Method Article
돼지 모델에서 이소성 신장자가 이식 : 단계별 프로토콜
요약
Porcine models of organ transplantation provide an important platform to study mechanisms of organ preservation. This article describes a heterotopic porcine renal autotransplantation model, which allows investigating new approaches to improve the outcome of transplantation using marginal kidney grafts.
초록
Kidney transplantation is the treatment of choice for patients suffering from end-stage renal disease. It offers better life expectancy and higher quality of life when compared to dialysis. Although the last few decades have seen major improvements in patient outcomes following kidney transplantation, the increasing shortage of available organs represents a severe problem worldwide. To expand the donor pool, marginal kidney grafts recovered from extended criteria donors (ECD) or donated after circulatory death (DCD) are now accepted for transplantation. To further improve the postoperative outcome of these marginal grafts, research must focus on new therapeutic approaches such as alternative preservation techniques, immunomodulation, gene transfer, and stem cell administration.
Experimental studies in animal models are the final step before newly developed techniques can be translated into clinical practice. Porcine kidney transplantation is an excellent model of human transplantation and allows investigation of novel approaches. The major advantage of the porcine model is its anatomical and physiological similarity to the human body, which facilitates the rapid translation of new findings to clinical trials. This article offers a surgical step-by-step protocol for an autotransplantation model and highlights key factors to ensure experimental success. Adequate pre- and postoperative housing, attentive anesthesia, and consistent surgical techniques result in favorable postoperative outcomes. Resection of the contralateral native kidney provides the opportunity to assess post-transplant graft function. The placement of venous and urinary catheters and the use of metabolic cages allow further detailed evaluation. For long-term follow-up studies and investigation of alternative graft preservation techniques, autotransplantation models are superior to allotransplantation models, as they avoid the confounding bias posed by rejection and immunosuppressive medication.
서문
Kidney transplantation is the treatment of choice for patients with end-stage renal disease, due to associated lower rates of morbidity and mortality when compared to dialysis 1-3. Despite major improvements in patient outcomes following kidney transplantation, graft shortage still poses a severe challenge worldwide. The number of patients waiting for a kidney transplant by far exceeds the number of organs available 4-6. To increase the number of kidneys available for transplantation and to reduce patient waiting times, further sources of kidney grafts are needed.
Commonly, standard criteria donor (SCD) and extended criteria donor (ECD) kidney grafts from donation after brain death (DBD) as well as kidneys recovered from live donors (LDKT) are utilized. Since the 1990s, an increasing number of kidney grafts have been recovered in a donation after circulatory death (DCD) scenario, to further expand the donor pool 7,8. However, DCD and ECD kidney grafts demonstrate acceptable but decreased outcomes after transplantation, depending on different factors, such as donor age, warm and cold ischemia times, and the preservation technique used 9-11. Thus, additional research is required to improve the outcome of patients receiving marginal kidney grafts and to further increase the donor pool.
The porcine model of renal transplantation is well established and provides a clinical important scenario to investigate innovative approaches for the improvement of marginal kidney graft outcomes. In contrast to rodent and canine kidneys, which are unilobular, porcine and human kidneys are multilobular and are anatomically similar, particularly in regard to the arterial, venous, and urinary collecting systems 12,13. In addition, porcine and human kidneys demonstrate similarities in the pathophysiology of ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI), biochemistry, and immunological parameters 14. Thus, porcine renal transplantation is well-suited to investigate new organ preservation methods for marginal kidney grafts 15-17, model human IRI 18, study immunological pathways and allograft tolerance 19, provide surgical training 20-22, test new pharmacological therapies 23, implement new medical devices, and study new immunological mechanisms in xenotransplantation 24-26.
The renal porcine and human transplantation settings are not completely analogous. This article focuses on important technical details that will facilitate successful establishment of a renal autotransplantation model. Species-adapted pre- and postoperative housing, administration of anesthesia with close monitoring, and matched surgical techniques are described in the protocol and demonstrated in the video. Resection of the contralateral native kidney provides the opportunity to assess the function of the transplanted kidney. The placement of venous and urinary catheters and the use of metabolic cages allow more in-depth assessment. For studies aimed at investigating alternative graft preservation methods and mechanisms of IRI, autotransplantation models are superior to allotransplantation models, as they avoid the complications and confounding bias associated with rejection and use of immunosuppressive medications.
프로토콜
모든 동물은 인간주의와 우리가 동물 관리에 캐나다 의회의 정책과 지침에 따라 수행하는 모든 연구를 받았다. 모든 절차는 대학 건강 네트워크 기관 동물 관리위원회에 의해 승인 된 동물 사용 프로토콜에 따라 수행 하였다.
참고 : 연구 프로토콜의 개략도를 그림 1에 제시되어있다.
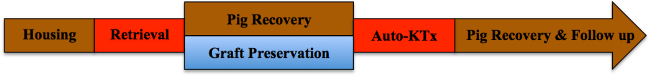
그림 1. 연구 프로토콜입니다. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
1. 동물
- 이 프로토콜에 남성 요크셔 돼지 (30kg)를 사용합니다.
2. 신장 이식 검색
- 수술 전 절차
- 하우스 남성 Yorkshir최소 1 주일 동안 연구 기관에서 전자 피그들을 순응. 스트렙토 SUIS 및 살모넬라 감염의 위험을 감소시키기 위해 3 일, 예컨대 세프 티오 푸르와 같은 3 세대 세 팔로 스포린의 근육 내 주사를 사용한다. 흡입을 방지하기 위해 마취 유도 전 6 시간 이상 동안 돼지 빠르게.
- 케타민 (20 ㎎ / ㎏), 아트로핀 (0.04 ㎎ / ㎏)과 미다 졸람 (0.3 ㎎ / ㎏)의 근육 내 주사하여 돼지의 마취를 시작합니다. 이어서, 수술실 (OR)에 하우징 동물 시설에서 전송.
- 또는 테이블에 앙와위에서 돼지를 놓습니다. 돼지가 자발적으로 이소 플루 란의 5 % 산소의 2 L를 흡입 할 수 있습니다. 후두경으로 성대를 노출하고 삽관에 의한기도 수축을 방지하기 위해 2 % 리도카인 국소 용액을 스프레이. 6.5 mm 튜브 삽관 후, 공기의 3-5 ml의와 커프를 차단합니다.
참고 : Capnometry 올바른하여 위치 될을 확인기관 튜브의 N. - 2.5 %로 이소 플루 란 가스를 줄입니다. 14 ~ 16 호흡 / 분, 10 ~ 15 ㎖ / kg 체중의 호흡량에 인공 호흡기를 설정합니다. 밀접하게 돼지를 모니터링합니다. 심박수와 산소 포화도는 펄스 oxymetry에 의해 기록된다. 감소 심장 박동에 의한 적절한 마취을 확인하고 돼지 운동의 혈액 (100 mmHg로 수축기 값 이하) 압력뿐만 아니라 부재 (근육 이완제없이 사용) (150 비트 / 분 이하).
- 무균 조건에서 9.5 천을 소개 Seldinger 기술 (27)를 사용하여 내 경정맥에 단일 루멘 영구 카테터. 간단히, 혈관에 구멍에 바늘을 사용합니다. 가이드 와이어를 도입 한 후, 혈관 카테터와 와이어를 교체 한 다음 필 멀리 도입기와 바늘을 교체합니다. 3-0 실크 또는 비 흡수성 모노 필라멘트 봉합사를 사용하여 피부에 카테터를 고정.
- 메트로니다졸 500 ㎎, 세파 졸린 1 g을 20 mg의 판토 프라 졸을 관리. 광고장관 5 % 덱 스트로스 (D5W)과 정맥 수술을 통해 시간 당 1 ml의 펜타닐 시트 레이트와 락 테이트 링거액 200 ㎖. 마취 동안 건조를 방지하기 위해 눈에 수의학 안과 연고를 적용합니다.
- 수술 절차
- 멸균 소독 및 수술 분야의 적용 범위에 따라, 길이 25 cm의 중간 선 절개를 수행합니다. 트랙터를 삽입합니다. 수건으로 크고 작은 창자를 덮고 오른쪽 신장에 최적의 액세스를 위해 왼쪽에 위치.
- 요관과 소작를 사용하여 부착 조직으로부터 오른쪽 신장 자체를 무료로 제공됩니다.
- 하대 정맥과 대동맥에서 기원까지 소작을 사용하여 오른쪽 신장 정맥과 동맥을 해부 각각 무료입니다. 동맥 혈관 경련을 방지하기 위해, 파파 베린의 30-65 mg을 투여가 고려되어야한다.
- 전체 신장 해부, 넥타이 (실크, 3-0) 후와 원심 요관를 잘라. 위해 준비 할얼음의 개 그릇 및 멸균 기관 가방.
- 첫째, 가까운 대동맥과 두 번째 신장 동맥 클램프 혈관 클램프를 사용하여 대정맥에 가까운 신장 정맥 클램프. 다음으로, 신장 이식을 절제하고 즉시 신장 동맥 정맥과 신장 동맥을 cannulate. 혈액을 플러시 얼음처럼 차가운 히스티딘 트립토판 - 케 토글 루타 레이트 (HTK) 용액 500 ml를 사용합니다. 이식까지 얼음에 신장을 저장합니다.
- 현장에서, 합자 (실크, 2-0) 및 실행 봉합사 (prolene의, 6-0)으로 신장 정맥으로 남아있는 신장 동맥을 닫습니다.
- 출혈에 대한 해부 영역을 확인 후, 실행 봉합 (monofil, 1)과 3-0 실크 또는 비 흡수성 모노 필라멘트 봉합사로 피부와 복부 벽을 닫습니다 ..
- 수술 후 절차
- 원치 않는 조작을 방지하기 위해 돼지의 뒷면에 봉합 (실크, 3-0)와 터널을 함께 정맥 카테터 피하을 수정합니다. 쉬운 돼지를 배치 한 후,이야uture (실크, 3-0) 피부에 단단히 카테터.
- 인공 호흡기에서 돼지를 유아하고 발관 후 그 주택 지역에 복구 할 수 있습니다. 볼륨 확장을위한 정맥 링거 락 테이트를 관리하고 진통제 0.3 mg을 부 프레 노르 핀을 관리 할 수 있습니다. 이 흉골 드러 누움을 유지하기 위해 충분한 의식을 회복 할 때까지 무인 동물을 두지 마십시오.
3. 신장 이식 이식
- 수술 전 절차
- 50 ~ 100 밀리그램 / hr의 속도로 프로포폴의 연속 주입 하였다 프로포폴의 정맥 내 주사 (1-2 ㎎ / ㎏ 체중)을 사용하여 돼지를 마취. 단계 2.1.3과 2.1.4에 설명 된대로 돼지를 다시 삽관 3-4 %로 이소 플루 란 가스를 설정합니다.
- 수술 중에 세파 졸린 1 g 및 판토 프라 졸 IV의 20 mg의 투여 2.1.4에 기재된 것과 같은 마취 프로토콜을 사용한다.
- 멸균 소독 후, 기관 옆에 4cm의 상처를합니다. TI를 해부하다경동맥을 노출 ssue. 오버 홀트 포셉과 동맥 주위에 실크 넥타이 (2-0)를 전달합니다. 수술 내내 연속적 동맥압을 측정하기 위해 플라스틱 카테터를 도입 Seldinger 기법을 사용한다. 대안 적으로, 비 침습적 혈압 측정 기술이 이용 될 수있다.
- 수술 절차
- 살균 소독 후에, 피부 및 근막 봉합 스티치 절단하여 복강을 다시 복강을 노출 수술 권취 재 도입 및 infrarenal 선박에 더 접근 할 수 있도록 좌측 장 재배치.
- 보존 신장 이식은 엔드 - 투 측 infrarenal 대정맥과 대동맥에 이식. 따라서, 픽업과 소작을 사용하여 장골 분기 위 5-8cm 이상 대정 맥과 대동맥을 해부하다. 가능하면, 림프 혈관을 방해하지 않는다; 가능하지 않을 경우, 5-0 prolene의 봉합로 닫습니다.
- 해부를 완료 한 후, fo를 확인출혈 R 및 선박에서 남은 조직을 제거합니다. Satinsky 클램프와 대정 맥과 대동맥의 완전한 체결이 가능 있는지 확인하십시오.
- 다음에, 반대측 (왼쪽)의 신장을 절제. 이렇게하려면 오른쪽에있는 장 위치; 요관, 신장 자체, 신장 정맥, 그리고 접착 조직에서 신장 동맥을 해부하다. 요관과 혈관을 묶어과 신장을 절제. 출혈이 있는지 확인합니다.
- infrarenal 대동맥과 대정맥을 노출 왼쪽에있는 장 위치를 조정합니다. 헤파린 (100 IU / kg 체중)을 주입하고, 적어도 2 분 동안 기다린다.
- 정맥 문합 :
- 완전히 대정맥을 클램프 (11)의 블레이드를 사용하여, 신장 혈관의 개구부의 크기와 일치하는 슬릿 절개를하기 Satinsky 클램프를 사용한다. POTT 위는 상기 슬릿을 연장 할 수있다.
- 멸균 얼음을 함유하는 직물에 신장을 배치 한 후, 얼음에서 분리하고, 수술 부위로 위치. 사용이 더블 무장 6-0뇌와 꼬리 코너 스티치를 수행 할 봉합을 prolene의.
- 신장에 근접 상단 모서리를 넥타이 다시 벽을 시작으로 6-0 prolene의를 사용하여 실행 봉합을 수행합니다. 2/3를 완료 한 후, 전면에 봉합사를 완료 타이 타 단부를 사용한다. 두개골 바늘을 묶는 후, 꼬리 모서리에 바늘 넥타이.
- 신장 정맥에 불독 클램프를 놓고 Satinsky 클램프를 엽니 다. 출혈의 문합을 확인합니다.
- 동맥 문합 :
- 완전히 대동맥을 고정하는 Satinsky 다시 클램프 사용합니다. 신장 동맥의 개통과 일치, 슬릿 절개를 만들기 위해 11 블레이드를 사용합니다. 깨끗한 구멍을 확보하기 위해 4.0 mm 라운드 펀치를 사용합니다.
- 수신자 측에서 시작, 동맥 문합을 수행하는 하나의 6-0 prolene의 봉합사를 사용합니다. 동맥 내피 세포가 박리를 방지하기 위해 각 봉합에 포함되어 있는지 확인합니다. 한편, norepinephr 10 ML의 연속 물방울을 시작합니다오프라인 (16 밀리그램 / 250 ml)에 링거 락 테이트 500ml에 희석하고, 100 mmHg의 상기 수축기 혈압을 유지하는 적정한다.
- 동맥 문합 완료 전에 베라파밀, 동맥 내 주사 및 연축 않도록 용기의 외부로 국소 베린 관리.
- 신장 동맥에 불독 클램프를 놓고 Satinksy 클램프를 엽니 다. 출혈의 문합을 확인합니다.
- 천 신장을 푸는과 얼음을 제거합니다. 동맥 불독 클램프 다음 먼저 정맥 불독 클램프를 엽니 다. 재관류 후, 소변 생산이 즉시 시작해야합니다.
- 이식 이식을위한 유리한 위치를 확보하고 균일 한 재관류를 유지하기 위해 헝겊을 사용하십시오.
- 요관 문합 :
- 이식에서 요관 0.5 cm의 길이 길이에 걸쳐받는 사람을 열 POTT 가위를 사용합니다.
- 이 6.0 폴리 에스테르, 폴리 (P-옥사 논)를 사용하면 좌우 URE에 대한 봉합teral 문합. 다음 전면 벽 뒤에 먼저 연속적으로 다시 벽, 실행, 각면에 모서리 스티치를 수행합니다.
- 출혈을 검사 한 후, 천을 제거하고 위치에 고정하기 위해 신장 주위에 작은 창자의 일부를 래핑합니다. 두 monofil 1 봉합과 복벽을 닫습니다. 3-0 실크 또는 비 흡수성 모노 필라멘트 봉합사로 피부를 닫습니다.
- 돼지가 발생하기 쉬운 위치에 배치 될 때까지 조심스럽게 노르 에피네프린 주입을 적정에 의해 연속적으로 100 mmHg로 위의 수축기 혈압을 유지한다.
- 수술 후 절차
- 위에서 언급 한 바와 같이 복부 폐쇄 후, 돼지 가열 패드와 열 순환 담요를 사용하여 따뜻하게 유지한다. , 동맥 줄을 제거 6-0 prolene의의 스티치와 동맥에 구멍 구멍을 닫고 절개 사이트를 닫습니다.
- , 발생하기 쉬운 위치에 돼지를 돌려 노르 에피네프린 드립을 중지하고 인공 호흡기에서 돼지를 유아. 알저 돼지는 주거 지역에 복구 절차에서의 원활한 복구를 보장하기 위해 긴밀히을 모니터링 할 수 있습니다. 혈액 가스 샘플을 이식 경정맥 카테터를 통해 각각의 시간을 가져 가라. 대체 볼륨에 링거 락 테이트를 제공하고 진통제 0.3 mg을 부 프레 노르 핀을 관리 할 수 있습니다.
- 자발적으로 마실 수있을 때까지 발관 후, 밀접하게 돼지를 모니터링 할 수 있습니다. 이 흉골 드러 누움을 유지하기 위해 충분한 의식을 회복 할 때까지 무인 동물을 두지 마십시오. 완전히 회복 될 때까지 다른 동물의 회사에 수술을 한 동물을 반환하지 않습니다.
4. 수술후 후속
- 필요한 경우 최소한 2 일 수술 후 이상 0.3 mg을 부 프레 노르 핀 정맥마다 8 시간을 관리 할 수 있습니다. 정기적으로 수술시 항생제의 단일 예방 복용량을 관리 할 수 있습니다. 감염의 징후의 경우, 하루에 한 번 하루 메트로니다졸 IV에 따라 두 번까지 세파 졸린 1g 정맥을 관리임상 적 개선이 발생합니다. 돼지 충분한 물을 마신다 때까지 링거 락 테이트를 관리 할 수 있습니다. 1000 IU 헤파린은 응고를 방지하기 위해 카테터를 잠그는 데 사용될 수있다.
- 돼지의 임상 상태와 신장 기능을 평가하기 위해 경정맥 카테터와 소변 샘플을 통해 정맥 혈액 샘플을 수집합니다.
- 안락사를 들어, 프로포폴 정맥 (5 ~ 10 ㎖)와 돼지의 마취 유도 및 이소 플루 란 5 %를 유지한다. 전술 한 바와 같이 돼지 삽관. relaparatomy 및 신장 조직 샘플 수집 후, 40 mval의 KCl의 정맥 주사에 의해 심장 마비를 유도한다.
결과
이하, 신장자가 이식 실험 결과 (N = 4) 증명되어있다. 초기 그래프트 회수 후에, 돼지는 하우징 영역에서 회수. 한편, 신장 이식 7 시간 35 분 (± 18 분)의 평균 시간을 얼음에 보관 하였다. 마취를 반복 개복술의 reinduction 후, 반대측 신장은 절제 설명대로 냉 저장 이식은 heterotopically 이식되었다. 인공 호흡기에서 이유 후 돼지는 수술에서 회복 한 10 일 (그림 1 참조)에 가입 하였다. 데일리 (1-4 수술 후 하루, 포드) 또는 모든 두 번째 날 (6-10 포드) 혈액 샘플은 혈액 가스 분석을 수행하기 위해 수집; 신장 기능, 혈청 크레아티닌 및 혈중 요소 질소을 평가하기 위해 (BUN) 값을 추정 하였다. 비교를 위해, 하나 allotransplanted 신장 이식의 결과가 표시됩니다. 면역 억제를 들어,이 돼지는 사이클로스포린 100 mg을 경구 및 공동 수신autotransplant 프로토콜과 동일한 사용 수술 기법 ivbid 250 mg의 rtisone이었다; 더 따뜻한 허혈 시간은 적용되지 않았다.
모든 돼지는 추적 관찰 기간 동안 좋은 임상 상태에 있었다. 혈청 크레아티닌 및 BUN 값은 BUN 10.7 ± 4 (크레아 2.8 ± 0.7 밀리그램 / DL, BUN 25.3 ± 7 밀리그램 / DL을) 수술 후 첫날에 가장 높은 증가를 공개하고 포드 (10) (크레아 1.7 ± 0.4 밀리그램 / DL까지 감소 초기 기준 값에 가까운 밀리그램 / DL). allotransplanted 신장 이식은 높은 크레아티닌 및 BUN 값을 보여 좋은 초기 이식 기능 이후 인해 거부 가능성이 가장 높은자가 이식에 비해 (그림 2, 3). 산 - 염기 지혈 (그림 4)와 전해질 수준 (그림 5) 개입없이 안정적이었다. 조직 학적 검사 autotransplanted 신장 보존 tubulointerstitium (Figur을 보여 주었다예 6) 및 allotransplanted 신장 간질 염증 tubulitis 한 사구 체 신염 확산 (도 7).
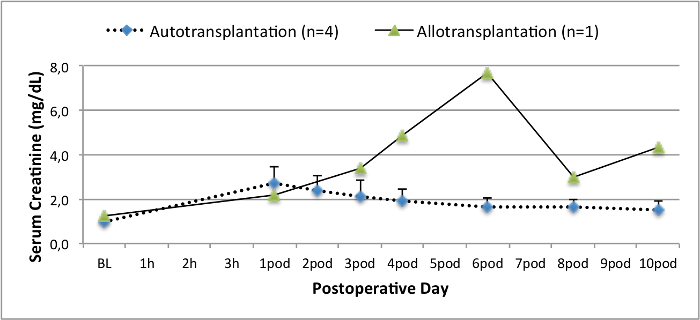
그림 2. 혈청 크레아티닌 값. 혈청 크레아티닌 기준 값 (평균 및 표준 편차) 및 (10) 수술 후. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
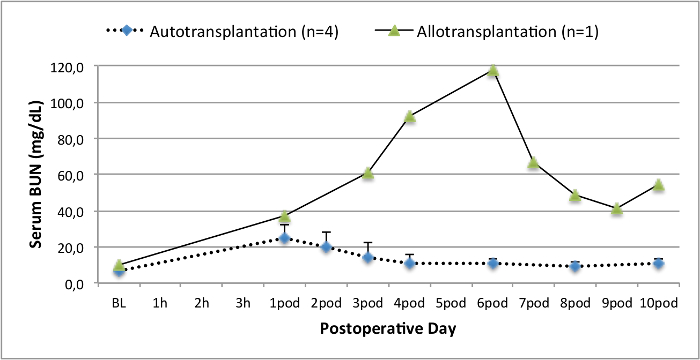
그림 3. 혈청 BUN 값.베이스 라인에 대한 혈청 BUN 값 (평균 및 표준 편차) 10 일 수술 후. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
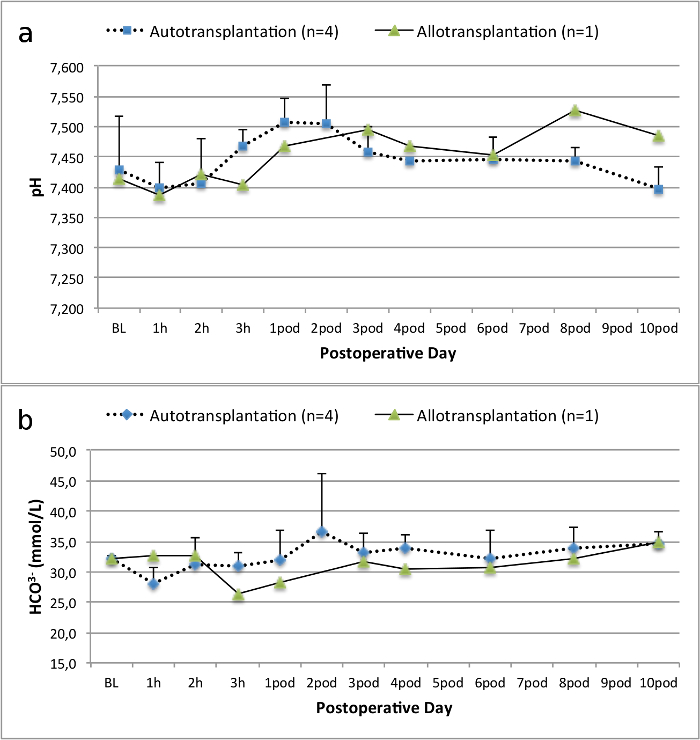
그림 4. 산 - 염기 지혈.베이스 라인을위한 산 - 염기 지혈 (평균 및 표준 편차) 10 일 수술 후. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
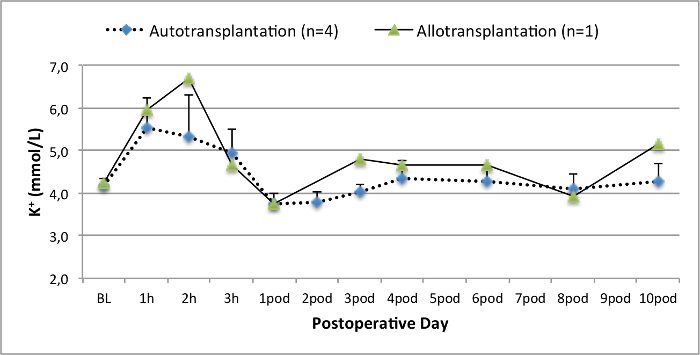
그림 5. 전해질 수준. 전해질 수준 (평균 및 표준 편차)베이스 라인을 위해 10 일 수술 후. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
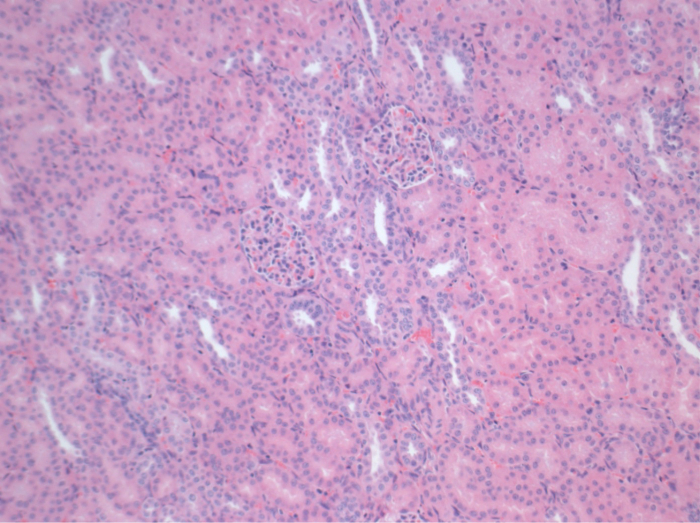
그림 6. 조직학 (H &# 38;.. E), 100X 배율 십일 수술 후 autotransplanted 신장의 정상 tubulointerstitium 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
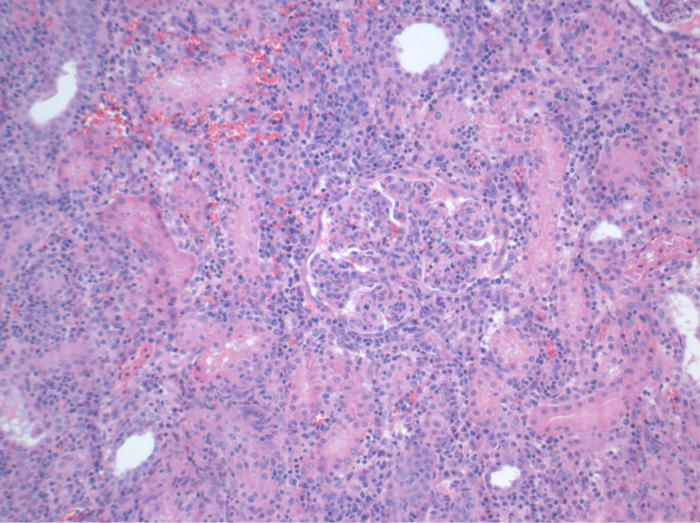
그림 7. 조직학 (H & E), 100X 배율. 광범위한 간질 성 염증, tubulitis 및 사구 체 신염, 거부와 일치하는 10 일 수술 후 allotransplanted 신장에. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
토론
돼지 신장 이식의 모델로 인해 수술 측면, 생리학, 생화학, 면역학 (14)의 유사성에 인간 이식 분야를 촉진 할 수있는 독특한 기회를 제공합니다.
실험적 연구의 목적에 따라,자가 이식의 신장 동종 이식 모델은 모델에 비해 여러 가지 장점을 갖는다. 여러 그룹이 동종 이식 (28) 후 좋은 신장 이식 기능을보고 있지만, 돼지에서 면역 억제, 특히 신장 이식에 도전한다. 수술 전 혈액 샘플은 돼지 백혈구 항원 (SLA)에 대한 호환성을 보장 가능하지만 비용이 14 비실용적하는 분석한다. 수술 후, 같은 타 크롤리 무스와 사이클로스포린과 같은 제안 면역 억제제 (칼시 뉴린 억제제, CNI)은 경구 투여하거나 정맥 28. 돼지는 일반적으로 구강 MEDICA 제비 거부로 경구 투여가 불가능하다기. 또한, 장 장애물은 면역 억제 약물 및 치료 약물 수준의 유지 보수의 충분한 흡수를 미연에 방지 할 수 있습니다. 활성 동물 CNI의 정맥의 연속 주입은 기술적으로 요구하고있다. 정맥 내 일시 투여 독성의 원인이 높은 피크 값에 연결됩니다. 따라서, 새로운 보존 기술 조사,자가 이식 신장의 모델은 몇 가지 장점을 갖는다. 위의 증명 allotransplantated 신장 이식, 크레아티닌 및 BUN의 지연 증가 피크의 대표적인 결과에서 조직 학적 평가에 의해 입증되었다 거부를 나타냅니다.
자가 이식의 돼지 모델은 이전에 새로운 보존 방법 14,18,29을 조사하는데 사용되었다. 그러나, 심장 박동 시나리오에서 autotransplanted 돼지의보고 수술 후 혈청 크레아티닌 및 BUN 값은 상당히 실험 시스템 22,30에 따라 달라집니다 . 우리가 여기서 제시 심장 박동 기증자 프로토콜은 2.8 밀리그램 / DL (± 0.7) 및 (7.4 ±) 25.3 밀리그램 / DL의 BUN 피크의 낮은 수술 후 혈청 크레아티닌 피크가 발생합니다. 이러한 결과는 Hanto와 동료 28 Snoeijs 및 동료 (31)가 제시 한 낮은 피크 값과 비교할 수 있습니다.
돼지자가 이식 모델에서 신장 이식 후 성공적인 결과를 보장하기 위해, 우리는 특정 합병증의 비율을 최소화 몇 가지 주요 기술 요소를 확인했다. 위스콘신 (UW) 용액 대학에 비해 트립토판, 히스티딘 - 케 토글 루타 레이트 용액 (HTK)의 사용으로 인해 칼륨 하부 콘텐츠 연축의 위험을 감소시킨다. 상기 재관류 시점 연축의 위험을 줄이기 위해, 베라파밀은 신장 동맥에 주입 될 수 있고, 파파 베린을 검색하는 동안 및 재관류 후 국소 투여 될 수있다. 또한, 노르 에피네프린의 연속 물방울 유지 적정100 mmHg의 상기 수축기 혈압 균질 재관류을 보장한다. 이는 돼지가 쉬운 위치까지이 적어도 혈압을 유지하는데 유용하다. 또한, 이식 이식 위치는 새롭게 문합 혈관의 꼬임을 방지하는 것이 중요하다. 따라서, 종래 광범위한 기계 조작을 방지하기 위해 이식 문합을 봉제 반대측 좌측 신장을 절제하는 것이 도움이된다. 이식 이식 주위에 소장을, 요관 문합술을 마무리 포장 후 복부 벽의 폐쇄 후 위치를 확보. 이러한 소장의 꼬임으로 인한 장폐색 등의 합병증은 거의 관찰되지 않지만 장폐색, 장 천공, 사망을 포함한 심각한 합병증으로 이어질 수 있습니다. 전반적으로, 정확한 수술 기법, 세심한 마취 및 후속 좋은 임상 결과 및 이식 기능을 확인하는 동안 가까운 모니터링.
동맥과 정맥 문합은 PERFO 할 수있다다른 기술들을 사용하여 rmed. 이식의 소성을 배치는 신장 동맥과 정맥의 엔드 - 투 - 엔드 문합이 가능합니다. 이소성 이식하는 경우, 이식편은 장골 용기에, 엔드 - 투 - 엔드 문합 대 측성 신 포사에 위치하거나 직접 원위 대동맥 수있다. 문합으로 이식 이소성 - 대동맥과 혈전증 및 32 연축의 위험을 줄일 수있는 카바 직접 엔드 - 투 - 사이드 기술이 모델에서 바람직하다. 초기 정맥 분기점와 해부학 적 변화는 두 개의 정맥 문합 봉제의 필요로 이어질 수 있습니다. 동맥 또는 정맥이 상대적으로 짧은 경우, 이식편 혈관의 길이를 얻기 위해 180도 돌릴 수있다. 요관 좌우 문합은 협착 또는 소변 누출을 복잡하게하지 않고 좋은 실험 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
일반적으로 신장 이식의 돼지 모델은 다른 동물 모델에 비해 이점을 제공한다. D로위의 escribed는 특정 유사성은 돼지 및 임상 실습에 새로운 기술의 상대적으로 빠른 변환을 할 수 있습니다 인간의 설정 사이에 존재한다. 이식 기술은 설치류 모델에 비해 기술적으로 용이하다. 또한, 정맥 카테터의 배치에 의해, 말초 혈액 쉽게 수집 할 수 있으며, 추가 조사를 위해 처리된다. 소변의 컬렉션은 신장 손상과 기능의 추가 평가를 할 수 있습니다. 뇨 샘플을 수집하기 위해, 경피적 카테터 방광에 삽입 될 수있다. 돼지에 의해 조작을 방지하기 위해, 선단 동물 후면 피하 터널링한다. 소변 수집을위한 다른 옵션은 장시간 수집 기간 소변 크레아티닌 청소율 추가적인 바이오 마커의 농도를 추정 할 수있는 신진 대사 케이지의 사용이다. 초음파 검사, CT 스캔 및 MRI 영상이 가능하다. 순환 죽음 프로토콜 후 기부 따뜻한 적용하여 모방 할 수있다허혈 검색하기 전에. 또한, 돼지 공격적인 행동을 제한하는 경우 거세 비교적 취급이 용이하다.
단점 동물 구입, 주택, 수술 등의 의료 장비 및 인력의 높은 비용을 포함한다. 이러한 요인은 각 연구 그룹 동물의 다수를 포함하는 가능하지 않을 것을 의미한다. 또한, 설치류 모델에 비해 참조 제한된 수의 돼지 규범 생물학적 데이터의 문학에서 사용할 수 있습니다. 이러한 신규의 보존 방법으로서 개발 된 새로운 기술의 평가를위한 대안으로서, 다른 그룹 (33, 34)는 신장 이식의 대안으로 정상 체온 생체 재관류 설명 하였다. 이 방법을 수행하기 쉽고 저렴하다. 그러나, 표준화 신장 이식 이식 임상 연습에 더 유사한 모델을 제공하고 장기간 후속 허용한다. 보다 현실적인 그래프트 평가위한 따라서 역할, 표준.
결론적으로, 이소성 신장자가 이식의 돼지 모델은 신장 이식 결과의 개선을위한 혁신적인 새로운 접근 방식을 조사하는 임상 중요한 시나리오를 제공합니다. 특히,이 프로토콜은 신장자가 이식 모델의 성공적인 설립을 용이하게 중요한 기술 정보를 제공하고 임상 시험에 대한 새로운 연구 결과의 빠른 변환을 할 수 있습니다.
공개
The authors have nothing to disclose.
감사의 말
We thank the Sorin Group (Milano, Italy), XVIVO Perfusion Inc. (Goteborg, Sweden), and Braun AG (Melsungen, Germany) for their support. We highly appreciate the support of the John David and Signy Eaton Foundation.
자료
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Anesthesia Equipment | |||
| Anesthesia Machine, Optimax | Moduflex Anesthesia Equipment | SN5180 | |
| Infusion Pump 3,000 | SIMS Graseby LTD. | SN300050447 | |
| Infusion Pump Line | Smith Medical ASD Inc. | 21-0442-25 | |
| Intravenous permanent catheter (9.5 Fr) | Cook Medical Company | G01865 | |
| Isoflurane Vapor 19.1 | Draeger Medical Canada Inc. | N/A | |
| Mallinckrodt, Tracheal Tube, 6.5 mm | Covidien Canada | 86449 | |
| Temperature Therapy Pad | Gaymar Industries Inc | TP26E | |
| Ventilator, AV 800 | DRE Medical Equipment | 40800AVV | |
| Warm Touch, Patient Warming System | Nellcor/ Covidien Canada | 5015300A | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Surgical Equipment | |||
| Abdominal Retractor | Medite GmbH | 07-0001-00 | |
| Aorta/vein punch 4.0 mm, round | Scanlan International Inc. | 1001-602 | |
| De Bakey, Atraumatic Peripheral, Clamp | Aesculap Inc. | FB463R | |
| De Bakey-Beck, Atraumatic Vena Cava, Clamp | Aesculap Inc. | FB519R | |
| De Bakey, Atraumatic Mini-Bulldog, Straight | Aesculap Inc. | FB422R | |
| De Bakey, Atraumatic Mini-Bulldog, Curved | Aesculap Inc. | FB423R | |
| De Bakey, Atraumatic Coarctation Clamp, Angled | Aesculap Inc. | FB453R | |
| Dissection Blade #11 | Feather Safety Razor Co. | 089165B | |
| Connector (1/4") with male luer lock | Sorin Group Inc. | AB1452 | |
| Liver Admin Set (flush line) | CardioMed Supplies Inc | 17175 | |
| Maxon, 1 | Covidien Canada | 606173 | |
| Med-Rx Suction Connecting Tube | Benlan Inc. | 70-8120 | |
| Organ Bag | CardioMed Supplies Inc | 2990 | |
| Potts – De Martel, Scissors | Aesculap Inc. | BC648R | |
| Renal artery cannula, 1.6" | Sorin Group Inc. | VC-11000 | |
| Sofsilk, 2-0 | Covidien Canada | S405 | |
| Sofsilk, 3-0 | Covidien Canada | S404 | |
| Satinsky, Suprahepatic Cava Clamp | Aesculap Inc. | FB605R | |
| Suction Tip | Tyco Healthcare Group LP | 8888501023 | |
| Surgipro II, 6-0 | Covidien Canada | VP733X | |
| Valleylab, Cautery Pencil | Covidien Canada | E2515H | |
| Valleylab, Force Tx | Valleylab Inc. | 216151480 | |
| Valleylab, Patient Return Electrode | Covidien Canada | E7507 | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Medication | |||
| Atropine Sulfate 15 mg/30 ml | Rafter 8 Products | 238481 | |
| Buprenorphine 0.3 mg/ml | RB Pharmaceuticals LDT | N/A | |
| Ceftiofur 3 mg/ml | Pfizer Canada Inc. | 11103 | |
| Cefazolin 1 g | Pharmaceutical Partners of Canada Inc. | 2237138 | |
| Fentanyl Citrate 0.25 mg/5 ml | Sandoz Canada Inc. | 2240434 | |
| Heparin 10,000 iU/10 ml | Sandoz Canada Inc. | 10750 | |
| Histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate (HTK) solution | Methapharm | CU001LBG | |
| Isoflurane 99.9%, 250 ml | Pharmaceutical Partners of Canada Inc. | 2231929 | |
| Ketamine Hydrochloride 5,000 mg/50 ml | Bimeda-MTC Animal Health Inc. | 612316 | |
| Lactated Ringer’s + 5% Dextrose 1 L | Baxter Corporation | JB1064 | |
| Lactated Ringer’s 1 L | Baxter Corporation | JB2324 | |
| Metronidazole 500 mg/100 ml | Baxter Corporation | 870420 | |
| Midazolam 50 mg/10 ml | Pharmaceutical Partners of Canada Inc. | 2242905 | |
| Norepinephrine 16 mg/250 ml Dextrose 5% | Baxter Corporation | N/A | |
| Pantoprazole 40 mg | Sandoz Canada Inc. | 2306727 | |
| Papaverine 65 mg/2 ml | Sandoz Canada Inc. | 9881 | |
| Propofol 1,000 mg/100 ml | Pharmascience Inc. | 2244379 | |
| Saline 0.9%, 1 L | Baxter Corporation | 60208 | |
| Solu-Medrol 500 mg | Pfizer Canada Inc. | 2367963 | |
| Verapamil | Sandoz Canada Inc. | 2166739 | |
| Xylocaine Endotracheal 10 mg/50 ml | AstraZeneca | 2003767 |
참고문헌
- Wolfe, R. A., Ashby, V. B., et al. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N Engl J Med. 341 (23), 1725-1730 (1999).
- Ingsathit, A., Kamanamool, N., Thakkinstian, A., Sumethkul, V. Survival advantage of kidney transplantation over dialysis in patients with hepatitis C: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transplantation. 95 (7), 943-948 (2013).
- Tonelli, M., Wiebe, N., et al. Systematic review: kidney transplantation compared with dialysis in clinically relevant outcomes. Am J Transplant. 11 (10), 2093-2109 (2011).
- Matas, A. J., et al. OPTN/SRTR Annual Data Report 2012: Kidney. Am J Transplant. 14, (2014).
- . Annual Report 2013 - Eurotransplant International Foundation. Available from: https://www.eurotransplant.org/cms/mediaobject.php?file=AR20135.pdf (2013)
- Morrissey, P. E., Monaco, A. P. Donation after circulatory death: current practices, ongoing challenges, and potential improvements. Transplantation. 97 (3), 258-264 (2014).
- Maggiore, U., Oberbauer, R., et al. Strategies to increase the donor pool and access to kidney transplantation: an international perspective. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 30 (2), 217-222 (2014).
- Summers, D. M., Johnson, R. J., Hudson, A., Collett, D., Watson, C. J., Bradley, J. A. Effect of donor age and cold storage time on outcome in recipients of kidneys donated after circulatory death in the UK: a cohort study. Lancet. 381 (9868), 727-734 (2013).
- Wadei, H. M., Heckman, M. G., et al. Comparison of kidney function between donation after cardiac death and donation after brain death kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 96 (3), 274-281 (2013).
- Moers, C., Smits, J. M., et al. Machine perfusion or cold storage in deceased-donor kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med. 360 (1), 7-19 (2009).
- Pereira-Sampaio, M. A., Favorito, L. A., Sampaio, F. J. B. Pig kidney: anatomical relationships between the intrarenal arteries and the kidney collecting system. Applied study for urological research and surgical training. J Urol. 172 (5 Pt 1), 2077-2081 (2004).
- Bagetti Filho, H. J. S., Pereira-Sampaio, M. A., Favorito, L. A., Sampaio, F. J. B. Pig kidney: anatomical relationships between the renal venous arrangement and the kidney collecting system. J Urol. 179 (4), 1627-1630 (2008).
- Giraud, S., Favreau, F., Chatauret, N., Thuillier, R., Maiga, S., Hauet, T. Contribution of large pig for renal ischemia-reperfusion and transplantation studies: the preclinical model. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011 (21), 532127 (2011).
- Gallinat, A., Paul, A., et al. Role of oxygenation in hypothermic machine perfusion of kidneys from heart beating donors. Transplantation. 94 (8), 809-813 (2012).
- Thuillier, R., Allain, G., et al. Benefits of active oxygenation during hypothermic machine perfusion of kidneys in a preclinical model of deceased after cardiac death donors. J Surg Res. 184 (2), 1174-1181 (2013).
- Hosgood, S. A., Barlow, A. D., Yates, P. J., Snoeijs, M. G. J., van Heurn, E. L. W., Nicholson, M. L. A pilot study assessing the feasibility of a short period of normothermic preservation in an experimental model of non heart beating donor kidneys. J Surg Res. 171 (1), 283-290 (2011).
- Delpech, P. O., Thuillier, R., et al. Effects of warm ischaemia combined with cold preservation on the hypoxia-inducible factor 1α pathway in an experimental renal autotransplantation model. Br J Surg. 101 (13), 1739-1750 (2014).
- Kirk, A. D. Crossing the bridge: large animal models in translational transplantation research. Immunol Rev. 196, 176-196 (2003).
- Golriz, M., Hafezi, M., et al. Do we need animal hands-on courses for transplantation surgery. Clin Transplant. 27, 6-15 (2013).
- He, B., Musk, G. C., Mou, L., Waneck, G. L., Delriviere, L. Laparoscopic surgery for kidney orthotopic transplant in the pig model. JSLS. 17 (1), 126-131 (2013).
- Faure, A., Maurin, C., et al. An experimental porcine model of heterotopic renal autotransplantation. Transplant Proc. 45 (2), 672-676 (2013).
- Hosgood, S. A., Yates, P. J., Nicholson, M. L. 1400W reduces ischemia reperfusion injury in an ex-vivo porcine model of the donation after circulatory death kidney donor. World J Transplant. 4 (4), 299-305 (2014).
- Ghanekar, A., Mendicino, M., et al. Endothelial induction of fgl2 contributes to thrombosis during acute vascular xenograft rejection. J Immunol. 172 (9), 5693-5701 (2004).
- Ghanekar, A., Lajoie, G., et al. Improvement in rejection of human decay accelerating factor transgenic pig-to-primate renal xenografts with administration of rabbit antithymocyte serum. Transplantation. 74 (1), 28-35 (2002).
- Cowan, P. J., Cooper, D. K. C., d'Apice, A. J. F. Kidney xenotransplantation. Kidney Int. 85 (2), 265-275 (2014).
- Seldinger, S. I. Catheter replacement of the needle in percutaneous arteriography; a new technique. Acta radiol. 39 (5), 368-376 (1953).
- Hanto, D. W., Maki, T., et al. Intraoperative administration of inhaled carbon monoxide reduces delayed graft function in kidney allografts in Swine. Am J Transplant. 10 (11), 2421-2430 (2010).
- Maathuis, M. -. H. J., Manekeller, S., et al. Improved kidney graft function after preservation using a novel hypothermic machine perfusion device. Ann Surg. 246 (6), 982-991 (2007).
- Gallinat, A., Paul, A., et al. Hypothermic reconditioning of porcine kidney grafts by short-term preimplantation machine perfusion. Transplantation. 93 (8), 787-793 (2012).
- Snoeijs, M. G., Matthijsen, R. A., et al. Autologous transplantation of ischemically injured kidneys in pigs. J Surg Res. 171 (2), 844-850 (2011).
- Golriz, M., Fonouni, H., Nickkholgh, A., Hafezi, M., Garoussi, C., Mehrabi, A. Pig kidney transplantation: an up-to-date guideline. Eur Surg Res. 49 (3-4), 121-129 (2012).
- Hosgood, S. A., Bagul, A., Yang, B., Nicholson, M. L. The relative effects of warm and cold ischemic injury in an experimental model of nonheartbeating donor kidneys. Transplantation. 85 (1), 88-92 (2008).
- Hoyer, D. P., Gallinat, A., et al. Influence of oxygen concentration during hypothermic machine perfusion on porcine kidneys from donation after circulatory death. Transplantation. 98 (9), 944-950 (2014).
재인쇄 및 허가
JoVE'article의 텍스트 или 그림을 다시 사용하시려면 허가 살펴보기
허가 살펴보기This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. 판권 소유