A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Electrochemical Exfoliation to Produce High-Quality Black Phosphorus
In This Article
Summary
We present a step-by-step procedure for electrochemical exfoliation of black phosphorus (BP), one of the most promising emerging 2D materials with applications in (opto)electronics, from its bulk crystals, as well as the morphological characterization by scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy.
Abstract
To obtain high-quality two-dimensional (2D) materials from the bulky crystals, delamination under an externally controlled stimulus is crucial. Electrochemical exfoliation of layered materials requires simple instrumentation yet offers high-quality exfoliated 2D materials with high yields and features straightforward upscalability; therefore, it represents a key technology for advancing fundamental studies and industrial applications. Moreover, the solution processability of functionalized 2D materials enables the fabrication of (opto)electronic and energy devices via different printing technologies such as inkjet printing and 3D printing. This paper presents the electrochemical exfoliation protocol for the synthesis of black phosphorus (BP), one of the most promising emerging 2D materials, from its bulk crystals in a step-by-step manner, namely, cathodic electrochemical exfoliation of BP in the presence of N(C4H9)4∙HSO4 in propylene carbonate, dispersion preparation by sonication and subsequent centrifugation for the separation of flakes, and morphological characterization by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
Introduction
Due to their superior mechanical, electrical, and optical properties in comparison to their layered bulk analogs, 2D materials have attracted considerable attention among the scientific community. Being the predecessor and the most studied of all 2D materials for several decades, graphene is still in the spotlight of cutting-edge discoveries such as membranes1, sensors2, catalysts3, energy technologies4, topological spintronic devices5, and condensed matter physics6. Inspired by that, numerous other 2D materials have been synthesized and investigated, such as metal chalcogenides7, layered double hydroxides8, and boron nitride9. Including the newest additions to the family of 2D materials (i.e., phosphorene10), MXenes (2D metal carbides or nitrides)11, and 2D polymers (single/few-layer 2D metal/covalent organic frameworks)12,13, the family of 2D materials has grown to consist of more than 150 members featuring intrinsic insulators, semiconductors, semimetals, and metals14.
The emerging 2D materials, such as BP15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2)23,24,25,26, and indium(III) selenide (In2Se3)27,28,29, have shown considerable potential in scientific discoveries; however, to extend their excellent physiochemical properties to a macroscopic scale, efficient, reproducible, and low-cost methods are urgently needed. Electrochemical exfoliation is a promising approach for the upscale production of such 2D materials30,31, mainly due to the fact that it can provide gram scales of high-quality and dispersible exfoliated materials in minutes to a few hours due to the efficient intercalation of ions under the electric force.
The accompanying video demonstrates the step-by-step production of dispersions of BP, one of the most promising emerging 2D materials with applications in (opto)electronics, using electrochemical exfoliation, followed by sonication and centrifugation for the separation of flakes from unexfoliated particles, the preparation of dispersions of exfoliated BP flakes in various solvents, and morphological characterization by SEM, AFM, and TEM.
Protocol
NOTE: See the Table of Materials for details related to the materials and equipment used in this protocol.
1. Synthesis of black phosphorus (BP) by electrochemical exfoliation
- Chop the large pieces of BP crystal into small pieces of ~1-2 mm (≤5 mg) and confine them inside a platinum gauze to serve as the cathode.
- Cut a piece of platinum foil with dimensions ~2 cm2 to serve as the anode and fix it in a way that it faces the cathode and is 2 cm away from it.
- To prepare the electrolyte, prepare a fresh solution of 0.1 M tetra-n-butyl-ammonium bisulfate (TBA·HSO4) in propylene carbonate (use anhydrous and degassed solvent). Fill the electrochemical cell until the solvent level reaches at least 5 mm above the top of the electrodes (Figure 1C).
- Apply a DC potential of −8.0 V to start the delamination. To prevent degradation during the exfoliation, carry out the whole process under an inert atmosphere (e.g., inside a glove box under argon or nitrogen).
NOTE: There is no need for continuous purging of the electrolyte by inert gases. - Upon completion of the delamination (ensure there is no more visible generation of expanded BP), transfer the whole electrolyte, including the exfoliated BP flakes and the larger unexfoliated particles, into a 50 mL centrifuge tube.
- Centrifuge at 5,292 × g at 15 °C for 10 min. Discard the electrolyte, add 35 mL of fresh propylene carbonate to the precipitate, and shake it gently. Repeat the centrifugation and washing process 2x with propylene carbonate and 2x with the final solvent of choice (e.g., 2-propanol, N,N-dimethylformamide [DMF], or N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone [NMP]).
- Add 5-50 mL of the desired solvent to the precipitated products (depending on the required concentration range) and sonicate the resulting product mixture in an ice-cooled sonication bath for 10 min.
- Centrifuge the mixture at 5,292 × g at 15 °C for 10 min to remove the thick-layered BP flakes.
- Decant the supernatant containing the monolayer and few-layer (<10 layers) BP flakes into a clean container and keep it in the glove box for further characterization or device fabrication.
- Calculate the delamination yield (η) using the gravimetric yield formula represented by equation (1):
η = m1/m2 × 100% (1)
where m2 represents the mass of the starting BP crystal and m1 the weight of the dispersed BP flakes. - To determine m1, measure the weight of the BP collected from the vacuum filtration of a certain volume of the BP dispersion (e.g., 0.5 mL). Use polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane (0.2 µm pore size) for vacuum filtration.
- For long-term storage, close the cap of the container bottle and keep it inside the glovebox (up to 3 months).
2. Sample preparation for characterization by SEM, SEM-EDS, AFM, and TEM
NOTE: To explore the quality and morphological aspects of the synthesized BP flakes, it is necessary to perform characterizations such as SEM32 (for studying the surface morphology of the BP flakes), SEM-EDS33 (for elemental analysis of the flakes), AFM34,35 (for analysis of the thickness and lateral size of the flakes), and TEM36,37 (for detection of the structural defects, shape, and size of the BP flakes). Sample preparation protocols for the abovementioned characterization techniques are explained below (sections 2.1-2.4). For operational procedures of the abovementioned characterization techniques, refer to the cited references32,33,34,35,36,37.
- Sample preparation for characterization by SEM
- Cut out a small piece (with dimensions around 5−7 mm) of a silicon wafer.
- Clean the silicon wafer piece using acetone, methanol, and water successively. Then, dry the substrate by blowing compressed air or nitrogen over it.
- Prepare a 0.5 mL diluted dispersion of the BP dispersion prepared in section 1 by the addition of anhydrous iso-propanol to reach a concentration of ~0.01 mg/mL.
- Spin coat 1−2 droplets of the prepared diluted dispersion on the clean and dry substrate in the glovebox and let it dry on a hotplate at 100 °C for 6 h (in the glovebox). After cooling to room temperature, use the sample for characterization.
- Sample preparation for characterization by SEM-EDS
- Follow the procedure mentioned in section 2.1; however, prepare a more concentrated dispersion of ~0.1 mg/mL instead of the one mentioned in step 2.1.3.
- Sample preparation for characterization by AFM
- Follow the procedure mentioned in section 2.1; however, use a silicon oxide wafer instead of the silicon wafer mentioned in step 2.1.1.
- Sample preparation for characterization by TEM
- Prepare the diluted dispersion of BP as explained in section 2.1.3.
- Drop cast one droplet of the dispersion on the carbon microgrids. Use the sample for characterization by TEM after drying it in the glovebox argon-atmosphere (without additional heating) for 24 h.
Results
Figure 1 demonstrates the electrochemical exfoliation of BP crystals, the mechanism of intercalation of TBA·HSO4 and subsequent delamination, and the reaction cell setup.
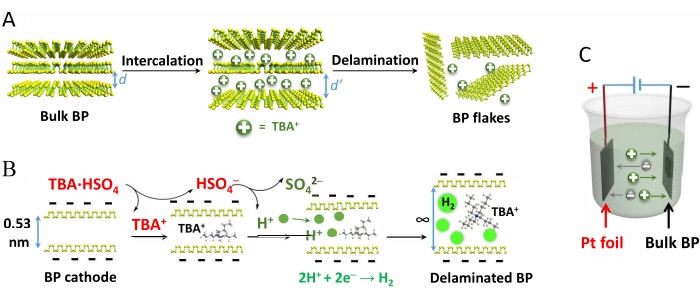
Figure 1: Schematic demonstration of the mechanism of electrochemical exfoliation of black phosphorus crystals...
Discussion
BP has a valence shell configuration of 3s2 3p3, and each phosphorus atom possesses a lone electron pair, which makes the phosphorus atoms vulnerable to fast oxidative degradation in the presence of oxygen, water, and light41. To prevent degradation, it is recommended to use degassed and anhydrous solvents and reagents and carry out the production process under an inert atmosphere.
During the exfoliation of BP crystals, part of the produced H+...
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge ERC Consolidator Grant on T2DCP, M-ERA-NET project HYSUCAP, SPES3 project funded by the German Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) under Forschung für neue Mikroelektronik (ForMikro) program, Graphene Flagship Core 3 881603, and Emerging Printed Electronics Research Infrastructure (EMERGE). The EMERGE project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme under grant agreement No. 101008701. The authors thank Dr. Markus Löffler for helpful discussions and characterization and also acknowledge the Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden (cfaed) and the Dresden Center for Nanoanalysis (DCN).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 2-Propanol | Sigma Aldrich | 278475 | anhydrous, 99.5% |
| Atomic force microscopy (AFM) | Bruker Multimode 8 system | ||
| Black phosphorus | Smart Elements | 4504 | Black Phosphorus 5.0 g sealed under Argon in ampoule |
| Centrifuge | Sigma 4-16KS | ||
| Propylene carbonate | Sigma Aldrich | 310328 | anhydrous, 99.7% |
| Scanning electron microscope (SEM) | Zeiss Gemini 500 | ||
| Tetra-n-butylammonium hydrogen sulfate | Sigma Aldrich | 791784 | anhydrous, free-flowing, Redi-Dri, 97% |
| Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) | Zeiss Libra 120 kV |
References
- Yang, Q., et al. Ultrathin graphene-based membrane with precise molecular sieving and ultrafast solvent permeation. Nature Materials. 16 (12), 1198-1202 (2017).
- Goossens, S., et al. Broadband image sensor array based on graphene-CMOS integration. Nature Photonics. 11 (6), 366-371 (2017).
- Yan, H., et al. Single-atom Pd1/graphene catalyst achieved by atomic layer deposition: Remarkable performance in selective hydrogenation of 1,3-butadiene. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 137 (33), 10484-10487 (2015).
- Qu, G., et al. A fiber supercapacitor with high energy density based on hollow graphene/conducting polymer fiber electrode. Advanced Materials. 28 (19), 3646-3652 (2016).
- Calleja, F., et al. Spatial variation of a giant spin-orbit effect induces electron confinement in graphene on Pb islands. Nature Physics. 11 (1), 43-47 (2014).
- Cao, Y., et al. Correlated insulator behaviour at half-filling in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature. 556 (7699), 80-84 (2018).
- Manzeli, S., Ovchinnikov, D., Pasquier, D., Yazyev, O. V., Kis, A. 2D transition metal dichalcogenides. Nature Reviews Materials. 2 (8), 1-15 (2017).
- Carrasco, J. A., et al. Liquid phase exfoliation of carbonate-intercalated layered double hydroxides. Chemical Communications. 55 (23), 3315-3318 (2019).
- Lei, W., et al. Boron nitride colloidal solutions, ultralight aerogels and freestanding membranes through one-step exfoliation and functionalization. Nature Communications. 6 (1), 1-8 (2015).
- Kang, J., et al. Solvent exfoliation of electronic-grade, two-dimensional black phosphorus. ACS Nano. 9 (4), 3596-3604 (2015).
- Ding, L., et al. A two-dimensional lamellar membrane: MXene nanosheet stacks. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 56 (7), 1825-1829 (2017).
- Dong, R., et al. High-mobility band-like charge transport in a semiconducting two-dimensional metal-organic framework. Nature Materials. 17 (11), 1027-1032 (2018).
- Liu, K., et al. On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers. Nature Chemistry. 11 (11), 994-1000 (2019).
- Choi, W., et al. Recent development of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides and their applications. Materials Today. 20 (3), 116-130 (2017).
- Yang, S., et al. A delamination strategy for thinly layered defect-free high-mobility black phosphorus flakes. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 57 (17), 4677-4681 (2018).
- Shi, H., et al. Molecularly engineered black phosphorus heterostructures with improved ambient stability and enhanced charge carrier mobility. Advanced Materials. 33 (48), 2105694 (2021).
- Woomer, A. H., et al. Phosphorene: Synthesis, scale-up, and quantitative optical spectroscopy. ACS Nano. 9 (9), 8869-8884 (2015).
- Youngblood, N., Chen, C., Koester, S. J., Li, M. Waveguide-integrated black phosphorus photodetector with high responsivity and low dark current. Nature Photonics. 9 (4), 247-252 (2015).
- Li, L., et al. Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nature Nanotechnology. 9 (5), 372-377 (2014).
- Perello, D. J., Chae, S. H., Song, S., Lee, Y. H. High-performance n-type black phosphorus transistors with type control via thickness and contact-metal engineering. Nature Communications. 6 (1), 1-10 (2015).
- Yuan, H., et al. Polarization-sensitive broadband photodetector using a black phosphorus vertical p-n junction. Nature Nanotechnology. 10 (8), 707-713 (2015).
- Huang, Z., et al. Layer-tunable phosphorene modulated by the cation insertion rate as a sodium-storage anode. Advanced Materials. 29 (34), 1702372 (2017).
- Desai, S. B., et al. MoS2 transistors with 1-nanometer gate lengths. Science. 354 (6308), 99-102 (2016).
- Wang, Q. H., Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Kis, A., Coleman, J. N., Strano, M. S. Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nature Nanotechnology. 7 (11), 699-712 (2012).
- Xu, X., Yao, W., Xiao, D., Heinz, T. F. Spin and pseudospins in layered transition metal dichalcogenides. Nature Physics. 10 (5), 343-350 (2014).
- Deng, Z., et al. 3D Ordered macroporous MoS2@C nanostructure for flexible Li-ion batteries. Advanced Materials. 29 (10), 1603020 (2017).
- Shi, H., et al. Ultrafast electrochemical synthesis of defect-free In2Se3 flakes for large-Area optoelectronics. Advanced Materials. 32 (8), 1907244 (2020).
- Ding, W., et al. Prediction of intrinsic two-dimensional ferroelectrics in In2Se3 and other III2-VI3 van der Waals materials. Nature Communications. 8 (1), 1-8 (2017).
- Island, J. O., Blanter, S. I., Buscema, M., Van Der Zant, H. S. J., Castellanos-Gomez, A. Gate controlled photocurrent generation mechanisms in high-gain In2Se3 phototransistors. Nano Letters. 15 (12), 7853-7858 (2015).
- Yang, S., Zhang, P., Nia, A. S., Feng, X. Emerging 2D materials produced via electrochemistry. Advanced Materials. 32 (10), 1907857 (2020).
- Li, J., et al. Electrochemically captured Zintl cluster-induced bismuthene for sodium-ion storage. Chemical Communications. 57 (19), 2396-2399 (2021).
- SEM Scanning Electron Microscope A To Z. Basic Knowledge for Using the SEM. JEOL Available from: https://jeol.co.jp/en/applications/pdf/sm/sem_atoz_all.pdf (2006)
- Lang, C., Hiscock, M., Larsen, K., Moffat, J., Sundaram, R. Characterization of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides in the scanning electron microscope using energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry, electron backscatter diffraction, and atomic force microscopy. Applied Microscopy. 45 (3), 131-134 (2015).
- Zhang, H., et al. Atomic force microscopy for two-dimensional materials: A tutorial review. Optics Communications. 406, 3-17 (2018).
- Zahl, P., Zhang, Y. Guide for atomic force microscopy image analysis to discriminate heteroatoms in aromatic molecules. Energy and Fuels. 33 (6), 4775-4780 (2019).
- Backes, C., et al. Guidelines for exfoliation, characterization and processing of layered materials produced by liquid exfoliation. Chemistry of Materials. 29 (1), 243-255 (2017).
- Chang, Y. Y., Han, H. N., Kim, M. Analyzing the microstructure and related properties of 2D materials by transmission electron microscopy. Applied Microscopy. 49 (1), 1-7 (2019).
- Cooper, A. J., Velický, M., Kinloch, I. A., Dryfe, R. A. W. On the controlled electrochemical preparation of R4N+ graphite intercalation compounds and their host structural deformation effects. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry. 730, 34-40 (2014).
- Kang, J., et al. Stable aqueous dispersions of optically and electronically active phosphorene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (42), 11688-11693 (2016).
- Hanlon, D., et al. Liquid exfoliation of solvent-stabilized few-layer black phosphorus for applications beyond electronics. Nature Communications. 6 (1), 1-11 (2015).
- Favron, A., et al. Photooxidation and quantum confinement effects in exfoliated black phosphorus. Nature Materials. 14 (8), 826-832 (2015).
- Sirisaksoontorn, W., Adenuga, A. A., Remcho, V. T., Lerner, M. M. Preparation and characterization of a tetrabutylammonium graphite intercalation compound. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 133 (32), 12436-12438 (2011).
- You, X., et al. Interfaces of propylene carbonate. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 138 (11), 114708 (2013).
- Hu, G., et al. Black phosphorus ink formulation for inkjet printing of optoelectronics and photonics. Nature Communications. 8 (1), 1-10 (2017).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved