A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Clinical Protocol of Producing Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction for Potential Cartilage Regeneration
In This Article
Summary
Here, we present a protocol to produce an adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and its application to improve knee functions by regenerating cartilage-like tissue in human patients with osteoarthritis.
Abstract
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common debilitating disorders. Recently, numerous attempts have been made to improve the functions of the knees by using different forms of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). In Korea, bone marrow concentrates and cord blood-derived stem cells have been approved by the Korean Food and Drug Administration (KFDA) for cartilage regeneration. In addition, an adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction (SVF) has been allowed by the KFDA for joint injections in human patients. Autologous adipose tissue-derived SVF contains extracellular matrix (ECM) in addition to mesenchymal stem cells. ECM excretes various cytokines that, along with hyaluronic acid (HA) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) activated by calcium chloride, may help MSCs to regenerate cartilage and improve knee functions. In this article, we presented a protocol to improve knee functions by regenerating cartilage-like tissue in human patients with OA. The result of the protocol was first reported in 2011 followed by a few additional publications. The protocol involves liposuction to obtain autologous lipoaspirates that are mixed with collagenase. This lipoaspirates-collagenase mixture is then cut and homogenized to remove large fibrous tissue that may clog up the needle during the injection. Afterwards, the mixture is incubated to obtain adipose tissue-derived SVF. The resulting adipose tissue-derived SVF, containing both adipose tissue-derived MSCs and remnants of ECM, is injected into knees of patients, combined with HA and calcium chloride activated PRP. Included are three cases of patients who were treated with our protocol resulting in improvement of knee pain, swelling, and range of motion along with MRI evidence of hyaline cartilage-like tissue.
Introduction
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are known to have the capability to regenerate cartilage1,2,3,4,5,6. They can be easily obtained from various sources: bone marrow, cord blood, and adipose tissue among many others. Among these sources, adipose tissue is the only source where a sufficient number of MSCs can be obtained without any culture expansion to regenerate cartilage in clinical settings7,8. Autologous bone marrow stromal vascular fraction (SVF) can be easily obtained as well. However, the number of stem cells contained in the non-culture expanded marrow is very low7,8. Cord-blood may contain a sufficient number of MSCs. However, cord blood is not a readily available source of autologous SVF.
Numerous methods of processing adipose tissue to obtain SVF are available for clinical applications. Among these, the method of obtaining MSCs from adipose tissue using collagenase, developed and confirmed by Zuk et al.5,6, is very well accepted. This method of using collagenase has been modified for clinical applications in orthopedics. In order to be applied to clinical settings, the system must be a closed system to maintain the sterility while keeping the convenience. One particular modification presented in this article involves homogenization of the lipoaspirates. Small sized lipoaspirates are digested relatively faster than the larger ones that are resulting in the uneven breakdown of adipose tissue. Furthermore, these larger sized lipoaspirates may produce fibrous tissues that can clog up the syringes and needles while performing joint injections9,10. In order to prevent these issues, the lipoaspirates may be homogenized by cutting and mincing the lipoaspirates before the incubation with collagenase. The resulting adipose tissue-derived SVF may contain more uniform extracellular matrix (ECM) compared to lipoaspirates that are not homogenized11. The broken-down ECM contained in the SVF may work as a scaffold12.
In 2009, autologous adipose tissue-derived SVF has been allowed by the Korean Food and Drug Administration (KFDA) when processed within a medical facility with minimal processing by a physician13. Afterwards, autologous adipose tissue-derived SVF has been utilized as a potential agent to improve knee functions in osteoarthritis (OA) patients by potentially regenerating cartilage-like tissue10,14,15,16,17,18.
In 2011, Pak showed for the first time that adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ASCs) contained in the adipose tissue-derived SVF can improve knee functions potentially regenerating cartilage-like tissue in human OA patients when injected with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) 14. In addition, Pak et al. have reported safety data in 2013 involving 91 patients. The mean efficacy rate reported in this safety data was 67%15. Subsequently, additional studies by Pak et al. showed improved knee functions potentially due to cartilage-like tissue regeneration in patients with a meniscus tear and chondromalacia patellae10,16,17,18. Based on articles reported, it is known that the number of stem cells contained in 100 g of adipose tissue processed by the protocol presented in this article may range from 1,000,000 - 40,000,000 depending on patients' characteristics8,19,20,21,22,23.
Here, we present a clinical protocol of human knee OA by using autologous adipose tissue-derived SVF with HA and PRP activated with calcium chloride. The first version of this clinical protocol, involving a closed, manual system to maintain the sterility, was reported in 201114. The identical protocol was optimized, maintaining sterility, and was reported in 2013 and 201610,15. Here, the optimized protocol is presented. The schematic overview of the protocol is presented in Figure 1.
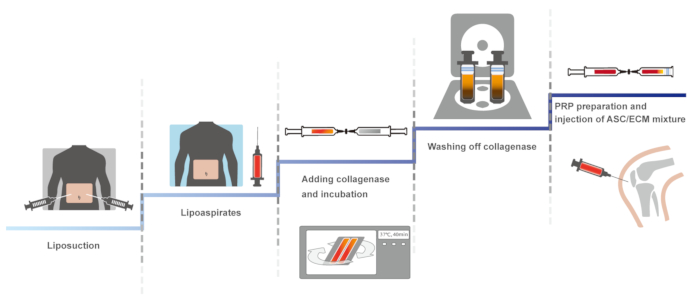
Figure 1: The schematic overview of the protocol. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
The approval and consent to report following case reports were waived by Myongji University Institutional Review Board committee (MJUIRB). Further, this clinical protocol was in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki and regulation guidelines of the KFDA. For the procedures, informed consents were obtained from the patients.
1. Liposuction
NOTE: Perform with sterile technique.
- Use the following inclusion criteria: (1) MRI evidence of stage 3 OA; (2) either male or female; (3) over 18 years of age; (4) sufficient (100-110 g) adipose tissue for liposuction; (5) unwillingness to proceed with surgical intervention; (6) failure of conservative management; and (7) ongoing disabling pain.
- Use the following exclusion criteria: (1) active inflammatory or connective tissue disease thought to impact pain condition (i.e.,, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia); (2) active endocrine disorder that might impact pain condition (i.e.,, hypothyroidism, diabetes); (3) active neurological disorder that might impact pain condition (i.e.,, peripheral neuropathy, multiple sclerosis); (4) active pulmonary disease requiring medication usage; and (5) no history of steroid joint injections past 3 months.
- Bring the patient into an operating room with a biohazard class A hood and place him (or her) in a supine position.
- Clean the abdominal area of the patient with 5% betadine (povidone-iodine) and drape the patient using the sterile technique, exposing the cleaned area of the abdomen for liposuction.
- Approximately 5 cm infero-laterally from the umbilicus, anesthetize two sites (the one on the left and the other on the right side of the umbilicus) of incision to-be-made using 2 mL of 2% lidocaine without epinephrine with a (25 gauge, 1½ inch) needle in a 5-mL syringe by injecting each site at the epidermal level.
- Anesthetize the site of incision to-be-made using 5 mL of tumescent solution (500 mL of normal saline, 40 mL of 2% lidocaine, 20 mL of 0.5% bupivacaine, 0.5 mL of 1:1000 epinephrine) in a 10-mL syringe with a needle (25 gauge, 1½ inch).
- Make 2 incisions of 0.5 cm approximately 5 cm below the umbilicus laterally by pinching the skin to raise the depth of the subcutaneous level.
- Using No. 11 blade, poke the raised skin to penetrate through to the subcutaneous level but not to penetrate through the abdominal wall.
- By using 20 cm 16-gauge cannula, anesthetize the subcutaneous level of the whole lower abdomen area, which is to-be-liposuctioned, with 700 to 800 mL of the tumescent solution.
- After finishing infiltration of the whole lower abdomen with the tumescent solution, prepare a liposuction apparatus by connecting a 3.0 mm cannula connected to a 60 mL (or a 30 mL) syringe for manual liposuction or a specially designed 3.0 mm cannula connected to a centrifuge kit, a closed-system syringe for the purpose of keeping the sterility, connected to a vacuum machine for vacuum-assisted liposuction.
- Perform liposuction to obtain 100-110 g of adipose tissue excluding tumescent solution. When performing liposuction, adipose tissue will be obtained along with the tumescent solution, which should be separated and removed.
- To separate the tumescent solution, first by gravity, transfer the adipose tissue in the centrifuge kit to a 60 mL syringe and place the syringe down (i.e., the portion of the syringe is at the bottom). By waiting 5-6 min, the adipose tissue and the tumescent fluid will be separated. Remove the fluid at the bottom of the syringe by pressing on the top part of the syringe plunger.
- Perform the above Steps 1.9-1.11 until a total of 100-110 g of adipose tissue (lipoaspirates) per knee has been accumulated.
2. Preparation of ASC/ECM Mixture with Sterile Closed System
- After separating the tumescent solution by gravity and accumulating 50-55 g of lipoaspirates per each 60 mL centrifuge kit, a sterile closed system, place the 2 centrifuge kits into a centrifuge container bucket and spin at 1600 x g for 5 min, condensing the lipoaspirates and separating fluid from the adipose tissue. In this process of further condenses, the lipoaspirates may produce fatty oil in certain cases.
- Being cautious not to shake, remove the safety cap and the plug at the bottom of the centrifuge kit.
- Remove the bottom fluid by slowly pressing down on the top of the plunger of the centrifuge kit.
- On separate 60 mL syringe, dissolve 10 mg of collagenase (5 mg of collagenase specific for connective tissue24 and 5 mg of collagenase specific for adipose tissue25) with 50 mL of normal saline.
- Mix approximately 25-30 mL of condensed lipoaspirate with dissolved collagenase (5 mg of collagenase specific for connective tissue and 5 mg of collagenase specific for adipose tissue) at a ratio of 1:1 (v:v) by connecting the 60 mL syringe to a centrifuge kit by using a specialized connector.
- Thoroughly mix the condensed lipoaspirate and the collagenase by pushing the content between the 60 mL syringe and the centrifuge kits by using a rod or a pusher.
- Transfer the mixture of the lipoaspirate and the collagenase back to 60 mL syringes.
- Connect each 60 mL syringe containing the mixture with a tissue homogenizer which contains blades.
- Connect an empty 60 mL syringe to the other end of the homogenizer.
- Push the mixture to the other 60 mL syringe through the homogenizer for 4 -6 times, resulting in cutting and mincing of the lipoaspirate.
- Transfer the homogenized lipoaspirate and the collagenase mixture back to 60 mL centrifuge kits through a specialized connector
- Place the centrifuge kits in a container to be placed in an incubator that has been pre-heated at 37 °C.
- Incubate the two centrifuge kits with the homogenized mixture at 37 °C for 40 min while rotating at 45 rpm.
- After the 40 min of incubation, remove the container from the incubator in a sterile fashion. Then, remove the centrifuge kits and place them in a centrifuge machine.
- Centrifuge the mixtures at 800 x g for 5 min to separate the adipose tissue-derived SVF.
- After the centrifuge, remove the supernatant (which includes collagenase and digested adipose tissue) from each centrifuge kits by removing the syringe cap on the top of the plunger and placing a 30 mL syringe on the plunger opening via syringe lock connection.
- Slowly press down the barrel part of the 30 mL syringe for the supernatant to fill into the 30 mL syringe.
- Press down the 30 mL syringe barrel all the way down to the last 3-4 mL of the bottom of the centrifuge kit, leaving only the last 3-4 mL of adipose tissue-derived SVF. The supernatant is discarded.
- Remove the 30 mL syringe from the top of the plunger and fill the syringe with 5% dextrose in lactated Ringer's solution (D5LR).
- By attaching the 30 mL syringe filled with D5LR on the top of the plunger opening, fill the centrifuge kits, containing 3-4 mL of adipose tissue-derived SVF, with D5LR up to 55 mL.
- Remove the 30 mL syringe, cap the plunger, and centrifuge the centrifuge kits again at 300 x g for 4 min.
- Repeat Steps 2.17-2.21 for a total of 4 washings. The used collagenase is xenogenic. Therefore, most collagenase is removed by 4 washings. However, for FDA approval, fine-tuning of the protocol may be necessary to completely remove the collagenase residues in the final volume, although the current amount of collagenase residues may be negligible enough for the patients that do not have any clinical side effects.
- After the 4th centrifugation, in order to obtain the final SVF for injection, remove the safety cap and the plug at the bottom opening of the centrifuge kit, without shaking or turning the centrifuge kit.
- Attach a 20 mL syringe to the centrifuge kit bottom opening by using a specially designed connector.
- Pull the plunger of the syringe several times back and forth to shake up the cells that have settled on the bottom of the centrifuge kit.
- Remove the desired total volume of the SVF containing both ASCs and ECM along with other cells and tissue (usually about 3-4 mL from each centrifuge kit for knee joint injections).
3. PRP Preparation with Sterile Technique
- While preparing the ASCs and ECM, draw 30 mL of autologous blood with 2.5 mL of anticoagulant citrate dextrose solution.
- Transfer the drawn blood to the 60 mL centrifuge kits.
- Centrifuge the drawn blood at 730 x g for 5 min and remove the supernatant into a new 60 mL centrifuge kit. Centrifuge the supernatant at 1300 x g for 4 min, resulting in 3-4 mL of PRP.
- Right before the injection, add 3% (w/v) calcium chloride at a ratio of 10:2 (PRP: calcium chloride, v:v) to the PRP to activate it.
- Add 0.5% (w/v) HA, as a scaffold, to the PRP activated with calcium chloride. These ASCs with ECM, along with PRP, activated by calcium chloride, and HA stand for the ASC/ECM mixture.
4. ASC/ECM Mixture-Based Treatment
- Clean the knee of the patient with 5% betadine and drape it in a sterile manner.
- Palpate the anterior of the knee for the joint space between the tibial and femoral bones.
- Anesthetize the injection site superficially with diluted lidocaine (1 mL of 1% lidocaine diluted with 4 mL of normal saline) from the skin to just outside of the joint capsule.
- Anesthetize the inside of the joint capsule with diluted ropivacaine (1 mL 0.75% ropivacaine diluted with 3 mL of normal saline).
- Mix 2 mL of HA to the 6-8 mL of SVF contained in a 20 mL syringe through the syringe-to-syringe connector.
- By using a syringe-to-syringe connector, add 0.4 mL of calcium chloride to the 3-4 mL of autologous PRP that has been already prepared and being ready in a 5-mL syringe.
- Combine 3.5 - 4.5 mL of PRP/calcium chloride in a 5 mL syringe with 8-10 mL of HA/SVF mixture in a 20 mL syringe via syringe-to-syringe connector.
- Immediately inject the mixture (about 12-15 mL) slowly into the anterior tibio-femoral joint of the knees using 38-mm 18-gauge needle with or without the ultrasound guidance.
- After the injection, bandage the injection site with pressure by folding 4x4 cotton gauze 4 times and placing tapes over the folded 4x4 gauze.
- Instruct the patient to remain still for 60 min to allow for cell attachment.
- Instruct the patient to limit activities for minimal of 1 week after discharge from the clinic.
- Return to the clinic for three additional injections of PRP activated by calcium chloride over 3 weeks.
5. Post-Treatment Follow Up
- Assess patient at the week of 2, 4, and 16 (18 or 22) for pain improvement in terms of visual analog scale (VAS) and function improvement in terms of physical therapy parameters. Determine functional rating index (FRI), VAS, and range of motion (ROM) as previously described26,27.
- Follow the patient by post-treatment MRI 3 months after the treatment.
Results
Three patients (one 87-year-old female with stage 3 OA, one 68-year-old male with stage 3 OA, and one 60-year-old female with stage 3 OA) without any significant past medical history presented to the clinic with persistent knee pain and desired for potential autologous adipose tissue-derived SVF treatment. All three patients had their knee examined by an orthopedic surgeon and were offered to have total knee replacement (TKR) and were reluctant to have the surgery. Prior to the procedure,...
Discussion
In 2001, Zuk et al. isolated stem cells from adipose tissue by breaking down the collagen matrix with collagenase6. Afterwards, the group showed that these stem cells isolated from the adipose tissue could transform into cartilage and other tissues of mesoderm in origin, proving that these stem cells were mesenchymal in origin.
Likewise, the procedure presented in this article is a modified protocol to apply the similar method to human patients. The main ...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges the support from the staff of Mipro Medical Clinic and the figure design by Jaepil/David Lee. This work was supported by research grants from the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the NRF funded by the MSIT (number NRF-2017M3A9E4078014); and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (numbers NRF-2017R1A2B4002315 and NRF-2016R1C1B2010308).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Material | |||
| 5% Betadine (povidone-iodine) | Firson Co., Ltd. | 657400260 | |
| 2% Lidocaine | Daehan Pharmaceutical Co. | 670603480 | |
| Tumescent solution | Myungmoon Pharm. Co. Ltd. | N01BB01 | The solution was composed of 500 mL normal saline, 40 mL 2% lidocaine, 20 mL 0.5% marcaine, and 0.5 mL epinephrine 1:1000. |
| Liberase TL and TM research grade | Roche Applied Science | 5401020001 | |
| D5LR | Dahan Pharm. Co., Ltd. | 645101072 | Dextrose 5% in lactated Ringer's solution |
| Anticoagulant citrate dextrose solution | Fenwal, Inc. | NDC:0942-0641 | The solution was composed of 0.8% citric acid, 0.22% sodium citrate, and 0.223% dextrose. |
| 3% (w/v) Calcium chloride | Choongwae Pharmaceutical Co. | 644902101 | |
| 0.5% (w/v) HA (Hyaluronic acid ) | Dongkwang pharm. Co., Ltd. | 645902030 | |
| 0.25% Ropivacaine | Huons Co., Ltd. | 670600150 | |
| Equipment | |||
| 3.0 mm Cannula | WOOJU Medical Instruments Co. | ML30200 | |
| 60-mL Luer-Lock syringe | BD (Becton Dickinson) | 309653 | |
| Centrifuge Barrel Kit | CPL Co., Ltd. | 30-0827044 | |
| Tissue homogenizer that contains blades | CPL Co., Ltd. | 30-0827045 | |
| Rotating incubator mixer | Medikan Co., Ltd | MS02060092 | |
| Centrifuge | Hanil Scientific Inc. | CE1133 | |
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging | Philips Medical Systems Inc. | 18068 | |
| Ultrasound Imaging System | Samsung Medison co., Ltd | CT-LK-V10-ICM-09.05.2007 |
References
- Arnoczky, S. P. Building a meniscus. Biologic considerations. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. (367 Suppl), S244-S253 (1999).
- Barry, F. P. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in joint disease. Novartis Foundation Symposium. 249, 86-241 (2003).
- Usuelli, F. G., et al. Adipose-derived stem cells in orthopaedic pathologies. British Medical Bulletin. 124 (1), 31-54 (2017).
- Zhang, H. N., Li, L., Leng, P., Wang, Y. Z., Lv, C. Y. Uninduced adipose-derived stem cells repair the defect of full-thickness hyaline cartilage. Chinese Journal of Traumatology. 12 (2), 92-97 (2009).
- Zuk, P. A., et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 13 (12), 4279-4295 (2002).
- Zuk, P. A., et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Engineering. 7 (2), 211-228 (2001).
- Baer, P. C., Geiger, H. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells: tissue localization, characterization, and heterogeneity. Stem Cells International. 2012, 812693 (2012).
- Zhu, Y., et al. Adipose-derived stem cell: a better stem cell than BMSC. Cell Biochemistry and Function. 26 (6), 664-675 (2008).
- Bellei, B., Migliano, E., Tedesco, M., Caputo, S., Picardo, M. Maximizing non-enzymatic methods for harvesting adipose-derived stem from lipoaspirate: technical considerations and clinical implications for regenerative surgery. Scientific Reports. 7 (1), 10015 (2017).
- Pak, J., Lee, J. H., Park, K. S., Jeong, B. C., Lee, S. H. Regeneration of Cartilage in Human Knee Osteoarthritis with Autologous Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells and Autologous Extracellular Matrix. BioResearch Open Access. 5 (1), 192-200 (2016).
- Alexander, R. W. Understanding Adipose-derived Stromal Vascular Fraction (AD-SVF) Cell Biology and Use on the Basis of Cellular, Chemical, Structural and Paracrine Components: A Concise Review. Journal of Prolotherapy. 4, e855-e869 (2012).
- Benders, K. E., et al. Extracellular matrix scaffolds for cartilage and bone regeneration. Trends in Biotechnology. 31 (3), 169-176 (2013).
- Korean Food and Drug Administration (KFDA). Cell therapy: Rules and Regulations. KFDA. , (2009).
- Pak, J. Regeneration of human bones in hip osteonecrosis and human cartilage in knee osteoarthritis with autologous adipose-tissue-derived stem cells: a case series. Journal of Medical Case Reports. 5, 296 (2011).
- Pak, J., Chang, J. J., Lee, J. H., Lee, S. H. Safety reporting on implantation of autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells with platelet-rich plasma into human articular joints. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 14, 337 (2013).
- Pak, J., Lee, J. H., Kartolo, W. A., Lee, S. H. Cartilage Regeneration in Human with Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Current Status in Clinical Implications. BioMed Research International. 2016, 4702674 (2016).
- Pak, J., Lee, J. H., Lee, S. H. A novel biological approach to treat chondromalacia patellae. PLoS One. 8 (5), e64569 (2013).
- Pak, J., Lee, J. H., Lee, S. H. Regenerative repair of damaged meniscus with autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells. BioMed Research International. 2014, 436029 (2014).
- Aust, L., et al. Yield of human adipose-derived adult stem cells from liposuction aspirates. Cytotherapy. 6 (1), 7-14 (2004).
- De Ugarte, D. A., et al. Comparison of multi-lineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow. Cells Tissues Organs. 174 (3), 101-109 (2003).
- Guilak, F., et al. Clonal analysis of the differentiation potential of human adipose-derived adult stem cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 206 (1), 229-237 (2006).
- Mitchell, J. B., et al. Immunophenotype of human adipose-derived cells: temporal changes in stromal-associated and stem cell-associated markers. Stem Cells. 24 (2), 376-385 (2006).
- Oedayrajsingh-Varma, M. J., et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell yield and growth characteristics are affected by the tissue-harvesting procedure. Cytotherapy. 8 (2), 166-177 (2006).
- . Liberase TL information available from Sigma Millipore online Available from: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/roche/05401020001?lang=en®ion=US (2018)
- . Liberase TM information available from Sigma Millipore online Available from: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/roche/Libtmro?lang=en®ion=US (2018)
- Childs, J. D., Piva, S. R. Psychometric properties of the functional rating index in patients with low back pain. European Spine Journal. 14 (10), 1008-1012 (2005).
- Price, D. D., McGrath, P. A., Rafii, A., Buckingham, B. The validation of visual analogue scales as ratio scale measures for chronic and experimental pain. Pain. 17 (1), 45-56 (1983).
- Pilgaard, L., Lund, P., Rasmussen, J. G., Fink, T., Zachar, V. Comparative analysis of highly defined proteases for the isolation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Regenerative Medicine. 3 (5), 705-715 (2008).
- D'Ambrosi, R., Indino, C., Maccario, C., Manzi, L., Usuelli, F. G. Autologous Microfractured and Purified Adipose Tissue for Arthroscopic Management of Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (131), e56395 (2018).
- Packer, J. D., Chang, W. T., Dragoo, J. L. The use of vibrational energy to isolate adipose-derived stem cells. Plastic Reconstructive Surgery-Global Open. 6 (1), e1620 (2018).
- Hanke, C. W., Bernstein, G., Bullock, S. Safety of tumescent liposuction in 15,336 patients. National survey results. Dermatologic Surgery. 21 (5), 459-462 (1995).
- Illouz, Y. G. Complications of liposuction. Clinics in Plastic Surgery. 33 (1), 129-163 (2006).
- Dixit, V. V., Wagh, M. S. Unfavourable outcomes of liposuction and their management. Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery. 46 (2), 377-392 (2013).
- Lehnhardt, M., et al. Major and lethal complications of liposuction: a review of 72 cases in Germany between 1998 and 2002. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 121 (6), 396e-403e (2008).
- Iyer, S. S., Rojas, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of mesenchymal stem cells: novel concept for future therapies. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 8 (5), 569-581 (2008).
- Zhang, J., Middleton, K. K., Fu, F. H., Im, H. J., Wang, J. H. HGF mediates the anti-inflammatory effects of PRP on injured tendons. PLoS One. 8 (6), e67303 (2013).
- Li, N. Y., Yuan, R. T., Chen, T., Chen, L. Q., Jin, X. M. Effect of platelet-rich plasma and latissimus dorsi muscle flap on osteogenesis and vascularization of tissue-engineered bone in dogs. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 67 (9), 1850-1858 (2009).
- Parsons, P., et al. The biological effect of platelet rich-plasma on the fracture healing process. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume. 91-B, 293 (2009).
- Wu, W., Chen, F., Liu, Y., Ma, Q., Mao, T. Autologous injectable tissue-engineered cartilage by using platelet-rich plasma: experimental study in a rabbit model. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 65 (10), 1951-1957 (2007).
- Cooper, T. W., Eisen, A. Z., Stricklin, G. P., Welgus, H. G. Platelet-derived collagenase inhibitor: characterization and subcellular localization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 82 (9), 2779-2783 (1985).
- Uzuki, M., Sawai, T. A. A comparison of the affinity of sodium hyaluronate of various molecular weights for degenerated cartilage: a histochemical study using hyaluronic acid binding protein. International Congress Series. 1223, 279-284 (2001).
- Pagano, C., et al. Molecular and morphometric description of adipose tissue during weight changes: a quantitative tool for assessment of tissue texture. International Journal of Molecular Medicine. 14 (5), 897-902 (2004).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved