このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Method Article
3D血管造影法を用いた In vivo ヒツジモデルにおける下大静脈のコンプライアンスと拡張性の定量化
* これらの著者は同等に貢献しました
要約
このプロトコルでは、カテーテル法と3D血管造影法を生存手順として使用して、静脈のコンプライアンスと伸展性の in vivo 定量化が可能になり、さまざまな潜在的なアプリケーションが可能になります。
要約
合成血管移植片は、同種移植片、自家移植片、および異種移植片のいくつかの課題を克服しますが、多くの場合、それらが移植される天然血管よりも剛性が高く、準拠性が低くなります。ネイティブの容器とのコンプライアンスマッチングは、グラフトの成功のための重要な特性として浮上しています。船舶のコンプライアンスを評価するための現在のゴールドスタンダードには、船舶の切除と ex vivo 二軸機械試験が含まれます。私たちは、自然な生理機能をよりよく反映し、流れる血液や存在する形態学的変化によって引き起こされる圧力変化の影響を考慮に入れた、静脈のコンプライアンスと伸展性を評価する ためのin vivo 法を開発しました。
この方法は、動物の使用の必要性を減らしながら、縦断的研究を容易にする生存手順として設計されています。私たちの方法では、20 mL/kg の生理食塩水ボーラスを静脈血管系に注入し、その後、ボーラスの前後の 3D 血管造影を取得して、ボーラスによって誘発される変化を観察し、同時に標的領域の血管内圧測定を行います。その後、ボーラスの前後に血管の円周と断面積を測定することができます。
これらのデータと血管内圧により、特定の方程式のコンプライアンスとディステンシビリティを計算することができます。この方法は、天然の未手術のヒツジにおける下大静脈のコンプライアンスとディステンシビリティを、長期拡張ポリテトラフルオロエチレン(PTFE)グラフトを移植したヒツジの導管と比較するために使用されました。天然の血管は、すべての測定場所でPTFEグラフトよりも準拠性が高く、伸縮性が高いことがわかりました。この方法は、静脈のコンプライアンスと伸展性の in vivo 測定を安全に提供できると結論付けています。
概要
重篤な心臓異常のある患者は再建手術が必要です。ほとんどの再建手術では、血管移植片などの補綴材料を使用する必要があります。この空間を橋渡しする可能性のある導管には、合成材料または生物学的材料が含まれます。当初、同種移植片はフォンタン導管として使用されていましたが、石灰化と急性期のインシデントの発生率が高いため、その後放棄されました1。現在、無機高分子に由来する合成血管グラフトが使用されています。これらの移植片は、移植される天然の血管よりも順応性が低く、狭窄、閉塞、石灰化などの長期的な合併症を引き起こすという課題が残っています1,2,3,4,5。
合成血管移植片の構造は、機械的な引張強度に適しており、天然組織と比較して常にコンプライアンスが低くなります2。血管コンプライアンスは、圧力の変化に対する血管の体積の変化を定義し、機械的負荷に対する血管の応答性の指標として機能します。移植片材料と天然血管特性の違いは、コンプライアンスの不一致を生じさせ、血流パターンを混乱させることが実証されており、その結果、再循環と流れ分離の領域が生じます2,6,7,8,9。この現象は、内皮壁のせん断応力を変化させ、内膜過形成を誘発します2,7,8,9。このような反応は、移植片関連の合併症を引き起こす可能性があり、移植片の交換または再介入が必要になります6。
血管コンプライアンスは移植片の結果を決定する上で重要な役割を果たすため、この特性を正確に測定することが不可欠です。血管コンプライアンスを測定するための現在のゴールドスタンダードは、 ex vivo 管二軸機械的試験です。この方法では、目的の移植片または血管を切除し、ラテックスチューブに接続し、加圧して、さまざまな圧力にわたる円周方向の応力伸張挙動を評価します。コンプライアンスは、圧力を内径10の測定値と比較することによって決定される。ただし、 ex vivo 法にはいくつかの欠点があります。移植移植片の 機能をex vivo 法で評価する場合、動物を犠牲にして移植片を移植する必要があるため、長時間の検討は不可能です。そこで、 in vivo コンプライアンス測定プロトコルを開発しました。
私たちのグループは、先天性心疾患である左心低形成症候群(HLHS)を改善するためのフォンタン手術で使用するための組織工学的血管移植片(TEVG)の開発に焦点を当てています。先天性心血管手術の分野における最近の発展により、術後の転帰が改善され、平均余命が長くなっています。これにより、植込み型血管導管の長期的な特性と成功がますます重要になります。現在、HLHSの動物モデルは存在しないため、加速大型動物下大静脈(IVC)介在グラフトモデルでグラフトを評価します。このモデルはフォンタン循環の流れを作り出そうとはしていませんが、独特の血行動態条件を効果的に再現します。この in vivo プロトコルの最近の使用は、我々のTEVGと従来の拡張ポリテトラフルオロエチレン(PTFE)グラフト11との間のグラフトコンプライアンスに大きな違いを示しました。この先行研究では方法論に焦点が当てられていなかったため、この新しい in vivo 法の詳細について追加の実験を行いました。
現在標準治療として機能している、膨張ポリテトラフルオロエチレン(PTFE)で構成される合成移植片をドーセット羊研究動物に移植し、外科的にナイーブな対照動物の天然IVCと比較しました。このプロトコルは、PTFE導管の移植後5〜7年でPTFEグループおよびさまざまな年齢の未操作の対照動物で実施されました。したがって、プロトコールおよび代表的な結果を説明する後続のセクションでは、関心領域を、例えば、IVC介在グラフトのグラフト(midgraft)領域の中央と呼ぶことがある。
このプロトコルにより、長期的な時点で非準拠であることが知られているPTFEコンジットの天然静脈との in vivo コンプライアンスを解析できます。臨床標準材料であるPTFEを、天然の未手術静脈と比較することを選択しました。PTFEコンジットは非準拠のままで石灰化しやすく、コンプライアンスがさらに低下することが知られているため、長期的な時点を選択しました11。全身の血行動態の変化がin vivo法で得られた測定値に正確に反映されるため、すべての比較をin vivoで実施することを選択しました。この比較から、このプロトコルはPTFEの非コンプライアンスを確認し、安全で再現性のある方法で in vivo 静脈コンプライアンスの測定値を取得できることがわかりました。この方法は、PTFE 導管と in vivo11 の組織改変血管移植片 (TEVG) との間に統計的に有意な差があることを実証するために、公開された研究で成功裏に実施されています。
このプロトコルの全体的な目標は、生存手順からの in vivo 測定値を使用して、ヒツジの大型動物モデルにおける胸部 IVC のコンプライアンスと拡張性を計算することです。この目的のために、胸部IVCの流体ボーラスに対する円周と断面積の変化を視覚化し、測定しました。同時に、血管内圧力の変化を測定し、これらの測定値を使用してコンプライアンスとディステンシビリティを計算しました。3D血管造影イメージングを使用すると、キャプチャ後の画像ビューを調整して静脈の断面から測定値を取得したり、血管に沿った複数の位置を測定できるなど、複数の利点が得られます。この研究で関心のある3つの領域は、中移植片領域、PTFE移植片の隣接する2つの吻合部位、およびネイティブIVCの同等の領域でした。 in vivoで実験を行うことで、実際の血液の流れの中で、組織や臓器に囲まれた移植片の機能を評価することに利点があります。この方法によって得られた測定値は、生体内の移植片の実際の機能を反映していると考えられています。
プロトコルは、羊の処置前準備、カテーテル法、ベースラインのボーラス前データの収集、研究データの収集、動物の回復、およびデータ分析を含む6つの主要なセクションに分かれています。動物調製のセクションでは、鎮静、麻酔の開始、カテーテル法中に使用されるモニタリング機器の配置について説明します。第2部では、データ取得に必要な2本のカテーテルシースを装着するプロセスを説明します。このプロトコルでは、両方のシースを右内頸静脈 (IJV) に配置して、2 つのマルチトラック カテーテルを血管に導入できるようにします。1 つは関心領域に配置されて圧力の変化を記録し、もう 1 つは造影剤注入のために静脈の下部に配置されます。カテーテルが配置されると、比較のためにベースラインのプレボーラス3D血管造影法が取得されます。研究データの収集は、投与のために加圧バッグシステムで生理食塩水ボーラスを準備し、生理食塩水ボーラスに血管内圧の記録を提供し、ボーラス後の3D血管造影法を採取することから始まります。次に、プロトコル後の羊の回復を促進するためのプロセスについて説明します。最後に、分析と統計的比較のための適切な画像と断面測定値を取得する方法について説明します。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
プロトコル
この研究プロトコルは、Nationwide Children's Hospital Abigail Wexner Research Institute(AR22-0004)のInstitutional Animal Care and Use Committeeによって承認されました。すべての動物は、国立衛生研究所が発行した「実験動物の世話と使用に関するガイド」に従って人道的なケアを受けました。
1.動物の調理
- カテーテル挿入の1週間前に獣医チームに羊を評価してもらい、身体検査やバイタルサインの分析などを行い、動物が安全に麻酔を受けられることを確認します。
- 麻酔導入時の胃内容物の誤嚥のリスクを制限するために、動物を一晩、または処置の12時間前まで絶食します。
- コントロールパネルのオンボタンを押して、Cアームと3D血管造影システムをオンにします(図1A)。システムが完全にロードされるまで待ちます。
注意: 透視検査が一時停止され、画像化の準備が整い、すべての人員が保護リードを着用していることを確認してください。 - 1,000 mLの0.9%生理食塩水に1 mLのヘパリン(1,000 USP単位/mLの濃度)を添加して、手順で使用するヘパリン化生理食塩水を準備します。
- 首の左側を剃り、アルコールでこすります。ケタミン(4 mg / kg)、ブトルファノール(0.1 mg / kg)、ジアゼパム(0.5 mg / kg)の組み合わせを左頸静脈に注射して鎮静剤を投与します。.
- 鎮静剤を投与した羊を病院のベッドに置き、挿管のために胸骨の横臥位に置きます。羊のサイズに基づいて、喉頭鏡で舌と喉頭蓋を押さえ、ETチューブを気管に挿入して、9〜14mmの気管内(ET)チューブで挿管します。
- 羊を右横の位置に置きます。ETチューブを人工呼吸器に取り付け、100〜3 L / minで100%酸素で機械的に換気します。
- 1〜3%の吸入イソフルランで麻酔を維持します。.呼吸数を15〜30呼吸/分に設定し、潮汐量を8〜10mL / kgに設定します。
- 右前脚に血圧計、右耳に酸素飽和度を監視するためのイヤークリップ、食道への温度プローブ、ETチューブに呼気終末CO2 モニターなどの標準的な監視機器を配置します。露の爪とかかとの間の各蹄の尾側からウールを剃ります。心電図(ECG)ノードを配置し、ECGノードをテープで固定します。
- 点眼軟膏を塗布して両眼を滑らかにし、口腔胃管を挿入してガスと食物の排出を確保します。
- プロポフォール定速度注入 (CRI) (20-40 mg・kg-1・h-1)、維持液 (10 mL・kg-1・h-1)、および生理食塩水ボーラスの投与を可能にするために、左 IJV に IV ラインを確立します。
- 羊を左横臥位に配置します。首の右側を剃って、カテーテル挿入部位にアクセスします(図2A)。クロルヘキシジンスクラブとアルコールでその領域を綿棒で拭きます。
- モニタリング機器と人工呼吸器から外し、羊をカテーテル検査台に移動します。再度、動物を左横臥位に置きます(図3A)。
- 人工呼吸器と監視機器(ECGリード、温度プローブ、血圧カフ、パルスオキシメータ)に再接続します。
- 吸入イソフルラン1-3%を100%O2、および/またはプロポフォールCRI(20-40 mg・kg-1・h-1)を投与することにより、処置中に麻酔を維持します。.
注:動物の動き、痛みを伴う刺激への反応、呼吸数、脈拍数、血圧を測定することにより、麻酔面を評価します。必要に応じて、5〜10 mLのプロポフォールボーラスを使用してより深い麻酔面を誘発するなど、鎮静を調整します。. - 大きなキャリパーを使用して、心臓の領域で羊の幅を測定します。幅を2で割って、圧力トランスデューサを設定します。
- 手術部位を無菌的に洗浄し、滅菌方法でドレープします(図2B、C)。
2. カテーテル法
- Cアームを駐車位置から羊の胸に移動し、必要に応じてテーブルを上げます。コントロールパネルのボタン7と3を押し、次にスタートボタンを押したままにして、事前にプログラムされた設定を使用して、テーブルとテーブルの左側にあるCアームを自動配置します(図1A)。
- 21 Gマイクロパンクニードルと10 ccルアースリップシリンジを使用して、適切なIJVにアクセスします。シリンジプランジャーを引き戻しながら、皮膚を通して頭蓋/尾方向にIJVにアクセスします。針が血管内にあることを確認するために、血液が吸引されていることを確認してください(図2A、B)。
- 針をしっかりと保持しながら、シリンジを慎重に外します。
- 0.018インチのステンレス鋼(SS)ワイヤーガイドを針を通して容器の約半分に挿入します。SSワイヤーの上から針を取り外します。
- 5-フレンチ(Fr)拡張器をSSワイヤーの上から容器に入れます。拡張器の内側の部分とSSワイヤーを取り外します。0.038インチのガイドワイヤーを拡張器から容器の約半分まで送り込み、拡張器を取り外します。
- 11枚刃のメスを使用して、ワイヤーが入る静脈の上の皮膚を切断します。9-Frシースをガイドワイヤーに通して容器に供給します。インナーシースセクションとガイドワイヤーを取り外します。
- 血液を吸引し、ヘパリン化生理食塩水でシースを洗い流すことにより、適切なシースの配置を確認します。
- 手順2.2〜2.7を繰り返して、右側のIJVに2つの9-Frシースがあることを確認します。
- 凝固を防ぐために、IVを介して150U / kgのヘパリンを投与します。
- フットペダルを使用して透視を開始します(図1B)。ジャドキンスライト(JR)カテーテルをシースに挿入し、胸部IVCを横切って腹部IVCに続いています。
- ローゼンワイヤーをJRカテーテルに通し、腹部IVCに到達し、先端がJRカテーテルから出てくるまで通します。ローゼンワイヤーを所定の位置に保持したまま、JRカテーテルをそっと取り外します。
- 2.10〜2.11を2番目のシースで繰り返します。
- 7-Frマルチトラックカテーテルを各Rosenワイヤーに通します。
- 透視法のガイダンスの下で、造影剤注射のために腹部IVCに1つのマルチトラック血管造影カテーテルを配置します。
- 透視法を使用して、圧力測定のために別のマルチトラック血管造影カテーテルを特定の関心領域(グラフトの中心など)に留置します(図2C)。
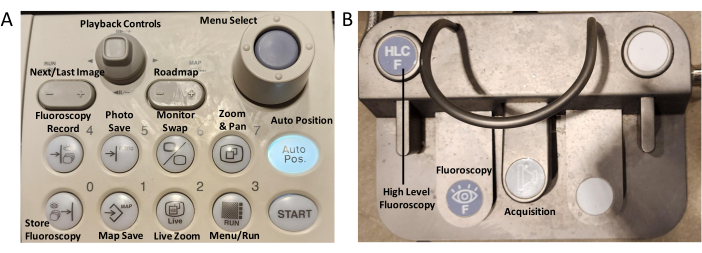
図1:コントロールパネル。(A) 3D血管造影システムのコントロールパネル (B) 透視フットペダル この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
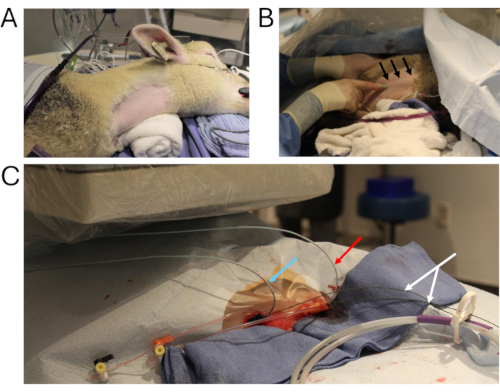
図2:動物のカテーテル法 (A)カテーテル法のために準備された主要な手術部位。(B)右内頸静脈を可視化する技術(黒矢印)。(C)2本のマルチトラック血管造影カテーテルを右内頸静脈に留置します(青矢印:グラフト内の圧力測定、赤矢印:腹部IVCへの造影剤注入、白矢印:硬いワイヤー)。略語:IVC =下大静脈。 この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
3. 事前データの収集
- 関心領域を中心とするマルチトラックを、三方活栓を使用して圧力トランスデューサーに接続します。ストップコックをマルチトラックに開いた状態で、気泡が取り除かれて血液が見えるまで10mLの注射器で引き戻します。
- 10mLのシリンジを逆さまにして、マルチトラックに空気を押し戻さないように注意して血液を羊に戻します。マルチトラックをヘパリン化生理食塩水で洗い流します。
- ストップコックのオフ位置をシリンジに戻し、圧力トランスデューサーとマルチトラックが互いに開くようにします。
- 造影剤を追加して造影剤を調製します。3D血管造影の最小容量は60 mLで、総造影剤は5 mL/kgまたは250 mLを超えることはできません。
- 造影剤インジェクターを腹部IVCの中央にあるマルチトラックに接続します。コントラストインジェクターを使用して、ノブを反時計回りにゆっくりと回し、血液が見えるまでマルチトラックから気泡を引き出します。ノブを時計回りに回すと、コントラストがゆっくりと前方に押し込まれ、マルチトラックに押し込まれます。
- 透視法を使用して、コントラストがマルチトラックの先端に達したことを確認します。
- 3D血管造影に使用したトータルコントラストを5で割ってmL/sを求めます。レート上昇を 0 と 600 psi に設定します。
- 画面右上の [プログラム ]ボタンと 3D DSA 110 8インチ ボタン(SIDが110cmの3D血管造影とフィールドをクリックして、Cアームを事前にプログラムされたモードに設定します View 8インチ)。
- すべてのオブジェクトと人をテーブルの前面または側面から離します。コントロールパネルの3番のボタンをクリックして、C-Armプログラムを開始します。ターゲット領域(例えば、midgraft)をx-y平面の中心に配置します(図3A-C)。
- コントロールパネルの4番のボタンをクリックして、2番目のプログラムに進みます。テーブルの高さを適宜調整して、対象領域を中央に配置します。
- 5 の番号が付いたボタンを押して、テスト画像を撮影します。
- C-Armの可動域を事前テストするには、[ Confirm Conditions ]ボタンをクリックします。 | 開始します (図3D、E)。
- 麻酔科医に換気を保持し、 中央取得ペダルでプログラムを開始して造影剤注射で3D回転血管造影を受けるように依頼します。ターゲット領域の平均圧力を同時に測定して記録します。
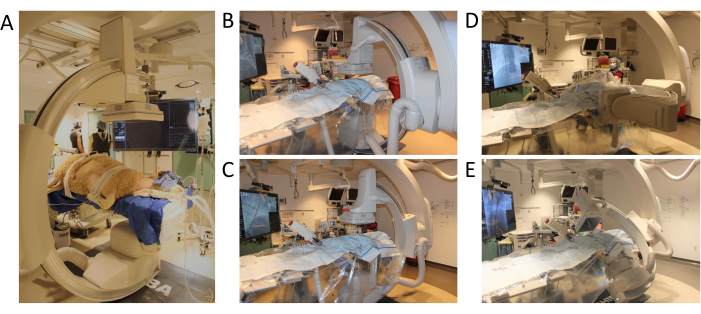
図3:Cアームの位置と可動域。 (A) 手順開始時の羊のポジショニング (B) 3D血管造影プログラムの最初の位置 (C) Cアームをxy軸に移動 (D) Cアームをz軸に移動 (E) Cアーム 全可動域でテストスピンを完了。 この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
4. 生理食塩水ボーラスの投与とデータ収集
- 20 mL/kg の 0.9% 生理食塩水を調製します。
- ボーラス加圧バッグを調製するには、0.9%生理食塩水の1,000mLバッグを加圧バッグユニットに加えます。必要に応じて、投与する総量を達成するために2台目のユニットを使用してください。
- 圧力計が赤の線(圧力250〜300 mmHg)の直前の緑のゾーンに上昇するまで、膨張電球を握ります。生理食塩水をラインに流し、気泡を取り除きます。
- 加圧された生理食塩水バッグを9-Frシースに接続し、ボーラスの速度を一定に保つために250-300 mmHgを維持します。羊が20 mL / kg相当のボーラスを受け取るか、平均圧力が15 mmHgに達するまで、それを流します。.
- ボーラスが流れている間、毎分ターゲット領域の血管内圧を記録します。
- 手順3.9〜3.12を繰り返して、C-Armを2回目の3D回転血管造影の準備をします。ボーラスが終了したらすぐに、圧力が下がり始める前に、ステップ 3.13 で説明されているように開始して、2 回目の 3D 血管造影と血管内圧測定を同時に行います。
5. リカバリー
- イメージングが完了したら、 77 番を入力し、Cアームがそれ自体の位置になるまで スタート ボタンを押し続けて、Cアームを事前にプログラムされた駐車位置に戻します。
- マルチトラック血管造影カテーテルとローゼンワイヤーを取り外します。
- 止血パッチで挿入部位に直接圧力をかけながら、両方のシースを少なくとも7分間取り外して、出血を止めます。
- 滅菌ロールのガーゼをパッチと首に巻き付けて、ラップが圧力を維持するためにしっかりと固定されるようにしますが、循環を遮断したり呼吸を妨げたりするリスクがあるほどきつくはありません。
- 麻酔薬(イソフルランおよび/またはプロポフォールCRI)をオフにします。.
- 羊が一貫して自力で呼吸するまで、100%O2 で人工呼吸器を維持します。
注:羊が目を覚ましている兆候には、動き、まばたき、痛みを伴う刺激への反応、顎のトーンや噛もうとする試み、人工呼吸器の補助なしでの呼吸などがあります。 - 羊が自力で呼吸できるようになったら、抜管(ETチューブを抜く)し、口腔胃管を抜く。
- すべての監視機器を取り外し、羊を病院のベッドに移します。それをハウジングルームに戻します。
- 羊が胸骨の横臥にとどまるとき、または羊が自分でバランスを保つことができるまで立とうとするときに、羊を助けます。彼らが壁にぶつかるのを防ぎます。
- 彼らが十分に目を覚ましているように見えたら、少量の干し草や穀物を与えます。
6. データの分析
- 血管造影イメージングソフトウェアから元の生の3D血管造影データをDICOMファイル形式でエクスポートします。
- DICOMビューアソフトウェアを起動します。3D血管造影ファイルをビューアにドラッグアンドドロップして開きます(図4A)。
- DICOMビューアソフトウェア内で、 3D MPR(Multi-Planar Reconstruction)ツール を選択して、血管造影データの3D再構築ビューを生成します。これにより、軸面、矢状面(図4B)、冠状面(図4C)の3つの異なる角度から3つの異なる2Dビューが表示されます。
- 矢状面と冠状面のターゲット領域の配置と向きを調整して、ターゲット領域を中央に配置し、ハンドツールで各平面上の参照線の方向を回転させることにより、目的の垂直位置を実現します(図4D)。
- DICOMビューア内の鉛筆ツールを使用して、ターゲット領域の軸ビューで血管壁の輪郭を描きます(図4E)。ソフトウェアは、軸方向ビューの中央にある領域の面積と周囲長(円周)の両方を自動的に計算して表示します。
- 式(1)を使用してコンプライアンスを計算します(Aは断面積(cm2)、Pは圧力(mmHg)です)。
 (1)
(1) - 式 (2) を使用して、C が円周 (cm)、P が圧力 (mmHg) である変位を計算します。
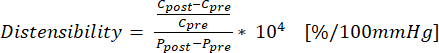 (2)
(2)
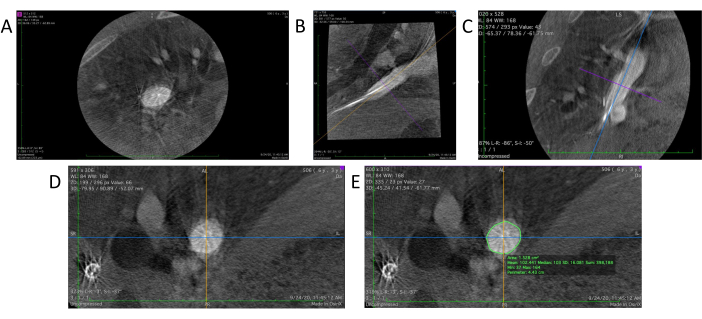
図4:DICOMビューアでのデータ分析。 (A)DICOMビューアにロードされた3D血管造影の生データ。(B)グラフトの矢状部分。(C)冠状切片。(D)矢状断面と冠状断面の角度を調整した後、真の断面を視覚化します。(E)ペンシルツールは、円周と断面積の測定を行うために、ターゲット血管の輪郭を描くために使用されます。 この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
結果
私たちは25頭以上の羊でこの手順を成功裏に実行しました。重要なことに、この手順に関連する罹患率と死亡率の事例はありませんでした。すべての羊は、単純な回復を示しました。これらの代表的な結果は、PTFEグラフトを移植した3頭のヒツジと3頭の未手術の在来ヒツジから得られたものです。 図5 は、プロトコル中に研究動物の両グループから取得した血管内圧測?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
ディスカッション
コンプライアンスと拡張性は、血管機能の主要な特性であり、潜在的な合併症や介入の指標として機能します。これらのパラメータの変化を正確に定量化し、比較することは、移植片の有効性を評価するために重要です。当社の in vivo 法は、 ex vivo 解析の限界を克服し、同等の結果を維持します。我々の in vivo データとBlumらによって提示された ex vivo データを比較...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
開示事項
この研究は、Gunze Ltd.が一部後援しました。
謝辞
この作業は、R01 HL163065とW81XWH1810518の支援を受けました。これもひとえに動物研究コアの献身的なスタッフの皆様に感謝申し上げます。また、Carmen Arsuaga氏の貴重な専門知識と研究期間中の慎重なケアにも感謝の意を表したいと思います。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.035" x 260 cm Rosen Curved Wire Guide | Cook Medical | G01253 | Guide for holding placement swapping caths (Multi-track, IVUS, etc) |
| 0.035"x 150 cm Glidewire | Terumo | GR3507 | Guide for JR cath |
| 0.9% Sodium Chloride Saline | Baxter Healthcare Corporation | NCH pharmacy | For diluting norepinpherine, pressure monitoring |
| 10.0 Endotracheal tube | Coviden | 86117 | To secure airway |
| 16 G IV catheter | BD | 382259 | To administer fluids and anesthetic drugs |
| 22 G IV catheter | BD | 381423 | For invasive blood pressure |
| 5Fr x .35" JR2.5 | Cook Medical | G05035 | Guide for rosen wire |
| 70% isopropyl alcohol | Aspen Vet | 11795782 | Topical cleaning solution |
| 7Fr x 100 cm Multi-track | B. Braun | 615001 | Collecting pressure, Administering contrast to specific intravascular location |
| 9Fr Introducer sheath | Terumo | RSS901 | Access catheter through skin into vessel for wires to pass through |
| ACT cartridge | Abbot Diagnostics | 03P86-25 | Activated Clotting Time |
| Angiographic syringe w/ filling spike | Guerbet | 900103S | For contrast injector |
| Bag decanter | Advance Medical Designs, LLC | 10-102 | Punctures saline bag to pour and fill sterile bowl with saline |
| Butorphanol | Zoetis | NCH pharmacy | Sedation drug: Concentration 10 mg/mL, Dosage 0.1 mg/kg |
| Cath Research Pack | Cardinal Health | SAN33RTCH6 | Cath pack with misc. supplies |
| Cetacaine | Cetylite | 220 | Topical anesthetic spray |
| Chloraprep | BD | 930825 | Topical cleaning solution |
| Chlorhexidine 2% solution | Vedco INC | VINV-CLOR-SOLN | Topical cleaning solution |
| Conform stretch bandage | Coviden | 2232 | Neck wrap to prevent bleeding |
| Connection tubing | Deroyal | 77-301713 | Connects t-port to fluid/drug lines |
| Diazepam | Hospira Pharmaceuticals | NCH pharmacy | Sedation drug: Concentration 5 mg/mL, Dosage 0.5 mg/kg |
| EKG monitoring dots | 3M | 2570 | |
| Fluid administration set | Alaris | 2420-0007 | |
| Fluid warming set | Carefusion | 50056 | |
| Hemcon Patch | Tricol Biomedical | 1102 | Patch for hemostasis |
| Heparin | Hospira, Inc | NCH pharmacy | Angicoagulant: 1,000 USP units/mL |
| Infinix-i INFX-8000C | Toshiba Medical Systems | 2B308-124EN*E | Interventional angiography system |
| Invasive pressure transducer | Medline | 23DBB538 | For invasive blood pressure |
| Isoflurane | Baxter Healthcare Corporation | NCH pharmacy | Anesthetic used in prep room |
| Ketamine | Hospira Pharmaceuticals | NCH pharmacy | Sedation drug: Concentration 100 mg/mL, Dosage 4 mg/kg |
| Lubricating Jelly | MedLine | MDS0322273Z | ET tube lubricant |
| Micropuncture Introducer Set | Cook Medical | G47945 | Access through skin into vessel |
| Needle & syringes | Cardinal Health | 309604 | For sedation |
| Norepinpherine Bitartrate Injection, USP | Baxter Healthcare Corporation | NCH pharmacy | 1 mg/mL |
| Optiray 320 | Liebel-Flarsheim Company, LLC | NCH pharmacy | Contrast |
| Optixcare | Aventix | OPX-4252 | Corneal lubricant |
| OsiriX MD | Pixmeo SARL | - | DICOM Viewer and Analysis software |
| Pressure infusor bag | Carefusion | 64-10029 | To maintain invasive blood pressure |
| Propofol | Fresenius Kabi | NCH pharmacy | Anesthetic drug: Concentration 10 mg/mL, Dosage 20-45 mg·kg-1·h-1 |
| Silk suture 3-0 | Ethicon | C013D | To secure IV catheter |
| SoftCarry Stretcher | Four Flags Over Aspen | SSTR-4 | |
| Stomach tube | Jorgensen Lab, INC | J0348R | To release gastric juices and gas and prevent bloat |
| T-port | Medline | DYNDTN0001 | Connects to IV catheter |
| Urine drainage bag | Coviden | 3512 | Connects to stomach tube to collect gastric juices |
| Warming blanket | Jorgensen Lab, INC | J1034B |
参考文献
- Hagler, D. J., et al. Fate of the Fontan connection: Mechanisms of stenosis and management. Congenit Heart Dis. 14 (4), 571-581 (2019).
- Nezerati, R. M., Eifert, M. B., Dempsey, D. K., Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Electrospun vascular grafts with improved compliance matching to native vessels. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 103 (2), 313-323 (2015).
- Bates, O., Semple, T., Krupickova, S., Bautisa-Rodriguez, C. Case report of a Gore-Tex TCPC conduit dissection causing severe stenosis. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 5 (11), 1-6 (2021).
- Sathananthan, G., et al. Clinical importance of Fontan Circuit thrombus in the adult population: Significant association with increased risk of cardiovascular events. Can J Cardiol. 35 (12), 1807-1814 (2019).
- Kumar, P., Bhatia, M. Computed tomography in the evaluation of Fontan Circulation. J Cardiovasc Imaging. 29 (2), 108-122 (2021).
- Abbott, W. M., Megerman, J., Hasson, J. E., L'Italien, G., Warnock, D. F. Effect of compliance mismatch on graft patency. J Vasc Surg. 5 (2), 376-382 (1987).
- Weston, M. W., Rhee, K., Tarbell, J. M. Compliance and diameter mismatch affect the wall shear rate distribution near an end-to-end anastomosis. J Biomech. 29 (2), 187-198 (1996).
- Ballyk, P. D., Walsh, C., Butany, J., Ojha, M. Compliance mismatch may promote graft-artery intimal hyperplasia by altering suture-line stress. J Biomech. 31 (3), 229-237 (1997).
- Lemson, M. S., Tordoir, J. H. M., Daemen, M. J. A. P., Kitslaar, P. J. E. H. M. Intimal hyperplasia in vascular grafts. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 19 (4), 336-350 (2000).
- Blum, K. M., et al. Tissue engineered vascular grafts transform into autologous neovessels capable of native function and growth. Commun Med. 2, 3(2022).
- Turner, M. E., et al. Tissue engineered vascular grafts are resistant to the formation of dystrophic calcification. Nat Commun. 15, 2187(2024).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved