A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Lipopolysaccharide Infusion as a Porcine Endotoxemic Shock Model
In This Article
Summary
We provide a protocol for an experimental endotoxemic shock model in pigs by infusion of lipopolysaccharide.
Abstract
Sepsis and septic shock are frequently encountered in patients treated in intensive care units (ICUs) and are among the leading causes of death in these patients. It is caused by a dysregulated immune response to an infection. Even with optimized treatment, mortality rates remain high, which makes further insights into the pathophysiology and new treatment options necessary. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a component of the cell membrane of gram-negative bacteria, which are often responsible for infections causing sepsis and septic shock.
The severity and high mortality of sepsis and septic shock make standardized experimental studies in humans impossible. Thus, an animal model is needed for further studies. The pig is especially well suited for this purpose as it closely resembles humans in anatomy, physiology, and size.
This protocol provides an experimental model for endotoxemic shock in pigs by LPS infusion. We were able to reliably induce changes frequently observed in septic shock patients, including hemodynamic instability, respiratory failure, and acidosis. This will allow researchers to gain valuable insight into this highly relevant condition and evaluate new therapeutic approaches in an experimental setting.
Introduction
Sepsis and septic shock rank among the leading causes of mortality in patients receiving intensive care treatment1,2,3. Sepsis arises when an infection triggers a dysregulated immune response resulting in multiorgan failure. It is characterized by life-threatening symptoms, including hemodynamic instability, respiratory distress, hepatic and renal failure, as well as cognitive impairment4,5. Septic shock represents a subset of sepsis with particularly severe symptoms that significantly increase mortality. These symptoms include persistent hypotension requiring vasopressor therapy and a serum lactate level exceeding 2 mmol∙L-1 4,5. Mortality rates in patients with septic shock have been estimated as high as 40%, even with hospital treatment1,3,5.
Gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas and Escherichia coli, often cause infections triggering this dysregulated immune response4. The underlying pathophysiological mechanisms are complex and not yet fully understood. One well-described aspect involves the activation of Toll-like receptors on immune cells by pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), leading to the release of cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) or Interleukin 1 (IL 1)4. One of these PAMPs is lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which constitutes a component of the cell membrane in gram-negative bacteria6. LPS has been employed in animal models to induce endotoxemia and endotoxemic shock7,8.
Animal models provide a controlled and standardized setting to develop and investigate novel treatment strategies. Due to its similar anatomy, immunological physiology, and comparable hemodynamic parameters, the pig model is particularly well-suited for studying the effects of endotoxemic shock9,10. Furthermore, standard medical equipment commonly used in human patients can be readily applied in pigs due to the similar size of their airways and blood vessels, facilitating instrumentation and hemodynamic monitoring.
With this protocol, we provide an experimental model for endotoxemic shock in pigs by intravenously infusing LPS derived from E. coli. To monitor the effects, we measured hemodynamic and pulmonary parameters, including arterial blood pressure, heart rate, peripheral oxygen saturation, pulmonary arterial pressure, and airway pressure. To evaluate the influence of endotoxemia on cerebral oxygen supply, we used near-infrared spectrometry (NIRS). With this method, the cerebral oxygen saturation can be evaluated via an adhesive electrode applied to the forehead11.
Protocol
The experiments in this protocol were approved by the State and Institutional Animal Care Committee (Landesuntersuchungsamt Rheinland-Pfalz, Koblenz, Germany, TVA G21-1-080). The experiments were conducted in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines. For this study, six healthy male German Landrace pigs aged 2-3 months and weighing 30-35 kg were used. The experimental timeline is summarized in Figure 1. The details related to all materials and instruments used in this protocol are listed in the Table of Materials.
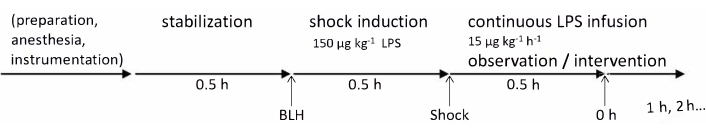
Figure 1: Experimental timeline. Baseline health measurements were taken after the preparation of the animal and a 30 min stabilization period. Endotoxemia was induced by LPS injection over 30 min and 0 h measurements were taken after another 30 min; after that, hourly measurements were continued for 4 h. Abbreviations: BLH = baseline healthy; LPS = lipopolysaccharide. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
1. Animal preparation
- Keep the animals in their usual environment for as long as possible to minimize stress. Withhold food for 6 h prior to the administration of anesthesia, while allowing free access to water.
- Sedate the animals with an intramuscular injection of azaperone (3 mg∙kg-1) and midazolam (0.5 mg kg-1) while still in their normal environment.
- Once the sedation takes effect, which typically occurs within approximately 15-20 min after administration, transport the pigs to the laboratory.
NOTE: It is crucial to ensure that continuous sedation is maintained throughout the transfer; depending on the regional legislature, this may require the permanent supervision of a veterinarian. - Pay close attention to maintaining the normal body temperature of the pigs (~38 °C) during transport. For instance, consider covering the animal with a blanket to prevent hypothermia.
NOTE: It is important to limit the transport time to not exceed the duration of sedation, which usually ranges from 30 min to 60 min. - Following disinfection, establish an intravenous access by inserting a 22 G catheter in the auricular vein. Before proceeding with any further movement of the pig or induction of anesthesia, ensure that the catheter is securely fixed to prevent dislocation by any sudden movements.
- Continuously monitor the peripheral oxygen saturation using a sensor clipped to the tail or ear.
2. Anesthesia and mechanical ventilation
- Administer intravenous fentanyl (4 µg kg-1) and propofol (3 mg kg-1) to induce anesthesia.
- Place the pig in a supine position.
- Administer atracurium (0.5 mg kg-1) as a muscle relaxant and immediately initiate non-invasive ventilation using a dog ventilation mask. Place the mask over the snout and apply firm pressure with the thumbs while pulling the lower jaw forward using the middle/ring finger. Set the ventilator to the following parameters: inspiratory oxygen fraction (FiO2 ) = 100%, tidal volume = 6-8 mL kg-1, Positive End Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) = 5 mbar, peak inspiratory pressure ≤ 20 mbar, respiratory rate = 18-20 min-1.
- Maintain anesthesia by initiating a continuous infusion of a balanced electrolyte solution (5 mL kg-1 h-1), fentanyl (10 µg kg-1 h-1), and propofol (6 mg kg-1 h-1).
- Perform endotracheal intubation using a standard endotracheal tube (ID 6-7 mm), a guidewire, and a laryngoscope equipped with a Macintosh Blade (size 4).
- Have an assistant open the mouth and hold the tongue to the left side.
- Insert the Macintosh Blade until the epiglottis is visible. Then, lift the laryngoscope upwards to move the epiglottis ventrally and visualize the vocal cords. Occasionally, the epiglottis may stick to the soft palate; in this case, mobilize it by gently swiping sideways with the tube or a bougie.
- Carefully insert the endotracheal tube through the vocal cords and remove the inducer. If encountering difficulty, try rotating the tube without applying excessive force. If necessary, use a smaller tube. Once the tube is in place, inflate the cuff with 10 mL of air.
- Connect the endotracheal tube to the ventilator and initiate ventilation. Confirm proper tube positioning by detecting end-expiratory CO2 and performing bilateral auscultation. Use the following ventilation settings: FiO2 = 40%, tidal volume = 6-8 mL kg-1, PEEP = 5 mbar, inspiration to expiration ratio = 1:2, respiratory rate = adjusted to achieve an end-tidal CO2 level of <45 mmHg, typically 30-40 min-1 .
NOTE: If the tube has been placed incorrectly in the esophagus, air will inflate the stomach, causing a visible bulge. In such cases, immediately remove the tube, administer non-invasive ventilation for 1-2 min, and reposition the tube correctly. - Insert a gastric tube to prevent reflux or vomiting. If insertion proves challenging, use the laryngoscope to obtain a better view of the esophageal entrance.
3. Instrumentation
- Place an arterial and a central venous line in the femoral artery and vein, respectively, for hemodynamic monitoring and intravenous volume therapy.
- Use bandages to retract and secure the hind legs, providing better access to the femoral vessels.
- Prepare all necessary materials prior to instrumentation. Fill all catheters with saline solution and ensure easy access to wires and catheters to minimize the need for multiple catheterization attempts and unnecessary blood loss.
- Apply an alcoholic disinfectant to the inguinal area and wipe it with a sterile swab. Repeat this process twice. Apply the disinfectant again without wiping and wait for 3 min. Place a sterile fenestrated drape over the inguinal area.
- Use ultrasound to identify the femoral blood vessels. Use an in-plane ultrasound-guided Seldinger's technique for catheterization to minimize tissue damage and blood loss.
- Visualize the femoral artery longitudinally. Puncture the artery with a syringe attached to the needle for continuous aspiration. Bright red, pulsating blood confirms arterial puncture. Remove the syringe and insert the prepared wire. Remove the needle while leaving the wire in place.
- Repeat the same procedure for the femoral vein. Venous puncture is confirmed by slow-flowing, dark red blood.
- Confirm the correct positioning of both wires by visualizing both femoral vessels using ultrasound.
- Use Seldinger's technique to insert the arterial introducer sheath first, followed by the venous introducer sheath. Confirm proper positioning through blood gas analysis of blood samples drawn from the two lines.
- Ensure that blood can be aspirated from all lines. Flush all lines with saline solution to prevent clot formation.
- Securely fix the lines to the skin using surgical sutures to prevent dislocation.
- Connect the arterial and central venous lines to transducers for the measurement of hemodynamic parameters.
- Insert a pulse contour cardiac output (PiCCO) catheter into the arterial introducer sheath and connect it to the arterial pressure transducer and temperature interface cable of the PiCCO monitor.
- Connect a Swan-Ganz catheter to a transducer.
- While continuously measuring pressure, insert the catheter into the central venous introducer sheath. Inflate the balloon after approximately 30 cm, when a central venous pressure curve becomes visible.
- Slowly advance the catheter while monitoring the pressure curve. As the catheter enters the right ventricle, look for a pulse curve with a high systolic and low diastolic value. Further advancement of the catheter will result in a consistent systolic value and an increased diastolic value, indicating placement in the pulmonary artery.
- Fix the catheter in this position (usually between 50 and 70 cm). Connect the injectate temperature sensor of the PiCCO system to the proximal lumen of the Swan-Ganz catheter.
- Shave the pig's forehead and apply the adhesive sensor electrode to measure Cerebral Regional Oxygen Saturation.
- After anesthesia induction and instrumentation, allow the animal to stabilize for 30 min or until hemodynamic parameters have stabilized before conducting baseline measurements and inducing endotoxemic shock.
4. Shock induction
NOTE: When working with LPS, always wear gloves, protective goggles, a mask, and a lab coat. Avoid direct contact with LPS.
- Prepare an LPS solution with a concentration of 100 µg mL-1 by dissolving 5 mg of LPS in 50 mL of 0.9% NaCl.
- Obtain baseline hemodynamic measurements immediately before initiating LPS infusion.
- Administer a 150 µg kg-1 dose of LPS over 30 min (equivalent to a continuous infusion rate of 300 µg kg-1∙h-1 for 30 min).
- After 30 min, reduce the infusion rate to 15 µg∙kg-1∙h-1 for the remainder of the experiment.
- Continuously monitor hemodynamic parameters, including arterial and pulmonary arterial blood pressure, heart rate, and ventilation parameters. Monitor the body temperature continuously to maintain normothermia.
5. Treatment of hemodynamic instability
- When the mean arterial blood pressure falls below 60 mmHg, use PiCCO to measure cardiac index (CI), Global End-Diastolic Volume Index (GEDI), and Extravascular Lung Water Index (ELWI). Treat the low blood pressure according to the recommendations in the flow chart in Figure 2.
- On the PiCCO monitor, press the thermodilution button (TD).
- Press the button for central venous pressure (CVP) input and enter the current CVP value.
- Press the Start button.
- When instructed to do so, inject 10 mL of cold saline solution into the injectate temperature sensor connected to the Swan-Ganz catheter.
NOTE: Do not inject anything else directly before or during PiCCO measurement as this would compromise the measurement.
- After obtaining measurements for CI, GEDI, and ELWI, treat hemodynamic instability according to the flow chart in Figure 2. If Volume loading is recommended, rapidly infuse 200 mL of balanced electrolyte solution. If catecholamine therapy is recommended, increase the rate of norepinephrine infusion by 1 µg kg-1 h-1.
- Repeat this process whenever the mean arterial blood pressure falls below 60 mmHg. In case of severe hemodynamic instability, opt for rapid escalation of therapy.
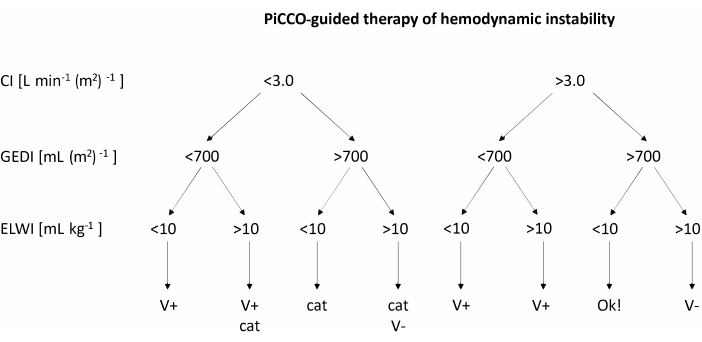
Figure 2: PiCCO-guided therapy of hemodynamic instability. After obtaining measurements for CI, GEDI, and ELWI, apply treatment according to the chart. This figure was adapted from the PiCCO user guidebook12. Abbreviations: PiCCO = pulse contour cardiac output; V+ = volume loading; cat = catecholamine therapy; V- = volume reduction; CI = cardiac index; GEDI = global end-diastolic volume index; ELWI = extravascular lung water index. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
6. End of experiment and euthanasia
- Inject 0.5 mg of fentanyl intravenously. Wait 5 min. Inject 200 mg of propofol.
- Euthanize the pig with a rapid injection of 40 mL of 1 M potassium chloride via the central venous line.
Results
For this study, six healthy male pigs aged 2-3 months and weighing 30-35 kg were anesthetized and received an infusion of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to induce endotoxemia. To determine the appropriate dosage of LPS required to consistently induce symptoms of shock, the pigs were administered various induction doses of LPS ranging from 100 µg kg-1 to 200 µg kg-1 over a 30-min period, followed by a maintenance dose of 1/10 of the initial dose per hour for the remainder of the experiment. All a...
Discussion
We present a protocol for inducing experimental endotoxemia in pigs through LPS infusion, aiming to reliably induce changes commonly observed in sepsis and septic shock. Several critical steps need to be considered in this protocol. Adequate sedation of pigs prior to transport is crucial to prevent stress-induced elevation of catecholamine levels, which could potentially compromise the results. Intubation of pigs may pose challenges compared to humans due to the anatomical features of their elongated snouts. To address t...
Disclosures
The NIRS device was unconditionally provided by Medtronic PLC, USA, for experimental research purposes. Alexander Ziebart received a lecture fee from Medtronic PLC. None of the authors report any financial or other conflicts of interest. The manuscript was proofread and edited by ChatGPT® (Python Software, Version: May 24, 2023).
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank Dagmar Dirvonskis for her excellent technical support.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Atracurium Hikma 50 mg/5mL | Hikma Pharma GmbH, Martinsried | ||
| Azaperone (Stresnil) 40 mg/mL | Lilly Deutschland GmbH, Bad Homburg, Germany | ||
| BD Discardit II Spritze 2, 5, 10, 20 mL | Becton Dickinson S.A. Carretera, Mequinenza Fraga, Spain | syringe | |
| BD Luer Connecta | Becton Dickinson Infusion Therapy, AB Helsingborg, Schweden | 3-way-stopcock | |
| Curafix i.v. classics | Lohmann & Rauscher International GmbH & Co. KG, Rengsdorf, Germany | Cannula retention dressing | |
| Datex Ohmeda S5 | GE Healthcare Finland Oy, Helsinki, Finland | hemodynamic monitor | |
| Engström Carestation | GE Heathcare, Madison USA | ventilator | |
| Fentanyl-Janssen 0.05 mg/mL | Janssen-Cilag GmbH, Neuss | fentanyl | |
| Führungsstab, Durchmesser 4.3 | Rüsch | endotracheal tube introducer | |
| Incetomat-line 150 cm | Fresenius, Kabi Deutschland, GmbH | perfusor line | |
| Intrafix Primeline | B. Braun Melsungen AG, Melsungen, Germany | Infusion line | |
| Introducer sheath 5 Fr. | Terumo Healthcare | arterial introducer | |
| INVOS | Medtronic, Dublin, Ireland | near infrared spectrometry | |
| JOZA Einmal Nitril Untersuchungshandschuhe | JOZA, München, Germany | disposable gloves | |
| Laryngoscope, 45.48.50, KL 2000 | Medicon | Laryngoscope handle | |
| Littmann Classic III Stethoscope | 3M Deutschland GmbH, Neuss, Germany | stethoscope | |
| LPS (E. coli; Serotype O111:B4) | Sigma-Aldrich, Switzerland | ||
| MAC Two-Lumen Central venous access set | Arrow international inc. Reading, PA, USA | venous introducer | |
| Maimed Vlieskompresse | Maimed GmbH, Neuenkirchen, Germany | Fleece compress to fix the tongue | |
| Masimo LNCS Adtx SpO2 sensor | Masimo Corporation Irvine, Ca 92618 USA | saturation clip for the tail | |
| Masimo LNCS TC-I SpO2 ear clip sensor | Masimo Corporation Irvine, Ca 92618 USA | Saturation clip for the ear | |
| Masimo Radical 7 | Masimo Corporation Irvine, Ca 92618 USA | periphereal oxygen saturation | |
| Midazolam 15 mg/3 mL | B.Braun Melsungen AG, Germany | ||
| Midmark Canine Mask Small Plastic with Diaphragm FRSCM-0005 | Midmark Corp., Dayton, Ohio, USA | dog ventilation mask | |
| Monocryl surgical suture | Johnson & Johnson, Belgium | ||
| B.Braun Melsungen AG, Germany | saline solution | ||
| NaCl 0.9 % | Sanofi- Aventis, Seutschland GmbH | ||
| Octeniderm farblos | Schülke & Mayr GmbH, Nordenstedt, Germany | Alcoholic disinfectant | |
| Original Perfusor syringe 50 mL | B.Braun Melsungen AG, Germany | perfusor syringe | |
| PA-Katheter Swan Ganz 7.5 Fr 110 cm | Edwards Lifesciences LLC, Irvine CA, USA | Swan-Ganz catheter | |
| Perfusor FM Braun | B.Braun Melsungen AG, Germany | syringe pump | |
| PiCCO catheter | PULSION Medical Systems SE, Feldkirchen, DE | ||
| Potassium chloride 1 M | Fresenius, Kabi Germany GmbH | ||
| Propofol 2% 20 mg/mL (50 mL flasks) | Fresenius, Kabi Deutschland, GmbH | ||
| Pulse-contour continous cardiac output System PiCCO2 | PULSION Medical Systems SE, Feldkirchen, DE | ||
| Rüschelit Super Safety Clear >ID 6/6.5 /7.0 mm | Teleflex Medical Sdn. Bhd, Malaysia | endotracheal tube | |
| Sonosite Micromaxx Ultrasoundsystem | Sonosite Bothell, WA, USA | ultrasound | |
| Stainless Macintosh Größe 4 | Welch Allyn69604 | blade for laryngoscope | |
| Sterofundin | B.Braun Melsungen AG, Melsungen, Germany | Balanced electrolyte solution | |
| Vasco OP sensitive | B.Braun Melsungen AG, Germany | sterile gloves | |
| Vasofix Safety 22 G-16 G | B.Braun Melsungen AG, Germany | venous catheter | |
| VBM Cuff Manometer | VBM Medizintechnik GmbH, Sulz a.N., Germany | cuff pressure gauge |
References
- Vincent, J. -. L., Jones, G., David, S., Olariu, E., Cadwell, K. K. Frequency and mortality of septic shock in Europe and North America: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Critical Care. 23 (1), 196 (2019).
- Reinhart, K., et al. Recognizing sepsis as a Global Health Priority - A WHO Resolution. New England Journal of Medicine. 377 (5), 414-417 (2017).
- Cecconi, M., Evans, L., Levy, M., Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. The Lancet. 392 (10141), 75-87 (2018).
- Font, M. D., Thyagarajan, B., Khanna, A. K. Sepsis and septic shock - basics of diagnosis, pathophysiology and clinical decision making. Medical Clinics of North America. 104 (4), 573-585 (2020).
- Singer, M., et al. The Third International Consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 315 (8), 801 (2016).
- Jerala, R. Structural biology of the LPS recognition. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 297 (5), 353-363 (2007).
- Copeland, S., Warren, H. S., Lowry, S. F., Calvano, S. E., Remick, D. Inflammation and the host response to injury investigators acute inflammatory response to endotoxin in mice and humans. Clinical and Diagnostic Laboratory Immunology. 12 (1), 60-67 (2005).
- Dickson, K., Lehmann, C. Inflammatory response to different toxins in experimental sepsis models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 20 (18), 4341 (2019).
- Bassols, A., Costa, C., Eckersall, P. D., Osada, J., Sabrià, J., Tibau, J. The pig as an animal model for human pathologies: A proteomics perspective. PROTEOMICS - Clinical Applications. 8 (9-10), 715-731 (2014).
- Meurens, F., Summerfield, A., Nauwynck, H., Saif, L., Gerdts, V. The pig: a model for human infectious diseases. Trends in Microbiology. 20 (1), 50-57 (2012).
- Ali, J., Cody, J., Maldonado, Y., Ramakrishna, H. Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for cerebral and tissue oximetry: analysis of evolving applications. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia. 36, 2758-2766 (2022).
- . Getinge Deutschland GmbH PiCCO Technologie Erweitertes hämodynamisches Monitoring auf höchstem Niveau Available from: https://www.getinge.com/dam/hospital/documents/german/picco_haemodynamisches_monitoring_broschuere-de-non_us.pdf (2023)
- Breslow, M. J., Miller, C. F., Parker, S. D., Walman, A. T., Traystman, R. J. Effect of vasopressors on organ blood flow during endotoxin shock in pigs. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 252 (2), H291-H300 (1987).
- Fink, M. P., et al. Systemic and mesenteric O2 metabolism in endotoxic pigs: effect of ibuprofen and meclofenamate. Journal of Applied Physiology. 67 (5), 1950-1957 (1989).
- Lado-Abeal, J., et al. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced septic shock causes profound changes in myocardial energy metabolites in pigs. Metabolomics. 14 (10), 131 (2018).
- Park, I., et al. Characterization of fecal peritonitis-induced sepsis in a porcine model. The Journal of Surgical Research. 244, 492-501 (2019).
- Jarkovska, D., et al. Heart rate variability in porcine progressive peritonitis-induced sepsis. Frontiers in Physiology. 6, 412 (2015).
- Kohoutova, M., et al. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates multiple organ dysfunction in resuscitated porcine progressive sepsis. Critical Care Medicine. 47 (6), e461-e469 (2019).
- Vintrych, P., et al. Modeling sepsis, with a special focus on large animal models of porcine peritonitis and bacteremia. Frontiers in Physiology. 13, 1094199 (2022).
- Stengl, M., et al. Reduced L-type calcium current in ventricular myocytes from pigs with hyperdynamic septic shock. Critical Care Medicine. 38 (2), 579-587 (2010).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved