A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Dissection and Flat-mounting of the Threespine Stickleback Branchial Skeleton
In This Article
Summary
The branchial skeleton, including gill rakers, pharyngeal teeth, and branchial bones, serves as the primary site of food processing in most fish. Here we describe a protocol to dissect and flat-mount this internal skeleton in threespine sticklebacks. This method is also applicable to a variety of other fish species.
Abstract
The posterior pharyngeal segments of the vertebrate head give rise to the branchial skeleton, the primary site of food processing in fish. The morphology of the fish branchial skeleton is matched to a species' diet. Threespine stickleback fish (Gasterosteus aculeatus) have emerged as a model system to study the genetic and developmental basis of evolved differences in a variety of traits. Marine populations of sticklebacks have repeatedly colonized countless new freshwater lakes and creeks. Adaptation to the new diet in these freshwater environments likely underlies a series of craniofacial changes that have evolved repeatedly in independently derived freshwater populations. These include three major patterning changes to the branchial skeleton: reductions in the number and length of gill raker bones, increases in pharyngeal tooth number, and increased branchial bone lengths. Here we describe a detailed protocol to dissect and flat-mount the internal branchial skeleton in threespine stickleback fish. Dissection of the entire three-dimensional branchial skeleton and mounting it flat into a largely two-dimensional prep allows for the easy visualization and quantification of branchial skeleton morphology. This dissection method is inexpensive, fast, relatively easy, and applicable to a wide variety of fish species. In sticklebacks, this efficient method allows the quantification of skeletal morphology in genetic crosses to map genomic regions controlling craniofacial patterning.
Introduction
An incredible amount of diversity exists in the head skeleton among vertebrates, especially among fishes. In many cases this diversity facilitates different feeding strategies1-4, and can involve major changes to both external and internal craniofacial patterning. The branchial skeleton is located internally in the throat of a fish and surrounds most of the buccal cavity. The branchial skeleton is comprised of 5 serially homologous segments, the anterior four of which support the gills. Together these five segments function as an interface between fish and their food5. Variation in a multitude of traits including gill rakers, pharyngeal teeth, and branchial bones contribute to efficient foraging on different types of food.
Sticklebacks have undergone an adaptive radiation after ancestral oceanic forms colonized freshwater lakes and creeks throughout the northern hemisphere. The shift in diet from small zooplankton in the ocean to larger prey in freshwater has resulted in dramatic trophic variation in several craniofacial traits6. While many studies have focused on external craniofacial differences in sticklebacks7-13, important craniofacial changes evolve repeatedly in the internal branchial skeleton. The ability to create fertile hybrids between morphologically distinct stickleback populations provides an excellent opportunity to map the genetic basis of evolved changes to the branchial skeleton.
One trophic trait of ecological significance is the patterning of gill rakers, periodic dermal bones that line the anterior and posterior faces of the branchial bones and are used to filter prey items. Fish that typically feed on small prey items tend to have longer and more densely spaced gill rakers compared to fish that feed on larger prey14,15. Variation in gill rakers has been reported both within and between species14-19, and aspects of gill raker patterning contribute to trophic niches and fitness16. Decades of research have extensively documented gill raker number and length variation in threespine sticklebacks17-21; however, these studies typically focus on the first row of gill rakers. Recent work has shown modularity in the genetic control of gill raker number across the branchial skeleton22,23 and across a single row in gill raker spacing23 and length24 highlighting the importance of studying more than row one or a single gill raker to understand the developmental genetic basis of gill raker reduction.
A second trophic trait of both ecological and biomedical significance is the patterning of pharyngeal teeth. Teeth in fishes can be located in both the oral jaw and in the branchial skeleton, known as pharyngeal teeth. Oral teeth are used primarily for prey capture while pharyngeal teeth are used for mastication and prey manipulation25-27. Both sets form via shared developmental mechanisms and are considered developmentally homologous28. Interesting modularity occurs whereby some species, such as zebrafish, lack oral and dorsal pharyngeal teeth29 while other species have multiple toothed ceratobranchials, pharyngobranchials, and sometimes toothed basihyal and hypobranchials30. In sticklebacks, pharyngeal teeth are found ventrally on the fifth ceratobranchial and dorsally on the anterior and posterior pharyngobranchials31. Kinematics on stickleback feeding show the oral jaw is used primarily for prey capture and facilitating suction feeding9 leaving mastication to the pharyngeal jaw. In cichlids, lower pharyngeal jaw morphology varies dramatically32,33 and has been shown to be adaptive and correlated with trophic niche34. Multiple freshwater stickleback populations have evolved dramatic increases in ventral pharyngeal tooth number23,35,36. Recent work has demonstrated that the developmental genetic basis of this evolved tooth gain is largely distinct in two independently derived populations of freshwater sticklebacks36. Unlike mammalian teeth, fish regenerate their teeth continuously throughout adult life37. Both of these previously described high toothed freshwater populations have evolved an accelerated tooth replacement rate, providing a rare vertebrate system to study the genetic basis of regeneration36.
A third trophic trait that has evolved repeatedly in freshwater sticklebacks is longer epibranchial and ceratobranchial bones, the branchial arch segmental homologs of the upper and lower jaw, respectively38. Longer branchial bones confer a larger buccal cavity and likely are adaptive for allowing larger prey items to be consumed. Furthermore, in other fish, epibranchial bones are important for depression of the dorsal pharyngeal tooth plates25. Like gill rakers and pharyngeal teeth, the branchial bones are internal and thus, difficult to easily visualize or quantify.
Here we present a detailed protocol to dissect and flat-mount the branchial skeleton, allowing easy visualization and quantification of a variety of important craniofacial traits. While this protocol describes a stickleback dissection, this same method works on a variety of other fishes.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
All fish work was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of California-Berkeley (protocol number R330). Euthanasia was performed using immersion in 0.025% Tricaine-S buffered with 0.1% sodium bicarbonate39. All steps are performed at room temperature.
1. Preparation
Note: Perform steps 1.1-1.5 in conical tubes or scintillation vials that can seal tightly and be laid horizontally. Fish do not need to be constantly shaken, but try to mix the solution as often as possible by gently inverting or shaking the rack of tubes or vials to expose all sides of the fish to the staining solution and allow stain to penetrate the tissue evenly. Do not place a large batch of fish on a platform shaker, as the heavy weight of the liquid will break the shaker.
- Fix either freshly euthanized fish or fish stored in ethanol with 10% Neutral Buffered Formalin (NBF) overnight. Alternatively, use 4% paraformaldehyde in 1x PBS solution instead of 10% NBF.
Note: If extracting DNA, clip a small portion of the caudal or pectoral fins prior to fixation and store in ethanol. - Dispose of fix properly in a chemical hood and replace with tap water (that is ~pH 7.0) for 2 hr. Avoid using de-ionized water as it can often be acidic and can decalcify bone.
- Remove water and stain fish with 0.008% Alizarin Red S in 1% KOH in water for 24 hr. For fish less than 20 mm standard length, use 0.004% Alizarin Red S. (Make a 100x (0.8%) stock solution of Alizarin Red S which can then be diluted).
- Remove stain (putting in appropriate waste container in hood) and place fish in tap water for a few hr. Change water as needed until water rinse is mostly clear.
- Remove water and place fish into 50% glycerol, 0.25% KOH for mild clearing and subsequent dissection.
Note: This staining protocol is modified from previously described methods40,41.
2. Dissection
Note: See Figure 1 for a review of relevant head skeletal morphology.

Figure 1: Stickleback head skeletal morphology. Alizarin Red stained threespine stickleback head imaged with fluorescence under a rhodamine B filter set. Useful morphology is labeled: Op = opercle, Subop = subopercle, BSRs = branchiostegal rays, Preop = preopercle, Infraorb 1-3 = infraorbital 1-3 (also called circumorbitals or suborbitals), Dent = dentary, Premax = premaxilla, Max = maxilla, Nas = nasal, Lat. ethm = lateral ethmoid, Psph = parasphenoid, Fron = frontal bone. For a more detailed description of the stickleback head skeleton, see Anker (1974)31. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Lay the fish flat (Figure 2A) and insert sharp #5 watchmaker's forceps into the side of the eye at a ~45° angle to puncture the membrane covering the eye.
- Peel the membrane away from the eye, similar to peeling a yogurt lid (Figure 2B).
- Insert open forceps behind the eye, grab hold of the optic nerve behind the eye, and remove the eye (Figure 2C). Do not puncture the eye as it will leak melanin. If punctured, melanin can be washed away during later steps.
- Repeat on other side.
- Starting from the posterior, place one small dissecting scissor blade under the opercle flap, drag scissor blade dorsally above opercle, then cut soft tissue through to the eye socket (Figure 2D). Cut dorsal to the opercle bone.
- Cut the frontal bone (dorsal to the eye socket) (Figure 2E).
- Cut the midline parasphenoid bone around the center of the eye sockets (Figure 2F).
- Repeat opercle cut on the opposing side.
- Insert forceps under the opercle and slowly peel the face away from the body, trimming any soft tissue still attached (Figure 2G-H). Take care not to disrupt the first row of gill rakers.
- With forceps, detach the ceratohyals on both sides from the midline basihyal while peeling away and removing the anterior craniofacial skeleton (the entire jaw including the dentary, premaxilla, and maxilla; the entire hyoid skeleton including the exterior dermal opercle, preopercle, subopercle, and branchiostegal rays and the underlying dorsal and ventral endochondral elements; and the anterior part of the skull including the nasal, lateral ethmoid, and infraorbital bones, see Figures 1 and 2I).
- Pelvic spines can be folded out from the body, and can serve as a handle for forceps to grab hold of when present. Spines lock into place. To unlock, gently pull spine with forceps directly away from fish body, then gently bend posteriorly to press spine flat against fish.
- Insert closed forceps posterior and ventral to the branchial skeleton (just below gut tube) and drag forceps anteriorly, teasing apart the remaining muscles and ligaments attached to the branchial skeleton (Figure 2J-K).
- Using the tips of closed forceps, scrape away the muscles attaching the dorsal branchial skeleton to the ventral braincase in a posterior to anterior direction (Figure 2L).
- Repeat 2.9 and 2.10 on the opposing side.
- Grasp the base of the gut tube and pull anteriorly to remove the branchial skeleton and gut tube (Figure 2M-N).
- Separate the gut tube by making a perpendicular cut posterior to the end of the fifth ceratobranchial (Figure 2O).
- After removing any remaining bone fragments from the braincase on the dorsal side of the branchial skeleton, insert scissors into the branchial basket to make a dorsal cut (cutting anterior to posterior) between the bilateral sets of dorsal tooth plates (Figure 3A-D). Ensure cut is centered to avoid damaging the dorsal tooth plates.
- Make two shallow lateral cuts in the rubbery gut lumen at the posterior end of the branchial skeleton (anterior end of gut tube) to assist with opening the branchial skeleton (Figure 3E).
- Place fish and all tissue pieces into a jar and place the branchial skeleton into a microcentrifuge tube with 50% glycerol, 0.25% KOH to continue gentle clearing, or 100% glycerol if no further clearing is required. Label jars and tubes with a unique identifier so they can be tracked. The amount of clearing required is largely a function of the size of the fish, large adult fish (over 40 mm in standard length) typically require additional clearing.
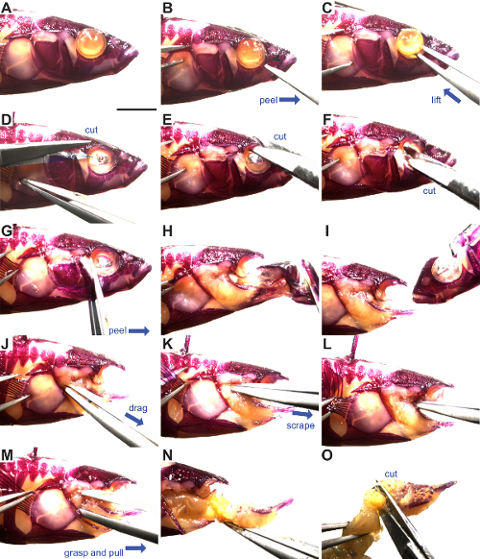
Figure 2: Stickleback branchial skeleton dissection. Alizarin Red stained threespine stickleback fish ready for dissection. The eye is depigmented from extensive clearing. Blue arrows indicate the direction of motion. (A) Lateral view of stickleback head, anterior is to the right. (B) Removal of membrane covering the eye. (C) Removal of the eye. (D) Dorsal cut above the opercle. (E) Frontal bone cut. (F) Parasphenoid cut. (G-I) Removal of the facial skeleton. (J) Removal of ventral branchial skeleton soft tissue connections. (K-L) Removal of dorsal branchial skeleton connections. (M-N) Removal of the branchial skeleton. (O) Separate the gut tube from the branchial skeleton. See steps 2.1 through 2.16 for more details. Scale bar = 5 mm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Branchial Skeleton Re-staining (If Necessary)
- To stain the branchial skeleton darker or clear tissue more, remove 50% glycerol, 0.25% KOH solution and wash with 1% KOH twice (one five minute wash followed by a second 24 hr wash while shaking horizontally on a platform shaker).
- Remove 1% KOH and re-stain with 0.008% Alizarin Red S in 1% KOH for 24 hr.
- Remove stain and replace with 1% KOH for 24 hr.
- Remove KOH solution and replace with 50% glycerol, 0.25% KOH.
4. Mounting Branchial Skeleton
- Remove branchial skeleton from 50% glycerol, 0.25% KOH or 100% glycerol and place near the bottom of a 22 mm x 60 mm glass cover slip with the dorsal side facing up (Figure 3F). Add a few drops of 50% glycerol, 0.25% KOH or 100% glycerol on top of branchial skeleton. If transitioning from 50% glycerol, 0.25% KOH to 100% glycerol, change solution in a microcentrifuge tube and shake for >5 min prior to mounting to equilibrate tissue.
- Roll out two small balls of modeling clay and place on either end of the cover slip to act as spacers.
- Loosely place a second coverslip on top with enough pressure to flatten the anterior branchial skeleton (Figure 3G).
- Peel open the left dorsal flap including dorsal tooth plates, flatten, and slide between the coverslips (Figure 3H).
- Repeat technique with right dorsal flap and push entire branchial skeleton away from the edge of the coverslip (Figure 3I).
- Alternatively, hold both dorsal flaps open with forceps and carefully place the coverslip on, flattening the branchial skeleton in one smooth motion.
- Alternatively, mount the branchial skeleton upside-down on one cover slip, splaying each dorsal side out laterally so gravity does not allow the branchial skeleton to close back up. Then cover with second 22 mm x 60 mm glass cover slip and invert prep.
Note: Different mounting techniques tend to work better or worse for each individual. Try each and see what feels most comfortable.
- Lightly press on top coverslip to flatten clay balls enough to keep the branchial skeleton mounted flat, but take care not to crush the specimen.
- During the mounting process, ceratobranchials may rotate and obscure a row of rakers. Remedy this by sliding forceps between the coverslips and re-orienting the ceratobranchials or entire branchial skeleton.
- Store preps flat in slide trays at room temperature. Mounted in 100% glycerol, preps can be stored between bridged coverslips for at least a decade. Clean forceps and scissors with isopropanol or ethanol and cover tips.
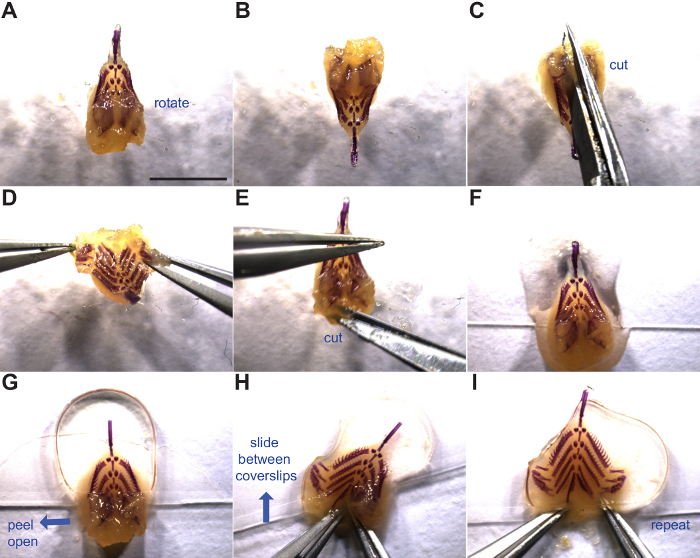
Figure 3: Flat mounting the branchial skeleton. Manipulation and mounting of the branchial skeleton is shown. Blue arrows indicate the direction of motion. (A) Branchial skeleton dorsal side up. (B-D) Rotation and incision between the dorsal tooth plates. (E) Lateral cut in soft tissue to further open the base of the gut tube. (F) Branchial skeleton placed at the bottom of a coverslip ready for mounting. (G) Second coverslip placed on the anterior half of the branchial skeleton (above dorsal tooth plates). (H-I) Flat mounting of the branchial skeleton by opening dorsal tooth plate flaps and sliding between two cover slips. See steps 4.1 through 4.6 for more details. Scale bar = 5 mm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
This protocol results in a dissected and flat mounted branchial skeleton (Figure 4) where a variety of important trophic traits can be quantified. From a dorsal view, all rows of gill rakers, all pharyngeal tooth plates, and nearly all branchial bones can be easily visualized and quantified22-24,35,36,38,42. Alizarin Red S also fluoresces on a rhodamine or similar red filter allowing double labeling with other markers (e.g., trans...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
The branchial skeleton is a complex set of bones in the throat of a fish that manipulates, filters, and masticates food items on their way to the esophagus. Many interesting trophic traits including the patterning of gill rakers, pharyngeal teeth, and branchial bones vary across and within species. The majority of these traits are difficult to near impossible to accurately measure with the branchial skeleton in situ (e.g., gill raker length, branchial bone length). This flat-mounting protocol places all...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by NIH R01 #DE021475 to CTM and an NSF Graduate Research Fellowship to NAE. Thanks to Miles Johnson for assistance with imaging and Priscilla Erickson for critical reading of the manuscript.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) | EMD | PX1480-1 | |
| Glycerol | Sigma-Aldrich | G7893-4L | |
| 10% Neutral Buffered Formalin (NBF) | Azer Scientific | NBF-4-G | |
| Alizarin Red S | EMD | AX0485-3 | |
| Microscope Cover Glasses 22 mm x 60 mm | VWR | 16004-350 | |
| 100 mm x 10 mm Glass Petri Dish | Kimble Chase | 23064-10010 | To dissect samples on |
| Sylgard 184 Silicone Elastomer Kit | Ellsworth Adhesives | 184 SIL ELAST KIT 0.5KG | Can be poured into glass or plastic Petri dishes to make dissecting plates |
| Modeling Clay | Sargent Art | 22-4000 | 1 lb cream |
| Scintillation Vials (case of 500) | Wheaton | 986586 | Borosilicate Glass with Screw Cap |
| Forceps-Dumont #5 Inox (Biologie tip) | FST | 11252-20 | Dumostars are an alternative |
| Dissecting Scissors | FST | 15003-08 | Alternate sizes are available depending on size of sample |
| Dissecting Microscope | Leica | S6E with KL300 LED | Many other models work nicely, having a flat base helps |
| Microcentrifuge Tubes 1.7 ml | Denville | C2170 | |
| Cardboard slide tray | Fisher | 12-587-10 |
References
- Cooper, W. J., Westneat, M. W. Form and function of damselfish skulls: rapid and repeated evolution into a limited number of trophic niches. BMC Evol. Biol. 9 (24), (2009).
- Albertson, R. C., Kocher, T. D. Genetic and developmental basis of cichlid trophic diversity. Heredity. 97 (3), 211-221 (2006).
- Martin, C. H., Wainwright, P. C. Trophic novelty is linked to exceptional rates of morphological diversification in two adaptive radiations of cyprinodon pupfish. Evolution. 65 (8), 2197-2212 (2011).
- Wainwright, P. C., et al. The evolution of pharyngognathy: A phylogenetic and functional appraisal of the pharyngeal jaw key innovation in labroid fishes and beyond. Syst. Biol. 61 (6), 1001-1027 (2012).
- Sibbing, F. Food capture and oral processing. Cyprinid Fishes. , 377-412 (1991).
- Bell, M., Foster, S. The Evolutionary Biology of the Threespine Stickleback. , Oxford University Press. New York. (1994).
- Kimmel, C. B., et al. Evolution and development of facial bone morphology in threespine sticklebacks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102 (16), 5791-5796 (2005).
- Mcgee, M. D., Wainwright, P. C. Convergent evolution as a generator of phenotypic diversity in threespine stickleback. Evolution. 67 (4), 1204-1208 (2013).
- McGee, M. D., Schluter, D., Wainwright, P. C. Functional basis of ecological divergence in sympatric stickleback. BMC Evol. Biol. 13, 277(2013).
- McGuigan, K., Nishimura, N., Currey, M., Hurwit, D., Cresko, W. A. Quantitative genetic variation in static allometry in the threespine stickleback. Integr. Comp. Biol. 50 (6), 1067-1080 (2010).
- Caldecutt, W. J., Bell, M. A., Buckland-Nicks, J. A. Sexual dimorphism and geographic variation in dentition of threespine stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus. Copeia. 2001 (4), 936-944 (2001).
- Berner, D., Moser, D., Roesti, M., Buescher, H., Salzburger, W. Genetic architecture of skeletal evolution in european lake and stream stickleback. Evolution. 68 (6), 1792-1805 (2014).
- Jamniczky, H. a, Barry, T. N., Rogers, S. M. Eco-evo-devo in the study of adaptive divergence: examples from threespine stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Integr. Comp. Biol. 55 (1), 166-178 (2015).
- Magnuson, J., Heitz, J. Gill raker apparatus and food selectivity among mackerels, tunas, and dolphins. Fish. Bull. 69 (2), 361-370 (1971).
- Kahilainen, K. K., et al. The role of gill raker number variability in adaptive radiation of coregonid fish. Evol. Ecol. 25 (3), 573-588 (2011).
- Arnegard, M. E., et al. Genetics of ecological divergence during speciation. Nature. 511 (7509), 307-311 (2014).
- Gross, H. P., Anderson, J. M., Gross, H. P., Anderson, J. Geographic variation in the gillrakers and diet of European threespine sticklebacks, Gasterosteus aculeatus. Copeia. 1984 (1), 87-97 (1984).
- Hagen, D., Gilbertson, L. Geographic variation and environmental selection in Gasterosteus aculeatus L in the Pacific Northwest, America. Evolution. 26 (1), 32-51 (1972).
- McPhail, J. D. Ecology and evolution of sympatric sticklebacks (Gasterosteus): morphological and genetic evidence for a species pair in Enos Lake, British Columbia. Can. J. Zool. 62 (7), 1402-1408 (1984).
- Schluter, D., McPhail, J. D. Ecological character displacement and speciation in sticklebacks. Am. Nat. 140 (1), 85-108 (1992).
- Robinson, B. Trade offs in Habitat-specific foraging efficiency and the nascent adaptive divergence of sticklebacks in lakes. Behaviour. 137 (7), 865-888 (2000).
- Glazer, A. M., Cleves, P. A., Erickson, P. A., Lam, A. Y., Miller, C. T. Parallel developmental genetic features underlie stickleback gill raker evolution. Evodevo. 5 (1), (2014).
- Miller, C. T., Glazer, A. M., et al. Modular skeletal evolution in sticklebacks is controlled by additive and clustered quantitative trait loci. Genetics. 197 (1), 405-420 (2014).
- Glazer, A. M., Killingbeck, E. E., Mitros, T., Rokhsar, D. S., Miller, C. T. Genome assembly improvement and mapping convergently evolved skeletal traits in sticklebacks with Genotyping-by-Sequencing. G3. 5, 1463-1472 (2015).
- Wainwright, P. Functional morphology of the pharyngeal jaw apparatus. Fish Physiol. Fish Biomech. , 77-102 (2006).
- Hulsey, C. D., Fraser, G. J., Streelman, J. T. Evolution and development of complex biomechanical systems: 300 million years of fish jaws. Zebrafish. 2 (4), 243-257 (2005).
- Lauder, G. Functional design and evolution of the pharyngeal jaw apparatus in euteleostean fishes. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 77, 1-38 (1983).
- Fraser, G. J., et al. An ancient gene network is co-opted for teeth on old and new jaws. PLoS Biol. 7 (2), e1000031(2009).
- Stock, D. Zebrafish dentition in comparative context. J. Exp. Zool. B. Mol. Dev. Evol. 308, 523-549 (2007).
- Liem, K., Greenwood, P. A functional approach to the phylogeny of the pharyngognath teleosts. Am. Zool. 21 (1), 83-101 (1981).
- Anker, G. C. Morphology and kinetics of the head of the stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus. Trans. Zool. Soc. London. 32 (5), 311-416 (1974).
- Meyer, A. Morphometrics and allometry in the trophically polymorphic cichlid fish, Cichlusomu citrinelfum: Alternative adaptations and ontogenetic changes in shape. J. Zool., Lond. 221, 237-260 (1990).
- Huysseune, A. Phenotypic plasticity in the lower pharyngeal jaw dentition of Astatoreochromis alluaudi (Teleostei: Cichlidae). Arch. Oral Biol. 40 (11), 1005-1014 (1995).
- Muschick, M., Indermaur, A., Salzburger, W. Convergent Evolution within an adaptive radiation of cichlid fishes. Curr. Biol. 22 (24), 2362-2368 (2012).
- Cleves, P. A., et al. Evolved tooth gain in sticklebacks is associated with a cis-regulatory allele of Bmp6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111 (38), 13912-13917 (2014).
- Ellis, N. A., et al. Distinct developmental and genetic mechanisms underlie convergently evolved tooth gain in sticklebacks. Development. (142), 2442-2451 (2015).
- Tucker, A. S., Fraser, G. J. Evolution and developmental diversity of tooth regeneration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 25-26, 71-80 (2014).
- Erickson, P. A., Glazer, A. M., Cleves, P. A., Smith, A. S., Miller, C. T. Two developmentally temporal quantitative trait loci underlie convergent evolution of increased branchial bone length in sticklebacks. Proc. R. Soc. B. 281, (2014).
- Leary, S., et al. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals. , American Veterinary Medical Association. Schaumburg, IL. (2013).
- Bell, M. A. Evolutionary phenetics and genetics. Evol. Genet. Fishes. , 431-528 (1984).
- Taylor, W. R., Van Dyke, G. C. Revised procedures for staining and clearing small fishes and other vertebrates for bone and cartilage study. Cybium. 9 (2), 107-119 (1985).
- Erickson, P. A., et al. A 190 base pair, TGF-β responsive tooth and fin enhancer is required for stickleback Bmp6 expression. Dev. Biol. 401 (2), 310-323 (2015).
- Miller, C. T., et al. cis-Regulatory changes in Kit ligand expression and parallel evolution of pigmentation in sticklebacks and humans. Cell. 131 (6), 1179-1189 (2007).
- Aigler, S. R., Jandzik, D., Hatta, K., Uesugi, K., Stock, D. W. Selection and constraint underlie irreversibility of tooth loss in cypriniform fishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111 (21), 7707-7712 (2014).
- Pasco-Viel, E., et al. Evolutionary trends of the pharyngeal dentition in Cypriniformes (Actinopterygii Ostariophysi). PLoS One. 5 (6), e11293(2010).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved