A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Activation of Apoptosis by Cytoplasmic Microinjection of Cytochrome c
In This Article
Summary
In this protocol, we describe the direct cytoplasmic microinjection of cytochrome c protein into fibroblasts and primary sympathetic neurons. This technique allows for the introduction of cytochrome c protein into the cytoplasm of cells and mimics the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, which occurs during apoptosis.
Abstract
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a conserved and highly regulated pathway by which cells die1. Apoptosis can be triggered when cells encounter a wide range of cytotoxic stresses. These insults initiate signaling cascades that ultimately cause the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondrial intermembrane space to the cytoplasm2. The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria is a key event that triggers the rapid activation of caspases, the key cellular proteases which ultimately execute cell death3-4.
The pathway of apoptosis is regulated at points upstream and downstream of cytochrome c release from mitochondria5. In order to study the post-mitochondrial regulation of caspase activation, many investigators have turned to direct cytoplasmic microinjection of holocytochrome c (heme-attached) protein into cells6-9. Cytochrome c is normally localized to the mitochondria where attachment of a heme group is necessary to enable it to activate apoptosis10-11. Therefore, to directly activate caspases, it is necessary to inject the holocytochrome c protein instead of its cDNA, because while the expression of cytochrome c from cDNA constructs will result in mitochondrial targeting and heme attachment, it will be sequestered from cytosolic caspases. Thus, the direct cytosolic microinjection of purified heme-attached cytochrome c protein is a useful tool to mimic mitochondrial cytochrome c release and apoptosis without the use of toxic insults which cause cellular and mitochondrial damage.
In this article, we describe a method for the microinjection of cytochrome c protein into cells, using mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and primary sympathetic neurons as examples. While this protocol focuses on the injection of cytochrome c for investigations of apoptosis, the techniques shown here can also be easily adapted for microinjection of other proteins of interest.
Protocol
1. Production of Microinjection Needles
- Pre-fabricated microinjection needles are available commercially (e.g. Femtotips from Eppendorf) and are useful if one is not performing a large number of microinjections. However, for those who wish to establish long-term capabilities for microinjecting, an alternative is to produce microinjection needles in the lab using thin wall borosilicate glass capillaries and a commercial needle puller. This also allows the shape of needles to be varied, which can be useful for different cell types.
- With the Narishige PC-10 Microinjection Needle Puller, attach all four weights and use a one-step pulling program (Step 1 setting) with the relative heat setting at 58.0 (No.2 heater). Be sure to place the heating element at the center of each capillary so that the two resulting needles are a similar length.
- Pull several capillaries (about 2 capillaries for each protein of interest).
- Store needles in a container while being sure not to damage the needle tip. Materials such as foam or Blu-Tack can be used in containers to hold microinjection needles.
2. Preparation of Protein Mixtures for Injection
- Prepare a 10x microinjection buffer containing 1 M potassium chloride and 0.1 M potassium phosphate (KPi) buffer (equimolar mixture of K2HPO4 and KH2PO4) at a pH of 7.4. This buffer can be stored long-term at room temperature.
- To visualize the injection, a fluorescent dye like rhodamine-dextran needs to be added. Dilute the10x microinjection buffer in water and dissolve rhodamine-dextran powder to make a 5x microinjection buffer solution containing 20-40 mg/mL rhodamine dextran.
- Store this solution in the dark at 4°C. It should be sufficient for up to 100 individual protein solution preparations. Other dyes, like fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran can substitute.
- Prepare cytochrome c stocks by dissolving purified cytochrome c in water to a concentration of 20 mg/mL. Store cytochrome c at -80°C for long-term storage and avoid freeze-thaw cycles by storing cytochrome c in small (~10 μL) aliquots.
- Prepare a 10 μL protein mixture for injection by combining 2 μL 5x microinjection buffer containing rhodamine-dextran with 3 μL water and 5 μL cytochrome c for a final concentration of 10 mg/mL cytochrome c in 1x buffer (100 mM KCl, 10 mM KPi, 4-8 mg/mL rhodamine dextran).
3. Cytoplasmic Microinjection of Cytochrome c
- Just prior to microinjection, centrifuge the mixture of cytochrome c and microinjection buffer at 16,000 g for 10 minutes at 4°C to separate any particulate matter which may clog microinjection needles.
- During centrifugation, turn on the microinjector to allow air pressure to build.
- Place a dish of cells on the center of the microscope stage and set the focus on the cells. To minimize the amount of time that the cells are kept outside the incubator, cells are typically returned to the incubator within 30 min.
- Pipette 0.5-1 μL from the top surface of the protein mixture into the blunt end of the capillary. Be careful to not pipette any particles which have been centrifuged to the bottom of the tube. Within a minute, the protein mixture will distribute to the needle tip through capillary action.
- Attach the needle firmly to the capillary holder of the micromanipulator and position the needle so that its tip passes through the transmitted light of the microscope at approximately a 45° angle.
- Adjust the position of the needle tip so that it is located directly in the center of the field of view. To center the needle, use the micromanipulator to move the needle while looking through the microscope eyepiece. The needle shadow should be visible. Adjust the needle so that its shadow is only seen in one half of the field of view, indicating that the needle tip is centered above the cells.
- Set the microinjector to the Continuous Flow mode and set the working pressure to 20 - 100 hPa. Each needle may require a different working pressure, and the working pressure will likely need adjustment during the microinjection procedure to maintain a steady flow.
- Lower the needle using the coarse knob to a position just above the cells. To do this, raise the focal plane of the microscope to a position just above the cells. Then lower the needle towards the cells using the coarse knob until the needle tip is in focus.
- Re-center the needle tip within the field of view and increase magnification by changing the microscope objective.
- Slowly lower the needle using the fine manipulator knob until the needle is just slightly above the focal plane of the cells.
- Check the flow of the protein mixture by looking at the red fluorescence of the rhodamine. The protein mixture should be exiting the needle as a thin, constant stream. Needles should be replaced and re-loaded if the needle is compromised or if the flow is far too strong. Sometimes, the tip of the glass capillary is closed and no flow is seen from the needle. If this occurs, replace the needle or carefully lower it to the bottom of the culture dish to gently rupture the tip of the needle.
- Position the needle tip so that it is pointing towards a cell at approximately a 45° angle. Then with one smooth motion, lower the needle while moving it towards the cell. With a second smooth motion, immediately reverse the direction of the needle to remove it from the cell.
- A successfully injected cell will often slightly swell and can be confirmed by visualizing the red fluorescent rhodamine within the cell. Occasionally, a cell will be accidentally injected in the nucleus, which will be visible.
- Continue to inject cells by adjusting the microscope stage until about 50-100 cells are injected. When moving the microscope stage, be sure to raise the microinjection needle so that it clears the top of cells.
4. Representative Results:
The cytoplasmic microinjection of cytochrome c mimics its release from mitochondria during apoptosis. Thus, as expected, fibroblasts rapidly undergo apoptosis upon cytosolic microinjection of bovine cytochrome c (Fig. 1A). To ensure that the injection procedure alone is not responsible for cell death, injection of yeast cytochrome c serves as an important control, since yeast cytochrome c is incapable of activating caspases12.
Interestingly, post-mitotic sympathetic neurons are remarkably resistant to cytosolic cytochrome c (Fig. 1B)8,13. Our lab has identified that the endogenous caspase inhibitor XIAP is a key inhibitor of caspase activation in neurons14. Thus, for neurons to die following cytochrome c injection, XIAP must first become inactivated. For example, microinjection of cytochrome c into xiap-/- sympathetic neurons is sufficient to allow caspase activation and apoptosis in these cells (Fig. 2).
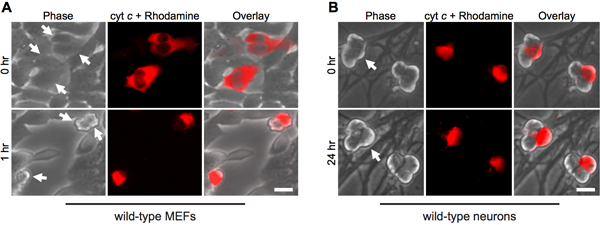
Figure 1. Cytoplasmic microinjection of cytochrome c induces rapid death in fibroblasts, but not neurons. A) Wild-type MEFs or (B) postnatal day 5 wild-type sympathetic neurons were microinjected with bovine cytochrome c (10 mg/mL) together with rhodamine-dextran to mark injected cells. Images show the same field of cells immediately following injection (0 hr), or at the indicated times. Arrows indicate injected cells. Scale bar, 20 μm.
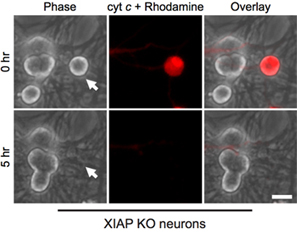
Figure 2. XIAP-deficient neurons are susceptible to cytoplasmic cytochrome c microinjection. Postnatal day 5 sympathetic neurons from XIAP knockout mice were microinjected with bovine cytochrome c (10 mg/mL) together with rhodamine-dextran to mark injected cells. Images show the same field of cells immediately following injection (0 hr), or 5 hours after cytochrome c microinjection (5 hr). Scale bar, 20 μm.
Discussion
The microinjection of cytochrome c directly into the cytoplasm of cells is a unique and powerful tool which allows for studies of the post-mitochondrial regulation of apoptosis. Importantly, this technique allows for the direct activation of apoptosis downstream of mitochondria without the use of agents which cause cellular or mitochondrial damage.
While this protocol has focused on microinjection of cytochrome c for studies on apoptosis, the general principles of protein ...
Disclosures
All experimental procedures on animals were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of North Carolina.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grant NS042197 to MD. AJK was supported by grants T32GM008719 and F30NS068006.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| DM IRE2 Inverted Microscope | Leica Microsystems | ||
| PC-10 Microinjection Needle Puller | Narishige International | ||
| MWO-202 Micromanipulator | Narishige International | ||
| FemtoJet Microinjector | Eppendorf | ||
| Thin-wall Boroscilicate Capillary Glass with Microfilament | A-M Systems | 615000 | 4 inch length, 1.00 mm outer diameter, 0.75 mm inner diameter |
| Rhodamine B isothiocyanate-Dextran | Sigma-Aldrich | R9379 | Average molecular weight ~70,000 Da |
| Bovine Cytochrome c Protein | Sigma-Aldrich | C3131 |
References
- Danial, N. N., Korsmeyer, S. J. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 116, 205-219 (2004).
- Wang, X. The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 15, 2922-2933 (2001).
- Hengartner, M. O. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature. 407, 770-776 (2000).
- Fuentes-Prior, P., Salvesen, G. S. The protein structures that shape caspase activity, specificity, activation and inhibition. Biochem. J. 384, 201-232 (2004).
- Tait, S. W., Green, D. R. Mitochondria and cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11, 621-632 (2010).
- Brustugun, O. T., Fladmark, K. E., Doskeland, S. O., Orrenius, S., Zhivotovsky, B. Apoptosis induced by microinjection of cytochrome c is caspase-dependent and is inhibited by Bcl-2. Cell Death Differ. 5, 660-668 (1998).
- Li, F. Cell-specific induction of apoptosis by microinjection of cytochrome c. Bcl-XL has activity independent of cytochrome c release. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 30299-30305 (1997).
- Deshmukh, M., Johnson, E. M. Evidence of a novel event during neuronal death: development of competence-to-die in response to cytoplasmic cytochrome c. Neuron. 21, 695-705 (1998).
- Vaughn, A. E., Deshmukh, M. Glucose metabolism inhibits apoptosis in neurons and cancer cells by redox inactivation of cytochrome c. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 1477-1483 (2008).
- Yang, J. Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science. 275, 1129-1132 (1997).
- Gonzales, D. H., Neupert, W. Biogenesis of mitochondrial c-type cytochromes. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 22, 753-768 (1990).
- Ellerby, H. M. Establishment of a cell-free system of neuronal apoptosis - comparison of premitochondrial, mitochondrial, and postmitochondrial phases. J. Neurosci. 17, 6165-6178 (1997).
- Neame, S. J., Rubin, L. L., Philpott, K. L. Blocking cytochrome c activity within intact neurons inhibits apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 142, 1583-1593 (1998).
- Potts, P. R., Singh, S., Knezek, M., Thompson, C. B., Deshmukh, M. Critical function of endogenous XIAP in regulating caspase activation during sympathetic neuronal apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 163, 789-799 (2003).
- Estus, S. Altered gene expression in neurons during programmed cell death: identification of c-jun as necessary for neuronal apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 127, 1717-1727 (1994).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved