Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
In vivo Calcium Imaging of Mouse Geniculate Ganglion Neuron Responses to Taste Stimuli
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
Here we present how to expose the geniculate ganglion of a live, anesthetized laboratory mouse and how to use calcium imaging to measure the responses of ensembles of these neurons to taste stimuli, allowing for multiple trials with different stimulants. This allows for in depth comparisons of which neurons respond to which tastants.
Streszczenie
Within the last ten years, advances in genetically encoded calcium indicators (GECIs) have promoted a revolution in in vivo functional imaging. Using calcium as a proxy for neuronal activity, these techniques provide a way to monitor the responses of individual cells within large neuronal ensembles to a variety of stimuli in real time. We, and others, have applied these techniques to image the responses of individual geniculate ganglion neurons to taste stimuli applied to the tongues of live anesthetized mice. The geniculate ganglion is comprised of the cell bodies of gustatory neurons innervating the anterior tongue and palate as well as some somatosensory neurons innervating the pinna of the ear. Imaging the taste-evoked responses of individual geniculate ganglion neurons with GCaMP has provided important information about the tuning profiles of these neurons in wild-type mice as well as a way to detect peripheral taste miswiring phenotypes in genetically manipulated mice. Here we demonstrate the surgical procedure to expose the geniculate ganglion, GCaMP fluorescence image acquisition, initial steps for data analysis, and troubleshooting. This technique can be used with transgenically encoded GCaMP, or with AAV-mediated GCaMP expression, and can be modified to image particular genetic subsets of interest (i.e., Cre-mediated GCaMP expression). Overall, in vivo calcium imaging of geniculate ganglion neurons is a powerful technique for monitoring the activity of peripheral gustatory neurons and provides complementary information to more traditional whole-nerve chorda tympani recordings or taste behavior assays.
Wprowadzenie
A key component of the mammalian peripheral taste system is the geniculate ganglion. In addition to some somatosensory neurons that innervate the pinna of the ear, the geniculate is comprised of the cell bodies of gustatory neurons innervating the anterior tongue and palate. Similar to other peripheral sensory neurons, the geniculate ganglion neurons are pseudo-unipolar with a long axon projecting peripherally to the taste buds, and centrally to the brainstem nucleus of the solitary tract1. These neurons are activated primarily by the release of ATP by taste receptor cells responding to taste stimuli in the oral cavity2,3. ATP is an essential neurotransmitter for taste signaling, and P2rx receptors expressed by the gustatory ganglion neurons are necessary for their activation4. Given that taste receptor cells express specific taste receptors for a particular taste modality (sweet, bitter, salty, umami, or sour), it has been hypothesized that gustatory ganglion neuron responses to taste stimuli would also be narrowly tuned5.
Whole nerve recordings have shown both the chorda tympani and the greater superior petrosal nerves conduct gustatory signals representing all five taste modalities to the geniculate ganglion6,7. However, this still left questions about the specificity of neuronal responses to a given tastant: if there are taste modality specific neurons, polymodal neurons, or a mixture of both. Single fiber recordings give more information about the activity of individual fibers and their chemical sensitivities8,9,10, but this methodology is limited to collecting data from small numbers of fibers. Similarly, in vivo electrophysiological recordings of individual rat geniculate ganglion neurons give information about the responses of individual neurons11,12,13, but still loses the activity of the population and yields relatively few neuron recordings per animal. In order to analyze the response patterns of neuronal ensembles without losing sight of the activity of individual neurons, new techniques needed to be employed.
Calcium imaging, especially using genetically encoded calcium indicators like GCaMP, has provided this technical breakthrough14,15,16,17,18. GCaMP uses calcium as a proxy for neuronal activity, increasing green fluorescence as calcium levels within the cell rise. New forms of GCaMP continue to be developed to improve the signal to noise ratio, adjust binding kinetics, and adapt for specialized experiments19. GCaMP provides single neuron resolution, unlike whole nerve recording, and can simultaneously measure responses of ensembles of neurons, unlike single fiber or single cell recording. Calcium imaging of the geniculate ganglia has already provided important information about the tuning profiles of these neurons in wild-type mice16,20, and has identified peripheral taste miswiring phenotypes in genetically manipulated mice18.
One major difficulty to applying in vivo calcium imaging techniques to the geniculate ganglion is that it is encapsulated within the bony tympanic bulla. In order to obtain optical access to the geniculate, delicate surgery is required to remove the layers of bones, while keeping the ganglion intact. For that purpose, we have created this guide to help other researchers access the geniculate ganglion and image the GCaMP mediated fluorescent responses of these neurons to taste stimuli in vivo.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protokół
Animal protocols were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of the University of Texas San Antonio.
1. Pre-operative setup
NOTE: Please note that initial setup of equipment is not addressed here, as it will vary based on pump system, microscope, camera, and imaging software used. For setup instructions please refer to instructional materials provided by equipment vendor. For equipment used by the authors, please see the Table of Materials.
- Ensure liquid flows through all vehicle (water) and tastant lines. If line is blocked, disconnect and flush with water. If the line is kinked, massage until liquid flows. Ensure that liquid starts and stops on cue.
- Once all lines are confirmed unblocked, run vehicle for 10 s then close all valves.
- Ensure imaging software is ready with all required variables (e.g., trial length, file names, frame rate, etc). Using µManager, an open-source image acquisition software package, input 200 ms into the field labeled Exposure Time for a frames per second of 5Hz, select x2 under binning, and press the button labeled Live. When the video starts, press the button on the left side labeled ROI. This will result in a 512x512 field of view.
2. Anesthetizing and immobilizing the animal
NOTE: The following protocol is a terminal procedure optimized for mice of either sex weighing 18-35 g. It is recommended for use with animals between 10 and 12 weeks of age. It may be used with transgenic animals expressing Genetically Encoded Calcium Indicators (GECIs) such as the Snap25-GCaMP6s, or animals stereotaxically injected with viral GECIs. Gloves, lab coat, and face mask should be worn for entirety of protocol.
- Scruff animal and perform an intraperitoneal injection of Ketamine (100 mg/kg) and Xylazine (10 mg/kg). Assess the depth of anesthesia via toe pinch before continuing.
- Shave the top of the head amd the surgical area at the front of the neck.
- Turn on the heating pad and place the animal prone on the pad.
- Apply ointment to the animal's eyes to avoid drying of the eyes.
- Make an incision (~1 cm) at the midline of the head to expose the animal's skull. Remove connective tissue using a sterile swab so that the bare bone is accessible. Use a cotton tipped applicator to ensure the skull is dry.
- Apply vet bond to the skull. Be sure to cover the exposed skull. Wait for the glue to dry.
- In a Petri dish lid, mix and apply a layer of dental cement to skull. The back end of the cotton tipped applicator used in step 2.5 will work well for this process. Place headpost on top of the dental cement and apply a second layer of dental cement to sandwich the headpost in place on the skull.
- Let it sit until the dental cement is dry and solid. Break the cotton tipped applicator in half and use the pointed ends to poke the dental cement to test. If the dental cement does not yield to being poked the animal may be turned to a supine position.
3. Tracheotomy
- Apply pre-surgical scrub to surgical area. Post-scrub, make a midline incision ~ 2 cm in the skin of the throat from the sternum to the chin.
- Retract the skin and sub-maxillary glands, being sure to fully expose the digastric muscles.
- Find the seam in the paratracheal musculature, separate it with blunt dissection, and retract open.
- Carefully cut an opening in the top of the trachea large enough to fit polyethylene tubing (I.D. 0.86 mm, O.D. 1.27 mm). Do not cut more than halfway through the diameter of the trachea. Insert tubing into the trachea towards the lungs.
- Reposition retractors to release paratracheal musculature and retract the submaxillary glands.
- Glue paratracheal musculature together over tubing with a minimal amount of veterinary glue (see Figure 1A).
4. Breaking open the tympanic bulla
- Gently tease desired digastric muscle (left or right) up and pull apart the connective tissue. Cut at the anterior end of the muscle, avoiding blood vessels, and pull back posteriorly until clear of the tympanic bulla.
- Tilt the head back slightly to lift the tympanic bulla. Locate the branch of the carotid artery anterior to the posterior insertion point of the digastric muscle. Feel just posterior to this blood vessel for the convex structure of the tympanic bulla.
- Look for a seam in the musculature at this location (see Figure 1B). Using two sets of fine forceps, blunt dissect at the seam until the bone of the tympanic bulla is visible. Use retractors to keep a clear view of the tympanic bulla.
- Find the seam running anterior to posterior on the bulla (see Figure 1C). Using a surgical probe, poke a hole in the bone at the center of this seam. Use a set of fine end scissors to cut a circular area in the bone, taking care not to cut blood vessels anterior, posterior, and deep beneath the bulla.
5. Exposing the geniculate
- Within this hole is a convex bit of bone, this is the cochlea. Anterior to the cochlea is a muscle, the tensor tympani (see Figure 1D). Using the spring scissors, cut the tensor tympani and remove it.
- Perform a toe pinch. If animal responds, give a ketamine/xylazine mixture ata 1/3 dose for redosing.
- Prepare irrigation fluid and a suction line. Using the surgical probe, poke a hole in the cochlear promontory. Immediately irrigate the liquid that flows out and remove it with suction. This liquid will flow more or less continuously from this point and will need to be addressed periodically.
- Enlarge the hole in the cochlea. Take care with the blood vessel encircling the cochlea to the posterior and lateral edge.
- Tilt the mouse's head forward. Locate the hole in the temporal bone beneath what was the cochlea (see Figure 1E). Take note of the ridge anterior to this hole, this ridge sits directly over the seventh nerve.
- Insert a surgical probe into the hole and carefully lift the temporal bone to expose the seventh nerve (see Figure 1F). Take stock of how much of the seventh nerve is visible and if the geniculate is not fully exposed, tilt the animal's head back and attempt to pull up bone from anterior to the nerve.
- If the ganglion is still not fully visible, pull up more bone from beneath. Be very careful not to place the probe deep beneath the bone as doing this may damage the geniculate.
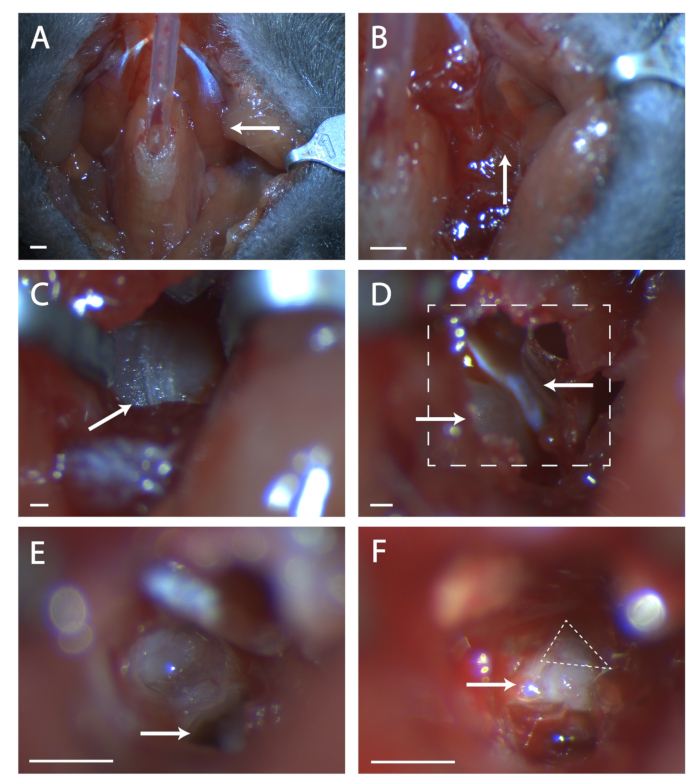
Figure 1: Surgical exposure of the geniculate ganglion. (A) Image of the mouse neck cavity post tracheotomy. Arrow is pointing to the digastric muscle lying over the surgical area explored in the rest of the figure. (B) Image of region under the previously indicated digastric muscle. Arrow indicates the seam in musculature for blunt dissection. (C) Image of the Tympanic Bulla. Arrow indicates seam in the bone to break with a surgical probe. (D) Image of surgical area after opening the bulla. Lower left arrow indicates the cochlea, upper arrow points to the tensor tympani. Boxed line indicates area in (E) and (F). (E) Image of surgical area after cochlea has been broken and the contents removed. White arrow indicates where to place surgical probe referenced in protocol step 5.6. (F) An image of the exposed geniculate ganglion. Arrow indicates body of the seventh nerve, dashed triangle surrounds the geniculate ganglion. Panels A-B, Scale = 5 mm. Panels C-F, Scale = 1 mm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
6. Run tastant panel
- Use suction to remove liquid from over the geniculate. Optionally place an absorbent point to help mitigate seepage and aid in microscope navigation.
- Place the animal on absorbent pad under the microscope. Locate the geniculate ganglion: useful landmarks include the hole left in the bulla, the hole in the temporal bone, and the seventh nerve. Using the FITC/GFP filter on the epifluorescence scope, check for individual GCaMP-expressing geniculate ganglion neurons. A 10x objective (workind distance 10mm) will provide sufficient resolution to track the activity of individual cells, but a 20x objective (working distance 12 mm) can also be used.
- Place dispensing needle for tastant line firmly in animal's mouth. Place a Petri dish below the animal's mouth to catch fluid.
- Ensure that the camera is viewing the microscope's field of view. Synchronize start of the video recording with the start of tastant presentation.
- During recording, watch live feed for responses, drift, and seepage.
- If seepage occurs, suction the liquid until the view of the geniculate is clear and repeat. If drift occurs, check that all parts of the head post are firmly tightened. If no responses occur check that liquid is flowing and that the microscope and camera are focused on the proper location without anything obscuring the field of view.
- Repeat until desired number of videos have been obtained. Gently ease retractors, then repeat steps 3-6 on the opposite side.
- After the desired videos have been obtained for all desired ganglia, euthanize the animal via cervical dislocation.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Wyniki
Following the protocol, a transgenic Snap25-GCaMP6s animal was sedated, geniculate ganglia were exposed, and tastant was applied to the tongue while video was recorded. The aim of the experiment was to define which tastants elicited responses from each cell. Tastants (30 mM AceK, 5 mM Quinine, 60 mM NaCl, 50 mM IMP + 1 mM MPG, 50 mM Citric Acid)18 were dissolved in DI water and were applied to the tongue for 2 s separated by 13 s of DI water.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Dyskusje
This work describes a step-by-step protocol to surgically expose the geniculate ganglion and visually record the activity of its neurons with GCaMP6s. This procedure is very similar to that described previously17, with a few notable exceptions. First, the use of a head post allows for easy adjustment of head positioning during surgery. Second, regarding stimulus delivery, the approach by Wu and Dvoryanchikov flows taste stimuli through esophageal tubing17, whereas this prot...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Ujawnienia
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Podziękowania
The authors thank S. Humayun for mouse husbandry. Funding for this work has been provided in part by UTSA's Brain Health Consortium Graduate and Postdoctoral Seed Grant (B.E.F.) and NIH-SC2-GM130411 to L.J.M.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1 x #5 Inox Forceps | Fine Science Tools | NC9792102 | |
| 1ml Syringe with luer lock | Fisher Scientific | 14-823-30 | |
| 2 x #3 Inox Forceps | Fine Science Tools | M3S 11200-10 | |
| 27 Gauge Blunt Dispensing Needle | Fisher Scientific | NC1372532 | |
| 3M Vetbond | Fisher Scientific | NC0398332 | |
| 4-40 Machine Screw Hex Nuts | Fastenere | 3SNMS004C | |
| 4-40 Socket Head Cap Screw | Fastenere | 3SSCS04C004 | |
| Absorbent Points | Fisher Scientific | 50-930-668 | |
| Acesulfame K | Fisher Scientific | A149025G | |
| Artificial Tears | Akorn | 59399-162-35 | |
| BD Allergist Trays with Permanently Attached Needle | Fisher Scientific | 14-829-6D | |
| Blunt Retractors | FST | 18200-09 | |
| Breadboard | Thor Labs | MB8 | |
| Citric Acid | Fisher Scientific | A95-3 | |
| Cohan-Vannas Spring Scissors | Fine Science Tools | 15000-02 | |
| Contemporary Ortho-Jet Liquid | Lang | 1504 | |
| Contemporary Ortho-Jet Powder | Lang | 1520 | |
| Cotton Tipped Applicators | Fisher | 19-062-616 | |
| Custom Head Post Holder | eMachineShop | See attached file 202410.ems | |
| Custom Metal Head Post | eMachineShop | See attached file 202406.ems | |
| DC Temperature Controller | FHC | 40-90-8D | |
| Digital Camera, sCMOS OrcaFlash4 Microscope Mounted | Hamamatsu | C13440 | |
| Disection Scope | Leica | M80 | |
| Hair Clippers | Kent Scientific | CL7300-Kit | |
| IMP | Fisher Scientific | AAJ6195906 | |
| Ketamine | Ketaved | NDC 50989-996-06 | |
| LED Cold Light Source | Leica Mcrosystems | KL300LED | |
| Luer Lock 1/16" Tubing Adapters | Fisher | 01-000-116 | |
| Microscope | Olympus | BX51WI | |
| Mini-series Optical Posts | Thorlabs | MS2R | |
| MPG | Fisher Scientific | AAA1723230 | |
| MXC-2.5 Rotatable probe Clamp | Siskiyou | 14030000E | |
| NaCl | Fisher Scientific | 50-947-346 | |
| petri dishes | Fisher Scientific | FB0875713A | |
| Pressurized air | Airgas | AI Z300 | |
| Quinine | Fisher Scientific | AC163720050 | |
| Self Sticking Labeling Tape | Fisher Scientific | 159015R | |
| Silicone Pinch Valve Tubing 1/32" x 1/16" o.d. (per foot) | Automate Scientific | 05-14 | |
| Sola SM Light Engine | Lumencor | ||
| Snap25-2A-GCaMP6s-D | JAX | 025111 | |
| Student Fine Scissors | Fine Science Tools | 91460-11 | |
| Surgical Probe | Roboz Surgical Store | RS-6067 | |
| Surgical Probe Holder | Roboz Surgical Store | RS-6061 | |
| Thread | Gütermann | 02776 | |
| BD Intramedic Tubing | Fisher Scientific | 22-046941 | |
| Two Stage Gas Regulator | Airgas | Y12FM244B580-AG | |
| Tygon vinyl tubing - 1/16" | Automate Scientific | 05-11 | |
| Valvelink8.2 digital/manual controller | Automate Scientific | 01-18 | |
| Valvelink8.2 Pinch Valve Perfusion System | Automate Scientific | 17-pp-54 | |
| Xylazine | Anased | NADA# 139-236 |
Odniesienia
- Krimm, R. F. Factors that regulate embryonic gustatory development. BMC Neuroscience. 8, Suppl 3 4(2007).
- Taruno, A., Matsumoto, I., Ma, Z., Marambaud, P., Foskett, J. K. How do taste cells lacking synapses mediate neurotransmission? CALHM1, a voltage-gated ATP channel. Bioessays. (35), 1111-1118 (2013).
- Taruno, A., et al. Taste transduction and channel synapses in taste buds. Pflugers Archiv-European Journal of Physiology. 473, 3-13 (2021).
- Kinnamon, S. C., Finger, T. E. A taste for ATP: neurotransmission in taste buds. Frontiers in Cell Neuroscience. 7, 264(2013).
- Chandrashekar, J., Hoon, M. A., Ryba, N. J., Zuker, C. S. The receptors and cells for mammalian taste. Nature. 444 (7117), 288-294 (2006).
- Yarmolinsky, D. A., Zuker, C. S., Ryba, N. J. Common sense about taste: from mammals to insects. Cell. 139 (2), 234-244 (2009).
- Ninomiya, Y., Tonosaki, K., Funakoshi, M. Gustatory neural response in the mouse. Brain Research. 244 (2), 370-373 (1982).
- Formaker, B. K., MacKinnon, B. I., Hettinger, T. P., Frank, M. E. Opponent effects of quinine and sucrose on single fiber taste responses of the chorda tympani nerve. Brain Research. 772 (1-2), 239-242 (1997).
- Frank, M. The classification of mammalian afferent taste nerve fibers. Chemical Senses. 1 (1), 53-60 (1974).
- Ogawa, H., Yamashita, S., Sato, M. Variation in gustatory nerve fiber discharge pattern with change in stimulus concentration and quality. Journal of Neurophysiology. 37 (3), 443-457 (1974).
- Sollars, S. I., Hill, D. L. In vivo recordings from rat geniculate ganglia: taste response properties of individual greater superficial petrosal and chorda tympani neurones. Journal of Physiology. 564, Pt 3 877-893 (2005).
- Yokota, Y., Bradley, R. M. Geniculate ganglion neurons are multimodal and variable in receptive field characteristics. Neuroscience. 367, 147-158 (2017).
- Breza, J. M., Curtis, K. S., Contreras, R. J. Temperature modulates taste responsiveness and stimulates gustatory neurons in the rat geniculate ganglion. Journal of Neurophysiology. 95 (2), 674-685 (2006).
- Chen, T. W., et al. Ultrasensitive fluorescent proteins for imaging neuronal activity. Nature. 499 (7458), 295-300 (2013).
- Luo, L., Callaway, E. M., Svoboda, K. Genetic dissection of neural circuits: A decade of progress. Neuron. 98 (4), 865(2018).
- Barreto, R. P. J., et al. The neural representation of taste quality at the periphery. Nature. 517, 373-376 (2015).
- Wu, A., Dvoryanchikov, G. Live animal calcium imaging of the geniculate ganglion. Protocol Exchange. , 106(2015).
- Lee, H., Macpherson, L. J., Parada, C. A., Zuker, C. S., Ryba, N. J. P. Rewiring the taste system. Nature. 548 (7667), 330-333 (2017).
- Dana, H., et al. High-performance calcium sensors for imaging activity in neuronal populations and microcompartments. Nature Methods. 16 (7), 649-657 (2019).
- Wu, A., Dvoryanchikov, G., Pereira, E., Chaudhari, N., Roper, S. D. Breadth of tuning in taste afferent neurons varies with stimulus strength. Nature Communications. 6, 8171(2015).
- Yarmolinsky, D. A., et al. Coding and plasticity in the mammalian thermosensory system. Neuron. 92 (5), 1079-1092 (2016).
- Li, K. The image stabilizer plugin for ImageJ. , Available from: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~ kangli/code/Image_Stabilizer. html (2008).
- Ackman, J. dF Over F movie ImageJ Plugin. , Available from: https://gist.github.com/ackman678/5817461 (2014).
- Cantu, D. A., et al. EZcalcium: Open-source toolbox for analysis of calcium imaging data. Frontiers in Neural Circuits. 14, 25(2020).
- Giovannucci, A., et al. CaImAn an open source tool for scalable calcium imaging data analysis. Elife. 8, (2019).
- Zhang, J., et al. Sour sensing from the tongue to the brain. Cell. 179 (2), 392-402 (2019).
- Lee, D., Kume, M., Holy, T. E. A molecular logic of sensory coding revealed by optical tagging of physiologically-defined neuronal types. bioRxiv. , 692079(2019).
- Moeyaert, B., et al. Improved methods for marking active neuron populations. Nature Communication. 9 (1), 4440(2018).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone