A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Assessment of Thermal Damage from Robot-Drilled Craniotomy for Cranial Window Surgery in Mice
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
Cranial windows have become a ubiquitously implemented surgical technique to allow for intravital imaging in transgenic mice. This protocol describes the use of a surgical robot that performs semi-automated bone drilling of cranial windows and can help reduce surgeon-to-surgeon variability and partially mitigate thermal blood-brain barrier damage.
Abstract
Cranial window surgery allows for the imaging of brain tissue in live mice with the use of multiphoton or other intravital imaging techniques. However, when performing any craniotomy by hand, there is often thermal damage to brain tissue, which is inherently variable surgery-to-surgery and may be dependent on individual surgeon technique. Implementing a surgical robot can standardize surgery and lead to a decrease in thermal damage associated with surgery. In this study, three methods of robotic drilling were tested to evaluate thermal damage: horizontal, point-by-point, and pulsed point-by-point. Horizontal drilling utilizes a continuous drilling schematic, while point-by-point drills several holes encompassing the cranial window. Pulsed point-by-point adds a "2 s on, 2 s off" drilling scheme to allow for cooling in between drilling. Fluorescent imaging of Evans Blue (EB) dye injected intravenously measures damage to brain tissue, while a thermocouple placed under the drilling site measures thermal damage. Thermocouple results indicate a significant decrease in temperature change in the pulsed point-by-point (6.90 °C ± 1.35 °C) group compared to the horizontal (16.66 °C ± 2.08 °C) and point-by-point (18.69 °C ± 1.75 °C) groups. Similarly, the pulsed point-by-point group also showed significantly less EB presence after cranial window drilling compared to the horizontal method, indicating less damage to blood vessels in the brain. Thus, a pulsed point-by-point drilling method appears to be the optimal scheme for reducing thermal damage. A robotic drill is a useful tool to help minimize training, variability, and reduce thermal damage. With the expanding use of multiphoton imaging across research labs, it is important to improve the rigor and reproducibility of results. The methods addressed here will help inform others of how to better use these surgical robots to further advance the field.
Introduction
Cranial windows have become ubiquitously used throughout the fields of neuroscience, neural engineering, and biology to allow for direct visualization and imaging of the cortex in living animals1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11. The powerful combination of transgenic mice and multiphoton imaging has provided extremely valuable insights into circuit activity and other biological insights in the in vivo brain12,13,14,15,16,17,18. Miniature microscopes mounted on the skull have further extended these capabilities to enable recordings in awake, freely moving animals19. The process of creating a cranial window requires power-drilling to thin or completely remove the cranial bone to produce large enough craniotomies to secure a transparent piece of glass over the cortex20. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and other polymers have also been tested as cranial window materials9,21. Ultimately, the ideal cranial window is one that does not alter or interfere with normal endogenous activity underneath. However, it is commonly accepted that cranial window drilling aggravates underlying tissue, leading to damage to the brain, disruption of the environment, and effecting meninges to the point of occluding multiphoton imaging depth22. The resulting neuroinflammation has a wide array of effects ranging from permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), to activation and recruitment of glial cells around the implant site23. Therefore, characterizing safer and more reproducible cranial window drilling methods is crucial for consistent imaging quality and reducing confounding factors.
While care is taken to minimize trauma to the underlying tissue, the act of drilling the bone has the potential to cause both thermal and mechanical perturbations to the brain24,25. Mechanical trauma from accidental drill penetration into the dura may further induce varying degrees of cortical injury24. In a study by Shoffstall et al.25, the heat from bone-drilling resulted in an increased BBB permeability, as indicated by the presence of Evans Blue (EB) dye in the brain parenchyma25. EB dye, injected intravenously, binds to circulating albumin in the bloodstream and therefore does not normally cross a healthy BBB in appreciable concentrations. As a result, EB dye is commonly used as a sensitive marker of BBB permeability26,27. While their study did not directly measure the impact of the BBB permeability on subsequent biological sequelae under study, prior studies have correlated BBB permeability to an increased neuroinflammatory response to chronically implanted microelectrodes and alterations in motor function28.
Depending on the goals of the study, the magnitude of thermal and mechanical damage may contribute a source of experimental error, negatively affecting the rigor and reproducibility of the study. There are dozens of cited methods for producing cranial windows, each using different drilling equipment, speeds, techniques, and users1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11. Shoffstall et al.25 reported that the observed variation in the heating outcomes was attributed to variability in the drill's applied force, feed rate, and angle of application, among other aspects that cannot be controlled for when drilling by hand25. There is a belief that automated drilling systems and other stereotaxic equipment can improve reproducibility and outcome consistency, but published method studies have not rigorously evaluated temperature or BBB permeability as one of the outcomes. Therefore, there is a need for more reproducible and consistently applied methods to produce cranial windows, as well as methods rigorously applied to assess the impact of cranial window drilling on underlying neural tissue.
The focus of this study is to determine and develop consistent and safe drilling methods for cranial windows. The size of the craniotomy for cranial window installation is significantly larger than standard craniotomies for brain implanted microelectrodes. Such craniotomies cannot be completed with a single burr hole when using standard equipment, thereby introducing more inter-surgeon technique variability when performed by hand20. Surgical drilling robots have been introduced to the field, but have not been widely adopted1,6,29. Automation of drilling offers control over variables contributing to observed trial-to-trial variation, suggesting that use of the equipment can reduce inter- and intra-surgeon effects. This is of particular interest given the added difficulty of the larger craniotomy needed for cranial window placement. While one could assume there to be clear benefits to the control provided by automating the drilling, there has been little assessment of the implementation of these equipment. Although visible lesions have not been observed5, the higher sensitivity test using EB is desired.
Here, BBB permeability is measured using a commercially available surgical drilling robot with corresponding software, which allows for programming of stereotaxic coordinates, craniotomy planning/mapping, and a selection of drilling styles ("point-by-point" vs "horizontal"), referring to the routed path of the drill bit. Initially, eight "seed" points are drilled (Figure 1A), outlining the cranial window. From here, the space in between the seeds is cut out using either the "point-by-point" or "horizontal" drill method. "Point-by-point" performs vertical pilot hole cuts (similar to a CNC drill press), while "horizontal" performs horizontal cuts along the circumference of the cranial window that outline the hole (similar to a CNC router). The result for both methods are a piece of skull that can be removed to reveal the cranial window. To isolate damage from drilling, the cranial window is not physically removed, so as to avoid any additional damage. A combination of EB dye coupled with fluorescent imaging is used to measure BBB permeability after performing craniotomies in mice, and an inserted thermocouple is used to directly measure temperature of the brain surface during drilling (Figure 1B,C). Previous observations indicated that pulsed drilling on/off with 2 s intervals was sufficient to mitigate drill heating25, and therefore is incorporated into the experimental approach for the surgical robot.
The intent of the presented work is to demonstrate methods of assessing thermal damage from craniotomy drilling. While the methods are presented in the context of automated drilling, such methods can be applied to manual drilling schemes as well. These methods can be used to validate the use of equipment and/or drilling schemes before adopting as a standard procedure.
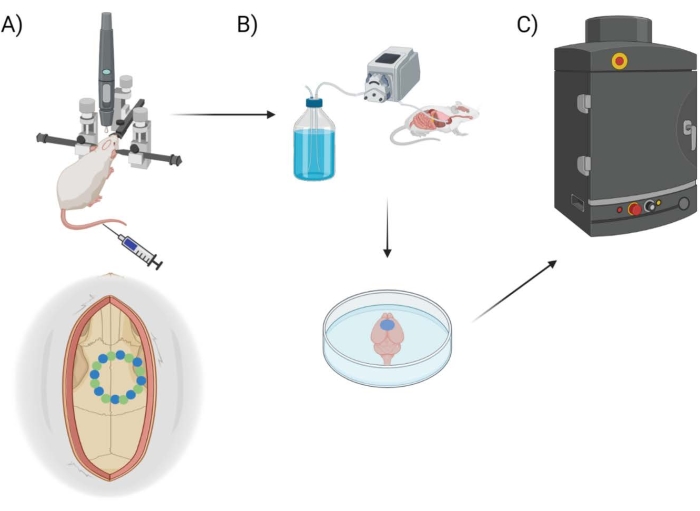
Figure 1: Experimental pipeline schematic. Schematic demonstrating the process animals underwent for EB quantification post-cranial window procedure. (A) Schematic setup of the mouse with the stereotaxic frame and surgical robot drill. An example cranial window is shown over the motor cortex with seed points (green) and edge points (blue). (B) The perfusion setup includes injecting 1x Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) throughout the animal to remove any blood, followed by extraction of the brain. (C) The brain is then put into the EB fluorescent imaging system chamber to conduct fluorescent imaging on the Evans Blue dye. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
All procedures and animal care practices were reviewed, approved by, and performed in accordance with the Louis Stokes Cleveland Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
1. Surgical robot hardware setup
- Before surgery, follow the surgical robot (see Table of Materials) manual and guide to set up the hardware and software. Perform frame calibration as detailed in the manual. If the drill or frame are moved, it is recommended to recalibrate the drill to ensure accuracy.
2. Software preparation
- Navigate to the surgical software (see Table of Materials) and create a new project by selecting Start with a clean project. Set the subject as Mouse at the top to designate the drilling coordinates to be used.
- Select Start new Project.
- From here, click on Planning in the bottom left corner to navigate to the drilling coordinate planning screen. Create the drilling scheme for the cranial window technique to be performed.
- To do this, click anywhere on the stereotaxic atlas. Use Bregma as the reference, and input the following coordinates for the motor cortex: AP = 1.50, ML = 1.25, DV = 0.00. Press Enter on the keyboard to update the selected coordinates.
NOTE: The Dorsal-Ventral (DV) coordinates denote the depth of drilling and so do not need an input here. - Click Store Target to save these coordinates and input an appropriate name. From here, click on the Move button in the bottom left to navigate back to the main drilling screen.
- To do this, click anywhere on the stereotaxic atlas. Use Bregma as the reference, and input the following coordinates for the motor cortex: AP = 1.50, ML = 1.25, DV = 0.00. Press Enter on the keyboard to update the selected coordinates.
- Click Tools > Project > Save As to reuse this template project for later projects. This will automatically retain the drilling coordinates for later use.
3. Preparation for surgery
- Anesthetize PrismPlus mice30,31 (see Table of Materials) in an isoflurane chamber (3.5% in 1.5 L/min O2). Apply eye lubricant to prevent drying of the eyes, shave the head using clippers, and trim the nails to prevent the mice from scratching sutures out.
NOTE: PrismPlus mice are a type of transgenic fluorescent species used in multiphoton imaging. The heterozygous PrismPlus mice lack the fluorescent genes and were therefore used here to reduce animal waste from other ongoing studies, and since there is no multiphoton imaging in this study. Wild-type mice are expected to show similar results. - Administer subcutaneous injections of antibiotic cefazolin (24 mg/kg), analgesic carprofen (5 mg/kg), and buprenorphine (0.05-0.10 mg/kg) to the anesthetized mice. Prior to any incision, administer a single subcutaneous injection of marcaine (0.25%, 100 µL) below the incision site (1 inch along the midline of the skull starting behind the eyes).
NOTE: Medications used here follow previously established IACUC protocols. However, it is recommended to consider EMLA cream as a topical anesthetic for a multi-modal effect before surgery and tail vein injection as well as Meloxicam SR in lieu of Carprofen. EMLA and Meloxicam SR can be provided prior to isoflurane anesthesia. - Mount the animal on the surgical robot stereotaxic frame, using supplied earbars, and maintain anesthesia with 0.5%-2% isoflurane via inhalation through a nose cone.
- Ensure anesthetic depth is closely monitored by a trained vet technician or staff, based on the responsiveness of the mouse, respiration (~55-65 breaths/min), heart rate (300-450 bpm), and color (pink). Whisker and regular toe pinch can also be used as a measure to determine the depth of anesthesia. The values of vitals are determined by institutional IACUC regulations.
- Maintain animal body temperature on a circulating water pad and monitor vitals using a blood-oxygen and heart rate measurement system.
- Scrub the surgical area with chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG) and 70% isopropanol for sterilization. To maintain sterility during surgery, place a sterile plastic wrap over the mouse and stereotaxic frame.
NOTE: While these protocols were developed for survival surgeries, the presented data reflects the use of non-survival animals, as the focus was to test and determine the appropriate drilling protocol methods.
4. Skull preparation
- Using a scalpel blade, perform a 1 inch incision on the midline of the skull, starting at the back of the eyes.
- Pull the skin back to expose the skull and (optionally) use retractors to maintain the surgical window. Remove any residual tissue and membrane using sterile cotton-tipped applicators.
- Dry out and clean the skull using 3% hydrogen peroxide with cotton-tipped applicators.
NOTE: This will make the sutures of the skull visible. Bregma and Lambda should be easily seen. If not, apply more hydrogen peroxide or increase the size of the incision. - Allow for "auto-stop" functionality by attaching the alligator clip cable from the surgical robot drilling setup to the mouse, per the manufacturer's recommendations. "Auto-stop" works by detecting a change in impedance, so once the drill bit contacts cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) instead of bone, the drill will stop drilling, thereby preventing damage to the brain.
5. Evans Blue tail vein injection
CAUTION: EB is a possible carcinogen. Use gloves when handling.
- To prepare the tail for easy injection, wipe down with an alcohol wipe. Optionally, wintergreen oil can be topically applied to dilate the vein35.
- Grasp the tail in one hand while handling the syringe containing EB in the other hand. Using the thumb and forefinger, bend the tail to expose the tail vein on top of the bend of the tail. Insert the syringe (1 or 2 mL, 30 G insulin syringe) parallel with the vein and slowly inject the volume of EB. EB (4% w/v) is administered at a concentration of 2 mL/kg body weight via tail vein injection.
NOTE: Minimal to no resistance to flow from the syringe into the tail can be felt if the needle is correctly inserted. If there is resistance or EB dye appears in the tail, then move down on the tail and try again. - Once injected, wait for 5 min to allow EB to circulate throughout the mouse before drilling commences. Successful injection is immediately verified as the mouse's extremities and surgical window turn blue.
6. Surgical robot drilling procedure
- Once the skull is prepared for drilling, navigate back to the surgical software. Open the template project defined in step 2.4 where the coordinates for drilling were designated.
- Follow Tools > Project > New > Select A Template Project and choose the template project that was designated in step 2 (software preparation).
- Select Same Protocol elements > Planning (Target points) > Drill Parameters to carry over to this new project.
- Click Start new project.
- Next, correct the drill and frame to account for the tilt and scaling of the mouse skull of the current animal. Click Tools and select Correct for Tilt and Scaling... to open the correction screen. At the top of the screen, ensure that the drill is active (not the syringe), by clicking on the light-red Drill button.
NOTE: Once activated, the Drill button will turn dark/bright red. The syringe button can be ignored, as that is not used in this protocol.- First, correct the Scale, Pitch, and Yaw by setting where Bregma and Lambda are located on the current animal. Utilize either the keyboard controls or the on-screen controls to move the drill bit. Once the drill bit is located over Bregma, lower it until it is just touching the skull and click Set Bregma. Repeat this for Lambda.
- Next, adjust for the specific Roll of the skull. Click on the Go to Midpoint button to adjust the drill bit automatically to the center of the skull. Click 2 mm to the Left and then slowly lower the drill bit until touching the skull. Click Set Left Point.
- Repeat step 6.2.2 for the right side of the brain. Now the system is set up for this specific skull.
NOTE: Correction here is critical to ensure proper drilling coordinates and depth. The mouse needs to be mounted as close to straight as possible to reduce the need for correction as much as possible. If large corrections are needed, it may result in poor accuracy of drilling.
- After correction has been performed, come out of the correction window by clicking Close in the bottom middle of the screen. Navigate to the drilling screen by clicking Tools and then selecting Drill... to begin the drilling procedure.
- Ensure that Craniotomy-Shape is chosen from the Drill dropdown at the top of the screen. Then, click Select drill center & shape and choose the predefined target that was named in step 2.3.1. Under this screen, select Circle as the shape for the target and input 2.60 mm as the diameter2 of the circle. Click Show.
NOTE: The diameter of the cranial window is created using the center of the drill bit as the center of the seed points. A small drill bit (diameter = 0.6 mm or the recommended bit size provided by vendor) is used to minimize the extra diameter added as a result of using a larger drill bit. Special drill bits are used specifically for the surgical robot. The eight seed points and edge points will now show up on the skull as green and blue dots, respectively. - Click on the main window and use the keyboard shortcut Control + Shift + D to bring up the Drill Points menu on the right side of the screen. This allows for viewing specific drill point depths and statuses.
- Before drilling begins, customize the auto-stop feature if required by clicking the button next to the Auto-Stop checkbox. This button defaults to Medium, which corresponds to the sensitivity for the auto-stop feature.
NOTE: This can be tested beforehand to find the right sensitivity for the animals. In this protocol, the highest sensitivity was used to ensure minimal drilling through the brain. - Once the auto-stop feature is enabled and customized, begin the drilling of the seed point. Click Auto Scan so that the drill automatically begins at Seed 1. Once the drill bit touches the CSF, the auto-stop feature will detect a change in impedance, leading to a stoppage in the drilling and retraction of the bit from the skull.
- Keep a close eye on the drilling in case the auto-stop fails to detect any changes. The Escape key can be pressed to manually cancel the drilling. The pink circle located at the bottom of the Drill menu and to the right of the impedance values can also be clicked to either start or stop drilling.
NOTE: The drill bit will automatically drill to a depth equal to the estimated skull thickness (or until the auto-stop feature is activated). - If auto-stop is not activated before the estimated depth is reached, a screen will pop up prompting the user to: 1) Continue drilling and descending # mm further, 2) Mark at current depth and continue, 3) Skip the current point and continue, or 4) Stop the process (may be continued later). Choose one of the options as described below.
- For Continue drilling and descending # mm further, enter a distance for the drill to advance. By default, 0.1 mm is used. A smaller distance may be suggested to prevent accidental penetration of the brain.
- If it is believed that the dura has been reached at this screen, select the Mark at current depth and continue option for the system to mark the dura at that depth and move on to the next seed.
- Use the Skip the current point and continue and Stop the process (may be continued later) to troubleshoot or clean off the drill bit and return once the auto-stop is functioning again.
- Once all the seed points have been drilled, if any were not finished using the auto-stop feature, check the depth of the hole manually using a dura pick. This will ensure that the drilled depth did penetrate through the skull.
- Before commencing edge point drilling, decide what type of 'edge-cut' is desired by selecting the drop down next to the Edge-Cut text on the Drill menu. The two options are Point-by-Point and Horizontally.
- Select Point-by-Point to drill each edge point individually and to a depth determined by the adjacent seed point depths. Adjust the scaling if required through the Edge Scaling... button below, although the default of No Scaling usually is sufficient.
- Select Horizontally to begin drilling at Edge Point 1 and use a continuous drilling motion to go around the entire circumference of the drilling circle. By default, the horizontal cut will cut at 100 µm intervals, going all the way around the circumference of the window before advancing another 100 µm deeper. If required, change the interval depth and drill speed under the Cut options... button below.
- Use the auto-cut offset (below Edge-Cut box) to adjust for the auto-cut depth by taking a predetermined offset from the adjacent seed points. In this protocol, an auto-cut offset of 20 µm was used. Further testing can be done to determine an optimal offset on a per-animal basis.
- Once the edge cut settings have been determined, commence edge point drilling by clicking the Auto Cut button in the middle of the Drill menu. For point-by-point drilling, once the last edge has been drilled, the drilling procedure is finished. For horizontal drilling, continue until enough skull has been drilled to release the cranial window.
NOTE: Although drilling is performed until the window can be released, the window is not physically released here to prevent any damage to underlying tissue. It is important to isolate the damage as a result of just drilling to evaluate different drilling schematics.- Once the horizontal drilling has reached the depth of one seed point, right-click on that seed (or select multiple points first) in the Drill Points menu and click Lock Depth. This will allow for horizontal cutting to continue without cutting deeper for that area (thus avoiding penetrating the brain).
NOTE: If there are seed points with differing dura depths, this can cause differences in the depth needed for the horizontal drilling procedure.
- Once the horizontal drilling has reached the depth of one seed point, right-click on that seed (or select multiple points first) in the Drill Points menu and click Lock Depth. This will allow for horizontal cutting to continue without cutting deeper for that area (thus avoiding penetrating the brain).
- If the auto-stop feature is not working correctly, ensure that the drill bit is fully clean from any debris or potential blood, saline, etc., as those may impact the base impedance of the bit. Additionally, choose from one of the several manual drilling options described below in case the auto-stop fails to work consistently.
- In the Drill menu, navigate manually to each seed by right-clicking on the seed or edge and choosing Go to Entry. There are also options to clear the depths marked, reset the hole, and other options that can assist with the drilling procedure.
- Manually control drill depth advancement by selecting a depth from the drop down located next to the Advance: text near the top of the Drill menu. Click the Advance button directly below to advance the drill the set distance.
NOTE: This feature can be used in conjunction with the Set Dura and Set Surface buttons below the Advance button to manually tell the system where both the surface of the skull and dura are located. Use the auto-stop function where possible, but if needed these manual options also suffice. - If manually drilling, take more caution between each drilling depth interval to ensure that the drill does not exceed the dura. Check the drilled hole using a dura pick in between depth intervals to confirm whether the dura was reached. Once all manual seed drilling is finished, continue the edge cut procedure normally as outlined above.
- Pulse method
- To carry out manual pulse drilling, turn off the auto-stop feature by unchecking the checkbox next to the Auto-Stop option in the Drill menu. This must be off in order to allow for controlling when the drill is off for the pulsing.
NOTE: Pulse drilling follows a pattern of 2 s of drilling followed by 2 s of no drilling to allow for the skull to cool down. - In the Drill menu, select 100 µm as the drill depth advancement, this will equate to ~2 s of downward drilling.
- Once ready, click Advance to commence drilling.
NOTE: Be ready to quickly stop the drill once it has advanced by 100 µm, as the drill continues to rotate at the depth until escape is pressed (generating unnecessary heat). - Once the drill has advanced 100 µm, press Escape twice to stop the drill. After 2 s, repeat this cycle for the depth of the skull.
NOTE: Only the point-by-point method can be performed using the pulsed method due to software and mechanical constraints. Continuous horizontal drilling cannot be performed this way. - Drill all seed and edge points using this method detailed above. Be sure to Set Dura using the button in the Drill menu once the dura has been reached.
- To carry out manual pulse drilling, turn off the auto-stop feature by unchecking the checkbox next to the Auto-Stop option in the Drill menu. This must be off in order to allow for controlling when the drill is off for the pulsing.
- Ensure that Craniotomy-Shape is chosen from the Drill dropdown at the top of the screen. Then, click Select drill center & shape and choose the predefined target that was named in step 2.3.1. Under this screen, select Circle as the shape for the target and input 2.60 mm as the diameter2 of the circle. Click Show.
7. Perfusion and brain extraction
- Once drilling of the seed and edge points is finished, keep the animal under isoflurane anesthesia for an additional 1 h to allow for the EB dye to circulate and extravasate through the damaged BBB. Perform cardiac perfusion to remove any blood or fluids from the vessels, and then remove the brain for imaging and analysis as described below.
- After the 1 h EB circulation period following the creation of the cranial window, inject a cocktail of ketamine (160 mg/kg) and xylazine (20 mg/kg) intraperitoneally into the animal. Once unresponsive, perform a cardiac perfusion.
- Cut open the abdomen of the mouse using scissors and expose the heart by cutting vertically through the rib cage and horizontally across the diaphragm. Retract the rib cage to view the heart clearly. Insert a butterfly needle into the left ventricle of the heart and begin infusing 1x phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) throughout the body. Snip a small portion of the right atrium of the heart to release pressure build up.
- After 25 mL of 1x PBS has perfused throughout the body, stop the perfusion and decapitate the mouse as a secondary means of euthanasia.
NOTE: Be sure to perform the institutionally approved method of euthanasia and/or endpoint perfusion for the animal to isolate the brain. - From here, extract the brain from the skull by removing the bone and tissue with rongeurs.
- Image the extracted brain with a fluorescent imaging system to observe the amount of EB located in the brain around the drilling sites.
NOTE: EB binds to circulating albumin. If vascular damage occurs in the brain, EB will leak out and bind to the brain tissue, leading to a clear visual indicator of damage.
8. Evans Blue imaging and analysis
- Hardware initialization
- Turn on the computer attached to the EB fluorescence imaging system and start the imaging software (see Table of Materials) as other items are being prepared. Turn on the light source, platform, and camera, in that order.
- Navigate to the imaging software and click Initialize under the Acquisition Control Panel. The system and chamber will signal from red to green as soon as initialization is complete.
NOTE: Initialize the EB fluorescent imaging system 30 min prior to any imaging to allow the temperature of the light source to reach optimal levels.
- Imaging of the brain
- Place the explanted brain in a clear dish on the center of the stage for imaging.
- Under the Acquisition Control Panel, adjust the settings for the image. Select the exposure time: 1 s; Binning: Medium; F/Stop: F1; Excitation: 535 to 675 nm; Emission: Cy 5.5; Lamp level: High; and FOV: 5 cm. Leave the filter locked and the overlay of photography and fluorescence checked. These settings are based off previous lab experience and other published methods of imaging EB36.
- Load EB fluorescent imaging system images into open access image processing software (see Table of Materials) and generate three freehand regions of interest (ROIs) to find the fluorescent intensity of EB by measuring the mean radiance over the background, whole brain, and cranial window.
- Normalize the cranial window and whole brain measurements against the corresponding background ROI.
- Image each brain under different excitation filters (535-675 nm) to find the wavelength with the highest signal to noise ratio (605 nm was chosen) between the experimental groups to the saline control.
- Isolate the mean radiance under the appropriate wavelength and average to obtain the average mean radiance or fluorescent intensity for the whole brain and cranial window ROIs.
- Find and normalize the average mean radiance over the cranial window area for each group against the saline control.
9. Thermocouple evaluation
- Measure the changes in temperature of the skull and brain using a thermocouple (see Table of Materials) in combination with the three different drilling schemes. The thermocouple is connected to a data acquisition system (DAQ) that allows for the measurement to be read into MATLAB.
- Mount a cadaver mouse onto the stereotaxic frame and robotic drill setup. Manually drill a small hole (same size as seed point) ~2 mm away from where the cranial window will be made into the side of the skull25. This hole will allow for the thermocouple to be slid into position under where drilling of the cranial window occurs (Figure 2D).
NOTE: Cadaver mice are used because drilling open the side of the skull is required to slide the thermocouple over the cranial window drilling region. This cadaver mouse is a different animal than the one previously used for Evans Blue analysis. - Begin the drilling process for each of the three schemes as done earlier (step 6). As the drill goes through the skull, there will be spikes in temperature change, indicating heating occurring near the brain.
- Record and plot the results in MATLAB to calculate the maximum temperature difference. This should be done separately for the seed drilling and the edge drilling to evaluate horizontal vs. point-by-point drilling along with the pulsed manual drilling method.
10. Statistics
- Perform statistical analysis for thermocouple and EB fluorescent imaging in R using a Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test with Benjamini-Hochberg correction followed by pairwise comparisons using the Wilcoxon rank sum exact test25.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Thermal evaluation
Potential for thermal damage was evaluated by measuring the change in temperature from baseline due to drilling using horizontal (Figure 2A), point-by-point (Figure 2B), and pulsed point-by-point (Figure 2C) methods. Figure 2D displays the experimental setup for obtaining thermal data. A sample size of N = 4 cranial windows was used for thermal evaluation. Horiz...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
The use of EB dye and imaging is straightforward, quick, and useful for evaluating vascular damage in the brain for new methods and techniques. Whether using a surgical robot or confirming methods currently done in the lab, it is important to validate surgical methods to isolate the effects of experimental treatments vs. surgical impact and improve animal welfare. A thermocouple setup is also useful in evaluating drilling methods to ensure no heating occurs. Increases in temperature due to bone drilling have been known t...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to report. The contents do not represent the views of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the National Institutes of Health, or the United States Government.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by Merit Review Awards GRANT12418820 (Capadona) and GRANTI01RX003420 (Shoffstall/Capadona), and Research Career Scientist Award # GRANT12635707 (Capadona) from the United States (US) Department of Veterans Affairs Rehabilitation Research and Development Service. Additionally, this work was also supported in part by the National Institute of Health, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke GRANT12635723 (Capadona), and the National Institute for Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, T32EB004314, (Capadona/Kirsch). This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship under Grant No. GRANT12635723. Any opinion, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1x Phosphate Buffered Saline Type: Reagent | VWR | MRGF-6235 | For Evans Blue dilution |
| Aura Software Type: Tool | Spectral Instruments Imaging | Open access imaging processing software for Lumina imaging sytems | |
| Buprenorphine Type: Drug | Sourced from Animal Facility | ||
| Carbide Drill Bit, 0.6mm (Robot Drill) Type: Tool | Stoelting | 58640-1 | |
| Carprofen Type: Drug | Sourced from Animal Facility | ||
| Cefazolin Type: Drug | Sourced from Animal Facility | ||
| Evans Blue Dye Type: Reagent | Millipore Sigma | E2129 | Reconstituted in 1x phosphate-buffered saline |
| Isoflurane Type: Drug | Sourced from Animal Facility | ||
| IVIS Lumina II Type: Tool | Perkin Elmer | CLS136334 | IVIS Lumina III currently in place of Lumina II on the market |
| Jenco Linearizing Thermometer Type: Tool | Jenco | 765JF | For Thermocouple setup |
| Ketamine Type: Drug | Sourced from Animal Facility | ||
| LivingImage Type: Tool | Perkin Elmer | Software for IVIS Lumina III | |
| Marcaine Type: Drug | Sourced from Animal Facility | ||
| Neurostar Software Type: Tool | Stoelting | Comes with surgical robot purchase | |
| Physiosuite with MouseSTAT® Pulse Oximeter & Heart Rate Monitor Type: Tool | Kent Scientific | PS-03 | Used to monitor vitals |
| PrismPlus mice Type: Animal | Jackson Labortory | 031478, RRID:IMSR_JAX:031478, Male, ~8 months old | Animals used for the study |
| Stoelting Drill and Injection Robot for Motorized Stereotaxic Instruments Type: Tool | Stoelting | 58640 | Main robotic drill with stereotaxic frame |
| Thermocouple Type: Tool | TC Direct | 206-557 | For Thermocouple setup |
| USB-6008 Multifunction I/O DAQ Type: Tool | National Instruments | USB-6008 | For Thermocouple setup |
| Xylazine Type: Drug | Sourced from Animal Facility |
References
- Kilic, K., et al. Chronic cranial windows for long term multimodal neurovascular imaging in mice. Frontiers in Physiology. 11, 612678(2020).
- Goldey, G. J., et al. Removable cranial windows for long-term imaging in awake mice. Nature Protocols. 9 (11), 2515-2538 (2014).
- Augustinaite, S., Kuhn, B. Intrinsic optical signal imaging and targeted injections through a chronic cranial window of a head-fixed mouse. STAR Protocols. 2 (3), 100779(2021).
- Wang, X., et al. A skull-removed chronic cranial window for ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging of the rodent brain. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 15, 673740(2021).
- Wang, Y., Xi, L. Chronic cranial window for photoacoustic imaging: a mini review. Visual Computing for Industry, Biomedicine, and Art. 4 (1), 15(2021).
- Augustinaite, S., Kuhn, B. Chronic cranial window for imaging cortical activity in head-fixed mice. STAR Protocols. 1 (3), 100194(2020).
- Kunori, N., Takashima, I. An implantable cranial window using a collagen membrane for chronic voltage-sensitive dye imaging. Micromachines. 10 (11), 789(2019).
- Beckmann, L., et al. Longitudinal deep-brain imaging in mouse using visible-light optical coherence tomography through chronic microprism cranial window. Biomedical Optics Express. 10 (10), 5235-5250 (2019).
- Heo, C., et al. A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology. Scientific Reports. 6, 27818(2016).
- Holtmaat, A., et al. Imaging neocortical neurons through a chronic cranial window. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2012 (6), 694-701 (2012).
- Holtmaat, A., et al. high-resolution imaging in the mouse neocortex through a chronic cranial window. Nature Protocols. 4 (8), 1128-1144 (2009).
- Sundaram, G. S., et al. Characterization of a brain permeant fluorescent molecule and visualization of Abeta parenchymal plaques, using real-time multiphoton imaging in transgenic mice. Organic Letters. 16 (14), 3640-3643 (2014).
- Spires, T. L., et al. Dendritic spine abnormalities in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice demonstrated by gene transfer and intravital multiphoton microscopy. Journal of Neuroscience. 25 (31), 7278-7287 (2005).
- Price, D. L., et al. High-resolution large-scale mosaic imaging using multiphoton microscopy to characterize transgenic mouse models of human neurological disorders. Neuroinformatics. 4 (1), 65-80 (2006).
- Kimchi, E. Y., Kajdasz, S., Bacskai, B. J., Hyman, B. T. Analysis of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease using in vivo multiphoton microscopy. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology. 60 (3), 274-279 (2001).
- Hyman, B. T. The natural history of Alzheimer disease dissected through multiphoton imaging of transgenic mice. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders. 20 (4), 206-209 (2006).
- Korzhova, V., et al. Long-term dynamics of aberrant neuronal activity in awake Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice. Communications Biology. 4 (1), 1368(2021).
- Chawda, C., McMorrow, R., Gaspar, N., Zambito, G., Mezzanotte, L. Monitoring immune cell function through optical imaging: a review highlighting transgenic mouse models. Molecular Imaging and Biology. 24 (2), 250-263 (2022).
- Courtin, J., et al. A neuronal mechanism for motivational control of behavior. Science. 375 (6576), (2022).
- Mostany, R., Portera-Cailliau, C. A craniotomy surgery procedure for chronic brain imaging. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (12), e680(2008).
- Cramer, S. W., et al. Through the looking glass: A review of cranial window technology for optical access to the brain. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 354, 109100(2021).
- Eles, J. R., Vazquez, A. L., Kozai, T. D. Y., Cui, X. T. Meningeal inflammatory response and fibrous tissue remodeling around intracortical implants: An in vivo two-photon imaging study. Biomaterials. 195, 111-123 (2019).
- Jorfi, M., Skousen, J. L., Weder, C., Capadona, J. R. Progress towards biocompatible intracortical microelectrodes for neural interfacing applications. Journal of Neural Engineering. 12 (1), 011001(2015).
- Cole, J. T., et al. Craniotomy: true sham for traumatic brain injury, or a sham of a sham. Journal of Neurotrauma. 28 (3), 359-369 (2011).
- Shoffstall, A. J., et al. Potential for thermal damage to the blood-brain barrier during craniotomy: implications for intracortical recording microelectrodes. Journal of Neural Engineering. 15 (3), 034001(2018).
- Saunders, N. R., Dziegielewska, K. M., Mollgard, K., Habgood, M. D. Markers for blood-brain barrier integrity: how appropriate is Evans blue in the twenty-first century and what are the alternatives. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 9, 385(2015).
- Wang, H. L., Lai, T. W. Optimization of Evans blue quantitation in limited rat tissue samples. Scientific Reports. 4, 6588(2014).
- Goss-Varley, M., et al. Microelectrode implantation in motor cortex causes fine motor deficit: Implications on potential considerations to Brain Computer Interfacing and Human Augmentation. Scientific Reports. 7 (1), 15254(2017).
- Oomoto, I., et al. Protocol for cortical-wide field-of-view two-photon imaging with quick neonatal adeno-associated virus injection. STAR Protocols. 2 (4), 101007(2021).
- Dougherty, J. D., Zhang, J., Feng, H., Gong, S., Heintz, N. Mouse transgenesis in a single locus with independent regulation for multiple fluorophores. PLoS One. 7 (7), 40511(2012).
- Jung, S., et al. Analysis of fractalkine receptor CX(3)CR1 function by targeted deletion and green fluorescent protein reporter gene insertion. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 20 (3), 4106-4114 (2000).
- Kiyatkin, E. A., Sharma, H. S. Permeability of the blood-brain barrier depends on brain temperature. Neuroscience. 161 (3), 926-939 (2009).
- Eriksson, A. R., Albrektsson, T. Temperature threshold levels for heat-induced bone tissue injury: a vital-microscopic study in the rabbit. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry. 50 (1), 101-107 (1983).
- Bonfield, W., Li, C. H. The temperature dependence of the deformation of bone. Journal of Biomechanics. 1 (4), 323-329 (1968).
- Hrapkiewicz, K., Medina, L. Clinical Laboratory Animal Medicine, second ed. , Blackwell Publishing. Ames Iowa. (2007).
- McLean, R., Moritz, A. R., Roos, A. Studies of thermal Injury. VI. Hyperpotassemia caused by cutaneous exposure to excessive heat. Journal of Clinical Investigations. 26 (3), 497-504 (1947).
- Kyweriga, M., Sun, J., Wang, S., Kline, R., Mohajerani, M. H. A large lateral craniotomy procedure for mesoscale wide-field optical imaging of brain activity. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (123), e52642(2017).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved