Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Modeling Oral-Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in 3D Organoids
* Wspomniani autorzy wnieśli do projektu równy wkład.
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
This protocol describes the key steps to generate and characterize murine oral-esophageal 3D organoids that represent normal, preneoplastic, and squamous cell carcinoma lesions induced via chemical carcinogenesis.
Streszczenie
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is prevalent worldwide, accounting for 90% of all esophageal cancer cases each year, and is the deadliest of all human squamous cell carcinomas. Despite recent progress in defining the molecular changes accompanying ESCC initiation and development, patient prognosis remains poor. The functional annotation of these molecular changes is the necessary next step and requires models that both capture the molecular features of ESCC and can be readily and inexpensively manipulated for functional annotation. Mice treated with the tobacco smoke mimetic 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4NQO) predictably form ESCC and esophageal preneoplasia. Of note, 4NQO lesions also arise in the oral cavity, most commonly in the tongue, as well as the forestomach, which all share the stratified squamous epithelium. However, these mice cannot be simply manipulated for functional hypothesis testing, as generating isogenic mouse models is time- and resource-intensive. Herein, we overcome this limitation by generating single cell-derived three-dimensional (3D) organoids from mice treated with 4NQO to characterize murine ESCC or preneoplastic cells ex vivo. These organoids capture the salient features of ESCC and esophageal preneoplasia, can be cheaply and quickly leveraged to form isogenic models, and can be utilized for syngeneic transplantation experiments. We demonstrate how to generate 3D organoids from normal, preneoplastic, and SCC murine esophageal tissue and maintain and cryopreserve these organoids. The applications of these versatile organoids are broad and include the utilization of genetically engineered mice and further characterization by flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry, the generation of isogeneic organoid lines using CRISPR technologies, and drug screening or syngeneic transplantation. We believe that the widespread adoption of the techniques demonstrated in this protocol will accelerate progress in this field to combat the severe burden of ESCC.
Wprowadzenie
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the deadliest of human squamous cell carcinomas, owing to its late diagnosis, therapy resistance, and metastasis1,2. ESCC arises from the stratified squamous epithelium, which lines the luminal surface of the esophagus. The squamous epithelium is comprised of proliferative basal cells and differentiated cells within the suprabasal cell layer. Under physiologic conditions, basal cells express markers such as p63, Sox2, and cytokeratin K5 and K14, while differentiated cells express K4, K13, and IVL. Basal cells themselves are heterogeneous and include putative stem cells defined by markers such as K153 and CD734. In homeostasis, basal cells undergo post-mitotic terminal differentiation within the suprabasal cell layer, whereas differentiated cells migrate and desquamate into the lumen to complete epithelial renewal. Reminiscent of their cells of origin, ESCC displays squamous cell differentiation to varying degrees. ESCC is often accompanied by multifocal histologic precursor lesions, known as intraepithelial neoplasia (IEN) or dysplasia, comprising atypical basaloid cells. In addition to epithelial changes, ESCC displays tissue remodeling within the subepithelial compartment, where the activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and the recruitment of immune/inflammatory cells take place to foster the tumor-promoting microenvironment.
The pathogenesis of ESCC involves genetic changes and exposure to environmental risk factors. Key genetic lesions include the inactivation of the tumor suppressor genes TP53 and CDKN2A (p16INK4A) and the activation of the CCND1 (cyclin D1) and EGFR oncogenes, which culminate in impaired cell cycle checkpoint function, aberrant proliferation, and survival under genotoxic stress related to exposure to environmental carcinogens. Indeed, genetic changes interact closely with behavioral and environmental risk factors, most commonly tobacco and alcohol use. Tobacco smoke contains human carcinogens such as acetaldehyde, which is also the major metabolite of alcohol. Acetaldehyde induces DNA adducts and interstrand DNA crosslinks, leading to DNA damage and the accumulation of DNA mutations and chromosomal instability. Given excessive mitogenic stimuli and aberrant proliferation from oncogene activation, the malignant transformation of esophageal epithelial cells is facilitated by mechanisms to cope with genotoxic stress, including the activation of antioxidants, autophagy, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Interestingly, these cytoprotective functions are often activated in ESCC cancer stem cells (CSCs) that are characterized by high CD44 (CD44H) expression and have the capabilities of tumor initiation, invasion, metastasis, and therapy resistance5,6,7.
ESCC has been modeled in cell culture and in rodent models8,9. In the last three decades, robust genetically engineered mouse models of ESCC have been developed. These include CCND1 and EGFR transgenic mice10,11 and p53 and p120Ctn knockout mice12,13. However, single genetic changes do not typically result in rapid-onset ESCC. This challenge has been overcome with the use of esophageal carcinogens that recapitulate well the human genetic lesions in ESCC14. For example, 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide (4NQO) accelerates ESCC development in CCND1 transgenic mice15. In recent years, putative esophageal epithelial stem cells, progenitor cells, and their respective fates have been investigated in cell lineage-traceable mouse models3,4. Furthermore, these cell lineage-traceable mice have been utilized to explore the cells of origin of ESCC and how such cells give rise to CD44H CSCs via conventional histology and omics-based molecular characterization7.
One emerging area related to these mouse models is the novel application of cell culture techniques to analyze live ESCC and precursor cells in a three-dimensional (3D) organoid system in which the architecture of the original tissues is recapitulated ex vivo7,8,9. These 3D organoids are rapidly grown from a single-cell suspension isolated from murine tissues, including primary and metastatic tumors (e.g., lymph node, lung, and liver lesions). The cells are embedded in basement membrane extract (BME) and fed with a well-defined serum-free cell culture medium. The 3D organoids grow within 7-10 days, and the resulting spherical structures are amenable for subculture, cryopreservation, and assays for analyzing a variety of cellular properties and functions, including CSC markers, EMT, autophagy, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptotic cell death.
These methods can be broadly applied to 3D organoid cultures established from any stratified squamous epithelial tissue, such as the head and neck mucosa (oral cavity, tongue, pharynx, and larynx) and even the forestomach. The head and neck mucosa are contiguous with the esophagus, and the two tissues share similar tissue organization, function, and susceptibility to disease. Both head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and ESCC share genetic lesions and lifestyle-related environmental risk factors such as tobacco and alcohol exposure. Underscoring this similarity, mice treated with the tobacco smoke mimetic 4NQO readily develop both HNSCC and ESCC. Given the ease with which the protocols described below can be applied to modeling HNSCC, we include specific instructions for establishing 3D organoid cultures from these lesions.
Herein, we provide detailed protocols for generating murine esophageal 3D organoids (MEOs) representing normal, preneoplastic, and ESCC lesions that develop in mice treated with 4NQO. Various mouse strains can be utilized, including common laboratory strains such as C57BL/6 and cell lineage-traceable and other genetically engineered derivatives. We emphasize the key steps, including the isolation of normal or diseased murine esophageal epithelium, the preparation of single-cell suspensions, the cultivation and monitoring of the growing 3D organoids, subculture, cryopreservation, and the processing for subsequent analyses, including morphology and other applications.
Protokół
The murine experiments were planned and performed in accordance with regulations and under animal protocol #AABB1502, reviewed and approved by Columbia University's Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. The mice were housed at a proper animal care facility that ensures the humane treatment of mice and provides appropriate veterinary care for the mice and laboratory safety training for the laboratory personnel.
1. Treatment of mice with 4NQO to induce esophageal IEN and ESCC lesions (time consideration: up to 28 weeks)
NOTE: To generate MEOs representing neoplastic esophageal lesions, the mice are subjected to 4NQO-mediated chemical carcinogenesis as previously described by Tang et al.14. Normal/non-neoplastic MEOs are generated from untreated mice.
- Mice
- House four to five mice per cage, and acclimate them to the animal facility for at least 1 week before starting an experiment. To reduce the possibility that age-related disorders result in premature termination of the full 28 week experiment, start with 8 week old to 16 week old mice.
NOTE: C57BL/6 mice weighing approximately 20-30 g were utilized in this protocol. For shorter experiments, older mice may be used. Male or female mice are acceptable. Control (no treatment, see section 1.3.1) mice must be matched in age and sex.
- House four to five mice per cage, and acclimate them to the animal facility for at least 1 week before starting an experiment. To reduce the possibility that age-related disorders result in premature termination of the full 28 week experiment, start with 8 week old to 16 week old mice.
- Preparation of drinking water containing 4NQO
- Prepare 1 mg/mL 4NQO stock solution in ethylene propylene glycol (Table of Materials). Dissolve 100 mg of 4NQO into 100 mL of 99.9% ethylene propylene glycol in a 500 mL glass beaker covered with sealing film. Mix thoroughly at room temperature (RT) using a magnetic stirrer at 800 rpm for 30 min. Store at 4 °C.
- Add 900 mL of autoclaved deionized water to 100 mL of 1 mg/mL 4NQO stock solution, and mix by inversion in a 2 L plastic graduated cylinder covered with sealing film. A volume of 1 L of 100 µg/mL 4NQO in 10% ethylene propylene glycol will serve two mouse cages equipped with a 500 mL drinking bottle.
CAUTION: Of note, 4NQO is a synthetic chemical carcinogen that may cause cancer. Handle with nitrile gloves and a long-sleeved lab coat, and wear closed-toe shoes. Consider proper eye protection, face protection, and head covering. For waste disposal, 4NQO should be placed in a labeled container in accordance with institutional guidelines for hazardous waste management by environmental health and safety.
- Treatment with 4NQO and monitoring
- Attach the drinking bottle, and administer 4NQO via the drinking water ad libitum to the mice for 16 weeks. Use 10% (w/v) propylene glycol as a vehicle (no treatment) control.
NOTE: Shorter durations of 4NQO treatment may be used to induce IEN. - Refill the water once per week.
- Weigh each mouse weekly by placing it in a plastic container on a laboratory balance.
- At the end of the 16 week 4NQO treatment period, start giving the mice regular drinking water during the post-4NQO observation period for up to 12 weeks (Figure 1).
- Monitor the mice daily for signs of distress (e.g., impaired mobility, hunched habitus, and withdrawn behavior), dysphagia, and dehydration. Additionally, evaluate the mice weekly for changes in body weight or food and liquid intake. Should the body weight drop by more than 10% from the initial body weight, feed the mice with a liquid dietary supplement.
NOTE: A loss of body weight refractory to liquid dietary supplements may be indicative of ESCC, and mice that lose more than 20% of their body weight should be euthanized. Importantly, MEOs can be generated from prematurely euthanized mice. Note that C57BL/6 mice without genetic modifications do not typically display signs of morbidity or have visible ESCC lesions until the end of the post-4NQO observation period.
- Attach the drinking bottle, and administer 4NQO via the drinking water ad libitum to the mice for 16 weeks. Use 10% (w/v) propylene glycol as a vehicle (no treatment) control.
- Animal preparation
- Euthanize the mice in a CO2 chamber filled with CO2 at a flow rate that displaces 30%-70% of the chamber volume per minute. Confirm death by cervical dislocation.
- Pin the limbs and nose of the mouse in the supine position to the dissection platform using 21 G needles.
- Disinfect the ventral surface of the mouse with 70% ethanol.
- Dissection (time consideration: 0.5 h)
- Open the skin by pinching the midabdominal fur and skin to ensure it is released from the viscera below. Use the surgical scissors to make a craniocaudal, ventral midline incision from the lower abdomen to the chin.
- Starting at the midline incision, use surgical scissors to make radial cuts extending to the limbs on both sides of the mouse. Flay the skin flaps open.
- To expose the cervical trachea, use the dissecting scissors to divide the salivary glands at the midline. The trachea lies deep in the glands.
- To expose the thoracic trachea, remove the sternum.
- Gently pinch and lift the peritoneum with forceps, and use scissors to divide the peritoneum craniocaudally and laterally along the rib cage.
- Gently retract the liver from the caudal surface of the diaphragm, and use scissors to make a small incision in the diaphragm at the sternal notch, specifically at the dorsal surface of the xiphoid process. This releases the lung and heart from the visceral pleura.
- Separate the ribcage from the thoracic contents. Insert scissors into the incision in the diaphragm, and dissect cranially to the cervical girdle. During this dissection, adhere closely to the dorsal surface of the sternum to avoid damage to the organs below. Ensure that the plane of dissection is anterior to the trachea.
- Cut the ribs on either side of the sternum using scissors, and remove the sternum. Ensure that the thoracic contents are exposed.
- Expose the abdominal esophagus. Gently lift the stomach anteriorly by holding the antrum with forceps. Dissect the spleen, pancreas, and mesentery off the stomach and esophagus with scissors.
- Expose the thoracic esophagus (Figure 2).
- Gently lift the trachea immediately caudal to the thyroid cartilage, and dissect the esophagus of the dorsal side of the trachea using iris scissors.
- Divide the trachea at the thyroid cartilage with iris scissors.
- Peel the trachea off the remainder of the esophagus via careful dissection in the caudal direction.
- Remove the lung, heart, and thymus en masse with the trachea. Take care to avoid damage to the esophagus when dissecting and dividing the aorta and vena cava.
- Divide the stomach at the pylorus with scissors.
- Separate the esophagus from the vertebra by holding the antrum with forceps and dissecting cranially.
- Divide the esophagus at the level of the thyroid cartilage, and harvest the esophagus and stomach en masse (Figure 3).
- Separate the stomach and esophagus by dividing the esophagus at the cardia (Figure 4, top panel, red line).
- Dissect off any fascia on the outer surface of the esophagus. To reserve a sample for histology (optional), remove half of the esophagus and split longitudinally with scissors. Place the remaining intact esophagus in cold PBS on ice.
- Open the stomach along the greater curvature, and wash with PBS sufficiently. Separate the forestomach, and wash with cold PBS. Place the forestomach in cold PBS on ice.
- To harvest the tongue, remove the 21 G needle on the nose, and pull out the tongue with tweezers. Cut the tongue as long as possible. Place the tongue in cold PBS on ice.
2. Establishment of murine esophageal organoid (MEO) culture
NOTE: This protocol can also be used to establish a murine tongue organoid culture with the addition of a step in which the tongue tissue is minced before trypsinization. See the note in step 2.2.3.
- Preparation of reagents
NOTE: A list of reagents may be found in the Table of Materials. Prepare and store the stock solutions according to the manufacturer's instructions unless otherwise indicated.- Ensure that the single-use aliquots of the basement membrane matrix (BME) utilized in this protocol are stored at −20 °C until the day of use, are subsequently thawed on ice or at 2-8 °C, and are kept on ice at all times when not in use.
- Dissolve 250 mg of soybean trypsin inhibitor (STI) in 1,000 mL of PBS (250 mg/mL stock concentration), and filter-sterilize (0.22 µm) it. Dispense 50 mL aliquots into conical tubes, and store for up to 6 months at 4 °C.
- Prepare the mouse organoid medium (MOM): Supplement advanced DMEM/F12 with 1 mM N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), 2% R-Spondin and Noggin conditioned medium (RN CM), 1x N-2 supplement, 1x B-27 supplement, 10 mM HEPES, 1x antibiotic-antimycotic, 1x GlutaMAX supplement, and 100 ng/mL mouse epidermal growth factor (mEGF). Prepare the MOM 500 mL at a time, divide it into 50 mL aliquots, and store at 2-8 °C until ready to use. Add 0.5 µg/mL amphotericin B and 10 µM Y-27632 just prior to use.
- Prewarm the MOM, 0.25% trypsin, and soybean trypsin inhibitor (STI) to 37 °C in a water or bead bath before use.
- Isolation of keratinocytes from the dissected mouse tissue (time consideration: 2 h)
- Transfer the esophageal tissue into 500 µL of dispase in PBS (2.5-5 units total), and incubate in a thermomixer for 10 min at 37 °C and 800 rpm.
- Transfer the tissue to a culture dish, and carefully remove the muscle layer from the epithelium using forceps (Figure 4).
NOTE: This step can also be performed by an experienced researcherprior to incubation with dispase. - Transfer the epithelium to a microcentrifuge tube containing 500 µL of 0.25% trypsin, and incubate in a thermomixer for 10 min at 37 °C and 800 rpm.
NOTE: If the starting material is tongue tissue, mince the tissue with a sterile scalpel into smaller pieces, approximately 1-2 mm2 in size, before adding the trypsin. - Briefly centrifuge for 5-10 s at 2,000 x g to pellet the tissue. Prepare a 50 mL conical tube with a 100 µm cell strainer. Transfer the tissue/cell suspension through the strainer with a wide bore tip using circular motions.
- Add 3 mL of STI through the strainer, using circular motions to wash.
- Scrub the strainer with the base of a 1 mL tuberculin syringe plunger to push the cells through.
- Wash the strainer with 3 mL of PBS 3-5 times, scrubbing the strainer with the base of the syringe between washes.
- Centrifuge the tube at 300 x g for 10 min at 4 °C to pellet the cells.
- Remove the supernatant, leaving 1 mL of solution in the tube.
- Resuspend the pellet in the remaining 1 mL, and transfer the cell suspension through a 70 µm cell strainer into a new 50 mL conical tube.
- Centrifuge the tube at 300 x g for 10 min at 4 °C to pellet the cells.
- Resuspend the pellet in 100 µL of MOM; adjust the volume as needed. Perform an automated cell count by trypan blue exclusion.
- Seeding of the initial cell suspension (time consideration: <1 h)
- Prewarm a 24-well cell culture plate in a 37 °C incubator.
- Plate 5,000 viable cells in 75% (v/v) BME/MOM with 50 µL total volume per well. Maximize the number of wells plated and prepare enough cells in BME for one extra well according to the example calculations below.
NOTE: Cryopreserve any excess cells in the cryopreservation medium (10% DMSO in FBS) at a maximum concentration of 1 x 106 cells/mL. Store the cryovials in a freezing container overnight at −80 °C. Transfer them to vapor phase liquid nitrogen for long-term storage. - In a microcentrifuge tube, prepare an appropriate cell dilution in MOM first, and then add BME using a wide bore tip just before plating.
- Using a 200 µL wide bore tip, slowly add a 50 µL droplet to the center of the well, avoiding contact between the tip and the bottom or sides of the well (Figure 5). Be careful not to use too much force to expel the liquid from the tip, or the dome will flatten.
- Allow the BME to solidify for 30 min in a 37 °C, 5% CO2, 95% relative humidity (RH) incubator.
- Carefully add 500 µL of MOM per well supplemented with 0.5 µg/mL amphotericin B and 10 µM Y-27632.
NOTE: Add amphotericin to all the MOM throughout the initial primary culture. Add Y-27632 only on the day of passaging (day 0) for all passages. - Change the MOM on days 3-4 and then every 2-3 days after that until ready to passage.
- On days 7-10, image the organoids, and measure the organoid formation rate (OFR) by dividing the number of organoids formed by the number of cells initially seeded.
Example calculations:
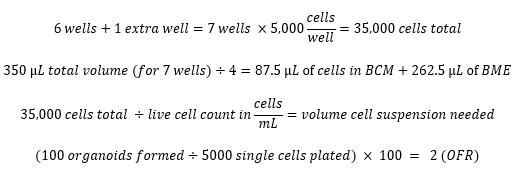
- Passaging and cryopreservation of murine esophageal organoids (MEOs) (time consideration: <1.5 h)
- Thaw and keep the BME on ice. Prewarm MOM, 0.05% trypsin, and STI to 37 °C in a water or bead bath before use. Prewarm a 24-well cell culture plate in a 37 °C incubator.
- Using a wide bore micropipette tip, collect the organoids in the BME dome along with the supernatant. Disrupt the BME by pipetting up and down.
NOTE: Combine the wells containing identical samples into a single microcentrifuge tube. - Briefly centrifuge for 10-15 s at 2,000 x g to pellet the organoids. Remove and discard the supernatant.
- Gently dislodge the pellet, and resuspend the pellet in 500 µL of 0.05% trypsin.
- Incubate the tube(s) in a thermomixer at 37 °C and 800 rpm for 10 min.
- Inactivate the trypsin with 600 µL of STI.
- Centrifuge the tube at 300 x g for 5 min at 4 °C to pellet the cells.
- Remove and discard the supernatant. Resuspend the cell pellet in 100 µL of MOM. Perform an automated cell count by trypan blue exclusion.
NOTE: The volume may be adjusted as needed. - Plate 2,000-5,000 viable cells in 75% (v/v) BME/MOM with 50 µL total volume per well. Maximize the number of wells plated and prepare enough cells in BME for one extra well according to the example calculations mentioned previously.
NOTE: Cryopreserve any excess cells in the cryopreservation medium (10% DMSO in FBS) at a maximum concentration of 1 x 106 cells/mL. Store the cryovials in a freezing container overnight at −80 °C. Transfer them to vapor phase liquid nitrogen for long-term storage. - In a microcentrifuge tube, prepare an appropriate cell dilution in MOM first, and then add BME using a wide bore tip just before plating.
- Using a 200 µL wide bore tip, slowly add a 50 µL droplet to the center of the well, avoiding contact between the tip and the bottom or sides of the well. Be careful not to use too much force to expel the liquid from the tip, or the dome will flatten.
- Incubate the plate for 30 min in a 37 °C, 5% CO2,95% RH incubator.
- Carefully add 500 µL of MOM per well supplemented with 10 µM Y-27632.
NOTE: Add Y-27632 only on the day of passaging (day 0). It is unnecessary to add it during the media changes. Adding amphotericin B is no longer necessary. - Change the MOM on days 3-4 and then every 2-3 days after that until ready to passage.
- On days 7-10, image the organoids, and measure the OFR.
- Thawing and recovery of the murine esophageal organoids (MEOs) (time consideration: <1 h)
- Thaw and keep the BME on ice. Prewarm a 24-well cell culture plate in a 37 °C incubator.
- Prepare 10 mL of cold or RT MOM or PBS in a 15 mL conical tube.
- Thaw a cryovial in a 37 °C water bath or bead bath for approximately 30 s to 1 min or until a small ice pellet remains.
- With a pre-wetted pipet tip, slowly transfer the cell suspension to the tube containing MOM or PBS in a dropwise manner.
- Centrifuge the tube for 300 x g and 4 °C for 5 min to pellet the cells.
- Remove and discard the supernatant. Resuspend the cell pellet in 100 µL of MOM; adjust the volume as needed. Perform an automated cell count by trypan blue exclusion.
- Plate 5,000-10,000 viable cells in 75% (v/v) BME/MOM with 50 µL total volume per well. Maximize the number of wells plated and prepare enough cells in BME for one extra well according to example calculations mentioned previously.
- Continue with the remaining steps of the protocol for the passaging and cryopreservation of murine esophageal organoids (MEO) (see step 2.4.11).
3. Preparation of organoids for paraffin embedding (time consideration: <1 h [plus 1.5 h for reagent preparation])
- Using a wide-bore micropipette tip, collect three wells per microcentrifuge tube. Collect the organoids in the BME dome along with the supernatant. Disrupt the BME by pipetting up and down.
- Briefly centrifuge for 10-15 s at 2,000 x g to pellet the organoids. Remove and discard the supernatant.
- Gently dislodge the pellet, and resuspend the pellet in 300 µL of 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA).
- Fix the organoids overnight at 4 °C.
- Briefly centrifuge for 10-15 s at 2,000 x g to pellet the organoids. Remove and discard as much PFA as possible.
- Gently dislodge the pellet, and resuspend the pellet in 500 µL of PBS.
NOTE: Fixed organoids can be stored at 4 °C for up to 2 weeks before proceeding to the next step. - Prepare a 50 mL stock of agar gel (2% agar plus 2.5% gelatin).
NOTE: Prepare the agar gel stock in advance, due to the incubation time, followed by carrying out the autoclave cycle.- Resuspend 1 g of Bacto-agar and 1.25 g of gelatin in 50 mL of water in a 150 mL autoclavable glass beaker.
- Swirl the suspension, and let it sit for 30-60 min at RT.
- Autoclave for 20 min at 121 °C.
- Cool slightly and dispense 5 mL aliquots in 15 mL conical tubes.
- Store for up to 6 months at RT.
- Prepare an embedding surface by inverting a microcentrifuge tube rack and covering the surface with a sheet of sealing film. Label with the corresponding organoid ID(s).
- Centrifuge the tube at 300 x g for 5 min to pellet the organoids. Remove and discard the supernatant.
- Meanwhile, liquefy the agar gel by placing a 15 mL conical tube containing the agar gel into a 150 mL glass beaker containing 100 mL of water and microwaving on the highest power setting for 1-2 min or until the water starts to boil and the agar gel is in a liquid state.
CAUTION: Loosen the cap of the conical tube containing the agar gel before microwaving. - Partially submerge the microcentrifuge tube containing the organoid pellet into the warm water without introducing any water into the microcentrifuge tube.
- Carefully overlay the organoid pellet by adding 50 µL of agar down the side of the tube.
- Without disturbing the pellet (do not resuspend, keep the pellet intact), transfer the pellet in the agar gel droplet to the sealing film on the embedding surface.
- Repeat step 3.12 and step 3.13 with an additional 50 µL of liquid agar gel to collect any remaining organoid pellet, and carefully add to the same gel droplet.
- Incubate the droplet containing the organoid pellet for 45 min at 4 °C.
- Using forceps, carefully transfer the droplet containing the organoid pellet to a labeled pathology cassette.
- Store the cassette in 70% ethanol at 4 °C for up to 1 month.
- Proceed with paraffin embedding via routine histological processing to prepare paraffin blocks.
Wyniki
This protocol describes the process of generating murine esophageal organoids (MEOs) from normal esophageal tissue or ESCC tumor tissue from 4NQO-treated mice according to a specific treatment regimen consisting of 16 weeks of 4NQO administered in drinking water, followed by a 10 week to 12 week observation period (Figure 1). The mice are then euthanized for the dissection of the tongue or esophageal tissue (Figure 2 and Figure 3). ...
Dyskusje
There are several critical steps and considerations for the generation and analysis of MEOs in the protocols described here. To ensure reproducibility and rigor in MEO experiments, biological and technical replicates are both important. For biological replicates, two to three independent mice bearing ESCC are generally sufficient per experimental condition. However, the appropriate number of biological replicates may vary depending on the parameters to be tested in individual studies. For example, it ...
Ujawnienia
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Podziękowania
We thank the Shared Resources (Flow Cytometry, Molecular Pathology, and Confocal & Specialized Microscopy) at the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center at Columbia University for technical support. We thank Drs. Alan Diehl, Adam J. Bass, and Kwok-Kin Wong (NCI P01 Mechanisms of Esophageal Carcinogenesis) and members of the Rustgi and Nakagawa laboratories for helpful discussions. This study was supported by the following NIH Grants: P01CA098101 (H.N. and A.K.R.), R01DK114436 (H.N.), R01AA026297 (H.N.), L30CA264714 (S.F.), DE031112-01 (F.M.H.), KL2TR001874 (F.M.H.),3R01CA255298-01S1 (J.G.), 2L30DK126621-02
(J.G.) R01CA266978 (C.L.), R01DK132251 (C.L.), R01DE031873 (C.L.), P30DK132710 (C.M. and H.N.), and P30CA013696 (A.K.R.). H.N. and C.L. are recipients of the Columbia University Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Multi-PI Pilot Award. H.N. is a recipient of the Fanconi Anemia Research Fund Award. F.M.H. is the recipient of The Mark Foundation for Cancer Research Award (20-60-51-MOME) and an American Association for Cancer Research Award. J.G. is the recipient of the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) award.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.05% trypsin-EDTA | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 25-300-120 | |
| 0.25% trypsin-EDTA | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 25-200-114 | |
| 0.4% Trypan Blue | Thermo Fisher Scientific | T10282 | |
| 1 mL tuberculin syringe without needle | BD | 309659 | |
| 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 05-408-129 | |
| 100 µm cell strainer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 22363549 | |
| 15 mL conical tubes | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 14-959-53A | |
| 200 µL wide bore micropipette tips | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 212361A | |
| 21 G needles | BD | 305167 | |
| 24 well plate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 12-556-006 | |
| 4-Nitroquinoline-1-oxide (4NQO) | Tokyo Chemical Industry | NO250 | |
| 50 mL conical tubes | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 12-565-270 | |
| 6 well plate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 12556004 | |
| 70 µm cell strainer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 22363548 | |
| 99.9% ethylene propylene glycol | SK picglobal | ||
| Advanced DMEM/F12 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 12634028 | |
| Amphotericin B | Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15290018 | Stock concentration 250 µg/mL, final concentration 0.5 µg/mL |
| Antibiotic-Antimycotic | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15240062 | Stock concentration 100x, final concentration 1x |
| B-27 supplement | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 17504044 | Stock concentration 50x, final concentration 1x |
| Bacto agar | BD | 214010 | |
| CO2 incubator, e.g.Heracell 150i | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 51026406 | or equivalent |
| Countess II FL Automated Cell Counter | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AMQAX1000 | or equivalent |
| Cryovials | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 03-337-7D | |
| DietGel 76A | Clear H2O | 72-07-5022 | |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | MilliporeSigma | D4540 | |
| Dispase | Corning | 354235 | Stock concentration 50 U/mL, final concentration 2.5–5 U/mL |
| Dissecting scissors | VWR | 25870-002 | |
| Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 14190250 | Stock concentration 1x |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | HyClone | SH30071.03 | |
| Forceps | VWR | 82027-386 | |
| Freezing container | Corning | 432002 | or equivalent |
| Gelatin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | G7-500 | |
| GlutaMAX | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 35050061 | Stock concentration 100x, final concentration 1x |
| HEPES | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15630080 | Stock concentration 1 M, final concentration 10 mM |
| Hot plate/stirrer | Corning | PC-420D | or equivalent |
| Lab Armor bead bath (or water bath) | VWR | 89409-222 | or equivalent |
| Laboratory balance | Ohaus | 71142841 | or equivalent |
| Matrigel basement membrane extract (BME) | Corning | 354234 | |
| Microcentrifuge Minispin | Eppendorf | 22620100 | or equivalent |
| Microcentrifuge tube rack | Southern Labware | 0061 | |
| N-2 supplement | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 17502048 | Stock concentration 100x, final concentration 1x |
| N-acetylcysteine (NAC) | Sigma-Aldrich | A9165 | Stock concentration 0.5 M, final concentration 1 mM |
| Parafilm M wrap | Thermo Fisher Scientific | S37440 | |
| Paraformaldehyde (PFA) | MilliporeSigma | 158127-500G | |
| Pathology cassette | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 22-272416 | |
| Phase-contrast microscope | Nikon | or equivalent | |
| Recombinant mouse epidermal growth factor (mEGF) | Peprotech | 315-09-1mg | Stock concentration 500 ng/µL, final concentration 100 ng/mL |
| RN cell-conditioned medium expressing R-Spondin1 and Noggin (RN CM) | N/A | N/A | Available through the Organoid and Cell Culture Core upon request, final concentration 2% |
| Sorval ST 16R centrifuge | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 75004380 | or equivalent |
| Soybean trypsin inhibitor (STI) | MilliporeSigma | T9128 | Stock concentration 250 µg/mL |
| ThermoMixer C | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 14-285-562 PM | or equivalent |
| Y-27632 | Selleck Chemicals | S1049 | Stock concentration 10 mM, final concentration 10 µM |
Odniesienia
- Rustgi, A. K., El-Serag, H. B. Esophageal carcinoma. The New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (26), 2499-2509 (2014).
- Dotto, G. P., Rustgi, A. K. Squamous cell cancers: A unified perspective on biology and genetics. Cancer Cell. 29 (5), 622-637 (2016).
- Giroux, V., et al. Long-lived keratin 15+ esophageal progenitor cells contribute to homeostasis and regeneration. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 127 (6), 2378-2391 (2017).
- DeWard, A. D., Cramer, J., Lagasse, E. Cellular heterogeneity in the mouse esophagus implicates the presence of a nonquiescent epithelial stem cell population. Cell Reports. 9 (2), 701-711 (2014).
- Kinugasa, H., et al. Mitochondrial SOD2 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell populations defined by differential CD44 expression. Oncogene. 34 (41), 5229-5239 (2015).
- Whelan, K. A., et al. Autophagy supports generation of cells with high CD44 expression via modulation of oxidative stress and Parkin-mediated mitochondrial clearance. Oncogene. 36 (34), 4843-4858 (2017).
- Natsuizaka, M., et al. Interplay between Notch1 and Notch3 promotes EMT and tumor initiation in squamous cell carcinoma. Nature Communications. 8 (1), 1758 (2017).
- Whelan, K. A., Muir, A. B., Nakagawa, H. Esophageal 3D culture systems as modeling tools in esophageal epithelial pathobiology and personalized medicine. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 5 (4), 461-478 (2018).
- Sachdeva, U. M., et al. Understanding the cellular origin and progression of esophageal cancer using esophageal organoids. Cancer Letters. 509, 39-52 (2021).
- Nakagawa, H., et al. The targeting of the cyclin D1 oncogene by an Epstein-Barr virus promoter in transgenic mice causes dysplasia in the tongue, esophagus and forestomach. Oncogene. 14 (10), 1185-1190 (1997).
- Andl, C. D., et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mediates increased cell proliferation, migration, and aggregation in esophageal keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (3), 1824-1830 (2003).
- Opitz, O. G., et al. A mouse model of human oral-esophageal cancer. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 110 (6), 761-769 (2002).
- Stairs, D. B., et al. Deletion of p120-catenin results in a tumor microenvironment with inflammation and cancer that establishes it as a tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Cell. 19 (4), 470-483 (2011).
- Tang, X. -. H., Knudsen, B., Bemis, D., Tickoo, S., Gudas, L. J. Oral cavity and esophageal carcinogenesis modeled in carcinogen-treated mice. Clinical Cancer Research. 10, 301-313 (2004).
- Fong, L. Y. Y., Mancini, R., Nakagawa, H., Rustgi, A. K., Huebner, K. Combined cyclin D1 overexpression and zinc deficiency disrupts cell cycle and accelerates mouse forestomach carcinogenesis. Cancer Research. 63 (14), 4244-4252 (2003).
- Zheng, B., et al. A new murine esophageal organoid culture method and organoid-based model of esophageal squamous cell neoplasia. iScience. 24 (12), 103440 (2021).
- Hisha, H., et al. Establishment of a novel lingual organoid culture system: generation of organoids having mature keratinized epithelium from adult epithelial stem cells. Scientific Reports. 3, 3224 (2013).
- Kalabis, J., et al. Isolation and characterization of mouse and human esophageal epithelial cells in 3D organotypic culture. Nature Protocols. 7 (2), 235-246 (2012).
- Nguyen, N., et al. TGF-β1 alters esophageal epithelial barrier function by attenuation of claudin-7 in eosinophilic esophagitis. Mucosal Immunology. 11 (2), 415-426 (2018).
- Sherrill, J. D., et al. Analysis and expansion of the eosinophilic esophagitis transcriptome by RNA sequencing. Genes and Immunity. 15 (6), 361-369 (2014).
- Ruffner, M. A., et al. Toll-like receptor 2 stimulation augments esophageal barrier integrity. Allergy. 74 (12), 2449-2460 (2019).
- Kabir, M. F., et al. Single cell transcriptomic analysis reveals cellular diversity of murine esophageal epithelium. Nature Communications. 13 (1), 1-15 (2022).
- Shimonosono, M., et al. Alcohol metabolism enriches squamous cell carcinoma cancer stem cells that survive oxidative stress via autophagy. Biomolecules. 11 (10), 1479 (2021).
- Flashner, S., Yan, K. S., Nakagawa, H. 3D organoids: An untapped platform for studying host-microbiome interactions in esophageal cancers. Microorganisms. 9 (11), 2182 (2021).
- Liu, K., et al. Sox2 cooperates with inflammation-mediated stat3 activation in the malignant transformation of foregut basal progenitor cells. Cell Stem Cell. 12 (3), 304-315 (2013).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone