A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Stereotactic Injection of MicroRNA-expressing Lentiviruses to the Mouse Hippocampus CA1 Region and Assessment of the Behavioral Outcome
In This Article
Summary
MicroRNAs have significant roles in brain structure and function. Here we describe a method to enforce hippocampal miRNA over-expression using stereotactic injection of an engineered miRNA-expressing lentivirus. This approach can serve as a relatively rapid way to assess the in vivo effects of over-expressed miRNAs in specific brain regions.
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small regulatory single-stranded RNA molecules around 22 nucleotides long that may each target numerous mRNA transcripts and dim an entire gene expression pathway by inducing destruction and/or inhibiting translation of these targets. Several miRNAs play key roles in maintaining neuronal structure and function and in higher-level brain functions, and methods are sought for manipulating their levels for exploring these functions. Here, we present a direct in vivo method for examining the cognitive consequences of enforced miRNAs excess in mice by stereotactic injection of miRNA-encoding virus particles. Specifically, the current protocol involves injection into the hippocampal CA1 region, which contributes to mammalian memory consolidation, learning, and stress responses, and offers a convenient injection site. The coordinates are measured according to the mouse bregma and virus perfusion is digitally controlled and kept very slow. After injection, the surgery wound is sealed and the animals recover. Lentiviruses encoding silencers of the corresponding mRNA targets serve to implicate the specific miRNA/target interaction responsible for the observed effect, with naïve mice, mice injected with saline and mice injected with "empty" lentivirus vectors as controls. One month post-injection, the animals are examined in the Morris Water Maze (MWM) for assessing their navigation learning and memory abilities. The MWM is a round tank filled with colored water with a small platform submerged 1 cm below the water surface. Steady visual cues around the tank allow for spatial navigation (sound and the earth's magnetic field may also assist the animals in navigating). Video camera monitoring enables measuring the route of swim and the time to find and amount the platform. The mouse is first taught that mounting the hidden platform offers an escape from the enforced swimming; it is then tested for using this escape and finally, the platform is removed and probe tests examine if the mouse remembers its previous location. Repeated tests over several consecutive days highlight improved performance of tested mice at shorter latencies to find and mount the platform, and as more direct routes to reach the platform or its location. Failure to show such improvement represents impaired learning and memory and/or anxiety, which may then be tested specifically (e.g. in the elevated plus maze). This approach enables validation of specific miRNAs and target transcripts in the studied cognitive and/or stress-related processes.
Introduction
The role of particular miRNAs in nervous system functioning has recently been challenged by lentiviral injection in several studies. MiRNAs have been found to be crucial for maintaining and re-shaping synapse structure 1, synaptogenesis 2 and synapse remodeling and maintenance 3. These studies strongly suggest that miRNAs are engaged, via multileveled regulatory effects in both the shaping up and in maintaining the main output of the nervous system, cognitive function. Stereotactic injection of lentivirus particles into specific regions in the rodent brain enables searching for alterations in synapse morphology and neuronal activity, and was used for establishing the functional significance of over-expressed transcripts 4,5. Direct infection of neurons at well-defined brain areas with miRNA-expressing lentiviruses may be implicated in studies of aging, brain disorders and neurodegeneration; Studies of miRNAs in the realm of behavioral regulation 6-8 are at a far less advanced state, and stereotactic injection of miRNA-expressing lentivirus particles followed by behavioral tests may be useful for such purposes. A considerably more laborious method for inducing over- or under-expression involves genetically engineered knock-in or knockout mice. Genetic systems can further allow for conditional and temporal control on expression (e.g. Cre-Lox, Tet systems), but these hardly offer the spatial specificity of the injection procedure and there is almost always a certain amount of leakiness. Also, the engineering procedures do not require surgery and can be used across laboratories with relatively good reproducibility; however, they are slower and require much more manpower and financial resources. In addition, the temporal control of the over- or under-expression in injected mice is far more accurate compared to genetically engineered mice.
Protocol
1. Lentivirus Preparation
- Grow HEK-293FT cells to 90% confluence.
- On the day of transfection change cell medium to serum-free DMEM supplemented with 1 mM glutamine and 50 mg/ml penicillin-streptomycin.
- Co-transfect the cells with a pLKO.1-Puro vector and with plasmids coding for the delta R8.2 and VSV-G moieties and the miRNA of interest, using 10 μl of 1 mg/ml polyethylenimine as a carrier 9.
- Collect packaged lentiviruses at 24 hr and 48 hr post-transfection, filter through 0.45 μm filter.
- Concentrate the lentiviruses using ultracentrifugation in 70,000 x g, for 2 hr and 15 °C, aliquot and store at -70 °C.
- Measure virus titer by infecting HEK-293T cells with serially diluted virus preparations (1 to 10-6 ml of vector per well). The resulting titer (a minimum of ~1×109 infectious particles per ml is recommended) is evaluated for expression of the gene of interest, using puromycin selection and by quantifying GFP expressing viruses through counting fluorescent cells.
For more detailed protocol of lentivirus preparation see 10.
2. Preparing Animals for Surgery
- Surgeons garb should include surgical gown, sterile gloves, cap and mask.
- Weigh the animal, then anesthetize it with an IP-injection of a Ketamine mixture, with the volume proportional to the animal weight as specified for each drug. For a Ketamine/Xylazine mixture, a dose range of 80-200 mg/kg Ketamine and 7-20 mg/kg Xylazine is usually used for mice.
- Wait until the animal is fully anesthetized, then check for lack of withdrawal reflex in the hind limb of the animal by extending the limb and then pressing it with your finger.
- Inject the animal subcutaneously with Rimadyl, as specified on the box, for pain relief. Typical dose range for Rymadil is 5-10 mg.
- Place the animal on a heating pad to keep a steady body temperature and moisten the eyes with ointment.
- Shave the area between the two ears with a trimming machine.
- Sanitize the skin with betadine.
3. Exposure of the Skull and Drilling
- Place the animal inside the stereotact by adjusting the rods into the crevices just anterior to the animal's ears.
- Use a scalpel to make an anterior-posterior incision of about 1.5 cm between the ears and keep it open with surgery clamps (serfines).
- Clean the surface of the skull with a cotton swab until the intersection between the coronal suture and sagittal sutures; i.e. the bregma and the intersection between the coronal and lambdoid sutures; i.e. lambda, are visible.
- Point the tip of the syringe, held by the stereotact, to the bregma point, at all three axes. Write down the coordinates. This point would be considered as the zero point in all three axes.
- Lift the syringe in the vertical axis so that a planar movement would not scratch the skull and move the syringe head to the correct location. Hippocampal CA1 injections require the following coordinates relative to the bregma in mm: -2 at the anterior/posterior axis, ±1.8 at the lateral/medial axis and -1.5 at the dorsal/ventral axis.
- Lower the tip of the syringe until it touches the skull and mark the spot with a marker. Remove the syringe back to avoid stabbing.
- Drill a shallow hole, only in the skull bone using a fine driller. Hold the driller steady so it would not continue to drill into the soft tissue underneath. You can prevent this by steadying one hand with the other and by drilling in short pulses.
4. Injection of the Lentivirus
- Withdraw 0.5 ml of the concentrated lentivirus solution.
- Place the syringe above the hole and slowly lower it vertically until it reaches the surface of the skull. Continue to lower the syringe into the brain very slowly. At this step some bleeding might occur which does not necessarily indicate a failed penetration. If bleeding occurs mop it up with a cotton swab.
- Set the digital pump to 0.02 ml/min (0.5 μl would be injected in 25 min) and start infusion. Slow infusion allows for effective spreading of the virus into the tissue and prevents back flow. In some syringe types consider inserting the syringe for an extra depth of 0.5 mm before retreating to original coordinates and infusing.
- After infusion is completed wait for additional 5 min to allow the material to spread into the brain instead of retreating back into the canal formed by the syringe.
- Remove the syringe very slowly and watch for back flows. If a back flow is observed at this step, a fraction of the injected material was probably lost.
5. Wound Sealing and Recovery
- Seal the wound with histoacryl. Be sure to avoid leaking of the histoacryl into the eyes.
- Inject the animal intraperitoneally (IP) with 1 ml pre-heated saline, to avoid dehydration.
- Place the animal in a recovery cage that is positioned on a heated pad. Watch the animal while it recovers for an additional hour.
In case of weight loss, inappetance, weakness/inability to obtain feed or water, moribund state or infection, euthanasia of the animal should be performed. Acceptable methods for euthanasia of rodents are barbiturates, inhalant anesthetics, CO2, CO, or potassium chloride in conjunction with general anesthesia.
After 4 to 6 weeks, assess the animal's navigation memory is assessed in the Morris Water Maze. The lentivirus will usually infect most cells within the injection sphere.
6. Behavioral Assessment in the Morris Water Maze
- Train the animals in the Morris Water Maze. For exact training and testing protocol see 11. After each trial, dry the animal with a dry towel, replace it in its cage and refresh the water in the tank.
- Test the animals in the Morris Water Maze for 3 consecutive days, 4 trials each day. Each day insert the animal into the maze in each of the 4 directions of the maze (north, south, east and west) in a changing order, for example day one: east-west-north-south, day two: west-south-north-east. Wipe the animals after each trial.
- During the test trials track the animal with a tracking system such as the Noldus tracking system.
- After the 12th test trial, insert the animal into the water tank without the platform for one minute. This would be used to analyze the searching strategy the animal is taking.
- Analyze the data as suggested in 12.
Results
Injection of 0.5 μl lentivirus into the CA1 region in the mouse hippocampus, with the flow rate indicated in the protocol section yields an infected sphere of about 1 mm in the rostral-caudal axis, and about 0.5 mm in the medial-lateral and the anterior-posterior axes (Figure 3).
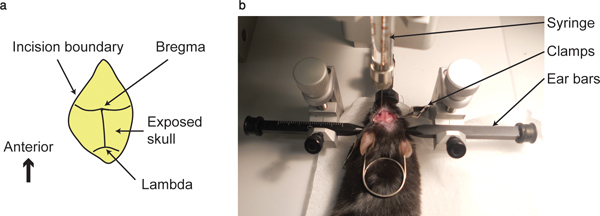
Figure 1. Bregma point and injection apparatus. (a)...
Discussion
Stereotactic injection of a lentivirus is a relatively rapid method for in vivo assessment for both up- or down- regulation of different genes and miRNAs. The main alternative is a genetically engineered mouse which is a much more laborious and time consuming technique then direct lentivirus injection. In addition, the up regulation, in lentivirus injection, occurs at a specific time in the adult mouse and does not include any possibility of leakiness during development, as is most often the case in the genetica...
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Acknowledgements
This study has been supported by the Edmond and Lily Safra Center for Brain Sciences (SB fellowship), The Legacy Heritage Biomedical Science Partnership Program of the Israel Science Foundation (Grant No. 378/11, to HS) and the German Israeli Foundation for Scientific Research and Development (G.I.F) (Grant No. 1093-32.2/2010, to HS).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Equipment | |||
| Rodent weigh scale | Burtons (UK) | 115-455 | |
| heating pad | FIRstTechnology | DCT-25 | |
| trimming machine | Stoelting | 51465 | |
| stereotact | Stoelting | 51730 | |
| Scalpel and blades | Kent scientific | INS500348 | |
| Harland syringe | Hamilton | 7632-01 | |
| driller | Stoelting | 51449 | |
| digital pump | Harvard apparatus | 704507 | |
| Water tank and platform | Stoelting | 60135 | |
| Reagents | |||
| ketamine | Vetoquinol(Lure France) | 3055503 | |
| domitor | Orion pharma | 107140-10 | |
| Rimadyl | Pfizer animal health | 24751 | |
| moisture ointment - Synthomycine 5% | Rekah Pharmaceutical | 195 | |
| histoacryl | Braun | 112101 | |
| saline | Sigma Aldrich | D8662 | |
References
- Siegel, G., et al. A functional screen implicates microRNA-138-dependent regulation of the depalmitoylation enzyme APT1 in dendritic spine morphogenesis. Nature Cell Biology. 11, 705-716 (2009).
- Jin, P., et al. Biochemical and genetic interaction between the fragile X mental retardation protein and the microRNA pathway. Nature Neuroscience. 7, 113-117 (2004).
- Simon, D. J. The microRNA miR-1 regulates a MEF-2-dependent retrograde signal at neuromuscular junctions. Cell. 133, 903-915 (2008).
- Consiglio, A. In vivo gene therapy of metachromatic leukodystrophy by lentiviral vectors: correction of neuropathology and protection against learning impairments in affected mice. Nature Medicine. 7, 310-316 (2001).
- Jakobsson, J., Lundberg, C. Lentiviral vectors for use in the central nervous system. Molecular Therapy: The Journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy. 13, 484-493 (2006).
- Berson, A. Cholinergic-associated loss of hnRNP-A/B in Alzheimer's disease impairs cortical splicing and cognitive function in mice. EMBO Molecular Medicine. , (2012).
- Haramati, S. MicroRNA as repressors of stress-induced anxiety: the case of amygdalar miR-34. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 31, 14191-14203 (2011).
- Shaltiel, G., et al. Hippocampal microRNA-132 mediates stress-inducible cognitive deficits through its acetylcholinesterase target. Brain Structure & Function. , 10-1007 (2012).
- Boussif, O., et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 92, 7297-7301 (1995).
- Mendenhall, A., Lesnik, J., Mukherjee, C., Antes, T., Sengupta, R. Packaging HIV- or FIV-based lentivector expression constructs & transduction of VSV-G pseudotyped viral particles. J. Vis. Exp. (62), e3171 (2012).
- Nunez, J. Morris Water Maze Experiment. J. Vis. Exp. (19), e897 (2008).
- Bromley-Brits, K., Deng, Y., Song, W. Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease model mice. J. Vis. Exp. (53), e2920 (2011).
- Regev, L., Ezrielev, E., Gershon, E., Gil, S., Chen, A. Genetic approach for intracerebroventricular delivery. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107, 4424-4429 (2010).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved