このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Method Article
変形性膝関節症ラットの炎症と軟骨喪失を軽減するためのTuina操作
要約
石膏固定化誘発変形性膝関節症ラットに対して実行されるTuina操作のプロトコルを提示します。予備的な結果に基づいて、この方法の有効性は炎症と軟骨喪失の減少に依存していることが示唆されました。
要約
臨床試験では、Tuina操作が変形性膝関節症(KOA)の治療に効果的であることが示唆されていますが、そのメカニズムを発見するにはさらなる研究が必要です。したがって、変形性膝関節症の動物モデルの操作は重要です。このプロトコルは、KOAラットに対するTuina操作の標準的なプロセスと、KOAに対するTuinaのメカニズムの予備的な調査を提供します。プレスと混練の操作方法(体表面の特定の領域を押して混練することを指す一種のTuina操作)は、ラットの膝関節の周りの5つのツボに適用されます。操作の力および頻度は指圧記録によって標準化され、操作中のラットの位置はプロトコルに詳細に記載されている。操作の効果は、滑膜および軟骨における疼痛行動試験および顕微鏡所見によって測定することができる。KOAラットは、疼痛行動の有意な改善を示した。滑膜組織炎症浸潤はTuina群で減少し、腫瘍壊死因子(TNF)-αの発現は有意に低かった。対照群と比較して、軟骨細胞のアポトーシスはTuina群で少なかった。この研究は、KOAラットに対するTuina操作の標準化されたプロトコルと、Tuinaの治療効果が滑膜の炎症と軟骨細胞の遅延アポトーシスの軽減に関連している可能性があるという予備的な証拠を提供します。
概要
変形性膝関節症(KOA)は、主に関節痛に現れる変性疾患です。線維症、ひび割れ、潰瘍形成、関節軟骨の喪失がこの病気の主な原因です1。KOAは有病率が高く、患者の日常生活に大きな影響を与え、重症の場合に障害を引き起こす可能性があります。45〜84歳の人々の間では、KOAの有病率は年齢とともに増加し、85歳以上の人々の有病率は15%であり、女性で優勢です2,3。さらに、KOAは個人と社会の両方に深刻な経済的負担をもたらす可能性があります。調査によると、一人当たりのKOAの直接医療費は、年間8,858ドル±5,120ドルに達しました4。高齢化社会の進展に伴い、KOAは世界的な健康問題、大きな社会問題となり、科学研究の話題となっています。
エビデンスに基づく研究は、KOA5の治療におけるTuina操作の有効性を示しています。Tuina操作はKOA患者の痛みを和らげ、機能障害を改善する可能性があり、そのメカニズムは抗炎症効果に関連しています6,7。学者らは、Tuina操作が炎症因子インターロイキン(IL)-βおよび5-ヒドロキシトリプタミンの発現を効果的に抑制し、ウサギKOAモデル8の関節軟骨の変性を遅らせることを発見しました。Tuinaが病変部位の血液循環と代謝を促進し、IL-1、IL-6、腫瘍壊死因子(TNF)-αなどの炎症因子を取り除き、それによってKOA9の臨床症状を緩和できることが示唆されました。さらに、Tuina操作による関節の受動的な動きは、関節軟骨への滑液の浸透と拡散を促進し、組織の栄養代謝を改善することができます10。他の研究では、Tuina操作がKOA患者の生体力学的指標を効果的に改善できることが示唆されました11。軟部組織に適用される操作は、四肢全体のストレス分布を改善し、バランス機能を強化することができます12,13。同時に、いくつかの関節調整操作により、下肢のアライメントを調整して、異常な歩行を矯正することもできる14、15。
KOAの治療におけるTuina操作の作用機序はまだ調査されていないため、実験的研究が必要です。実験動物におけるTuinaの適用の鍵は、モデリング、動物の固定および介入方法の標準化です16。モデリング方法は、実験動物が疾患の特徴を示すことができるかどうかを決定する。一方、適切な固定方法は、Tuina操作の介入を容易にし、Tuinaの効果をよりよく反映することができます。介入方法の標準化は、Tuina操作の最も難しい部分です。2010年、中国の鍼灸基準の基本システムは、実験動物の鍼治療基準に言及し、動物実験における鍼治療とTuina手術の可能性を提供しました17。ただし、Tuinaの操作を標準化することにはまだ困難があります。Tuina操作には複数の種類があります18。特定の操作の選択は、主に治療する疾患とパフォーマーが好む治療理論に依存します。Tuina for KOAの研究では、ポイントプレス操作(親指または肘で特定のツボを押す)、Yizhichanプッシュ操作(親指を小刻みに動かすことによるプッシュ操作)、およびプレスおよび混練操作(指または手のひらで体表面の特定の領域を押してこねることを指す)にさらに注意が払われています19.プレスおよび混練操作は、最も広く用いられているTuina操作の1つであり、皮下組織20を移動させるためにプレスおよび混練を組み合わせたものである。ツボに適用されるプレスと混練の操作は、血液循環を促進し、痛みを和らげることができ、KOA19に対するTuinaの治療効果を表します。
このプロトコルでは、KOAラットに対するプレスおよび混練操作の操作について、将来の研究の参照を提供するために、選択された経穴、操作の強度と頻度、およびラットの体位を含めて詳細に説明します。
プロトコル
この研究は、上海中医薬大学(YYLAC-2022-166)と提携している伝統的な中国と西洋の統合の岳陽病院の実験動物倫理委員会によって実施された動物倫理レビューに合格しました。
1. 実験動物の準備とグルーピング
- 動物の準備
- 室温(18〜21°C)、湿度40%〜50%、12時間:12時間の概日リズム交互で200〜220gの合計10匹の健康なSPF SD雌ラットを後方投与する。動物倫理ガイドラインおよびガイドラインの関連規定に厳密に準拠して、痛みに関連する動物実験を実施します。
- 動物のグループ化
- ラットをTuina群と対照群にランダムに分けます。Tuinaグループのラットをモデリング後21日間、プレスおよび混練操作で処理します。対照群のラットを同じTuinaルームに入れ、Tuinaグループが治療を受けている間、それらを黒い布袋に同時に入れます。
2. 動物のモデリング
- 動物に麻酔をかける
- ガス麻酔にはイソフルランを使用してください。ラットを誘導濃度3%の誘導ボックスに入れます。ラットを寝かせた後、箱をぐらつに動かし、ラットが腹臥位に戻ろうとせずに転倒したときの麻酔を確認します。
- ラットを誘導ボックスから取り出し、麻酔マスクに鼻を固定します。麻酔を維持するためにイソフルラン濃度を2%に調整します。ラットが足をつまんだときに反応しない場合は、麻酔を確認してください。まぶたを閉じることができないため、ラットに麻酔をかけるときの乾燥を防ぐために、ラットに目の軟膏を塗ります。
- モデリング方法21
- シェービングマシンを使用して、右後肢の毛を取り除きます。ラットの右足首と股関節の間に医療用コットンパッドを置きます。右膝関節を180°伸ばして、5〜6層の湿った石膏包帯を均等に固定します。足首から始まり、前の包帯の1/3を覆う石膏包帯をスパイラルで包みます。ヘアドライヤーを使用して、石膏を乾かして固めます。
- 石膏包帯が乾いて固まった後、石膏を義歯基材で外部的に包み、石膏を固定し、かじるのを防ぎます。
- 義歯の基材を混合して粘着性にし、混合物を石膏の外側に接着します(混合物は包帯の端を超えてはなりません、 図1)。混合物が硬くなったら、麻酔器の電源を切り、動物が自然に目覚めるのを待ちます。ラットが目を覚ます前に麻酔事故を防ぐためにラットを監督します。
- きつい固定は血液循環を制限するが、緩い固定は落ちる傾向があるので、ラットの右後肢に石膏を適切に固定する。終末肢の血液循環を観察します。末端の腫れや紫色の顔色が検出された場合は、循環を回復するために石膏の一部を速やかに切り取ってください。石膏が壊れていて、下肢の伸展を維持できない場合は、石膏を作り直します。
- 3週間の連続固定後に石膏を取り除きます。外科用ハサミを使用して、義歯の基材を外側に切り取り、石膏包帯を貼ります。ラットの下肢を生理食塩水ですすぎ、ガーゼで乾かします。局所皮膚病変がある場合は、ヨードフォアで滅菌してください。
- モデル検証22
- X線ベースの検証
- モデリング終了後1日目に右膝のX線検査を行う。仰臥位で前後X線写真を撮り、股関節屈曲を30°、膝を伸展0°、股関節外転を15°にします。膝蓋骨を膝の真正面に保ち、ラジエーターチューブを膝関節から110 mm離します。
- 右股関節屈曲を30°、右膝伸展を0°で、右外側褥瘡の位置で横方向のX線写真を撮ります。左肢の股関節屈曲を70°、膝屈曲を45°にし、ラジエーターチューブを膝関節から110mm離します。検出パラメータを露光電圧50kV、電流250mA、露光量32mA、露光時間128msに設定します。
- 正常なラットのX線と比較して、モデル化された膝のX線が、端に骨棘過形成を伴うより狭い関節スペースを示していることを確認します。
- 国際変形性関節症研究会(OARSI)スコア23
- ラットを安楽死ボックスに入れ、毎分30%〜70%のケージ容量の割合でCO2 を灌流する。ラットが動かず、呼吸しておらず、瞳孔が拡張していることを検出した後、CO2 の灌流を停止します。さらに2分間観察して死亡を確認します。
注:子宮頸部脱臼は、死亡を確認するための二次形態として、CO2ベースの安楽死後に行うことができます。ラットをテーブルに固定し、片手で尾をつかみます。もう一方の手の親指と人差し指でラットの頭を押し下げます。亀裂の音を聞いたときに死を確認すると、ラットは同時に動きと心拍を失います。 - 右後肢を外転および外旋で曲げた状態で、フォームボード上にシリンジ針を用いてラットを仰臥位に固定する。手術用ハサミで膝関節の周りの皮膚をつまみます。皮膚を切断してから皮下筋膜を切断することにより、膝関節の周りの筋肉を露出させます。
- 骨はさみで大腿骨と脛骨骨幹を切り取り、右膝関節を切除します。関節の外側にある筋肉や靭帯などの余分な軟組織をそっと取り除きます。
- ジョイントを4%パラホルムアルデヒドで4°Cで24〜48時間固定します。 骨組織が針で簡単に突けるようになるまで、10%ギ酸溶液で関節を3日間脱灰します。
- 脱灰した組織をドラフトに入れてトリミングし、脱水機の脱水ボックスに移します。75%エタノールを4時間加え、次に90%エタノールを2時間、続いて95%エタノールを1時間、無水エタノールを30分間、別のラウンドの新鮮な無水エタノールを30分間、アルコールベンゼンを5〜10分間、キシレンを5〜10分間、新鮮なキシレンを5〜10分間、ワックスを1時間、新鮮なワックスを1時間、 脱水と透明なワックス浸漬のために1時間の新鮮なワックスの最終ラウンド。
- 次に、ティッシュを機械に入れて埋め込みます。パラフィンが固まった後、ワックスブロックを4μmのワックススライスにカットし、スライスを温水で平らにします。スライスをスライドガラスの上に置き、乾燥させます。室温で保管してください。
- 軟骨サンプルを観察し、OA軟骨組織病理学グレード評価(表1)23に従ってスコア付けします。モデリング後のラットのスコアが正常なラットのスコアよりも有意に高い場合、モデリングは成功しました。
- ラットを安楽死ボックスに入れ、毎分30%〜70%のケージ容量の割合でCO2 を灌流する。ラットが動かず、呼吸しておらず、瞳孔が拡張していることを検出した後、CO2 の灌流を停止します。さらに2分間観察して死亡を確認します。
- X線ベースの検証
表 1.OA軟骨組織病理学グレード評価。 グレードは軟骨への深さの進行です。合計スコア=グレードxステージング。正常な関節の場合は0、重度の関節炎の場合は24。 この表をダウンロードするには、ここをクリックしてください。

図 1.ラットは石膏に固定された。 ラットに麻酔をかけた後、右下肢を石膏包帯で包み、過伸展位に固定し、外側の義歯基材の層で覆った。 この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
3.トゥイナ操作
- 応用分野
- ラットの右後肢にあるST34、ST35、SP10、EX-LE4、BL40の合計5つの経穴を選択します(図2)。24のツボの位置の原則に従ってツボを見つけます。
- 応募ポジション
- 黒い布を片側が開いている9 cm x 15 cmの袋に切り、ロープで開口部を締めます。Tuinaの操作の前に、ラットの尻尾をそっと引っ張ってバッグに穴を掘り、後肢をバッグの外に露出させます。
- 片方の手でラットを腹臥位に保ち、尾と後ろ足を持ち、もう一方の手で特定の経穴にプレスと混練操作を適用します(図3)。
- トゥイナ操作
- 右後肢の5つのツボをプレス・練り込み操作で2分間ずつ操作する。選択した経穴にパフォーマーの親指を置き、リズミカルなプレスと揉みを行い、皮膚と皮下組織を円を描くように動かします。
- 指圧記録(ニュートンの単位)を使用して、操作の強度と頻度が一定になるようにします。強度を3〜5 N、周波数を2 Hzに保ちます(図4)。21日間一日一回操作を適用します。

図 2.経穴の位置。 SP10は、ラットの膝関節の内側から5 mm上にあります。ST34は、ラットの外側膝関節から5mm上に位置しています。EX-LE4はラットの膝靭帯の内側に位置しています。ST35はラットの膝靭帯の外側に位置しています。BL40は横膝窩縞の中点に位置しています。 この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
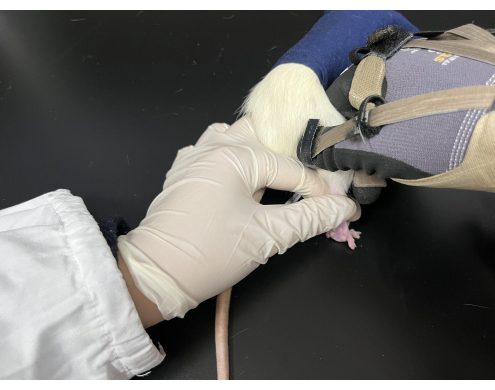
図 3.ラットに適用されたTuina操作。 ラットは、後肢が露出した状態で黒い袋に入れられました。パフォーマーは左手でネズミの尻尾を持ち、右手で操作を行いました。 この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。

図 4.指圧の記録。 指の圧力の力と周波数を記録するデバイスは、Tuina操作のプロセスにおける強度と周波数に関するリアルタイムのフィードバックに使用されます。(A)圧力センサーおよびトランスミッション機器。(B)指圧の記録。(C)トゥイナ操作中に記録された力。 この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
4.痛み行動テスト
- 疼痛行動のモデリング前後、および1日後(D1)、7日後(D7)、14日後(D14)および21日後(D21)のTuina操作を、機械的離脱閾値および足離脱潜時試験を含む。
- 機械的離脱閾値(MWT)
- ラットを、開口部10 mm x 10 mmのサイズのワイヤー格子で構成された高さ40 cmのステージにある20 cm x 10 cm x 20 cmの透明な強化ガラスのキュービクルに置きます。室温を23°C±2°Cに保ちます。
- 正式な試験の開始時に動物が環境に適応していないことによる試験結果への干渉を避けるために、行動試験段階でラットを行動実験室に少なくとも2時間定着させる。正式なテストの開始前にラットを行動実験室に30分間置き、環境への適応を促進し、気を散らす要因を減らします。
- 電子フォンフレイファイバーを使用してMWTを測定します。繊維を足の中心にしてラットを刺激し、ラットが脚を上げたり避けたりするなどの明らかな動きを示したら繊維を抜く。機械は、この時点で最大圧力値(N)を自動的に記録することができます。
- 電流刺激の少なくとも15秒後に同じラットで次の刺激を開始する。ラットの足の触覚刺激に対する感作を防ぐために、各刺激中に5秒を超えないようにしてください。3つの連続した測定値の差がわずか(10 N以内)になるまで、テストを5回繰り返します。
- 大きな差のある値(最大値と最小値)を削除し、残りの3つの値の平均を機械的撤退しきい値として取ります。
- 足離脱潜時(PWL)
- ラットを20 cm x 10 cm x 20 cmのサイズの透明な強化ガラスの小さなコンパートメントに置きます。通気孔のある透明なガラスカバーでコンパートメントの上部を覆います。透明なガラス板の温度を、コンパートメントが置かれている28〜30°Cに保ちます。
- ラットをこの環境に少なくとも30分間定着させ、各正式な試験の開始前に順応させます。ラットがコンパートメント内で排尿または排便する場合は、その後の光放射熱伝達に影響を与えないように、時間内に吸収紙で清掃してください。
- ラットの足の中心にスポットライトを集中させ、 スタート ボタンを押します。ラットが足の引っ込めや足の舐めなどの明らかな行動を示したら、 停止 ボタンを押して、この時点で時間を記録します。スポットライトの照射時間は、ラットの皮膚への損傷を避けるために20秒を超えてはなりません。
- 感作を防ぐために、少なくとも10分後に同じラットに次の照射を行う。各ラットで5倍を測定します。
- 大きな差のある値(最大値と最小値)を削除します。残りの値の平均をPWLとして取ります。
5. サンプル調製
- 2.3.2.1で説明されているように、マウスで安楽死を実行します。
- 滑膜の準備
- 外転および外旋で右後肢を曲げた状態で、フォームボード上にシリンジ針でラットを仰臥位に固定する。手術用ハサミで膝関節周辺の皮膚をつまみ、ラットの膝関節周辺の筋肉を皮膚を切ってから皮下筋膜を切断して露出させます。
- 膝蓋靭帯を目印として、膝蓋骨靭帯の上の筋肉群を取り除きます。膝蓋靭帯の端(脛骨結節)を注意深く切開し、靭帯を下から上向きにつまんだときに滑膜を見つけます。
- 眼科用ハサミで滑膜組織を慎重に切断し、予冷した生理食塩水で血液と滑液を洗い流します。きれいなガーゼで組織表面から水分を吸収した後、滑膜を4%パラホルムアルデヒドに少なくとも48時間固定します。
- 手順 2.3.2.5- 2.3.2.6 のようにサンプルを準備します。手順 2.3.2.7 のようにスコアリングを実行します。
- ヘマトキシリンおよびエオジン染色の実施
- キシレンで20分間水に脱ワックスし、20分間別のラウンドの新鮮なキシレンと交換し、続いて無水エタノールで5分間処理し、別のラウンドの新鮮な無水エタノールと5分間交換し、次に90%体積エタノールを5分間加え、体積80%エタノールを5分間、体積70%エタノールを5分間加え、 そして最後に5分間蒸留水を入れた。
- スライドをヘマトキシリン染色溶液に3〜8分間浸します。スライドを取り外し、蒸留水で汚れを洗い流します。それを分化液(1%塩酸アルコール)にほぼ30秒間移動させると、スライドは淡い青色にフェードします。蒸留水ですすぎ、エオジン染色液に1〜3分間入れます。
- スライドを95%エタノール体積分率で5分間脱水し、別のラウンドの新鮮な95%エタノールと5分間交換し、続いて無水エタノールを5分間、別のラウンドの新鮮な無水エタノールと5分間交換します。
- キシレンを5分間添加してスライドを透明にし、別のラウンドの新鮮なキシレンと5分間交換してから、中性樹脂で密封します。
- 軟骨の末端-デオキシヌクレオチジルトランスフェラーゼ媒介ニックエンドラベリング(TUNEL)
- 脱ろう水和が完了するまで、無水エタノール、90%エタノール、85%エタノール、75%エタノールで軟骨サンプルを脱水します。PBSに5分間浸します。3%H 2O2を10分間滴下する。
- プロテイナーゼK作業溶液を滴下し、37°Cで10分間消化します。スライスあたり20 μLの標識バッファーを加えて湿らせ、作業溶液を調製した後、余分な液体を振り落とします。各スライドに20 μLの作業溶液を加え、ウェットボックス内で37°Cで2時間インキュベートします。
- 50 μLの閉鎖溶液を滴下して30分間閉じます。次に、希釈したビオチン化抗ジゴキシン抗体50 μL(1:100希釈)を滴下し、ウェットボックス内で37°Cで2時間インキュベートします。10 μLのSABC抗体希釈液(1:100希釈)を滴下し、ウェットボックス内で37°Cで2時間インキュベートします。
- DAB発色溶液(1000μLの蒸留水に各50μLの試薬A、B、C)を10〜15分間滴下します。発色が茶色がかった黄色の粒状になると完了します。
- ヘマトキシリンで3秒間再染色します。グラジエント脱水と透明化処理の後、室温で乾燥させ、スライドをニュートラルガムで慎重に密封します。泡や接着剤の溢れを残さないように注意してください。
- IL-1βおよびTNF-αの免疫組織化学的解析
- スライドをキシレンで日常的に脱ワックスし、グラジエントアルコールで水和させます。切片中の内因性ペルオキシダーゼを3%H 2 O2で不活性化する。スライドホルダーを95°Cのクエン酸緩衝液(pH 6.0)に入れ、95°C以上の水浴中で20分以上インキュベートします。インキュベーションボックスを取り出し、室温で少なくとも20分間放置します。
- 5%正常ヤギ血清をPBSで37°Cで10分間インキュベートし、余分な液体を振り落とします。抗体Iを150 μLずつ滴下し、37°Cで1時間静置した後、4°Cで一晩保存します。 翌日、37°Cで45分間再温めます。
- PBSで3回ずつ5分間洗います。スライド上の組織を3%BSAで覆い、37°Cで30分間密封します。150 μLの抗体IIを一滴ずつ加え、室温で1時間静置します。PBSで3回ずつ5分間洗浄し、150 pLのDAB発色液を滴下します。サンプルが肉眼でも茶色がかった黄色になるまで、顕微鏡で染色の程度を観察します。
- すぐに、PBSで10分間すすいでください。再度ヘマトキシリンで染色し、グラジエントアルコールで脱水し、キシレンでスライドを透明にし、中性ガムで密封します。
- 統計解析
- 関連タンパク質の陽性発現を有する免疫組織化学的に染色された切片は、黄色または茶色がかった黄色である。免疫組織化学切片の各群についてImage Jソフトウェアによる陽性発現の強度をスコアリングし、IODを面積で割って算出した平均光学濃度(AOD)の評価基準を用いた。
- 統計分析には分析ソフトウェアを使用します。データが正規分布に適合している場合はt検定を使用し、カイ二乗は正規分布に適合しない場合はノンパラメトリック検定を使用します。一般化推定式により繰り返し測定データを解析します。
結果
疼痛行動テスト
MWTの結果、モデリング後の右後肢のMWTは以前よりも有意に低下したことが示されました(p<0.05)。対照群と比較して、ラットのMWTはTuina後に有意に上昇した(p<0.05; 図5 および 表2)。
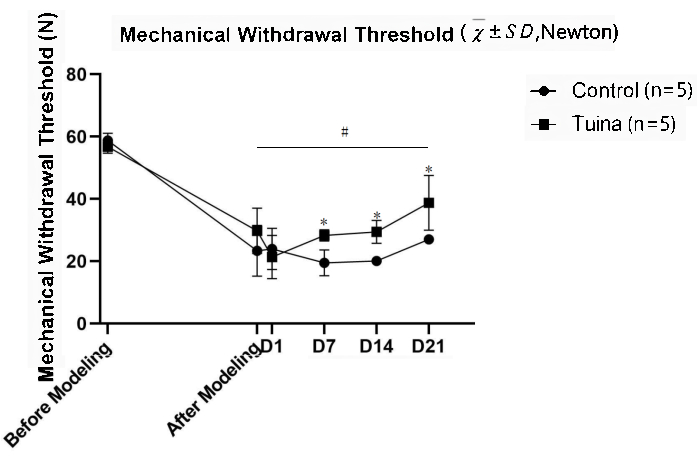
図 5...
ディスカッション
この研究は、KOAラットに対するTuina操作のプロトコルを提供します。疼痛行動試験と組織形態学的所見を通じて、KOAラットに適用されたこのような一連のTuina操作は、滑膜炎症と軟骨アポトーシスを減少させる可能性があることが示唆され、これはKOAの動物モデルにおけるTuina操作の参照となる可能性があります。
プロトコルにはいくつかの重要な手順があります。まず?...
開示事項
著者は、競合する利益がないことを宣言します。
謝辞
この作業は、上海クリティカルクリニカルスペシャリティ建設プロジェクト(助成金番号:Shslczdzk04001)によってサポートされました。上海科学技術委員会のセーリングプログラム(助成金番号:22YF1444300);上海中医薬大学の予算内のプロジェクト(助成金番号:2021LK091)。
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| absolute ethanol | Supelco | PHR1070 | For making specimen |
| ALMEMO admeasuring apparatus | ahlborn | 2450-1 | For Mechanical Withdrawal Threshold test |
| Anti-Digoxin antibody | Sigma-Aldrich | SAB4200669 | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| Anti-IL-1 beta | abcam | ab283818 | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| DAB Substrate kit | Solarbio | DA1010 | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| Denture base materials | Shanghai New Century | 20000356 | For model making |
| eosin | bioswamp | PAB180016 | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| Finger pressure recordings | Suzhou Changxian Optoelectronic Technology | CX1003w | For Tuina manipulation |
| formic acid solution | Sigma-Aldrich | 695076 | For decalcification |
| H2O2 | Sigma-Aldrich | 386790-M | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| hematoxylin | bioswamp | PAB180015 | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| Isoflurane | Shanghai Yuyan Scientific Instrument Company | S10010533 | For gas anesthesia |
| neutral resins | bioswamp | PAB180017 | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| Paraformaldehyde Fix Solution | Sigma-Aldrich | 100496 | For histology |
| PBS | Sigma-Aldrich | P3813 | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| Plantar Test Apparatus | IITC Life Science | / | For Paw Withdrawal Latency test |
| plaster of Paris bandage | WANDE | 20150023 | For model making |
| Proteinase K | Sigma-Aldrich | 124568 | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| TNF Alpha Monoclonal antibody | Proteintech | 60291-1-Ig | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| TUNEL | Servicebio | GDP1042 | For HE stain IHC or TUNEL |
| Wax | Sigma-Aldrich | 327204 | For making specimen |
| xylene | Shanghai Sinopharm Group | 100092 | For making specimen |
参考文献
- Joint Surgery Group of Chinese Orthopaedic Association, Chinese Association of Orthopaedic Surgeons, National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Diseases, Chinese Journal of Orthopaedics. Chinese Osteoarthritis Treatment Guidelines (2021 Edition). Chinese Journal of Orthopaedics. 41 (18), 24 (2021).
- David, S., et al. Epidemiology of knee osteoarthritis in general practice: a registry-based study. BMJ Open. 10 (1), 031734 (2020).
- Callahan, L. F., Cleveland, R. J., Allen, K. D., Golightly, Y. Racial/Ethnic, Socioeconomic, and Geographic Disparities in the Epidemiology of Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America. 47 (1), 1-20 (2021).
- Wang, K., Dong, X., Lin, J. H. Investigation of Medical Costs of Disease In Patients With Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint. National Medical Journal of China. 97 (1), 4 (2017).
- Perlman, A., et al. Efficacy and Safety of Massage for Osteoarthritis of the Knee: a Randomized Clinical Trial. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 34 (3), 379-386 (2019).
- Xing, H., et al. Therapeutic massage for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science. 19 (5), 354-363 (2021).
- Seo, B. R., et al. Skeletal muscle regeneration with robotic actuation-mediated clearance of neutrophils. Science translational medicine. 13 (614), (2021).
- Wu, J. H., Zhang, C., Dong, S. J., Yin, H. Effects of Massage with #34;Relaxing Tendons" Technique on the Interleukin-1B and 5-hydroxytryptamine Levels in the Joint Fluid of a Rabbit Knee Osteoarthritis Model. Chinese General Practice. 21 (6), 688-693 (2018).
- Luo, R. The effects of IL-1B,IL-6,IL-13,IL-26,TNF-a by patellar manipulations on rabbit knee osteoarthritis model. Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. , (2017).
- Qiu, F., Li, C., Wu, X., Liu, Y., Zhang, X. Effect of Massage on the Function of Foot-Yangming Meridian-Muscle in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. Acta Chinese Medicine. 36 (3), 649-655 (2021).
- Yang, B., Li, S. Research Progress of Massage in Improving Biomechanical Indexes of Knee Osteoarthritis. Acta Chinese Medicine. 37 (12), 2571-2576 (2022).
- Li, C., Qiu, F., Ding, J., Hu, G., Zhang, X. Curative Observation of Retaining of Heated Needle at Trigger Points Combined with Manipulation for Muscles along Meridians in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 37 (11), 2157-2162 (2020).
- Ding, X., Zhang, X., Hou, Y., Zhao, Z., Ye, X. Effect of massage manipulation on joint stiffness of knee osteoarthritis patients based on "spine-pelvis-knee" holistic diagnosis and treatment pattern. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 55 (08), 54-57 (2021).
- Fu, Y., Gong, L., Li, Y. The clinical studies of Rolling combined with Pulling Manipulation on Early and Middle-term. Jilin Journal of Chinese Medicine. 40 (07), 958-962 (2020).
- Jiang, J., Hu, X., Tang, R., Qiu, F., Huang, L. Change of lower limb force line in treating knee osteoarthritis with manipulation. Journal of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine. 34 (01), 129-132 (2018).
- Liang, Y., et al. Some issues on animal experiments standardization of acupuncture and moxibustion. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research. 25 (09), 2299-2300 (2014).
- Guo, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, Q., Chen, Z., Zhao, X. Basic System of Chinese Acupuncture Standard. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion. 31 (6), 549-550 (2011).
- YAN, X., Yan, J. Study on the Standardization of Classification of Tuina Manipulation. Acta Chinese Medicine. 32 (5), 875-878 (2017).
- Aikebaier, G., Lu, X., Liu, J., Liu, l., Wang, S. Analysis on Manipulation and Acupoint Selection Laws of Massage for Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis Based on Data Mining Technology. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine. 29 (5), 23-29 (2022).
- Gong, L., Wuquan, S., Zhang, H., Chen, Z. Research of Yan Juntao's Academic Experiences of Differential Treatment and Manipulation for Treating of Knee Osteoarthritis. Chinese Journal of Traditional Medical Traumatology & Orthopedics. 24 (7), 16-19 (2016).
- Qian, J., Xing, X., Liang, J. Two Methods to Establish Rat Model of Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Research and Exploration in Laboratory. 33 (11), 23-27 (2014).
- Liu, J., et al. Experimental study of a modified Videman method for replicating knee osteoarthritis on rabbit. Rehabilitation Medicine. 30 (03), 212-219 (2020).
- Moskowitz, R. W. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 14 (1), 1-2 (2005).
- Shen, M., Li, Z., Shen, J. Preliminary Exploration of Experiment Teaching on Experiment Acupuncture Science. Chinese Medicine Modern Distance Education of China. 7 (02), 130-131 (2009).
- Jeong, J., et al. Anti-osteoarthritic effects of ChondroT in a rat model of collagenase-induced osteoarthritis. BMC complementary and alternative medicine. 18 (1), 131 (2018).
- Hulth, A., Lindberg, L., Telhag, H. Experimental osteoarthritis in rabbits. Preliminary report. Acta orthopaedica Scandinavica. 41 (5), 522-530 (1970).
- Tawonsawatruk, T., Sriwatananukulkit, O., Himakhun, W., Hemstapat, W. Comparison of pain behaviour and osteoarthritis progression between anterior cruciate ligament transection and osteochondral injury in rat models. Bone & Joint Research. 7 (3), 244-251 (2018).
- Zhou, Q., et al. Cartilage matrix changes in contralateral mobile knees in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis induced by immobilization. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 16, 224 (2015).
- Zeng, J., et al. Establishment and identification of experimental rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis. Chinese Journal of Clinical Research. 29 (5), 679-682 (2016).
- Shang, P., et al. Comparison with two kind osteoarthritis animal models reduced by plaster immobilization in extend excessive position and bend excessive position respectively. Orthopaedic Biomechanics Materials and Clinical Study. (1), 11-14 (2006).
- He, Y., et al. Evaluation of the effect of improved cast immobilization method on rabbit knee osteoarthritis model. Chinese Imaging Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine. 18 (2), 198-219 (2020).
- Pengfei, S., et al. Possible mechanism underlying analgesic effect of Tuina in rats may involve piezo mechanosensitive channels within dorsal root ganglia axon. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 38 (6), 834-841 (2018).
- Wang, Y. Mechanisms of Massage Mediating Chondrocyte Apoptosis in Knee Osteoarthritis Through Piezo 1/JAK2 Signaling Pathway. Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. , (2019).
- Liu, J. Effect of Massage on TLR4/MyD88 Signal Transduction Pathway in Rat Knee Osteoarthritis Model. Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. , (2019).
- Yu, S., Zhou, J., Pang, X. Advances in induced animal models of knee osteoarthritis. Journal of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine. 25 (5), 50-55 (2022).
- Tan, Q., et al. Acupuncture combined with moxibustion regulates the expression of circadian clock protein in the synovium of rats with osteoarthritis. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research. 26 (11), 1714-1719 (2022).
- Zhang, Z., et al. A Review of Massage Therapy for Knee Osteoarthritis. Henan Traditional Chinese Medicine. 39 (1), 146-149 (2019).
- Gong, L., Sun, W., Zhang, H., Chen, Z. Research of Yan Juntao's Academic Experiences of Differential Treatment and Manipulation for Treating of Knee Osteoarthritis. Chinese Journal of Traditional Medical Traumatology & Orthopedics. 24 (7), 16-19 (2016).
- Chen, C., Zhang, H. Research on the rules of acupoint selection for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with massage based on data mining. Hainan Medical Journal. 29 (18), 2617-2619 (2018).
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請さらに記事を探す
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved