A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Registration of Calcium Transients in Mouse Neuromuscular Junction with High Temporal Resolution using Confocal Microscopy
In This Article
Summary
The protocol describes the method of loading a fluorescent calcium dye through the cut nerve into mouse motor nerve terminals. In addition, a unique method for recording fast calcium transients in the peripheral nerve endings using confocal microscopy is presented.
Abstract
Estimation of the presynaptic calcium level is a key task in studying synaptic transmission since calcium entry into the presynaptic cell triggers a cascade of events leading to neurotransmitter release. Moreover, changes in presynaptic calcium levels mediate the activity of many intracellular proteins and play an important role in synaptic plasticity. Studying calcium signaling is also important for finding ways to treat neurodegenerative diseases. The neuromuscular junction is a suitable model for studying synaptic plasticity, as it has only one type of neurotransmitter. This article describes the method for loading a calcium-sensitive dye through the cut nerve bundle into the mice's motor nerve endings. This method allows the estimation of all parameters related to intracellular calcium changes, such as basal calcium level and calcium transient. Since the influx of calcium from the cell exterior into the nerve terminals and its binding/unbinding to the calcium-sensitive dye occur within the range of a few milliseconds, a speedy imaging system is required to record these events. Indeed, high-speed cameras are commonly used for the registration of fast calcium changes, but they have low image resolution parameters. The protocol presented here for recording calcium transient allows extremely good spatial-temporal resolution provided by confocal microscopy.
Introduction
The problem of measuring fast calcium waves in excitable cells is one of the most important and challenging aspects of studying signal transmission in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Calcium ions play an important role in triggering neurotransmitter release, synaptic plasticity, and modulation of the activity of various intracellular proteins1,2,3,4,5. Studying calcium signaling is also important for finding ways to treat neurodegenerative diseases6. To measure changes in the calcium levels, fluorescent calcium-sensitive dyes are commonly used, and changes in their fluorescence level are analyzed7,8,9.
Loading of calcium dyes into cells can be achieved in different ways. Predominantly, cell-permeant dyes are used10,11. However, in such a case, it is not only difficult to control the concentration of a dye inside the cell, but it is also hard to select target cells for loading. This method is not applicable for studying peripheral nerve endings since the dye enters postsynaptic cells. Instead, cell impermeant dyes are more suitable for such preparations. In this case, the dyes are delivered to the cells by microinjection or through a patch pipette12,13,14. There is also a method of loading through a nerve stump. The latter method is most suitable for neuromuscular junction preparations15,16,17,18,19,20. It allows performing staining for only cells of interest. Although this method does not provide an accurate evaluation of the concentration of the dye in the target cell, the concentration can be estimated approximately by comparing the level of fluorescence of the cells at rest in solutions with a known concentration of calcium21. In this study, a modification of this method applied to synapses of mammals is presented.
Calcium entry during the depolarizing phase of the action potential is a fast process, especially in the neuromuscular junction; therefore, for its registration, appropriate equipment is required1. A recent study using a voltage-sensitive fluorescent dye demonstrated that the duration of the action potential in the peripheral synapse of a mouse is approximately 300 µs22. Calcium transient, evaluated using calcium-sensitive dyes in the peripheral synapses of the frog, has a longer duration: the rise time is about 2-6 ms and the decay time is about 30-90 ms, depending on the calcium dye used23,24. To measure fast processes with the help of fluorescent dyes, CCD or CMOS cameras are generally used, with fast and sensitive CCD matrices. However, these cameras have the disadvantage of low resolution, limited by the size of the sensitive elements of the matrix25,26,27,28. The fastest cameras with sufficient sensitivity to record both action potentials and calcium transients in response to low frequency stimulation of cells have a scanning frequency of 2,000 Hz, and a matrix with a dimension of 80 x 8029. To obtain signals with a higher spatial resolution, confocal microscopy is used, especially if it is necessary to assess some volumetric changes in the signal30,31,32. But it should be kept in mind that confocal microscopy has a high scanning speed in line scan mode, but there are still significant limitations on the speed of recordings of fast processes when building a spatial image33. There are confocal microscopes based on rotating Nipkow disks (slit-scanning microscopy) and Multipoint-Array Scanners, which have a higher scanning speed. At the same time, they are inferior to the classical confocal microscopes in confocal image filtering (pinholes crosstalk for microscopes with a Nipkow disk)32,34,35. Confocal imaging with resonance scanning can also provide a high spatio-temporal resolution required for high temporal measurements36. However, take into account that the registration of weak fluorescent responses at a high scanning speed when using resonance scanners requires highly sensitive detectors such as hybrid detectors36.
This article presents a method for increasing the temporal resolution of signals recorded with the Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (LSCM) while maintaining the spatial resolution37. The current method is a further development of the methods described earlier and transferred to the LSCM platform38,39,40. This approach does not require changes in the microscope hardware and is based on the application of an algorithm for recording periodically evoked fluorescent signals with a time shift relative to the moment of stimulation.
Protocol
Experiments were performed on isolated nerve-muscle preparations of levator auris longus (m. LAL) from the Mice BALB/C (20-23 g, 2-3 months old)41. The experimental procedures were performed in accordance with the guidelines for the use of laboratory animals of the Kazan Federal University and the Kazan Medical University, in compliance with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The experimental protocol met the requirements of the European Communities Council Directive 86/609/EEC and was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Kazan Medical University.
1. Preparation of the Ringer's and Filing solutions
- Prepare the Ringer's solution for mammalian muscle by mixing the following ingredients: NaCl (137 mM), KCl (5 mM), CaCl2 (2 mM), MgCl2 (1 mM), NaH2PO4 (1 mM), NaHCO3 (11.9 mM), and glucose (11 mM). Bubble through the solution with 95% O2 and 5% CO2 and adjust its pH to 7.2-7.4 by adding HCl/NaOH if necessary.
- Prepare the dye loading solution.
- Prepare HEPES (10 mM) solution with pH in the 7.2-7.4 range. 500 µg of commercial dye comes in a 500 µL vial. Dissolve the dye in 14 µL of the HEPES solution to obtain a dye concentration of 30 mM. Shake well and centrifuge until totally dissolved.
- Dilute the solution of Ca2+ indicator with HEPES solution down to 1 mM concentration. Keep it in a freezer (-20 °C) and avoid exposure to light.
2. Dye loading procedure
NOTE: The dye loading procedure is performed according to the protocol for loading through the nerve stump, adapted from the protocols previously published19,42,43,44,45,46.
- Dissect LAL muscle according to the dissection procedure for this preparation as described in the previously published protocols47,48.
- Fix the tissue slightly stretched (no more than 30% from initial length) in the elastomer-coated Petri dish with fine stainless-steel pins and add Ringer's solution until the muscle is fully covered.
NOTE: The Petri dish was pre-filled with elastomer according to the manufacturer's instructions (see Table of Materials).
- Fix the tissue slightly stretched (no more than 30% from initial length) in the elastomer-coated Petri dish with fine stainless-steel pins and add Ringer's solution until the muscle is fully covered.
- Prepare the Filling Pipette
- Using a micropipette puller (see Table of Materials), prepare a micropipette with a fine tip which is as sharp as possible for the intracellular recordings. Use capillaries without internal filaments (1.5 mm in outer diameter and 0.86 or 1.10 mm in inner diameter).
- Break off the micropipette tip after scoringthe taper with an abrasive, leaving the tip open to about 100 µm in diameter. Fire-polish the tip down to limit when the internal diameter shrinks from >80 µm to 12-13 µm. Attach a silicone tube to one side of the Filling Pipette and a syringe (without a needle) to the other side.
- Under a stereomicroscope, find the place where the nerve trunk turns into separate nerve branches. Place the Filling Pipette with the mounted tube and the syringe on the Petri dish using wax. Move the pipette tip until it stands above the nerve.
- With fine scissors, cut the nerve close to the muscle fiber, leaving a small piece of the nerve stump about 1 mm long. Gently aspirate the nerve stump together with some Ringer's solution, without pinching it, into the tip of the Filling Pipette. Remove the silicone tube from the Filling Pipette.
- Draw some amount of the dye loading solution (~0.3 µL) using a syringe with a long filament. This volume corresponds to approximately 3 cm of the filament.
NOTE: Initially, it is necessary to make a filament from a pipette tip with a volume of 10 µL by pulling on the fire using an alcohol lamp or a gas burner. - Gently insert the filament tip with loading solution into the Filling Pipette. Release the mixture directly onto the nerve stump. Incubate the preparation at room temperature in dark for 30 min.
- After that, rinse the preparation with fresh Ringer's solution and incubate at 25 °C for up to 2 h in a glass beaker with 50 mL (or more) Ringer's solution (preparation must be covered with the solution). During this time, the dye will reach the synapses.
3. Video capture with confocal microscopy
NOTE: Registration of calcium transients is performed with a laser scanning confocal microscope (LSCM) (see Table of Materials). To register fast calcium transients, an original protocol that permitted recordings of signals with a sufficient spatial and temporal resolution was used. The method has been described thoroughly in the publication by Arkhipov et al37. The microscope was equipped with a 20x water immersion objective (1.00 NA). The 488 nm laser line was attenuated to 10% intensity and emission fluorescence was collected from 503 to 558 nm.
- Mount the preparation into the silicon elastomer-coated experimental chamber and fix it, slightly stretched, with a set of steel micro-needles. Rinse the preparation extensively with Ringer's solution.
NOTE: A simple custom-made perfusion experimental chamber made of organic glass with the bottom of the chamber covered with an elastomer (prepared in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions; see Table of Materials) was used. The chamber has a solution supply tube. The solution is pumped out via a syringe needle, mounted on a magnetic holder (see Table of Materials). As an experimental chamber, a Petri dish could be used (like the one used for incubation of the preparation) but with attached supply and suction tubes. - Install suction electrode which will be used to stimulate the nerve.
NOTE: Construction of the electrode is similar to what was published in the 2015 paper by Kazakov et al49. Place and fix the electrode by waxing beside the bath. Move the tip close to the nerve stump and aspirate it into the electrode. - Mount the preparation chamber onto the microscope stage and place the inlet and outlet fittings into the chamber.
- To perfuse the preparation, use a simple gravity-flow-driven system. Turn on the perfusion suction pump to remove the excess solution.
- Plug the stimulating suction electrode into an electric stimulator and ensure that muscular contractions occur after stimuli. See section 3.9-3.12 for stimulation conditions and recording.
- Fill up the perfusion system with the Ringer's solution with d-tubocurarine (10 µM).
NOTE: This solution helps to prevent muscular contractions. D-tubocurarine or alpha-bungarotoxin-specific blockers of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the postsynaptic membrane would completely or partially block muscle contractions50. Also, for preventing muscular contractions, specific blockers of postsynaptic sodium channels such as µ-conotoxin GIIIB could be used51. - Switch on the perfusion suction pump and start perfusion of the preparation with the Ringer's solution containing d-tubocurarine.
- Set imaging parameters in the LSCM software as follows.
- In the LSCM software (LAS AF; see Table of Materials), choose Electrophysiology.
NOTE: In this mode, when an image is captured at the time point, a synchronizing pulse is sent to the stimulator with the help of the trigger box. This elicits action potential generation in the preparation (Figure 1; stimulator unit). - Select Acquisition Mode. For triggering the stimulator using the microscope sync pulse, in the Job menu settings, select the Trigger settings. Set the Trigger Out On Frame field to the out1 channel.
- Use the following settings: Scanning Mode: XYT, Frequency of Scanning: 1400 Hz, Zoom Factor: 6.1, Pinhole: fully open. Ensure that sequential trans-passing Bidirectional X mode is on.
- Set minimum time to form a frame at 52 ms and frames to be collected in a raw video at 20 frames.
NOTE: These settings permit image capturing with a resolution of 128 x 128 pixels while taking a single frame every 52 ms. - Set excitation wavelength of the argon laser at 488 nm with 8% of output power.
- In the LSCM software (LAS AF; see Table of Materials), choose Electrophysiology.

Figure 1: The schematic of the experimental setup. 1. Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope (LSCM). 2. Synchronization module of LSCM (trigger box). 3. Stimulator. 4. Isolation unit. 5. The biological sample. 6. Suction electrode for electrical stimulation of nerve. 7. Perfusion systems (7a: perfusate reservoir, 7b: dropper, 7c: flow regulator, 7d: vacuum flask). Arrows point to the direction of propagation of synchronizing pulse. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Press the Live Mode button to switch to Live mode, which helps to get a preview of nerve terminals loaded with the dye.

Figure 2: Mouse nerve and terminals loaded with the Ca2+ indicator. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Stimulation unit
NOTE: In this work, the stimulator described in the article by Land et al.52 was used. This device allows for setting temporal parameters of stimulation via the MatLab software.- Create a new file, paste the code from the above-mentioned article to the MatLab code window, and save the file. Click on Run, so a window with stimulation parameters appears. Set the delay time and duration of the stimulus.
NOTE: The delay determines the temporal resolution of the reconstituted fluorescent signal. The electric pulse of 0.2 ms duration is delayed, and then sent to the isolation unit. The latter forms the amplitude and polarity of the stimulating pulse and electrically isolates the biological object from the recording equipment. - To stimulate the nerve, select supramaximal amplitude of the stimulating impulse (25%-50% greater than the maximum stimulation intensity necessary to activate all the nerve fibers).
NOTE: The presented method is based on a special algorithm for recordings of single fast fluorescent signals using LSCM with the minimized sweep. At each step of the developed algorithm, the recorded fluorescent signal is shifted from the previous one by a time interval that is shorter than the microscope sweep. The value of time shifts determines the temporal resolution of the required signal. The number of steps (shifts) in the algorithm depends on the required temporal resolution and original temporal resolution. With this method of registration, the stimulation of the preparation is carried out with a frequency of 0.25 Hz.
- Create a new file, paste the code from the above-mentioned article to the MatLab code window, and save the file. Click on Run, so a window with stimulation parameters appears. Set the delay time and duration of the stimulus.
- In the Live mode, search for the ROI and obtain the best focus. Run the data acquisition software.
- Shift the delay on the stimulator by 2 ms less relative to the previous value and run the data acquisition software.
- Repeat step 3.11 26 times to acquire 26 sequences, with each sequence shifted by 2 ms from the previous one.
4. Video processing
NOTE: A series of video images acquired by the confocal microscope is exported in the TIFF format with the free software LAS X (see Table of Materials). This series was divided into frames and exported to a folder. For generating the image sequence with higher time resolution, the ImageJ software, which has an open initial code for the analysis and processing of the data, was used. The algorithm of signals processing is represented schematically in Figure 3.
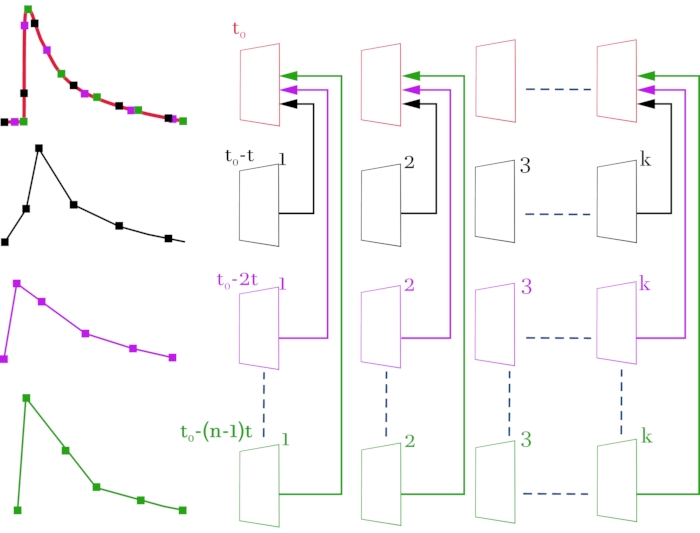
Figure 3: Scheme for compiling a high-resolution video file (2 ms on frame) from original video files with a low temporal resolution (52 ms on frame). The original video files and the corresponding signals are colored in black, magenta, and green. The compiled video file and the resulting signal are colored red. The scheme on the right, line by line, shows the video images obtained with a confocal microscope. On the left, the corresponding signals of fluorescence change from the selected ROI. The topmost line is formed frame by frame from the received frames according to the scheme. The result is a video image consisting of the entire array of frames so that there is a delay time of 2 ms between frames instead of 52 ms. Each line corresponds to an offset of the stimulation signal by (n - 1) * t, where t is time shift (2 ms), and n is the number of shift iterations. k denotes the number of frames in the original video files (lines 2-4) and depends on the duration of the recorded signal. In this case, to register a signal with a duration of 1 s, it is necessary to select k = 20 (52 ms * 20 = 1040 ms). t0 is the required delay before stimulation. To calculate the number of shift iterations n, the initial temporal resolution between frames (52 ms) must be divided by the required temporal resolution (2 ms). In this case, n = 26, which corresponds to 26 registered sweeps. As a result of the performed manipulations, a video image consisting of n * k = 520 frames is obtained. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Run LAS X software. Open the project which was created during performing experiment. Click on Export, and then on Save As to save frames in .tiff format in the destination folder.
- Run the ImageJ software. Click on File > Import > Image Sequence.
- In the Open Image Sequence window, choose the destination folder and open the first frame.
- In the Sequence Options window, in the Starting Image field, set the frame number to 1 for the first frame. In the Increment field, set the value equal to the number of frames in the initial signal recording (20 for the present case) and click on OK.
- To save the generated file of stitched first frames in a separate folder, click on File > Save > Folder.
- Repeat steps 4.3-4.5 for the next 19 frames. In the Sequence Options window, set the corresponding frame number in the Starting Image field.
- To generate the full high-time-resolution video, stitch all the frames together. To do this, click on File > Import > Image Sequence and select 1 in the Starting Image and Increment fields. The result will be the final video with increased temporal resolution. Save the file in .tiff or any other suitable format.
5. Video analysis
NOTE: In ImageJ, select ROI and background. Subtract background from ROI. Data is represented as the ratio, (ΔF / F0 - 1) * 100%, where F0 is the intensity of fluorescence at rest and ΔF is the intensity of fluorescence during stimulation.
- Click on Image > Stacks > Tools > Stack Sorter. Then, click on Analysis > Tools > ROI Manager.
- Drag and drop the .tiff file saved in step 4.7 into the ImageJ window. Expand the image for a better view. To improve image visualization, click on Image > Adjust > Brightness/Contrast > Auto. This step will not affect the data.
- Set the background close to the nerve terminal by drawing ROI. Add it to the ROI manager. Calculate the background by clicking on More > Multi Measure. Copy mean values, paste to the Spreadsheet program, and calculate the average.
- Subtract the calculated average value from the stacks by clicking on Process > Main > Subtract. Enter the value.
- Draw ROI around a nerve terminal via a polygon line. Add it to the ROI manager.
- Measure the intensity of the nerve terminal: Click on More > Multi Measure. Copy mean values and paste them to the Spreadsheet program.
- Calculate the average offset of signals.
NOTE: Use the corresponding points depending on the delay time before stimulation. This step establishes the F0 value that will be used in subsequent calculations. - Divide the signal values by the average offset value.
NOTE: After this step, the signal does not contain the contribution of the background and raw fluorescence to the amplitude values for the selected ROI. - Subtract 1 from values obtained in step 5.8, and then multiply by 100%.
- Plot a graph of Ca2+- transient and calculate the amplitude.
Results
After loading the preparation with dye according to the presented technique, most of the synapses located close to the nerve stump had a sufficient level of fluorescence (see Figure 2). After loading preparation with the dye andapplying the described method of registration and image processing, calcium transients with the desired spatial and temporal resolution were obtained (see Figure 4). The calcium transient has been recovered by the proposed method (see
Discussion
The method for loading Ca2+-sensitive dye into mouse nerve endings through the nerve stump and for registering a fast calcium transient using a confocal microscope is presented in this article. As a result of the implementation of this loading method, most of the synapses located close to the nerve stump had a sufficient level of fluorescence to enable registration of the entry of calcium into the nerve endings in response to low-frequency stimulation of the motor nerve.
Unlike the ...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Fluorescence studies of this work were carried out with the financial support of the Russian Science Foundation Grant (project No. 19-15-00329). The method was developed under financing from the government assignment for FRC Kazan Scientific Center of RAS АААА-А18-118022790083-9. The research was developed with the use of the equipment of the Federal Research Center "Kazan Scientific Center of RAS". The authors would like to thank Dr. Victor I. Ilyin for critical reading of this manuscript.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Capillary Glass | Clark Electromedical instruments, UK | GC150-10 | |
| Confocal and multiphoton microscope system Leica TCS SP5 MP | Leica Microsystems , Heidelberg, Germany | ||
| Flaming/Brown Micropipette Puller P 97 | Sutter Instrument, USA | P-97 | |
| Flow regulator | KD Medical GmbH Hospital Products, Germany | KD REG | Disposable infusion set with Flow regulator |
| HEPES | Sigma-Aldrich, USA | H0887 | 100mL |
| Illumination system Leica CLS 150X | Leica Microsystems, Germany | ||
| ImageJ | National Institutes of Health, USA | http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/download.html | |
| Las AF software | Leica Microsystems, Heidelberg, Germany | ||
| Las X software | Leica Microsystems, Heidelberg, Germany | https://www.leica-microsystems.com/products/microscope-software/p/leica-las-x-ls/ | |
| Magnetic Holder with Suction Tubing | BIOSCIENCE TOOLS, USA | MTH-S | |
| Microspin FV 2400 | Biosan, Latvia | BS-010201-AAA | |
| Minutien Pins | Fine science tools, Canada | 26002-20 | |
| Multi-spin MSC 3000 | Biosan, Latvia | BS-010205-AAN | |
| Oregon Green 488 BAPTA-1 pentapotassium salt | Molecular Probes, USA | O6806 | 500 μg |
| Pipette | Biohit, Russia | 720210 | 0.5-10 µL |
| Pipette tip | Biohit, Russia | 781349 | 10 µL |
| Plasticine | local producer | ||
| Single-use hypodermic needles | Bbraun | 100 Sterican | 0.4×40 mm |
| Spreadsheet program | Microsoft, USA | Microsoft Office Excel | |
| Stereomicroscope, Leica M80 | Leica Microsystems , Germany | ||
| Suction electrode | Kazakov A. SIMPLE SUCTION ELECTRODE FOR ELECTRIC STIMULATION OF BIOLOGICAL OBJECTS / A. Kazakov, M. Alexandrov, N. V. Zhilyakov et al. // International research journal. - 2015. - No. 9 (40) Part 3. - P. 13-16. | http://research-journal.org/biology/prostoj-vsasyvayushhij-elektrod-dlya-elektricheskoj-stimulyacii-biologicheskix-obektov/ | |
| Sylgard 184 elastomer | Dow Corning, USA | ||
| Syringe | local producer | 0.5 mL | |
| Syringe | local producer | 60 mL |
References
- Llinas, R., Steinberg, I. Z., Walton, K. Presynaptic calcium currents and their relation to synaptic transmission: voltage clamp study in squid giant synapse and theoretical model for the calcium gate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 73 (8), 2918-2922 (1976).
- Augustine, G. J. How does calcium trigger neurotransmitter release. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 11 (3), 320-326 (2001).
- Burnashev, N., Rozov, A. Presynaptic Ca2+ dynamics, Ca2+ buffers and synaptic efficacy. Cell Calcium. 37 (5), 489-495 (2005).
- Schneggenburger, R., Neher, E. Presynaptic calcium and control of vesicle fusion. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 15 (3), 266-274 (2005).
- Pang, Z. P., Südhof, T. C. Cell biology of Ca2+-triggered exocytosis. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 22 (4), 496-505 (2010).
- Leal, S. S., Gomes, C. M. Calcium dysregulation links ALS defective proteins and motor neuron selective vulnerability. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 9, 225 (2015).
- Grynkiewicz, G., Poenie, M., Tsien, R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 260 (6), 3440-3450 (1985).
- Tsien, R. Y. Fluorescent indicators of ion concentrations. Methods in Cell Biology. 30, 127-156 (1989).
- Adams, S. R. How calcium indicators work. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2010 (3), (2010).
- Macleod, G. T. Topical application of indicators for calcium imaging at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2012 (7), 786-790 (2012).
- Regehr, W. G. Monitoring presynaptic calcium dynamics with membrane-permeant indicators. Imaging in Neuroscience and Development: A Laboratory Manual. , 307-314 (2005).
- Eilers, J., Konnerth, A. Dye loading with patch pipettes. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2009 (4), 5201 (2009).
- Coleman, W. L., et al. Synapsin II and calcium regulate vesicle docking and the cross-talk between vesicle pools at the mouse motor terminals. Journal of Physiology. 586 (19), 4649-4673 (2008).
- Macleod, G. T. Direct injection of indicators for calcium imaging at the drosophila larval neuromuscular junction. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2012 (7), 797-801 (2012).
- Peng, Y. Y., Zucker, R. S. Release of LHRH is linearly related to the time integral of presynaptic Ca+ elevation above a threshold level in bullfrog sympathetic ganglia. Neuron. 10 (3), 465-473 (1993).
- Tsang, C. W., Elrick, D. B., Charlton, M. P. α-Latrotoxin releases calcium in frog motor nerve terminals. The Journal of Neuroscience. 20 (23), 8685-8692 (2000).
- Newman, Z., et al. Endocannabinoids mediate muscarine-induced synaptic depression at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction. The European Journal of Neuroscience. 25 (6), 1619-1630 (2007).
- Macleod, G. T. Forward-filling of dextran-conjugated indicators for calcium imaging at the drosophila larval neuromuscular junction. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2012 (7), 791-796 (2012).
- Rossano, A. J., Macleod, G. T. Loading drosophila nerve terminals with calcium indicators. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (6), e250 (2007).
- Wu, L. G., Betz, W. J. Nerve activity but not intracellular calcium determines the time course of endocytosis at the frog neuromuscular junction. Neuron. 17 (4), 769-779 (1996).
- Suzuki, S., et al. Ca2+ dynamics at the frog motor nerve terminal. Pflugers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology. 440 (3), 351-365 (2000).
- Ojala, K. S., et al. A high-affinity, partial antagonist effect of 3,4-diaminopyridine mediates action potential broadening and enhancement of transmitter release at NMJs. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 296, 100302 (2021).
- Samigullin, D., et al. Estimation of presynaptic calcium currents and endogenous calcium buffers at the frog neuromuscular junction with two different calcium fluorescent dyes. Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience. 6, 29 (2015).
- DiGregorio, D. A., Vergara, J. L. Localized detection of action potential-induced presynaptic calcium transients at a Xenopus neuromuscular junction. The Journal of Physiology. 505, 585-592 (1997).
- Bullen, A., Patel, S. S., Saggau, P. High-speed, random-access fluorescence microscopy: I. High-resolution optical recording with voltage-sensitive dyes and ion indicators. Biophysical Journal. 73 (1), 477-491 (1997).
- Bullen, A., Saggau, P. High-speed, random-access fluorescence microscopy: II. Fast quantitative measurements with voltage-sensitive dyes. Biophysical Journal. 76 (4), 2272-2287 (1999).
- Bullen, A., Saggau, P. Optical recording from individual neurons in culture. Modern Techniques in Neuroscience Research. (4), 89-126 (1999).
- Bullen, A., Saggau, P. Indicators and optical configuration for simultaneous high-resolution recording of membrane potential and intracellular calcium using laser scanning microscopy. Pflugers Archiv European Journal of Physiology. 436 (5), 788-796 (1998).
- Wilson, T. Optical aspects of confocal microscopy. Confocal Microscopy. , 93-141 (1990).
- Cox, G. Biological confocal microscopy. Materials Today. 5 (3), 34-41 (2002).
- Mukhitov, A., Arkhipova, S., Nikolsky, E. Modern Light Microscopy in Biological and Medical Research. Nauka. , (2011).
- Mertz, J. Optical sectioning microscopy with planar or structured illumination. Nature Methods. 8 (10), 811-819 (2011).
- Webb, R. H. Confocal optical microscopy. Reports on Progress in Physics. 59 (3), 427-471 (1996).
- Toomre, D., Pawley, J. B. Disk-scanning confocal microscopy. Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy: Third Edition. , 221-238 (2006).
- Venkateswarlu, K., et al. Three-dimensional imaging and quantification of real-time cytosolic calcium oscillations in microglial cells cultured on electrospun matrices using laser scanning confocal microscopy. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 117 (10), 3108-3123 (2020).
- Arkhipov, A. Y., Khaziev, E. F., Skorinkin, A. I., Bukharaeva, E. A., Samigullin, D. V. Enhancement of the temporal resolution of fluorescent signals acquired by the confocal microscope. Microscopy and Microanalysis. 26 (2), 204-210 (2020).
- Rama, S. Shift and mean algorithm for functional imaging with high spatio-temporal resolution. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 9, (2015).
- Chan, K. G., Streichan, S. J., Trinh, L. A., Liebling, M. Simultaneous temporal superresolution and denoising for cardiac fluorescence microscopy. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging. 2 (3), 348-358 (2016).
- Veeraraghavan, A., Reddy, D., Raskar, R. Coded strobing photography: compressive sensing of high speed periodic videos. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 33 (4), 671-686 (2011).
- Angaut-Petit, D., Molgo, J., Connold, A. L., Faille, L. The levator auris longus muscle of the mouse: A convenient preparation for studies of short- and long-term presynaptic effects of drugs or toxins. Neuroscience Letters. 82 (1), 83-88 (1987).
- Macleod, G. T. Calcium imaging at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 7 (7), 758-766 (2012).
- Samigullin, D. V., Khaziev, E. F., Zhilyakov, N. V., Bukharaeva, E. A., Nikolsky, E. E. Loading a calcium dye into frog nerve endings through the nerve stump: calcium transient registration in the frog neuromuscular junction. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (125), e55122 (2017).
- Samigullin, D. V., et al. Calcium transient registration in response to single stimulation and during train of pulses in mouse neuromuscular junction. BioNanoScience. 7 (1), 162-166 (2017).
- Luo, F., Dittrich, M., Stiles, J. R., Meriney, S. D. single-pixel optical fluctuation analysis of calcium channel function in active zones of motor nerve terminals. Journal of Neuroscience. 31 (31), 11268-11281 (2011).
- Luo, F., Dittrich, M., Cho, S., Stiles, J. R., Meriney, S. D. Transmitter release is evoked with low probability predominately by calcium flux through single channel openings at the frog neuromuscular junction. Journal of Neurophysiology. 113 (7), 2480-2489 (2015).
- Wright, M., Kim, A., Son, Y. -. J. Subcutaneous administration of muscarinic antagonists and triple-immunostaining of the levator auris longus muscle in mice. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (55), e3124 (2011).
- Burke, S. R. A., Reed, E. J., Romer, S. H., Voss, A. A. Levator Auris Longus preparation for examination of mammalian neuromuscular transmission under voltage clamp conditions. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (135), e57482 (2018).
- Kazakov, A., Alexandrov, M., Zhilyakov, N. V., Khaziev, E. F., Samigullin, D. V. A simple suction electrode for electrical stimulation of biological objects. Meždunarodnyj naučno-issledovatel'skij žurnal (International Research Journal). 9 (40), 13-16 (2015).
- Bowman, W. C. Neuromuscular block. British Journal of Pharmacology. 147, 277-286 (2006).
- Hill, J. M., Alewood, P. F., Craik, D. J. Three-dimensional solution structure of µ-conotoxin GIIIB, a specific blocker of skeletal muscle sodium channels. Biochemistry. 35 (27), 8824-8835 (1996).
- Land, B. R., Johnson, B. R., Wyttenbach, R. A., Hoy, R. R. Tools for physiology labs: Inexpensive equipment for physiological stimulation. Journal of Undergraduate Neuroscience Education. 3 (1), 30-35 (2004).
- Samigullin, D. V., Zhilyakov, N. V., Khaziev, E. F., Bukharaeva, E. A., Nikolsky, E. E. Calcium transient and quantal release in mouse neuromuscular junction under extracellular calcium concentration change. BioNanoScience. 8 (4), 984-987 (2018).
- Khaziev, E., et al. acetylcholine-induced inhibition of presynaptic calcium signals and transmitter release in the frog neuromuscular junction. Frontiers in Physiology. 7, 621 (2016).
- Zhilyakov, N., Arkhipov, A., Malomouzh, A., Samigullin, D. Activation of neuronal nicotinic receptors inhibits acetylcholine release in the neuromuscular junction by increasing ca2+ flux through cav1 channels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 22 (16), 9031 (2021).
- Sabatini, B. L., Regehr, W. G. Optical measurement of presynaptic calcium currents. Biophysical Journal. 74 (3), 1549-1563 (1998).
- McArdle, J. J., et al. Advantages of the triangularis sterni muscle of the mouse for investigations of synaptic phenomena. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 4 (2), 109-115 (1981).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved