hydrochloric acid | Sigma Aldrich | 258148 | |
| hydroxypropyl cellulose | Aladdin | H113415 | MW 100000 |
| magnetic stirrers | DLAB | 8030101212 | |
| methanol | Fisher Chemical | A456-4 | MS grade |
| microvolume UV-Vis spectrophotometer | DeNovix | 84677JK7731 | |
| myoglobin | Sigma Aldrich | M1882 | |
| Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometer | Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA | ||
| PA 800 Plus Pharmaceutical Analysis CE System | Beckman Coulter, USA | ||
| Q Exactive UHMR mass Spectrometer | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germany | ||
| sodium hydroxide | Sigma Aldrich | S5881 | |
| ubiquitin | Sigma Aldrich | U6253 | |
| ultrasonicator | SCIENTZ | SB-5200 | |
| β-lactoglobulin | Sigma Aldrich | L0130 |
References
- Kaltashov, I. A., Bobst, C. E., Pawlowski, J., Wang, G. Mass spectrometry-based methods in characterization of the higher order structure of protein therapeutics. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 184, 113169(2020).
- Engen, J. R., Botzanowski, T., Peterle, D., Georgescauld, F., Wales, T. E. Developments in hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry. 93 (1), 567-582 (2021).
- Pan, J., Han, J., Borchers, C. H., Konermann, L. Conformer-specific hydrogen exchange analysis of Abeta(1-42) oligomers by top-down electron capture dissociation mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry. 83 (13), 5386-5393 (2011).
- Pan, J., Han, J., Borchers, C. H., Konermann, L. Structure and dynamics of small soluble Abeta(1-40) oligomers studied by top-down hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry. Biochemistry. 51 (17), 3694-3703 (2012).
- Pan, J., Borchers, C. H. Top-down structural analysis of posttranslationally modified proteins by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance-MS with hydrogen/deuterium exchange and electron capture dissociation. Proteomics. 13 (6), 974-981 (2013).
- Wang, G., Abzalimov, R. R., Bobst, C. E., Kaltashov, I. A. Conformer-specific characterization of nonnative protein states using hydrogen exchange and top-down mass spectrometry. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United. States of America. 110 (50), 20087-20092 (2013).
- Mironov, G. G., Clouthier, C. M., Akbar, A., Keillor, J. W., Berezovski, M. V. Simultaneous analysis of enzyme structure and activity by kinetic capillary electrophoresis-MS. Nature Chemical Biology. 12 (11), 918-922 (2016).
- Shen, Y., Zhao, X., Wang, G., Chen, D. D. Y. Differential hydrogen/deuterium exchange during proteoform separation enables characterization of conformational differences between coexisting protein states. Analytical Chemistry. 91 (6), 3805-3809 (2019).
- Kontopidis, G., Holt, C., Sawyer, L. Invited review: β-lactoglobulin: binding properties, structure, and function. Journal of Dairy Science. 87 (4), 785-796 (2004).
- Qin, B. Y., et al. Structural basis of the Tanford transition of bovine β-lactoglobulin. Biochemistry. 37 (40), 14014-14023 (1998).
- Qin, B. Y., Bewley, M. C., Creamer, L. K., Baker, E. N., Jameson, G. B. Functional implications of structural differences between variants A and B of bovine beta-lactoglobulin. Protein Science. 8 (1), 75-83 (1999).
- Wang, L., et al. High resolution capillary isoelectric focusing mass spectrometry analysis of peptides, proteins, and monoclonal antibodies with a flow-through microvial interface. Analytical Chemistry. 90 (15), 9495-9503 (2018).
- Busch, M. H. A., Kraak, J. C., Poppe, H. Cellulose acetate-coated fused-silica capillaries for the separation of proteins by capillary zone electrophoresis. Journal of Chromatography A. 1695 (2), 287-296 (1995).
- Zhao, X., Shen, Y., Tong, W., Wang, G., Chen, D. D. Y. Deducing disulfide patterns of cysteine-rich proteins using signature fragments produced by top-down mass spectrometry. Analyst. 143 (4), 817-823 (2018).
- Sutera, S. P., Skalak, R. The history of Poiseuille's law. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics. 25 (1), 1-20 (1993).
- Wang, G., Kaltashov, I. A. Approach to characterization of the higher order structure of disulfide-containing proteins using hydrogen/deuterium exchange and top-down mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry. 86 (15), 7293-7298 (2014).
- Wang, G., Johnson, A. J., Kaltashov, I. A. Evaluation of electrospray ionization mass spectrometry as a tool for characterization of small soluble protein aggregates. Analytical Chemistry. 84 (3), 1718-1724 (2012).
- Fellers, R. T., et al. ProSight Lite: graphical software to analyze top-down mass spectrometry data. Proteomics. 15 (7), 1235-1238 (2015).
- Cai, W., et al. MASH Suite Pro: A comprehensive software tool for top-down proteomics. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 15 (2), 703-714 (2016).
- Paterson, G. R., Hill, J. P., Otter, D. E. Separation of β-lactoglobulin A, B and C variants of bovine whey using capillary zone electrophoresis. Journal of Chromatography A. 700 (1), 105-110 (1995).
- Wang, G., Kaltashov, I. A. Approach to characterization of the higher order structure of disulfide-containing proteins using hydrogen/deuterium exchange and top-down mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry. 86 (15), 7293-7298 (2014).
- Nicolardi, S., et al. On-line electrochemical reduction of disulfide bonds: improved FTICR-CID and -ETD coverage of oxytocin and hepcidin. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry. 24 (12), 1980-1987 (2013).
- Adhikari, S., Xia, Y., McLuckey, S. A. Top-down analysis of disulfide-linked proteins using photoinduced radical reactions and ET-DDC. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 444, 116173(2019).
- Rush, M. J. P., Riley, N. M., Westphall, M. S., Coon, J. J. Top-down characterization of proteins with intact disulfide bonds using activated-ion electron transfer dissociation. Analytical Chemistry. 90 (15), 8946-8953 (2018).
- Zhong, X., Maxwell, E. J., Chen, D. D. Y. Mass transport in a micro flow-through vial of a junction-at-the-tip capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry interface. Analytical Chemistry. 83 (12), 4916-4923 (2011).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved