A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
In Vitro Analysis of PDZ-dependent CFTR Macromolecular Signaling Complexes
In This Article
Summary
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), an epithelial chloride channel, has been reported to interact with various proteins and regulate important cellular processes; among them the CFTR PDZ motif-mediated interactions have been well documented. This protocol describes methods we developed to assemble a PDZ-dependent CFTR macromolecular signaling complex in vitro.
Abstract
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), a chloride channel located primarily at the apical membranes of epithelial cells, plays a crucial role in transepithelial fluid homeostasis1-3. CFTR has been implicated in two major diseases: cystic fibrosis (CF)4 and secretory diarrhea5. In CF, the synthesis or functional activity of the CFTR Cl- channel is reduced. This disorder affects approximately 1 in 2,500 Caucasians in the United States6. Excessive CFTR activity has also been implicated in cases of toxin-induced secretory diarrhea (e.g., by cholera toxin and heat stable E. coli enterotoxin) that stimulates cAMP or cGMP production in the gut7.
Accumulating evidence suggest the existence of physical and functional interactions between CFTR and a growing number of other proteins, including transporters, ion channels, receptors, kinases, phosphatases, signaling molecules, and cytoskeletal elements, and these interactions between CFTR and its binding proteins have been shown to be critically involved in regulating CFTR-mediated transepithelial ion transport in vitro and also in vivo8-19. In this protocol, we focus only on the methods that aid in the study of the interactions between CFTR carboxyl terminal tail, which possesses a protein-binding motif [referred to as PSD95/Dlg1/ZO-1 (PDZ) motif], and a group of scaffold proteins, which contain a specific binding module referred to as PDZ domains. So far, several different PDZ scaffold proteins have been reported to bind to the carboxyl terminal tail of CFTR with various affinities, such as NHERF1, NHERF2, PDZK1, PDZK2, CAL (CFTR-associated ligand), Shank2, and GRASP20-27. The PDZ motif within CFTR that is recognized by PDZ scaffold proteins is the last four amino acids at the C terminus (i.e., 1477-DTRL-1480 in human CFTR)20. Interestingly, CFTR can bind more than one PDZ domain of both NHERFs and PDZK1, albeit with varying affinities22. This multivalency with respect to CFTR binding has been shown to be of functional significance, suggesting that PDZ scaffold proteins may facilitate formation of CFTR macromolecular signaling complexes for specific/selective and efficient signaling in cells16-18.
Multiple biochemical assays have been developed to study CFTR-involving protein interactions, such as co-immunoprecipitation, pull-down assay, pair-wise binding assay, colorimetric pair-wise binding assay, and macromolecular complex assembly assay16-19,28,29. Here we focus on the detailed procedures of assembling a PDZ motif-dependent CFTR-containing macromolecular complex in vitro, which is used extensively by our laboratory to study protein-protein or domain-domain interactions involving CFTR16-19,28,29.
Protocol
1. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Tagged Fusion Proteins in Bacteria
- Amplify defined regions of the C-tails (the last 50-100 amino acids containing the PDZ motifs at C-terminus) for CFTR, LPA2, MRP2, MRP4, β2AR, and NHERFs (full-length or PDZ1 or PDZ2 domains) by PCR approach.
- Clone the PCR products into pGEX4T-1 vector for GST-fusion proteins (such as GST-NHERFs, GST-MRP4 CT), pMAL-C2 vector for MBP-fusion proteins (such as MBP-β2AR CT, MBP-CFTR CT), and pET30 for His-S-fusion proteins (such as His-S-CFTR CT, His-S-PDZK1).
- Transform in a protease-deficient E. coli strain (BL21-DE3) to minimize possible recombinant protein degradation.
- Grow the culture overnight at 37 °C in Luria-Bertani medium (pH 7.0) containing appropriate antibiotics (such as ampicillin or kanamycin). Dilute the overnight culture at 1:10 and grow for another 2 hr at 37 °C. Induce with 0.5-1 mM IPTG for the next 4 hr at 30 °C. Pellet the cells by centrifugation at 8,000 × g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Lyse the cells in Sucrose Buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM PMSF, and 10% sucrose) containing lysozyme (1 mg/ml), 0.2% Triton X-100, and protease inhibitors. Use 20 ml for cell pellet originating from 1 L of culture.
- Mix on a rotary shaker for 30 min at 4 °C.
- Spin at 20,000 × g for 30 min at 4 °C. Collect the clear supernatant.
- Into the clear supernatant, add 1 ml of the following resin/agarose beads (50% slurry in Sucrose Buffer):
- Glutathione agarose beads for GST fusion proteins.
- Talon beads for His-S fusion proteins.
- Amylose resin for MBP fusion proteins.
- Mix for 4 hr at 4 °C on a rotary shaker.
- Wash the beads by resuspending in 1x PBS (15 ml), mixing for 2 min, spinning at 800 × g for 2 min, and discarding the supernatant. Repeat this step for 6 times.
- Elute the protein from the beads by using respective elution buffer (2 ml elution buffer per 1 ml of beads).
- Elution buffer for GST fusion proteins: 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 140 mM NaCl, and 20 mM reduced glutathione.
- Elution buffer for His fusion proteins: 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 500 mM NaCl, and 200 mM imidazole.
- Elution buffer for MBP fusion proteins: 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, and 10 mM maltose.
- Dialyze the eluted proteins against 2 L of 1x PBS at 4 °C (to avoid possible protein degradation). Change PBS every 4 hr for 4 times. Concentrate the protein using a Centricon filter (10,000 MW cutoff, Millipore) and store as small aliquots at -80 °C.
- Determine the protein concentration by the Bradford method. Assess protein quality by SDS-PAGE using BSA as standards. If the integrity of the protein is not satisfactory, secondary purification procedures such as gel filtration or ion exchange may be used. (e.g., we have used a G-75 Sepharose column to further purify GST-fusion protein).
2. Cell Culture and Cell Lysate Preparation
- Culture baby hamster kidney (BHK) cells that stably over-express CFTR-wt and CFTR-his10 or BHK cells that transiently over-express Flag-LPA2-wt or Flag-LPA2-ΔSTL, and Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells that stably over-express MRP2 in Eagle's minimum essential medium (MEM) containing 10% fetal calf serum and penicillin/streptomycin in polystyrene flasks at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
- Culture human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells that stably over-express CFTR-wt and CFTR-his10 in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and penicillin/streptomycin in polystyrene flasks at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
- Lyse the cells in Lysis Buffer (PBS - 0.2% Triton-X-100 supplemented with a mixture of protease inhibitors containing 1 mM phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride, 1 μg/ml aprotinin, 1 μg/ml leupeptin, 1 μg/ml pepstatin); use 500 μl lysis buffer for each 60-mm Petri dish, and 1000 μl lysis buffer for each 100-mm Petri dish.
- Rock the cell lysates for 20 min at 4 °C, and remove the insoluble material by centrifugation at 16,000 × g for 15 min at 4 °C. Determine the protein concentration by the Bradford assay.
3. In Vitro Assembly of a CFTR-containing Macromolecular Complex (CFTR-PDZK1-MRP4)
- Into 200 μl of lysis buffer (PBS - 0.2% Triton-X 100 + protease inhibitors), add 20 μg purified GST-MRP4-C terminal 50 a.a. (CT50) fusion protein.
- Add various amounts (0-40 μg) of purified His-S-PDZK1 fusion protein.
- Mix the two proteins on a rotary mixer at 22 °C for 1-2 hr.
- Add 20 μl glutathione beads (50% slurry) into the protein mixture, and continue to mix for another 1 hr. This step is also referred to as pair-wise binding.
- During this time, prepare the HEK293 cell lysates that overexpress Flag-CFTR (wt) as described above in Step 2).
- Wash the complex twice with lysis buffer. Spin at 800 × g for 1 min for each wash and carefully aspirate the supernatant after each wash. Use caution not to suck off the beads in the bottom.
- Add the above-prepared HEK293 cell lysates to the beads, and gently mix at 4 °C for 3 hr (or overnight).
- Wash the beads extensively 3 times with lysis buffer as described in Step 3.6).
- Elute the proteins using 30 μl Sample Buffer (5×): 0.6 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 50% glycerol, 2% SDS, and 0.1% bromophenol blue; containing 5% β-mercaptoethanol.
- Incubate in 37 °C water bath for 10-15 min, and spin at 5,000 × g for 30 s to precipitate the beads.
- Load all the eluate onto 4-15% gel.
- Run SDS-PAGE for about 30-40 min.
- Transfer protein bands to the PVDF membrane, for 1.5 hr.
- Block the membrane in TBS-Tween containing 5% non fat milk.
- Incubate the membrane with primary antibody (such as anti-CFTR IgG, R1104) at 4 °C, overnight.
- Wash the membrane with TBS-Tween for 5 min, 6 times.
- Incubate the membrane with secondary antibody (such as goat anti-mouse HRP-conjugated 2nd antibody) for 45 min at 22 °C.
- Wash the membrane with TBS-Tween for 5 min, 6 times.
- Visualize the protein bands via ECL.
- Representative data are shown in Figure 1.
4. Representative Results
An example of CFTR-containing macromolecular signaling complex that was assembled in vitro is shown in Figure 1. A macromolecular complex was formed between MRP4 C-terminal 50 amino acids (MRP4-CT50), PDZK1, and full-length CFTR (Figure 1, bottom). The complex formation increased dose-dependently with increasing amounts of the intermediary protein, PDZK1 (Figure 1, bottom)18.
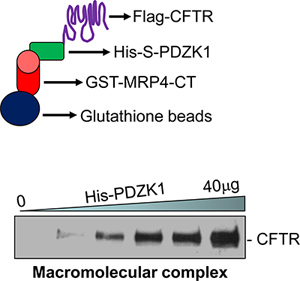
Figure 1. A pictorial representation of the macromolecular complex assay (top). A macromolecular complex was detected in vitro with three proteins (GST-MRP4-CT50, His-S-PDZK1, and Flag-CFTRwt) in a dose-dependent manner (bottom)18.
| CFTR-NHERF1-β2AR (ref.14) | CFTR-NHERF2-LPA2 (ref. 15) | CFTR-PDZ proteins-MRP2 (ref. 17) | CFTR-PDZK1-MRP4 (ref. 16) | |
| Affinity beads | Amylose resin | S-protein agarose | Amylose resin | Glutathione agarose |
| Purified protein-1 | MBP-β2AR CT | His-S-CFTR CT | MBP-CFTR CT | GST-MRP4 CT |
| Purified protein-2 | GST-NHERF1 | GST-NHERF2 | GST-PDZ proteins | His-S-PDZK1 |
| Purified protein-3 (or cell lysates) | CFTR-wt or CFTR-his10 (BHK or HEK cell lysates) | Flag-LPA2-wt or Flag-LPA2-ΔSTL (BHK cell lysates) | MRP2 (MDCK cell lysates) | Purified Flag-CFTR-wt or CFTR-his10 (or cell lysates) |
| Antibody | Anti-CFTR IgG | Anti-Flag HRP | Anti-MRP2 IgG | Anti-Flag HRP |
Table 1. Summary of various CFTR-containing macromolecular complexes assembled in vitro.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
In this protocol we demonstrated a method for in vitro assembling and detection of a CFTR containing macromolecular signaling complex using purified proteins (or protein fragments) and/or cell lysates as reported previously16-19,29,30. To achieve best results the following critical points during the preparation process require special attention:
- It is important that the pH of the elution buffer be adjusted to 8.0 after adding reduced glutathione when purifying the GST-fusion protein as d...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest declared.
Acknowledgements
Our work has been supported by grants from American Heart Association (Greater Southeast Affiliate) Beginning-grant-in-aid 0765185B, the Elsa U. Pardee Foundation research grant, and Wayne State University intramural startup fund and Cardiovascular Research Institute Isis Initiative award. This method of in vitro CFTR macromolecular complex assembly was originally pioneered by Dr. A.P. Naren (University of Tennessee Health Science Center).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| pGEX4T-1 vector | GE Healthcare | 28-9545-49 | formerly Amersham Biosciences |
| pMAL-C2 vector | New England BioLabs | ||
| pET30 vector | EMD Chemicals | 69077-3 | formerly Novagen |
| Glutathione agarose beads | BD Biosciences | 554780 | |
| Amylose resin | New England BioLabs | E8021S | |
| Talon beads | Clontech | 635501 | |
| reduced glutathione | BD Biosciences | 554782 | |
| imidazole | Fisher | BP305-50 | |
| maltose | Fisher | BP684-500 | |
| S-protein agarose | EMD Chemicals | 69704-3 | formerly Novagen |
| Anti-Flag HRP | Sigma | A8592 | |
| Anti-CFTR IgG | Custom-made | R1104 | mAb recognizing CFTR epitope at a.a. 722-734 |
| Anti-MRP2 IgG | Chemicon International | MAB4148 | Now a part of Millipore |
Table 2. Specific reagents and equipment. | |||
References
- Anderson, M. P. Demonstration that CFTR is a chloride channel by alteration of its anion selectivity. Science. 253, 202-205 (1991).
- Bear, C. E. Purification and functional reconstitution of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR. Cell. 68, 809-818 (1992).
- Quinton, P. M. Chloride impermeability in cystic fibrosis. Nature. 301, 421-422 (1983).
- Cheng, S. H. Defective intracellular transport and processing of CFTR is the molecular basis of most cystic fibrosis. Cell. 63, 827-834 (1990).
- Gabriel, S. E., Brigman, K. N., Koller, B. H., Boucher, R. C., Stutts, M. J. Cystic fibrosis heterozygote resistance to cholera toxin in the cystic fibrosis mouse model. Science. 266, 107-109 (1994).
- Li, C., Naren, A. P. CFTR chloride channel in the apical compartments: spatiotemporal coupling to its interacting partners. Integr. Biol (Camb). 2, 161-177 (2010).
- Chao, A. C. Activation of intestinal CFTR Cl- channel by heat-stable enterotoxin and guanylin via cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Embo. J. 13, 1065-1072 (1994).
- Gabriel, S. E., Clarke, L. L., Boucher, R. C., Stutts, M. J. CFTR and outward rectifying chloride channels are distinct proteins with a regulatory relationship. Nature. 363, 263-268 (1993).
- McNicholas, C. M. Sensitivity of a renal K+ channel (ROMK2) to the inhibitory sulfonylurea compound glibenclamide is enhanced by coexpression with the ATP-binding cassette transporter cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 93, 8083-8088 (1996).
- Schreiber, R., Nitschke, R., Greger, R., Kunzelmann, K. The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator activates aquaporin 3 in airway epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 11811-11816 (1999).
- Shumaker, H., Amlal, H., Frizzell, R., Ulrich, C. D. 2nd, Soleimani, M. CFTR drives Na+-nHCO-3 cotransport in pancreatic duct cells: a basis for defective HCO-3 secretion in CF. Am. J. Physiol. 276, 16-25 (1999).
- Ahn, W. Regulatory interaction between the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and HCO3- salvage mechanisms in model systems and the mouse pancreatic duct. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 17236-17243 (2001).
- Sugita, M., Yue, Y., Foskett, J. K. CFTR Cl- channel and CFTR-associated ATP channel: distinct pores regulated by common gates. Embo. J. 17, 898-908 (1998).
- Naren, A. P. Regulation of CFTR chloride channels by syntaxin and Munc18 isoforms. Nature. 390, 302-305 (1997).
- Naren, A. P. Syntaxin 1A is expressed in airway epithelial cells, where it modulates CFTR Cl(-) currents. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 377-386 (2000).
- Naren, A. P. A macromolecular complex of beta 2 adrenergic receptor, CFTR, and ezrin/radixin/moesin-binding phosphoprotein 50 is regulated by PKA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100, 342-346 (1073).
- Li, C. Lysophosphatidic acid inhibits cholera toxin-induced secretory diarrhea through CFTR-dependent protein interactions. J. Exp. Med. 202, 975-986 (2005).
- Li, C. Spatiotemporal coupling of cAMP transporter to CFTR chloride channel function in the gut epithelia. Cell. 131, 940-951 (2007).
- Li, C., Schuetz, J. D., Naren, A. P. Tobacco carcinogen NNK transporter MRP2 regulates CFTR function in lung epithelia: implications for lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 292, 246-253 (2010).
- Hall, R. A. A C-terminal motif found in the beta2-adrenergic receptor, P2Y1 receptor and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator determines binding to the Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor family of PDZ proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 8496-8501 (1998).
- Short, D. B. An apical PDZ protein anchors the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator to the cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 19797-19801 (1998).
- Wang, S., Yue, H., Derin, R. B., Guggino, W. B., Li, M. Accessory protein facilitated CFTR-CFTR interaction, a molecular mechanism to potentiate the chloride channel activity. Cell. 103, 169-179 (2000).
- Sun, F. E3KARP mediates the association of ezrin and protein kinase A with the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in airway cells. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 29539-29546 (2000).
- Cheng, J. A Golgi-associated PDZ domain protein modulates cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator plasma membrane expression. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 3520-3529 (1074).
- Scott, R. O., Thelin, W. R., Milgram, S. L. A novel PDZ protein regulates the activity of guanylyl cyclase C, the heat-stable enterotoxin receptor. The Journal of biological chemistry. 277, 22934-22941 (1074).
- Lee, J. H. Dynamic regulation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator by competitive interactions of molecular adaptors. The Journal of biological chemistry. 282, 10414-10422 (2007).
- Gee, H. Y., Noh, S. H., Tang, B. L., Kim, K. H., Lee, M. G. Rescue of DeltaF508-CFTR trafficking via a GRASP-dependent unconventional secretion pathway. Cell. 146, 746-760 (2011).
- Naren, A. P. Methods for the study of intermolecular and intramolecular interactions regulating CFTR function. Met. Molecul. Med. 70, 175-186 (2002).
- Li, C., Roy, K., Dandridge, K., Naren, A. P. Molecular assembly of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in plasma membrane. The Journal of biological chemistry. 279, 24673-24684 (2004).
- Li, C., Naren, A. P. Analysis of CFTR Interactome in the Macromolecular Complexes. Met. Molecul. Med. 741, 255-270 (2011).
- Wu, Y. A chemokine receptor CXCR2 macromolecular complex regulates neutrophil functions in inflammatory diseases. J. Biol. Chem. , (2011).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved