A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Quantitative PCR of T7 Bacteriophage from Biopanning
In This Article
Summary
A reproducible, accurate, and time efficient quantitative PCR (qPCR) method to enumerate T7 bacteriophage is described here. The protocol clearly describes phage genomic DNA preparation, PCR reaction preparation, qPCR cycling conditions, and qPCR data analysis.
Abstract
This protocol describes the use of quantitative PCR (qPCR) to enumerate T7 phages from phage selection experiments (i.e., "biopanning"). qPCR is a fluorescence-based approach to quantify DNA, and here, it is adapted to quantify phage genomes as a proxy for phage particles. In this protocol, a facile phage DNA preparation method is described using high-temperature heating without additional DNA purification. The method only needs small volumes of heat-treated phages and small volumes of the qPCR reaction. qPCR is high-throughput and fast, able to process and obtain data from a 96-well plate of reactions in 2–4 h. Compared to other phage enumeration approaches, qPCR is more time-efficient. Here, qPCR is used to enumerate T7 phages identified from biopanning against in vitro cystic fibrosis-like mucus model. The qPCR method can be extended to quantify T7 phages from other experiments, including other types of biopanning (e.g., immobilized protein binding, in vivo phage screening) and other sources (e.g., water systems or body fluids). In summary, this protocol can be modified to quantify any DNA-encapsulated viruses.
Introduction
Bacteriophage (phage) display technology, developed by George Smith in 1985, is a powerful, high-throughput approach to identify peptide or protein ligands against targets or receptors from the cell membrane, disease antigens, cellular organelles or specific organs and tissues in the past two decades1,2. Here, random libraries of polypeptides or single chain antibodies are displayed on the coat proteins of phages (typically M13 or T7), and specific ligands can be identified from panning against immobilized proteins in vitro or in vivo biological systems through an iterative selection process. Then, ligands can be coupled with imaging or therapeutic agents for diagnosis and treatment of diseases3,4. It is critical to accurately enumerate phages during multiple steps of biopanning: (1) to quantify phages that bind to the substrate and (2) to quantify phages to determine if there is enrichment with each round of selection (phage enrichment indicates biopanned phage affinity for the target). The current gold standard for quantification, double-layer plaque assay, presents multiple challenges; it is tedious, cumbersome, and potentially inaccurate for a large number of samples. Therefore, our group has developed a sensitive, reproducible, accurate and time-efficient quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) method to enumerate M13 and T7 phage particles from biopanning5.
qPCR is an attractive and feasible method to accurately quantify T7 and M13 phages. Since each individual phage particle can only contain one copy of genomic DNA (dsDNA or ssDNA), one phage genome is equivalent to one phage particle; by quantifying the number of phage genomes, it is feasible to quantify the number of phages. During qPCR, fluorescent reporter dyes bind phage genomic DNA non-specifically or specifically through sequence-specific primers during PCR amplification, and the fluorescence signal increases with each round of amplification. When the fluorescence signal reaches the threshold, that round/cycle of amplification is noted as the threshold cycle (Ct). The known concentrations of reference phage DNA are plotted against their Ct values to establish a standard curve. Using the standard curve with the Ct values of DNA samples, the concentrations of phages can be interpolated.
While numerous strategies have been previously developed and extensively used to quantify phages from biopanning, each of them has specific challenges. The most popular and conventional method is double-layer plaque assay. Here, host bacteria are infected with phages prepared at serial dilutions, are plated on a solid agar substrate, and are overlaid with agar; phages are enumerated with the number of plaques formed (i.e., plaque forming units or pfu) on the agar plate. Plaque assay is sensitive but tedious, time-consuming and inaccurate, especially for numerous samples and with high concentrations5. Additionally, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) have been adapted to enumerate M13 and T7 phage particles6,7,8. Here, phages at different dilutions are bound and captured on a solid substrate (i.e., a microplate), probed with phage-specific antibodies, and detected by using reporters (e.g., enzyme sensitive chromogenic substrates, fluorophores) to determine the number of phage particles present. The readouts (e.g., fluorescence, absorbance) of samples can be used to quantify unknown concentrations against phage standards at known concentrations. Different phage-based ELISAs have been developed but they have potential limitations. One group developed a paper-based sandwich ELISA with a quantification range that spanned seven orders of magnitude (102-109 pfu/mL); however, this method required multiple steps of antibody coating and took up to an entire day for the assay8. Our group also developed an ELISA method to quantify M13 phage particles but had a less sensitive detection range of 106 to 1011 pfu/mL5. Switchable lanthanide fluorescence probes have been developed to enumerate M13 and quantification data could be obtained within 20 min; however, this assay has a narrow dynamic range of 109 to 1012 pfu/mL9. One group used atomic force microscopy to enumerate M13 phage particles in solution, but this requires advanced electron microscopy and only worked within a narrow range of concentrations10. Another study used monodisperse emulsions to trap fluorescent M13 and T4 reporter phages and count phages by the number of fluorescent droplets; however, this approach also exhibited a narrow quantification range from 102 to 106 pfu/mL11. While droplet digital PCR has been used to quantify M13 phages, this approach is unable to differentiate between the number of infectious and non-infectious phage particles12.
Our group has recently developed qPCR methods to enumerate T7 and M13 phages identified from biopanning against a blood-brain barrier cell model using two different fluorescent reporter dyes5. Compared to aforementioned quantification methods, the qPCR methods we developed were high-throughput and time-efficient to quantify numerous samples and able to differentiate between infectious and non-infectious phages with DNase I pre-treatment of the phage samples. Importantly, this approach can reproducibly and accurately quantify M13 and T7 bacteriophages from biopanning samples. To guide novice researchers in the area of phage qPCR, here we describe a detailed qPCR method to enumerate T7 phage particles from a cysteine-constrained library (CX7C) panned against an in vitro cystic fibrosis (CF) mucus barrier. From this work, qPCR method can be extended to quantify phage particles from other types of biopanning and from other sources, including water, soil, and body fluids.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. Primer Design and Analysis for T7 Phage Genomic DNA
- Design primers for amplification of T7 phage genomic DNA.
NOTE: F (forward) and R (reverse) primers (see Table of Materials) amplify the T7 DNA sequence located upstream of the library variable region (Figure 1). - Choose an appropriate primer analyzer to evaluate parameters of the primers, including melting temperature (Tm), percent GC content (GC%), primer dimers, hairpin formation and PCR suitability (Figure 1).
- Order the primer oligonucleotides (oligos), and upon arrival, resuspend the lyophilized oligos in DNase and RNase free ultra-pure water to make 100 µM stock concentrations in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, and store at -20 °C for several months.
- Make several aliquots (around 50 µL in each 1.5 mL tube) of the 100 µM primer stock.
NOTE: This step is used to prevent frequent freeze-thaw cycles.
2. Prepare Standards for Quantification of T7 Phage Genomic DNA
- Serially dilute 0.1 µg/µL (1.0 x 108 fg/µL) reference T7 phage DNA (purchased; at a known concentration of 0.1 µg/µL, see materials) 10-fold from 1.0 x 106 to 1.0 x 100 fg/µL with ultra-pure H2O in 0.2 mL PCR tubes. Prepare each concentration in a total volume of 20 µL (Figure 2).
- Vortex the PCR tubes to ensure thorough mixing at each step of dilution. Also, change tips when adding the DNA sample to the following dilution.
NOTE: It is recommended to prepare new solution of DNA standards for a standard curve for every batch of the qPCR experiment. - Use the equation 1 (below) to convert for T7 phage reference DNA concentrations from fg/µL to genome copies (gc) /µL (Figure 2).
- T7 phage DNA concentration in gc/µL=
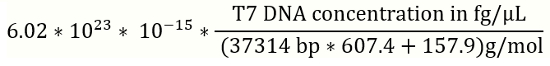 (1)
(1)
NOTE: bp: base pair; reference T7 genomic DNA is 37314 bp.
3. Pre-treatment of Phage Samples Before qPCR Reaction Preparation
- (Option 1) Pipet 20 µL of one T7 clone (phage) selected from biopanning against in vitro cystic fibrosis (CF)-like mucus model into 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes. Add 1.25 units of DNase I (0.5 µL) to each 20 µL sample.
NOTE: T7 phage cysteine constrained heptapeptide library (CX7C) was biopanned against CF-like mucus coated on 24-well membrane inserts (see Table of Materials) for 15 min. Further details are provided in the results section. One T7 clone was chosen for qPCR sample preparation from the eluate.- Option 2: Pipet 200 µL of the T7 clone into a 1.5 mL tubes, and add 5 units of DNase I
(2 µL) to each sample.
NOTE: The volume of phage sample selected at this step depends on the collected volume from biopanning. While the focus of the protocol is on the qPCR of biopanned phage, the steps for biopanning are detailed in the user protocol of the T7 phage kit (see Table of Materials)13.
- Option 2: Pipet 200 µL of the T7 clone into a 1.5 mL tubes, and add 5 units of DNase I
- Cap the T7 phage sample tubes (step 3.1) and incubate them at 37 °C for 10 min in a heated dry bath (i.e., heat block).
- Incubate tubes (from step 3.2) at 100 °C for 15 min in a heated dry bath (Figure 3A).
CAUTION: Since evaporation and condensation occur during the heating step, make sure that the 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes are capped completely. - Spin the heat-treated phages from step 3.3 at 18,534 x g for 10 s. Mix the phages by placing the tube on a vortex mixer set at touch-activation mode for 10 s, and spin at 18,534 x g for 10 s again.
NOTE: The spin-mix-spin cycle is to make sure the heated phage samples are well mixed. - Cool down the sample tubes at room temperature (RT) by leaving them on the experiment bench or store at 4 °C in a refrigerator overnight.
NOTE: Experiment can be paused at this step.
4. Prepare qPCR Reactions
NOTE: One PCR reaction is for one sample. Each PCR reaction contains 5 µL of qPCR master mix (see materials), 1 µL of 5 µM primer pair mix, 2 µL of H2O and 2 µL of heat-treated T7 phage sample. For multiple PCR reactions, all the reagents except phage sample are premixed in one 1.5 mL tube. The volume of each reagent in the premix depends on the number of phage samples for qPCR.
- Prepare the qPCR premix for 10 biopanned phage samples of unknown concentration and 7 samples of standard concentrations in triplicate. As a result, there are 51 total samples and therefore, 51 qPCR reactions (i.e., one reaction per sample). For 51 reactions, prepare a premix of 255 µL of qPCR master mix (51x 5 µL), 51 µL of primers (51x 1 µL), and 102 µL of H2O (51x 2 µL).
NOTE: It is recommended to prepare a few extra PCR reactions to compensate for the volume loss during aliquoting the PCR mix into each well of the 96-well qPCR plate. - Aliquot 8 µL of PCR premix into each well of 96-well qPCR plate for a total of 51 wells (i.e., 51 qPCR reactions). There is no need to change tips during aliquoting.
- Add 2 µL of heat-treated T7 phage samples (step 3.4) or T7 phage reference DNA (Step 2.1) to each well (Figure 3B); change tips when adding different DNA samples to the well to prevent cross-contamination. Also, dispense the 2 µL DNA samples underneath the surface of the qPCR premix (i.e., into the 8 µL PCR premix).
- Seal the qPCR plate with adhesive film.
NOTE: This step is critical, regardless of the type of qPCR plate. Use the recommended kit to seal the plate completely; otherwise, any non-sealed region in the plate will cause volume loss during PCR cycling. - Wrap the qPCR plate with aluminum foil to minimize fluorescence photobleaching and proceed to run it on the qPCR equipment.
5. qPCR Cycling Conditions
NOTE: qPCR cycling conditions were set up on the specific qPCR equipment (see Table of Materials).
- Run the 96-well qPCR plate on the qPCR equipment. On the equipment, select settings from the menu to set up the following experimental conditions (Figure 3C).
- Set up cycling conditions as follows for a sample volume of 10 µL: one cycle at 50 °C for 2 min, one cycle at 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles of (95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 1 min). After, run the melt curve settings: one cycle of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 1 min, and 95 °C 15 s.
- Proceed to analyze the data as described in step 6.
6. Analyze the qPCR Raw Data and Convert from qPCR Ct Value to gc/µL for T7 Bacteriophages
- Analyze the raw qPCR data and evaluate data quality by analyzing the characteristic plots of the raw data (Figure 4).
NOTE: Amplification plot, multicomponent plot and melt curve plot are the key characteristic plots to validate the data quality of qPCR. - Calculate the mean threshold cycle (Ct) values from the triplicate samples at each concentration of the standard curve (step 2.1).
- Plot mean Ct (Y) against log (gc/µL) (X) to get the linear curve Y = kX + b (k is the slope of the linear curve, b is the intercept).
- Calculate the linear coefficient14 R2 (R2 must be >0.99).
- Use the standard curve Y = kX + b to calculate the number of T7 phages in the biopanning samples (i.e., phages selected against CF-like mucus) in gc/µL (Figure 5).
NOTE: k is the slope of the standard curve. - Calculate the amplification efficiency by the following equation
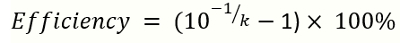 (2)
(2)
NOTE: k is the slope of the standard curve generated from reference DNA qPCR. The ideal range of amplification efficiency is 90–110% .
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Different primer design tools can be used to design qPCR primers. Typically, primer design programs have their own built-in algorithms to calculate and validate the key parameters of the primers, e.g., GC%, Tm, primer dimer or hairpin formation, etc. Generally, the key criteria are similar in different primer design tools, and primers can be designed following their instructions. Primer BLAST can be used to confirm the specificity of the primers. One primer pair that tar...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
We developed qPCR methods to quantify phage genomic DNA5, and here we described and adapted a qPCR method to enumerate T7 phages selected against a CF-like mucus barrier. Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines were adapted to develop and validate the qPCR method for enumeration of T7 phages15. The protocol we developed to quantify phages from biopanning experiments is a time-efficient, reliable, and economical approac...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by PhRMA Foundation Research Starter Grant and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health grant under award number R01HL138251.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Materials and Reagents | |||
| Primers for T7 genomic DNA | IDT | F: CCTCTTGGGAGGAAGAGATTTG R: TACGGGTCTCGTAGGACTTAAT | |
| T7 Select packaging control DNA | EMD Millipore | 69679-1UG | |
| MicroAmp optical 96-well reaction plate | ThermoFisher Scientific | N8010560 | |
| qPCR master mix--Power up SYBR Green master mix | Applied biosystems | A25742 | |
| MicroAmp optical adhesive film kit | ThermoFisher Scientific | 4313663 | |
| T7Select 415-1 Cloning Kit | EMD Millipore | 70015 | User protocols : http://www.emdmillipore.com/US/en/product/T7Select-415-1-Cloning-Kit,EMD_BIO-70015#anchor_USP |
| DNase I solution | ThermoFisher Scientific | 90083 | |
| 24-well transwell plate | Corning | 3472 | |
| UltraPure DNase/RNase-Free Distilled H2O | Invitrogen | 10977015 | |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline (1x) | Corning | 21040CV | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Equipments | |||
| ViiA7 Real-Time PCR System with Fast 96-Well Block | ThermoFisher Scientific | 4453535 | |
| Heraeus Pico 21 Microcentrifuge | ThermoFisher Scientific | 75002415 | |
| Fisherbrand Digital Vortex Mixer | Fisher Scientific | 02-215-370 | |
| HERMO SCIENTIFIC Multi-Blok Heater | ThermoFisher Scientific | Model:2001 | |
| Sorvall Legend X1 Centrifuge | ThermoFisher Scientific | 75004220 | |
| M-20 Microplate Swinging Bucket Rotor | ThermoFisher Scientific | 75003624 | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Software | |||
| QuantStudio Real-time PCR software | ThermoFisher Scientific | v1.2 | |
| Real-time qPCR primer design | IDT | ||
| OligoAnalyzer 3.1 | IDT |
References
- Smith, G. Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science. 228 (4705), 1315-1317 (1985).
- Smith, G. P., Petrenko, V. A. Phage Display. Chemical Reviews. 97 (96), 391-410 (1997).
- Sergeeva, A., Kolonin, M. G., Molldrem, J. J., Pasqualini, R., Arap, W. Display technologies: Application for the discovery of drug and gene delivery agents. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 58 (15), 1622-1654 (2006).
- Dias-Neto, E., et al. Next-generation phage display: Integrating and comparing available molecular tools to enable costeffective high-throughput analysis. PLoS ONE. 4 (12), 1-11 (2009).
- Peng, X., Nguyen, A., Ghosh, D. Quantification of M13 and T7 bacteriophages by TaqMan and SYBR green qPCR. Journal of Virological Methods. 252 (June 2017), 100-107 (2017).
- Khan, M. S., Pande, T., Mvan de Ven, T. G. Qualitative and quantitative detection of T7 bacteriophages using paper based sandwich ELISA. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 132, 264-270 (2015).
- Brasino, M., Lee, J. H., Cha, J. N. Creating highly amplified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay signals from genetically engineered bacteriophage. Analytical Biochemistry. 470, 7-13 (2014).
- Yu, X., Burgoon, M., Shearer, A., Gilden, D. Characterization of phage peptide interaction with antibody using phage mediated immuno-PCR. J immunol Methods. 326 (1-2), 33-40 (2007).
- Lehmusvuori, A., Manninen, J., Huovinen, T., Soukka, T., Lamminmäki, U. Homogenous M13 bacteriophage quantification assay using switchable lanthanide fluorescence probes. BioTechniques. 53 (5), 301-303 (2012).
- Schlaman, H. R. M., et al. Analysis of interactions of signaling proteins with phage-displayed ligands by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 13 (8), 766-776 (2008).
- Tjhung, K. F., Burnham, S., Anany, H., Griffiths, M. W., Derda, R. Rapid enumeration of phage in monodisperse emulsions. Analytical Chemistry. 86 (12), 5642-5648 (2014).
- Reitinger, S., Petriv, O. I., Mehr, K., Hansen, C. L., Withers, S. G. Purification and quantitation of bacteriophage M13 using desalting spin columns and digital PCR. Journal of Virological Methods. 185 (1), 171-174 (2012).
- T7Select Biopanning Kit. , Millipore Sigma. Available from: https://www.emdmillipore.com/US/en/product/T7Select-Biopanning-Kit,EMD_BIO-70018#anchor_USP (2018).
- Schneider, A., Hommel, G., Blettner, M. Linear Regression Analysis. Deutsches Ärzteblatt international. 107 (44), 776-782 (2010).
- Bustin, S. A., Benes, V., Garson, J. A., Hellemans, J., Huggert, J. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimun information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clinical Chemitry. 55 (4), 611-622 (2009).
- Lock, M., Alvira, M. R., Chen, S. -J., Wilson, J. M. Absolute Determination of Single-Stranded and Self-Complementary Adeno-Associated Viral Vector Genome Titers by Droplet Digital PCR. Human Gene Therapy Methods. 25 (2), 115-125 (2014).
- Fittipaldi, M., et al. Discrimination of infectious bacteriophage T4 virus by propidium monoazide real-time PCR. Journal of Virological Methods. 168 (1-2), 228-232 (2010).
- Lodder, W. J., et al. Reduction of bacteriophage MS2 by filtration and irradiation determined by culture and quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Journal of Water and Health. 11 (2), 256-266 (2013).
- Brown-Jaque, M., et al. Antibiotic resistance genes in phage particles isolated from human feces and induced from clinical bacterial isolates. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. , (2017).
- Naveca, F. G., et al. Multiplexed reverse transcription real-time polymerase chain reaction for simultaneous detection of Mayaro, Oropouche, and oropouche-like viruses. Memorias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz. 112 (7), 510-513 (2017).
- Jia, J., et al. Simultaneous detection and differentiation of human parvovirus B19 and human parvovirus 4 by an internally controlled multiplex quantitative real-time PCR. Molecular and Cellular Probes. 36, 50-57 (2017).
- Bliem, R., et al. A novel triplex quantitative pcr strategy for quantification of toxigenic and nontoxigenic Vibrio cholerae in aquatic environments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 81 (9), 3077-3085 (2015).
- Wan, Z., Goddard, N. L. Competition Between Conjugation and M13 Phage Infection in Escherichia coli in the Absence of Selection Pressure: A Kinetic Study. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics. 2 (10), 1137-1144 (2012).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved