Method Article
Fast Colony Forming Unit Counting in 96-Well Plate Format Applied to the Drosophila Microbiome
In This Article
Summary
This method quantifies microbial abundance using a 96-well plate format to plate colony forming units (CFUs) and is applied to the Drosophila microbiome in whole fly homogenate samples. CFUs are counted with an automated image analysis software provided here.
Abstract
The intestines of animals are colonized by commensal microbes, which impact host development, health, and behavior. Precise quantification of colonization is essential for studying the complex interactions between host and microbe both to validate the microbial composition and study its effects. Drosophila melanogaster, which has a low native microbial diversity and is economical to rear with defined microbial composition, has emerged as a model organism for studying the gut microbiome. Analyzing the microbiome of an individual organism requires identification of which microbial species are present and quantification of their absolute abundance. This article presents a method for the analysis of a large number of individual fly microbiomes. The flies are prepared in 96-well plates, enabling the handling of a large number of samples at once. Microbial abundance is quantified by plating up to 96 whole fly homogenates on a single agar plate in an array of spots and then counting the colony forming units (CFUs) that grow in each spot. This plating system is paired with an automated CFU quantification platform, which incorporates photography of the plates, differentiation of fluorescent colonies, and automated counting of the colonies using an ImageJ plugin. Advantages are that (i) this method is sensitive enough to detect differences between treatments, (ii) the spot plating method is as accurate as traditional plating methods, and (iii) the automated counting process is accurate and faster than manual counting. The workflow presented here enables high-throughput quantification of CFUs in a large number of replicates and can be applied to other microbiology study systems including in vitro and other small animal models.
Introduction
The relationship between intestinal microbiota and their animal host is increasingly at the forefront of biological studies1, which show that the strain composition of the microbiome is important for host physiology2,3,4. The pace of discovery has been limited by confounding factors such as high natural inter-individual variation and high diversity of colonizing bacteria5,6,7. The fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, has emerged as a promising model due to its naturally low-diversity microbiome, ease of handling, and robust host genetics8,9,10,11. Flies can be made germ-free and re-associated with a defined microbiota12, and it has been shown that the flora influence fly physiological traits13,14. The innate flora consists of a limited set of bacteria that are all culturable, and close relatives of these are also endogenous to the mammalian gut, including Lactobacilli, Proteobacteria, and Enterococci15.
Studying the influence of the microbiome on host traits requires quantification of the microbiome in terms of both which species are present and their absolute abundances16. The predominant ways of analyzing the fly microbiome are colony forming unit (CFU) counts17, 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing9, and qPCR of the 16S rRNA gene18. CFU counts can be obtained without expensive reagents, and they confirm the viability of the bacterial cells19. The 16S techniques including qPCR have advantages in that taxonomic identities of microbes can be ascertained without regard to their growth requirements or colony morphologies20.
In the case where experiments use flies with a defined microbiome of known bacteria (gnotobiotic flies), CFU counts have particular advantages over sequencing21. Sequencing is expensive, requiring DNA extraction, PCR-based library preparation, and high-throughput sequencing to obtain relative abundances22. Due to the high cost, high-throughput sequencing methods typically need to be performed in bulk to reduce the per-sample price23. Further methods such as qPCR are required to obtain absolute abundances16. In contrast, CFU counts are fast and cheap and give the absolute numbers of viable cells. Drosophila8 and other small microbiome models24, including the worm, Caenorhabditis elegans25,26, and the larval zebrafish, Danio rerio, grown gnotobiotically27, have a limited range of bacteria, which have known growth characteristics28. In these cases, particularly with gnotobiotic animals, CFU counting can differentiate all the species of bacteria within the multispecies gut communities21,27,29. Higher-throughput CFU counting methods would further improve the cost-effectiveness and speed of measuring the composition of the microbiome and could be applied to many other microbiology experiments.
Counting CFUs by serial dilution plating of a bacterial suspension on agar-based growth media is a standard method across the field of microbiology. The colonies that grow on the plates are then counted manually. The dilutions allow the researcher to select a density of colonies that is countable (e.g., ~100 CFUs per plate), meaning the colonies are not growing into one another and can be counted in a reasonable amount of time. Most microbiologists use essentially the same CFU counting method developed 140 years ago in the lab of Robert Koch, and for many applications, this method is still adequate. However, a problem arises when seeking to quantify a large number of samples. A single sample may require plating 1 to 10 serial dilutions of the sample to obtain countable CFUs, so experiments involving more than a few dozen samples become taxing. Various methods have been developed to increase the efficiency of CFU enumeration. Automated spiral plating eliminates the need for serial dilutions30, making only one plate necessary for CFU counting but increasing the time to plate the sample. Single plate-serial dilution spotting (SP-SDS) allows CFU estimations from fewer plates per sample31. These methods are an improvement on the traditional spread-plating method but still require handling and plating of bacterial samples singly and are, thus, not ideal for high throughput. Handling samples in 96-well plates and spot plating those 96 samples on rectangular agar plates greatly improves the throughput of samples19.
Microbiomes are typically composed of multiple strains and species. While species can often be distinguished by colony morphology or growth media, fluorescence can be employed to further distinguish different types of bacteria and their growth traits32. For instance, different genotypes of the same species can be labeled with different genetically-encoded fluorescent proteins. Plate imaging methods that incorporate fluorescence allow researchers to take advantage of these genetic techniques in CFU-based assays32. Incorporating fluorescence into high-throughput CFU counting methods would further enhance their utility.
Counting CFUs manually becomes cumbersome when there is a large number of samples. Automated counting of CFUs can be conducted by photographing the plate and processing the image using specialized software33. Sieuwerts et al. combined the improved plating efficiency of spot-plating with automated colony counting using conventional digital photography and ImageJ software19.
A high-throughput method to screen the phenotypes of specific microbe and host associations would aid studies of microbiome community assembly and the impact on host health and fitness. For studies of the Drosophila microbiome, a high-throughput microbiology platform would incorporate handling of fly samples in 96-well plate format, fly lysis without bacterial lysis, the efficiency of spot-plating, the ability to use fluorescence and distinguish multiple fluorophores, a controlled light environment for reproducible imaging of CFU plates, and a reliable automated colony counting software. This article describes a method optimized for the assay of CFUs in gnotobiotic flies, which is simple, fast, and automated. This protocol outlines a novel workflow combining the best of previously published methods and optimized for exploring the gut microbiome in Drosophila.
Protocol
1. Fly colonization
NOTE: This method is suitable for quantitative analysis of flies with a culturable gut microbiome by growth plating of CFUs. A detailed protocol for rearing gnotobiotic flies has been previously published12.
- Establish stable colonization by a commensal bacterial species.
- Prepare a fresh bacterial culture, pellet by centrifugation at 400 x g for 3 min at room temperature, and resuspend the cell pellet in PBS to an OD600 of 1.0. For this protocol, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (previously known as Lactobacillus plantarum) was grown overnight to an OD600 of 2.0.
- Pipette 100 µL onto the food in a fly vial (see Table of Materials). Spread evenly and allow the liquid to absorb for 15-30 min.
- Transfer 20 germ-free flies into this vial using the standard vial to vial flipping technique34. Each fly will eat a roughly equal quantity of the bacterial dose35. Alternatively, germ-free eggs can be added.
- Transfer the flies to fresh sterile food daily for 3 days. Do all this in a biosafety cabinet and use sterile technique (Figure 1A-1).
- Prior to measuring CFU load, transfer the flies to a vial containing sterile agar-water for 4 h to clear transient bacteria from the gut. The agar-water vials provide a source of moisture for the fly but no nutrition for the fly or bacteria on the surface. They are prepared in the same sterile fly vials as with standard food but contain only deionized water and 1.5% agar.
2. Homogenizing flies individually in a 96-well PCR plate
- Prepare bead beater plates in advance.
- Pour 0.5 µm glass beads (see Table of Materials) onto the bead measuring tray (3D printed with the help of Supplemental Coding File 1 S1-bead-measurer.stl). Spread the beads on the tray so that all the wells are full and level, and then brush off excess beads into a conical tube to recover them.
- Place a semi-skirted PCR plate (see Table of Materials) upside down on the measuring tray and align it with the wells by fitting it into the indentation on the measuring tray. Then, quickly flip it over to transfer the beads.
- Remove excess beads from the PCR plate surface and cover it with foil. Inspect the PCR plate to ensure that all the wells contain beads. Use a weigh scoop if required to add beads to a single well. If static electricity is causing beads to stick on the plate surfaces, wipe or spray the back of the measuring tray and PCR plate with 70% ethanol.
- Cover with aluminum foil. Many plates can be prepared in this way and then autoclaved and stored for later use. When ready for use, add 100 µL of PBS to each well using the 96-channel pipettor (see Table of Materials).
- Surface-sterilize the microbe-colonized flies (see step 1) with 70% ethanol before homogenization.
- Anesthetize the flies with 100% CO2 for 5 s. Transfer anesthetized flies from the vial into a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube using a small funnel (Figure 1A-2). In this study, 25 flies were typically added per tube.
- Immediately spray ~1 mL of 70% ethanol into the tube, close the tube and mix by inversion for 10 s. Then, aspirate the ethanol with a P1000 pipette, being careful not to aspirate any flies. Repeat once again with ethanol, then twice with sterile PBS (Figure 1A-3).
- After the final PBS wash, close the tube and, with the cap side down, tap it hard a few times on the bench so the flies go into the cap.
- Open the tube and dispense flies into the wells using forceps (Figure 1A-4). Place one fly in each well (Figure 1A-5). Keep the plate on ice while loading to keep the flies anesthetized.
- Seal the plate using Thermal Bond heat sealing foil (see Table of Materials).
- First, remove any stray beads that are close to the wells as these can cause leakage in the foil seal. Make sure the dull side of the foil is oriented down on the plate and the shiny side up toward the heat sealer. Press the heat sealer (see Table of Materials) down firmly for 5 s (Figure 1A-6). Burnish with the hand applicator (see Table of Materials) to secure the foil.
NOTE: Poor sealing is a cause of sample loss.
- First, remove any stray beads that are close to the wells as these can cause leakage in the foil seal. Make sure the dull side of the foil is oriented down on the plate and the shiny side up toward the heat sealer. Press the heat sealer (see Table of Materials) down firmly for 5 s (Figure 1A-6). Burnish with the hand applicator (see Table of Materials) to secure the foil.
- Secure the plate in the plate shaker. Homogenize for 5 min (Figure 1A-7). Spin down the bead plate for 30 s in a mini-plate spinner (see Table of Materials) at 350 x g to remove liquid from the sealing foil.
- Remove the foil while holding the plate so as not to splash droplets of fly homogenate out of the wells.
3. Serial dilution of fly homogenate and spotting onto CFU plates
- Place four rectangular MRS agar growth plates (see Table of Materials) in the biosafety cabinet and remove their lids. In this protocol, MRS agar was used for the growth of L. plantarum. Leave these plates to dry for at least 10 min (20 min if they are freshly poured or cold from storage).
NOTE: If the plates are wet, the droplets from the 96-well plate will run together and ruin the counts. - Prepare three dilution plates by adding 100 µL of PBS to each well of a sterile 96-well plate using a 96-channel pipettor. Load a rack of P20 tips onto the 96-channel pipettor.
- Make a 1:10 dilution by aspirating 11.1 µL of homogenate from the sample plate prepared in section 2 (Figure 1A-8). Be sure to draw from the middle of the wells rather than the bottom of the wells because the fly homogenate and glass beads will clog the pipettes. The beads sink, and the fly particulates float, leaving the middle layer mostly clear.
- Dispense the 11.1 µL into the first dilution plate, which already contains 100 µL of sterile PBS per well. Keep the dilution plate on the plate shaker for 10 s at 600 rpm. Mix again by pipetting up and down for five cycles. Transfer 11.1 µL from the first dilution plate to the second dilution plate, and repeat the mixing steps for the next two dilution plates.
- Perform dilution series plating as described below.
- Retrieve the growth plates from the biosafety cabinet.
- Starting with the most dilute plate, spot 2 µL from each well onto the agar plates using the 96-well pipettor (Figure 1A-9).
- Lower the pipettor head slowly onto the plate, taking care not to stab into the agar. Examine the plate carefully and ensure all the spots have been dispensed; if not, manually add 2 µL to the appropriate position. Check that the liquid spots quickly soak into the agar and do not run together.
- If the spots run together, dry a new set of fresh agar plates for a longer period and redo the spotting. If there are multiple plate types (e.g., different media or with antibiotics), spot those too. Dispense any remaining solution back into the dilution plate and proceed to the next higher concentration.
NOTE: When spotting dilutions, mix the next dilution five times to ensure that the contents of the pipette tips are cleared of the previous dilution. The dilution plates can be stored >8 h at 4 °C without affecting the colony counts35.
- Repeat the plating process as described in step 3.5 for the remaining dilution plates, progressing from most dilute to most concentrated until the plate with the original homogenate.
- When all the liquid has been absorbed into the agar, invert the plates and place them in the incubator (Figure 1A-10). For Lactiplantibacillus and Acetobacter from Drosophila, the optimal temperature is 30 °C on MRS media. Incubate until the colonies have reached optimal size: colonies are large enough to clearly see them but not so large that they merge or interfere with one another's growth (see the representative results for quantification of the optimal size).
NOTE: Optimal growth conditions are strain-dependent and must be determined empirically. For Lactiplantibacillus from Drosophila, the optimal time of incubation is 26 h to 30 h on MRS agar. For Acetobacter from Drosophila, the optimal time of incubation is 30 h to 48 h on MRS depending on the strain. - After incubation, store the plates at 4 °C if required until ready for counting.
4. Quantification of CFUs
- Quantify CFUs by photographing the plates and then counting the colonies using automated software, as detailed below. If the plates were stored at 4 °C, first allow them to reach room temperature so there is no condensation on the plates, which produces glare.
- Organize the plates in a logical sequence and keep them in that order while photographing — it makes it easier to name the files. Orient all the plates so that A1 is in the upper left corner for all the plates. It is recommended to label the A1 corner with a unique ID to ensure no mix up of the photos. Stack each dilution series in order.
- Remove the plate lid and place the plate on the stage with A1 oriented in the correct corner. Designs are included for the plate photo box (Supplemental File 1, Supplemental File 2), which is optimized for photographing these tray plates and includes lighting and filter options to image fluorescent colonies.
- Image the plates. Use the camera (see Table of Materials) with manual settings to achieve a consistent exposure level between plates. A long focal length setting is recommended to minimize perspective distortion. Capture the photo using a remote shutter to minimize blur from camera shake.
- Transfer the images to a computer and rename them, including the experiment name, the type of media, the dilution factor, and any other pertinent details. Some operating systems (see Table of Materials) have a useful batch renaming feature in Finder by right-clicking on a selection of files.
5. Automated colony counting using the Count-On-It suite (Supplemental File 3)
- Crop the images using the provided Croptacular plugin (Supplemental Coding File 2) for ImageJ. This plugin helps to divide the image into an orderly array of subregions (e.g., 8 x 12 for a 96-well plate). The subregions will be counted individually.
NOTE: A separate plugin for counting circular plates called Circus is described in the Supplemental Coding File 3 Circus_.ijm.- Organize the images to be processed for quantification into a folder. Choose filenames that distinguish the plates, as these filenames become column titles for each set of counts . Within this folder, make subfolders named "cropped" and "receipts" .
- Launch Croptacular, and click OK to start cropping.
NOTE:The default settings are displayed and are usually sufficient. Depending on the resolution of the image, the lighting, the spot size, etc., it can be helpful to adjust the base parameters. - If the image is already straight, simply press Space. Otherwise, straighten the image by drawing a line along an edge that should become horizontal. Redraw the line as many times as needed if the image still does not appear straightened.
- Next, draw a boundary box of the area for which counting is to be done. Adjust the size and proportion until all the spots are within their cells. Drag the cursor outside the boundary box to refresh the grid. When the grid looks good, press Space.
- Ensure that the next image automatically rotates to the same angle as the first one; the plugin assumes all the photos are aligned the same. If this is accurate, press Space to continue. Otherwise, straighten the image as before. The grid also recalls the same position as the previous image; adjust if necessary, and then press Space.
- Enumerate the colonies on the plates using the provided Count-On-It: Gridiron plugin for ImageJ (Supplemental Coding File 4). Detailed instructions for installing and using the plugin are included in Supplemental File 3.
- Launch Count-On-It > Gridiron. Use the same grid settings as with Croptacular. Users can batch an entire folder, analyze a single image, or start from the current image.
- Set the threshold based on an upper and a lower pixel intensity value. Make the threshold as stringent as possible while still selecting all the colonies. Ideally, there will be some space between the selected colonies, but the software is capable of segmenting the blobs to a degree. Click OK on the "Action Required" dialogue box when the threshold is satisfactory .
- To inspect the results, zoom in and look more closely at the colony counts. Clicking cancel will abort the plugin. Click OK to continue.
- On the first image, ensure that the option is given to proceed or return to the setup menu, for example, to change the minimum colony size. To proceed with the batch process, click OK. Then, select a folder to keep the receipts and results table. Use the "receipts" folder or create a new folder.
- After the first image, the next images will default to the same threshold as the previous settings. Click OK to use these settings or adjust the settings. If the photos are consistent and the setting is accurate, Click OK on the "Action Required" dialogue box.
NOTE: Once all the images in the batch are completed, the results table saves automatically in the same folder as the receipts. - Review the count receipts that are produced by the software and manually correct any counting errors. The ImageJ plug-in is statistically accurate, but errors do occur. Proof the receipts to examine outliers and identify miscounts. The software saves the CFU data as a .csv file in the same folder as the receipts.
- Analyze the data using the user-preferred software.
Results
Enumeration of CFUs in hundreds of individual flies in 96-well plate format using colonization assay
To understand the composition of many individual fly microbiomes, CFUs were measured using the accompanying protocol, which enabled identification of the species present, the percent of flies colonized, and the absolute abundance of bacteria in each fly. The reasons for the large observed individual-to-individual variation in microbiome composition are poorly understood, and quantifying the statistical distribution of colonization can help to study this variation36,37. To obtain a significant number of biological replicates, a high-throughput pipeline was developed for the quantification of microbe abundance in many individual flies using CFU counts (Figure 1A).
The final quantification of CFUs can be impacted by how flies are handled prior to analysis, for example, factors including surface sterilization, time since consumption of bacteria, and clearance of transient bacteria from the gut. First, focusing on the Drosophila commensal bacterial species L. plantarum (Lp; see Lp strain WF in Obadia et al.36), flies were fed a dose of ~105 CFUs of Lp and kept in groups of 25 flies per vial. These flies were either kept in the same vial for 3 days or transferred daily (Transferred) to fresh, sterile food (Figure 1B). Untransferred flies were then either washed in ethanol to remove surface bacteria (Washed) or not washed (Unwashed). Washing produced a non-significant reduction in the total CFUs measured (Figure 1B), indicating that under these highly-controlled inoculation conditions, the fly surface does not become significantly colonized by bacteria in 3 days. The other groups of flies were transferred every day to reduce the accumulation of bacteria from growth on food (Transferred); additionally, a group was transferred to fresh food for 4 h before sampling (Post-Transferred), or they were put in vials with only sterile agar-water for 4 h (Cleared) to allow transiently ingested microbes to clear from the gut. Each of these steps to provide more stringent colonization measurement produced a statistically significant reduction in the abundance of CFUs in the flies, with the exception of surface washing in ethanol. Transferring to sterile food (Post-Transferred) or agar-water (Cleared) for 4 h before measurement produced indistinguishable effects, indicating that transfer to sterile conditions 4 h prior to measurement reduces the bacterial load. This result is consistent with the interpretation that some gut bacteria in the fly gut are transient, while others are more stably associated35. The abundance of Lp ranged from 1 x 104.3 CFUs/fly in cleared flies to 1 x 104.9 CFUs in the unwashed flies (n = 724 flies).
Next, the same assay was conducted using Acetobacter indonesiensis (Ai), a gram-negative bacterium that colonizes the fly gut (Figure 1C; see strain Ai SB003 in Obadia et al.36). As with Lp-colonized flies, surface sterilization produced a non-significant reduction in CFUs. Likewise, daily transfer to sterile food significantly reduced the bacterial load, and transfer to sterile conditions for 4 h prior to homogenization produced a further reduction in bacterial load. The abundance of Ai ranged from 1 x 104.7 CFUs/fly in cleared flies to 1 x 105.0 CFUs in the unwashed flies (n = 528 flies). Thus, accurate quantification of gut bacteria depends upon the frequency of transfer, including on the day of transfer. Removing the external bacterial load by washing in ethanol had a non-significant effect, but more significant effects may be observed for different strains of bacteria or different culture conditions. These factors should be controlled experimentally.
The potential effect of the homogenization method on CFU counts was also tested. The flies were homogenized using a bead beater with 0.5 µm glass beads in 100 µL of PBS, which could reduce the viability of bacterial cells. First, a suspension of Lp bacteria from culture was prepared in PBS and then plated to count CFUs as a positive control. The same culture was placed into the bead beater plate and (i) homogenized with beads, (ii) homogenized with beads and a germ-free fly, or (iii) homogenized in PBS without beads (Figure 1D). Homogenization in beads when a fly was present did not significantly impact the abundance of viable cells in solution, whereas the homogenization of bacteria in the absence of a fly killed a significant number of bacterial cells. Homogenization in PBS without beads also significantly reduced the number of viable cells. Similarly, Ai viability was preserved when homogenized in the presence of a fly, while homogenization without a fly reduced the number of viable cells in solution (Figure 1E). These results indicate that the fly tissue protects the bacteria from being destroyed by the beads during homogenization. However, the experiments in Figure 1D and Figure 1E were performed with more than 108 CFUs per well. In practice, wells with ~106 cells per well or less were found to show little cell loss when beads were used without a fly. Cooling the plate on ice halfway through bead beating also improves cell viability. The significance of these results is that readers should be aware of these potential issues and design appropriate controls for their specific use case.
Accuracy of spot plating 96-well plates for high-throughput CFU quantification
Since the goal is to measure the CFU abundances for hundreds to thousands of individual flies, traditional spread plating methods are prohibitively time and material intensive. Spot plating is an effective and efficient method for CFU growth and enumeration19,31. The spot plating method uses a 96-channel pipettor to dispense 2 µL of bacterial suspension onto media prepared in rectangular tray plates (Figure 2A). Each spot represents the bacterial load of a single sample, so 96 flies can be analyzed with a single plate (Figure 2B). The accuracy of spot plating was compared with traditional plating by inoculating growth plates using the exact same 0.0001 OD suspension of Lp for both methods. The suspension was two-fold serially diluted five times in PBS. As a head-to-head comparison, 50 µL of the inoculum was spread onto individual round plates, or 2 µL spots were made on rectangular MRS plates. The plates were then incubated at 30 °C until the colonies were countable. The resulting CFU counts for each dilution were used to calculate the original concentration of the suspension and compared (Figure 2C). Round plates with 50-500 CFUs were counted as the control. No significant difference was observed between the high-throughput and traditional round plating methods.
As the density of colonies can affect their growth and quantification, the effect of CFU density on final counts was tested. Spots with 2 to 25 colonies per spot showed no difference in final count as compared with the traditional round plate method (Figure 2C). Spots with an average of 35 colonies produced results that skewed slightly lower than the control spread plates (Figure 2C; p = 0.0017). Close examination of the photographs of individual spots indicated that this skew was due to colonies overlapping in dense spots. Measurements based on spots with an average of 11 colonies per spot resulted in concentrations closest to those based on the spread plates (Figure 2C; Spread plates: mean = 1 x 104.4 CFUs; SD = 0.086 vs. spots with 11 average colonies: mean = 1 x 104.4 CFUs; SD = 0.12, p = 0.42, Welch's t-test).
Generating high-quality images for quantification using a specialized photography platform with either white light or fluorescence
High-throughput spot-plating naturally generates a large number of target areas, which must be counted accurately. Quality photographs can be used to document the data and to facilitate the counting of CFUs. A robust and straightforward photography platform was developed using commercially available materials (Figure 3A). A digital camera was attached to a bracket on top of a custom-constructed light box, called FluoroBox, and was pointed directly down, perpendicular to the center of the plate. A colored emission filter was optionally positioned in front of the lens using a filter slider. A light shield prevented lens flare by blocking direct light from the LED strips below. LED strips illuminated the plate from the sides, rather than above, to prevent glare on the plate. In addition to white light, single-color blue and green LEDs were used to excite green and red fluorescent proteins, respectively. The plate was held in place by a plate holder on the drawer, and the drawer was equipped with drawer sliders to make inserting the plate easy. Complete designs are available in Supplemental File 1 and Supplemental File 2.
A photo of a spot plate of Lp colonies was taken using white light LEDs and a digital camera to aid in counting colonies and distinguishing different colors and morphologies (Figure 3B). To validate that the lighting intensity was even, the background intensity of the agar was measured across different regions of a plate photograph (Figure 3C). To demonstrate that the colonies can be clearly distinguished from the background, the intensity across the diameter of 10 different colonies on different parts of the plate was measured and found to be approximately ~300% higher than background (Figure 3C). The plate was inoculated with Lp with an mCherry fluorescent protein-expressing plasmid, as well as some Lp that did not contain the plasmid, so colonies were either mCherry-positive or mCherry-negative. To distinguish these two types of colonies, the plate was photographed using the same camera with green LED light (515-525 nm) and a red filter (Tiffen #29), causing mCherry-positive colonies to fluoresce (Figure 3D). The difference in intensity between mCherry-positive and mCherry-negative was quantified by measuring the intensity across a sample of colonies (n = 10 colonies). mCherry-positive colonies were ~1,000% higher intensity than mCherry-negative (Figure 3E). Colonies of Ai expressing GFP and colonies of Ai expressing no fluorescence were photographed using blue LED lights (465-475 nm) and a green filter (Tiffen #58) (Figure 3F). GFP-positive colonies showed 200% higher intensity than GFP-negative (Figure 3G).
Automated counting of CFUs on spot plates using the custom ImageJ plug-in Count-On-It
Photos alone aid in counting colonies (e.g., by storing the data, sharing the data, zooming in, marking an overlay, separating colors, etc.). However, the act of manually counting and organizing the results of hundreds of spots can be tedious, time-consuming, and prone to human-to-human differences in final counts. To speed up the counting process and standardize the reproducibility of counts, a specialized ImageJ plug-in called Count-On-It (Figure 4A) was developed. This plug-in enables accurate semi-automated counting of CFUs on agar plates. The user prepares images for counting by first cropping and straightening them using the additional Croptacular plug-in. The photos can optionally be batch processed, and the threshold can be adjusted for each plate. Several other options let the user increase the accuracy of plate counting, including adjusting the light wavelengths (RGB images), setting a range of colony size (in pixels), changing the maximum aspect ratio, and customizing the dimensions of the active selection grid. Count-On-It outputs a table of results with each plate represented as a column of CFU counts. It also generates a photo receipt showing an overlay to visually document its counting results and aid in manual error correction (Figure 4B). While errors do occur, when the number of colonies counted manually was compared with the number of colonies counted using this plug-in (Figure 4C), the relationship was generally equivalent, with linear regression between the manual and automated counts showing a slope of 0.95 with over 90% accuracy (R2 = 0.93), although the error increased when the number of colonies exceeded 20.
Count-On-It can also be used to separately count fluorescent colonies using the fluorescence feature of the FluoroBox. mCherry-positive colony counts (Figure 4D) by software plug-in versus manual had an R2 of 0.92 (Figure 4E). Similarly, GFP-positive colonies (Figure 4F) counted with software plug-in versus manual had an R2 of 0.90 (Figure 4G). Fluorescent versus non-fluorescent colonies can be distinguished within a single sample, and colony size and shape can additionally be used to distinguish separate subpopulations (Figure 4H-K). The photo receipts provide a record that allows the user to quickly check the accuracy of the counts and manually correct errors. In Figure 4C,E,G,I,K, the photo receipts have not been used to improve the count accuracy so that readers can see the raw output of the method. Cases such as in Figure 4G, where a manual count of 1 yielded an automated count of 21, can quickly be detected using the photo receipts. In this case, glare on the edge of the plate created blobs that were counted as colonies. For each use case, the optimal settings for the software plug-in need to be determined before high throughput counting.

Figure 1: The colonization assay measures CFUs in hundreds of individual flies using a 96-well plate format. (A) Pictorial overview of the colonization assay and high-throughput quantification method used as described in the protocol section. (B) Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (Lp) abundance in flies following the colonization assay was measured under varying conditions using the high-throughput CFU quantification method. Flies were kept in the same vial for 3 days and then homogenized and plated (Unwashed), washed in ethanol before plating (Washed), both washed and transferred every day (Transferred), transferred daily then kept on sterile food before plating (Post-Transferred), or kept in vials with only water for 4 h (Cleared) (n = 724 flies total, 3 biological replicates and ~72 flies total per treatment). (C) The same assay as in (B) was conducted using Acetobacter indonesiensis (Ai) (n = 528 flies). (D) Lp bacterial suspension was prepared in PBS and then plated to count CFUs or first homogenized by bead beating, bead-beaten in combination with a germ-free (GF) fly, or shaken on the bead beater without beads or a fly (n = 236 sample wells). (E) Ai viability post homogenization was tested in the same way as in (D) (n = 282 sample wells). Statistical significance for panels (B-E) was computed using a Kruskal-Wallis test followed by pairwise Wilcoxon rank-sum tests with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons correction. Box gives interquartile range. Line indicates median. Whiskers give total range. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
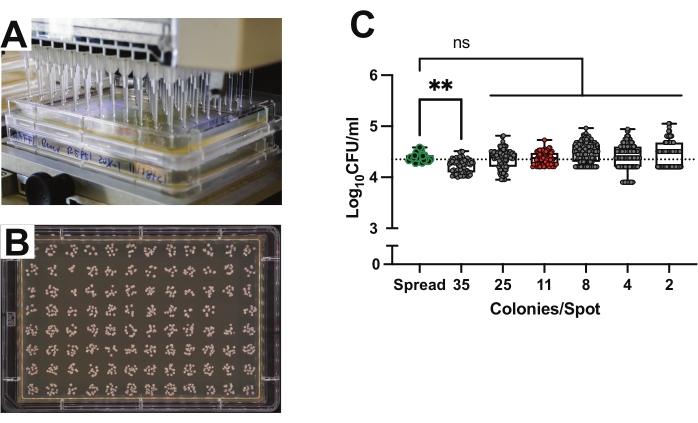
Figure 2: Accuracy of spot plating 96-well plates for high-throughput CFU quantification. (A) Spot-plating using a 96-channel pipettor to dispense 2 µL onto media prepared in rectangular tray plates. (B) MRS-agar growth plate with 96 spots of Lp colonies. (C) Concentration of Lp suspension based on CFU counts from traditional round plates (n = 24 plates) compared to concentration based on CFU counts from spot plates (n = 680 spots) serially diluted and arranged by average colony count per spot (~48 spots for each single dilution factor for three replicate plates were counted). Each data point represents the exact colonies per spot, while each column represents the average colonies for that dilution. Horizontal dotted line indicates the calculated CFU count of the culture that was plated. Green outlined points highlight the traditional round plate counts. Red-filled points highlight the optimal colony density of 11 CFUs per 2 µL spot. Statistical significance was computed using ordinary one-way ANOVA comparing the mean of each column against the mean of the spread plate control column with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons correction. Box gives interquartile range. Line indicates median. Whiskers give total range. **p < 0.01. ns = not significant. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 3: A photography platform produces quantifiable images of plates using white light or fluorescence. (A) Overview of the FluoroBox design. (B) Photo of a spot plate of Lp colonies using white light. (C) Intensity profile of single colonies under white light compared to the intensity of the background (BKG) (n = 10 colonies, dashed line represents standard deviation). (D) Photo of the same spot plate as in (B), using single-color green lights and the red filter to select for mCherry-positive Lp colonies. (E) Intensity profile of single colonies illustrating the difference between colonies with and without mCherry emission. (F) Photo of a spot plate containing Ai colonies, some of which have a GFP label. (G) Intensity profile of single colonies illustrating the difference between GFP-negative and GFP-positive colonies. E, F, G: n = 10 colonies for each plot. Colony diameters are approximately 1.5 mm. Dashed line is SD. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
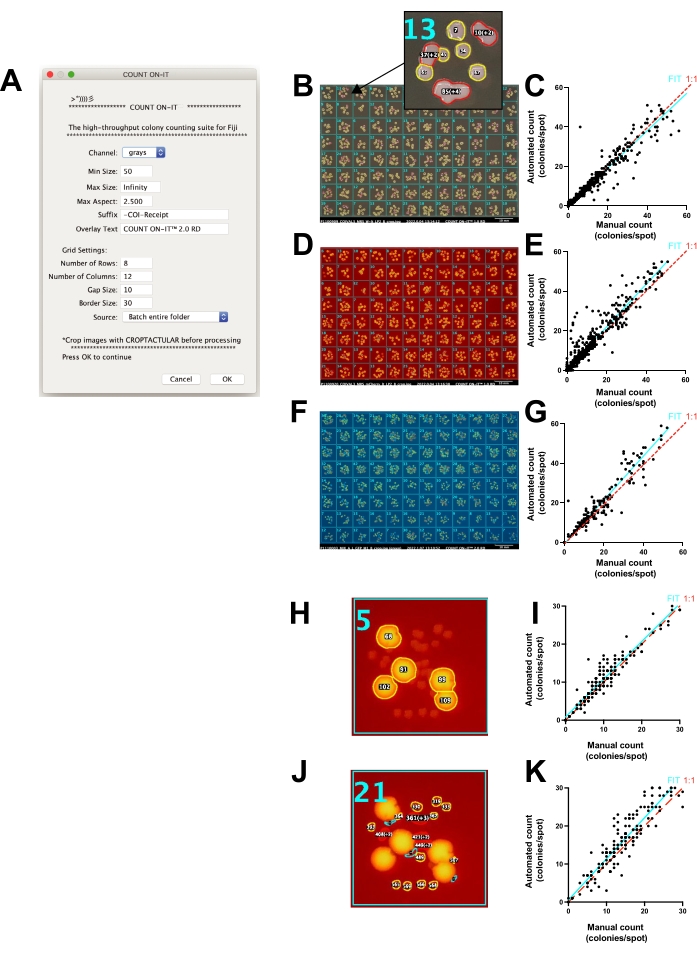
Figure 4: Accurate counting of spot plates by the Count-On-It ImageJ plug-in. (A) Screenshot of the plug-in setup window. (B) The plug-in generates a receipt to document counting and aid in error correction. Inset: Overlay with the number of colonies counted for each spot region; the yellow outline indicates that a single colony was counted and red that multiple colonies were counted. (C) Plot showing the number of colonies manually counted compared with the number of colonies counted using the plug-in (automated) when a white light image was used, where each point on the graph represents a single spot counted manually or automatically (slope of fit = 0.95, cyan line; 1:1 line is dotted red; R2 = 0.93, Pearson's coefficient of correlation, p < 0.0001). (D) Photo receipt image from the plug-in when mCherry-positive colonies were selected using the fluorescence feature of the photo box. (E) Plot showing the number of mCherry-positive colonies counted using manual compared to automated method when red fluorescence was used (slope of fit = 1.1, cyan line; 1:1 line is dotted red; R2 = 0.92, Pearson's coefficient of correlation, p < 0.0001). Note that outliers and errors have not been corrected using the analysis receipts for E,G,I,K. (F) Photo receipt image from the plug-in when GFP-positive colonies were selected using the green fluorescence feature of the photo box and selecting the green channel with the plug-in. (G) Plot showing the number of GFP-positive colonies counted using manual compared to automated method when green fluorescence lighting was used (slope of fit = 1.1, cyan line; 1:1 line is dotted red; R2 = 0.90, Pearson coefficient of correlation, p < 0.0001). (H) mCherry-positive colonies selected from mixed colony morphologies using a high fluorescence threshold in the plug-in. (I) Plot showing the number of mCherry-positive colonies counted using manual compared to automated method when red fluorescence lighting was used (slope of fit = 0.99; R2 = 0.91, Pearson's coefficient of correlation, p < 0.0001). (J) mCherry-negative colonies selected from mixed colony morphologies using a low fluorescence threshold. (K) Plot showing the number of mCherry-negative colonies counted using manual compared to automated method when the intensity threshold was set to select non-fluorescent colonies (slope of fit = 1.1; R2 = 0.85, Pearson's coefficient of correlation, p < 0.0001). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Supplemental File 1: FluoroBox assembly instructions. This file walks the reader step-by-step through the construction of the controlled lighting box used in the video. Please click here to download this File.
Supplemental File 2: FluoroBox acrylic laser cut. This file provides a cut template to laser cut the acrylic pieces for the controlled lighting box. The file can be sent to a laser cut acrylic vendor. See the Table of Materials for the vendor used in this protocol. Please click here to download this File.
Supplemental File 3: Software instructions. This file walks the reader step-by-step through the installation and usage of the Croptacular and Count-On-It software provided with this protocol. Please click here to download this File.
Supplemental Coding File 1: 3D printing code for bead measuring tray (S1-bead-measurer.stl). Please click here to download this File.
Supplemental Coding File 2: Rectangular plate photo cropper ImageJ plugin (Croptacular_.ijm). Please click here to download this File.
Supplemental Coding File 3: Round plate photo cropper plugin (Circus_.ijm). Please click here to download this File.
Supplemental Coding File 4: Rectangular plate 96 spot counter plugin (Gridiron_.ijm). Please click here to download this File.
Discussion
The detailed techniques presented here enable a >100-fold increase in the number of samples that can be evaluated in a CFU counting experiment. This technique advances existing methods for microbiome experiments in Drosophila12,35,36 by using the 96-well plate format to assay individual flies. Furthermore, it applies a more efficient spot plating method19,31 and an automated workflow with a photography and colony counting platform. The significance of this method for Drosophila is to standardize experiments to the 96-well plate format, which enables the simultaneous handling of a large number of biological replicates with automation to achieve high-throughput quantification of CFUs.
The 96-well platform shows that increased frequency of transfer and the "clearing" of transient bacteria causes a significant reduction in both the mean abundance and the variation between samples (Figure 1B,C), demonstrating the stringency of this improved protocol. One limitation of co-housing flies is the horizontal transfer of bacteria between flies. A proposed solution is to keep flies individually in a 96-well plate format, such as the Whole Animal Feeding Flat38.
Although a significant reduction in bacterial load was not observed when flies were washed in ethanol, these flies had only been kept in the presence of external bacteria for 3 days. Housing for longer time periods could allow a greater bacterial load to accumulate39. Therefore, washing in ethanol is still recommended.
Transferring flies into the 96-well plate is the critical first step for setting up the workflow (Figure 1A). Once the flies are washed, they are distributed into the wells one at a time. A plate chart is useful at this stage to note which conditions are present in each well and add any notes such as "fly was lost". Homogenization is another critical step with some important caveats. Bacteria survive the homogenization process when in the presence of a fly (Figure 1D,E), and presumably, this principle is also true when the bacteria are inside the fly's gut. However, bacteria are also killed when they are homogenized in bead beater plates alone, demonstrating that the homogenization can kill the bacterial cells in certain circumstances, a limitation which may be important if one is homogenizing dissected guts, for example. Notably, the loss of CFUs when homogenizing is dependent on the number of CFUs in the sample, and the loss is minimal when ~105 CFUs per well are used. Further preservation of CFUs can be achieved by stopping homogenization halfway through and cooling the plate on ice.
Homogenization was performed for 5 min in this protocol based on control experiments where a known number of CFUs were mixed with a germ-free fly, and this worked empirically for fly bacteria. Less beating caused larger fly parts to be present, which interferes with pipetting, while significantly longer homogenization times of ~10 min made CFU counts more variable. The smaller volume and angled shape of conical plate wells were observed to reduce the efficiency of bead beating as compared to cylindrical 2 mL tubes. Many variations on this general approach are possible, including which bacterial strains, which bead beating container, which beads, and which fly genotype are used. Individual user cases need to use positive controls to establish their approach.
The spot plating method was employed in a specific way: 1:2 dilutions of L. plantarum WF in PBS were spotted onto MRS plates and incubated at 30 °C for 2 days (shorter incubation times may be implemented to generate smaller colony sizes). The method requires some up-front investment in equipment, primarily the bead beater and the 96-channel pipettor (Figure 2A), which is necessary for both the dilution series and spot plating. However, less expensive options are available, including a 96-well plate replicator with slotted pins. The dilution series is a critical step that affects the accuracy of the CFU counting results. In terms of failure modes, it is possible to clog the pipette tips with fly parts or glass beads and for the pipette tips to not seal properly onto the pipettor or to fail for some other reason. All these problems result in undercounting of the affected wells and should be monitored. Adequate mixing at each step of the dilution series is also crucial. Each dilution should be mixed thoroughly either by putting the plate on a plate shaker or by pipetting up and down 15-20 times, which also serves to rinse the tips. By spotting from the most dilute to least dilute plate, the tips can be reused for the whole dilution series. With 1:2 dilutions, counting is accurate over a range of 2-25 colonies, spanning an order of magnitude (Figure 2C). Therefore, 1:10 dilutions save time and materials. Another variable that can be taken advantage of is incubation time, which can be adjusted to produce smaller colonies and, thus, increase the range of countable spots by preventing the merging of adjacent colonies.
A quality photo of the plate is essential as it becomes the raw source data from which the CFUs are analyzed and can be archived indefinitely. The FluoroBox is designed to produce photos of the plates with uniform light intensity, which minimizes glare on the agar surface. Additionally, the design is capable of selectively photographing fluorescent colonies using single-color LED lights and colored photo filters (Figure 3A). The construction of a setup like the FluoroBox, with controlled lighting and camera settings, can greatly increase the reproducibility of CFU images, which is important for automated analysis. Colony morphologies, fluorescence intensity, and the effects of time or density on colony growth are just a few of the properties that can be analyzed using the photographs. The photo box can be constructed without the color filters and single-color lights if no fluorescent bacteria are used, reducing the cost and complexity. Different excitation lights and emission filters could be substituted for the ones recommended here if a different fluorophore is used by a lab. A camera that is connected to a tablet over WiFi using an app is useful both for the automated shutter feature to prevent shaking and for ease of data transfer. Images can be transferred to the tablet and then to a laptop using wireless file transfer software. Recommended cameras with these capabilities are indicated in the Table of Materials.
Count-On-It is a plug-in written in ImageJ. The automated CFU counting software segments the plate image into a uniform 96-well grid, counts the colonies in each grid cell, and batches the results into a simple spreadsheet. As there is always variation in the position of the spot grid on the plate and in the photo, the user must manually conform the grid to the photo using the Croptacular plug-in. This also helps exclude areas near the plate edge, which have glare. Setting the threshold is key to getting the most accurate CFU count from the image. If the threshold is set too high, the colonies will merge; if the threshold is set too low, the colonies will be excluded. Once the threshold is set, the macro applies gaussian blur to soften the edges and reduce aliasing, the watershed filter divides overlapping colonies, and the blobs are counted using analyze particles.
Sometimes, the density of colonies is too high in a particular spot. Count-On-It provides a way to deal with this. To estimate the number of colonies in a grid cell with partially merged colonies, first the average area of a circular blob from the entire plate is taken as Cavg. Then, the area of blob A1 is divided by the average area of a circular blob A1/Cavg. This number is rounded to the nearest integer, and that is the estimate for how many colonies are in a blob. This function is one reason why the threshold can influence the counting results: the relative average colony area versus a merged blob area will be different depending on how the threshold affected merged blobs.
The methods presented have several limitations. These include the need for equipment to dispense liquid media accurately from 96-well plates. This equipment, either a 96-channel pipettor or a slotted replicator pin tool, can cost thousands of dollars to obtain. Cheaper alternatives exist but are less accurate. Automated counting via Count-On-It also presents some limitations. For instance, if two colony types in a mixed population were delimited based on size alone, blob counting would not be able to assign colonies to the correct type. In this case, spots with blobs would need to be eliminated from counts. Further differentiation of colonies based on morphology would be a valuable extension of the method that is not currently implemented. The use of selective media including strain-specific nutrients and antibiotics simplifies the need for complex image analysis.
Maintaining fruit fly experiments in 96-well plates multiplies the number of samples and conditions that can be tested in a single experiment and can facilitate high-throughput screens in Drosophila-bacteria association phenotypes. We envision that this method can be extended by using selective media to differentiate many bacterial strains in complex mixtures. The method is not limited to the study of the fly microbiome. Quantification of CFUs is common in many applications of microbiology, from coliform counts in drinking water to the identification of pathogens. The CFU plating system presented here enables high-throughput screens, as well as automated acquisition, processing, storage, and delivery of results.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Dr. Kerwyn Casey Huang, Dr. Andrés Aranda-Díaz, Ted Cooper, and members of the Ludington lab gave valuable input on the development of this protocol. Funding was provided by NSF IOS grant 2032985, NIH grant DP5OD017851, a Carnegie Institution of Canada grant, and the Carnegie Institute for Science's Endowment.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Bead beating and spot plating | |||
| Fly vials | Genesee | 32-121 | autoclavable |
| Fly vial stoppers | Genesee | 59-201 | autoclavable |
| Hand Applicator | 3M | 3M PA1 | |
| Heat Sealer | Eppendorf | 5390 | |
| Mini-Beadbeater 96 | BioSpec | 1001 | |
| Mini-BeadBeater Glass Mill Beads, 0.5 mm | BioSpec | 11079105 | |
| MPS 1000 Mini PCR Plate Spinner | Labnet | LI-CF-P1000 | |
| Rainin BenchSmart 96 semi-automated pipettor | Mettler Toledo | 30296705 | Less expensive options available, including slotted 96 well pin tool from VP Scientific |
| TempPlate semi-skirted 96-well PCR plate, straight skirt, natural | USA scientific | 1402-9220 | Must be polypropylene for heat sealer |
| Thermal Bond Heat Seal Foil | 4titude | 4ti-0591 | Keep sterile |
| Tray Plate,128 x 85 mm, Polystyrene, Sterile | SPL Life Sciences | 31001 | For making rectangular agar plates |
| Photobox construction | |||
| ¼”-20 X ½” Bolts (X2) | Amazon | ASIN: B07BP1WR3H | To attach the camera bracket. Brand not important. Any 1/4"-20 1/2" bolt works. |
| ¼”-20 x ½” Connector Nut | Amazon | UPC: 799862376780 | AKA cap nut or connector bolt. This is for attaching the rubber bands on the plate holder. Brand not important. |
| ¼”-20 x ¾” bolts (X3) | Amazon | ASIN: B003QZSZY4 | For the plate holder. Brand not important. |
| 1/8” x ½” washer | Amazon | UPC: 611982484599 | Washer for the cap nuts on outside of box. Brand not important. Spray paint black before attaching to blend with the acrylic. |
| 18 Gauge Wire - Two Conductor Power Wire - 18 AWG Power Wire – 10ft | Superbrightleds.com | WP18-2 | |
| 22-10 AWG Red Wire Nut - WN-R2210 – Quantity 4 | Superbrightleds.com | WN-R2210 | |
| 22-18 AWG 3/16in Female Push On Connector - 22-18 AWG – Quantity 3 | Superbrightleds.com | SCFP-2218 | |
| 4" Solderless Clamp-On Jumper Connector - 8mm Single Color LED Strip Lights - Quantity 3 | Superbrightleds.com | SBL-MA2P-8-2 | |
| 4" Solderless Clamp-On Pigtail Adaptor - 8mm Single Color LED Strip Lights – Quantity 3 | Superbrightleds.com | SBL-MA2P-8-1 | |
| 6” drawer handle | Amazon | ASIN: B07Z331P99 | Any drawer handle should work. |
| 6” Drawer slides | Btibpse | UPC: 712243424979 | Trim the soft close rubber stoppers on the drawer sliders. |
| 8-32 x ½” Cap Nuts (x4) | Amazon | ASIN: B00HYLZB98 | Attaches drawer slide bolts on outside of box. Brand not important. Nylon won't damage the acrylic. Spray paint black before attaching to blend with the acrylic. |
| 8-32 x ½” Nylon Bolts (x4) | Amazon | ASIN: B07KX9T7NF | To attach drawer slides. Brand not important. Any bolt or machine screw meeting the specifications works. Nylon won't damage the acrylic and allows you to cut the bolt flush with the nut. Spray paint black before attaching to blend with the acrylic. |
| Acrylic Glue | SCIGRIP | Ean: 7844908489337 | SCIGRIP Weld-On #4 Adhesive, Pint and Weld-On Applicator Bottle with Needle |
| Black Cable Ties - 10 Pack - 4 Inch Long | Superbrightleds.com | CT-B04-10 | |
| Camera L-Bracket | WLPREOE, Vikerer, Unbranded | ASIN: B09X46YKQZ | The bracket should be "reversed" from its intended configuration so that the camera is on the "outside" of the L. Some brackets come in two pieces and allow for this alternate configuration, some don't, you'll need one that can be flipped. Also should have 1/4" holes for attachment. WLPREOE, Vikerer, Unbranded. Amazon Serial Identification Number given as an example. |
| Canon T series camera for tethering option OR | Canon, Panasonic, Sony, Nikon, etc.. | 1894C002 | The Canon Ti series cameras are a good option and can tether to a computer. Use with the 18-55mm standard kit lens. Used options are recommended from the Canon T5 to T7 (current model). |
| Custom Length Single Color LED Strip Light - Eco Series Tape Light - 24V - IP20 - 250 lm/ft - Blue - 2 meters | Superbrightleds.com | STN-BBLU-B6A-08C1M-24V | |
| Custom Length Single Color LED Strip Light - Eco Series Tape Light - 24V - IP20 - 250 lm/ft - Green – 2 meters | Superbrightleds.com | STN-BGRE-B6A-08C1M-24V | |
| Custom Length Single Color LED Strip Light - Eco Series Tape Light - 24V - IP20 - 250 lm/ft - Natural White 4000K – 2 meters | Superbrightleds.com | STN-A40K80-B6A-08C1M-24V | |
| Drill with ¼”, 1/8” drill bits | Black & Decker | BDCDD12PK | Brand not important. |
| Flat Black Spray Paint, 2X Ultra-Matte | Rustoleum | 331182 | Paint the interior of everything FLAT black. Brand not important. |
| Laser Cut Acrylic Walls | Big Blue Saw | www.bigbluesaw.com | Use the attached PDF, delete all cutouts in the top piece except desired hole for camera |
| Mean Well LED Switching Power Supply - LPV Series 20-100W Single Output LED Power Supply - 24V DC - 20 Watt | Superbrightleds.com | LPV-20-24 | |
| Panasonic ZS100 for wifi connection to a phone, tablet, or computer | Canon, Panasonic, Sony, Nikon, etc. | DMC-ZS100K | Panasonic cameras can be wirelessly connected to a computer for data transfer and remote shutter options. Used options are good. |
| Quick Release Plate | Neewer Aluminium 50mm Quick Release Plate QR Clamp 3/8-inch with 1/4-inch | ASIN: B07417F21D | Add this to the bracket so the camera can be easily removed for changing color filters. Amazon Serial Identification Number given as an example. |
| Rubber Bands, Assorted sizes | BAZIC Products | Alliance Rubber 26649 | Rubber bands go on the plate holder. Brand not important. |
| Screw/Adhesive Cable Tie Mounting Bases - 3/4 inch base – Quantity 4 | Superbrightleds.com | CTMB-20 | |
| SPST Round Rocker Switch - No LED – Quantity 3 | Superbrightleds.com | RRS-SP | |
| Tiffen 29 Filter (Red) 72 mm | Tiffen | 72R29 | |
| Tiffen 58 Filter (Green) 72 mm | Tiffen | 7258 | |
| Software | |||
| ImageJ64 | https://imagej.net/downloads | N/A | Free. Just cite: Schindelin, J., Arganda-Carreras, I., Frise, E., Kaynig, V., Longair, M., Pietzsch, T., … Cardona, A. (2012). Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nature Methods, 9(7), 676–682. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2019 |
| MacOSX | Apple | N/A | Has a useful batch rename feature in Finder to rename a group of photos to facilitate organizing and analyzing in Count-on-it. |
| Unix | BSD | N/A | 64 bit |
| Windows | Microsoft | N/A | 64 bit |
References
- McFall-Ngai, M., et al. Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110 (9), 3229-3236 (2013).
- Shepherd, E. S., Deloache, W. C., Pruss, K. M., Whitaker, W. R., Sonnenburg, J. L. An exclusive metabolic niche enables strain engraftment in the gut microbiota. Nature. 557 (7705), 434-438 (2018).
- Taur, Y., et al. Intestinal domination and the risk of bacteremia in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 55 (7), 905-914 (2012).
- Buffie, C. G., et al. Precision microbiome reconstitution restores bile acid mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile. Nature. 517 (7533), 205-208 (2015).
- Callahan, B. J., et al. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nature Methods. 13 (7), 581-583 (2016).
- Vandeputte, D., et al. Temporal variability in quantitative human gut microbiome profiles and implications for clinical research. Nature Communications. 12 (1), 6740 (2021).
- D'hoe, K., et al. Integrated culturing, modeling and transcriptomics uncovers complex interactions and emergent behavior in a three-species synthetic gut community. eLife. 7, 2892 (2018).
- Ludington, W. B., Ja, W. W. Drosophila as a model for the gut microbiome. PLoS Pathogens. 16 (4), 1008398 (2020).
- Chandler, J. A., Lang, J. M., Bhatnagar, S., Eisen, J. A., Kopp, A. Bacterial communities of diverse Drosophila species: Ecological context of a host-microbe model system. PLoS Genetics. 7 (9), 1002272 (2011).
- Pais, I. S., Valente, R. S., Sporniak, M., Teixeira, L. Drosophila melanogaster establishes a species-specific mutualistic interaction with stable gut-colonizing bacteria. PLoS Biology. 16 (7), 2005710 (2018).
- Adair, K. L., et al. Host determinants of among-species variation in microbiome composition in drosophilid flies. The ISME Journal. 14, 217-229 (2019).
- Koyle, M. L., et al. Rearing the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster under axenic and gnotobiotic conditions. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (113), e54219 (2016).
- Lesperance, D. N. A., Broderick, N. A. Microbiomes as modulators of Drosophila melanogaster homeostasis and disease. Current Opinion in Insect Science. 39, 84-90 (2020).
- Grenier, T., Leulier, F. How commensal microbes shape the physiology of Drosophila melanogaster. Current Opinion in Insect Science. 41, 92-99 (2020).
- Broderick, N. A., Lemaitre, B. Gut-associated microbes of Drosophila melanogaster. Gut Microbes. 3 (4), 307-321 (2012).
- Tkacz, A., Hortala, M., Poole, P. S. Absolute quantitation of microbiota abundance in environmental samples. Microbiome. 6 (1), 110 (2018).
- Téfit, M. A., Gillet, B., Joncour, P., Hughes, S., Leulier, F. Stable association of a Drosophila-derived microbiota with its animal partner and the nutritional environment throughout a fly population's life cycle. Journal of Insect Physiology. 106, 2-12 (2017).
- Ryu, J. -. H., et al. Innate immune homeostasis by the homeobox gene caudal and commensal-gut mutualism in Drosophila. Science. 319 (5864), 777-782 (2008).
- Sieuwerts, S., De Bok, F. A. M., Mols, E., De Vos, W. M., Van Hylckama Vlieg, J. E. T. A simple and fast method for determining colony forming units. Letters in Applied Microbiology. 47 (4), 275-278 (2008).
- Eckburg, P. B., et al. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science. 308 (5728), 1635-1638 (2005).
- Newell, P. D., Douglas, A. E. Interspecies interactions determine the impact of the gut microbiota on nutrient allocation in Drosophila melanogaster. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 80 (2), 788-796 (2013).
- Costello, E. K., et al. Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time. Science. 326 (5960), 1694-1697 (2009).
- Fadrosh, D. W., et al. An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome. 2 (1), 6 (2014).
- Vega, N. M., Ludington, W. B. From a parts list to assembly instructions and an operating manual: How small host models can re-write microbiome theory. Current Opinion in Microbiology. 64, 146-151 (2021).
- Samuel, B. S., Rowedder, H., Braendle, C., Félix, M. -. A., Ruvkun, G. Caenorhabditis elegans responses to bacteria from its natural habitats. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (27), 3941-3949 (2016).
- Berg, M., et al. Assembly of the Caenorhabditis elegans gut microbiota from diverse soil microbial environments. The ISME Journal. 10, 1998-2009 (2016).
- Sundarraman, D., et al. Higher-order interactions dampen pairwise competition in the zebrafish gut microbiome. mBio. 11 (5), 1-15 (2020).
- Douglas, A. E. Simple animal models for microbiome research. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 17, 764-775 (2019).
- Friedman, J., Higgins, L. M., Gore, J. Community structure follows simple assembly rules in microbial microcosms. Nature Ecology & Evolution. 1, 0109 (2017).
- Gilchrist, J. E., Campbell, J. E., Donnelly, C. B., Peeler, J. T., Delaney, J. M. Spiral plate method for bacterial determination. Applied Microbiology. 25 (2), 244-252 (1973).
- Thomas, P., Sekhar, A. C., Upreti, R., Mujawar, M. M., Pasha, S. S. Optimization of single plate-serial dilution spotting (SP-SDS) with sample anchoring as an assured method for bacterial and yeast cfu enumeration and single colony isolation from diverse samples. Biotechnology Reports. 8, 45-55 (2015).
- Nuñez, I., et al. Low cost and open source multi-fluorescence imaging system for teaching and research in biology and bioengineering. PLoS One. 12 (11), 0187163 (2017).
- Putman, M., Burton, R., Nahm, M. H. Simplified method to automatically count bacterial colony forming unit. Journal of Immunological Methods. 302 (1-2), 99-102 (2005).
- Ashburner, M. . Drosophila. A Laboratory Handbook. , (1989).
- Dodge, R., et al. A gut commensal niche regulates stable association of a multispecies microbiota. bioRxiv. , (2021).
- Obadia, B., et al. Probabilistic invasion underlies natural gut microbiome stability. Current Biology. 27 (13), 1999-2006 (2017).
- Vega, N. M., Gore, J. Stochastic assembly produces heterogeneous communities in the Caenorhabditis elegans intestine. PLoS Biology. 15 (3), 2000633 (2017).
- Jaime, M., et al. The high-throughput WAFFL system for treating and monitoring individual Drosophila melanogaster adults. bioRxiv. , (2018).
- Ren, C., Webster, P., Finkel, S. E., Tower, J. Increased internal and external bacterial load during Drosophila aging without life-span trade-off. Cell Metabolism. 6 (2), 144-152 (2007).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved