A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Semi-quantitative Assessment Using [18F]FDG Tracer in Patients with Severe Brain Injury
In This Article
Summary
[18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography-computed tomography is useful for studying glucose metabolism related to brain function. Here, we present a protocol for an [18F]FDG tracer set-up and semiquantitative assessment of the region-of-interest analysis for targeted brain areas associated with clinical manifestations in patients with severe traumatic brain injury.
Abstract
Patients with severe traumatic brain injury (sTBI) have difficulty knowing whether they are accurately expressing their thoughts and emotions because of disorders of consciousness, disrupted higher brain function, and verbal disturbances. As a consequence of an insufficient ability to communicate, objective evaluations are needed from family members, medical staff, and caregivers. One such evaluation is the assessment of functioning brain areas. Recently, multimodal brain imaging has been used to explore the function of damaged brain areas. [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography ([18F]FDG-PET/CT) is a successful tool for examining brain function. However, the assessment of brain glucose metabolism based on [18F]FDG-PET/CT is not standardized and depends on several varying parameters, as well as the patient's condition. Here, we describe a series of semiquantitative assessment protocols for a region-of-interest (ROI) image analysis using self-produced [18F]FDG tracers in patients with sTBI. The protocol focuses on screening the participants, preparing the [18F]FDG tracer in the hot lab, scheduling the acquisition of [18F]FDG-PET/CT brain images, and measuring glucose metabolism using the ROI analysis from a targeted brain area.
Introduction
Patients with sTBI are presented with unforeseeable neurological difficulties over the course of rehabilitation that include motor deficits, sensory deficits, and psychiatric instability1. Although clinical assessment is generally performed verbally, patients with sTBI such as unresponsive wakefulness syndrome or minimally conscious state have particular difficulty in knowing whether they are accurately expressing their thoughts and emotions because of disorders of consciousness, disrupted higher brain function, and verbal disturbances2,3. Family members, medical staff, and caregivers are sometimes confounded by unforeseeable neurological changes or the lack of response that can result from insufficient communicatory ability4,5.
Recently, multimodal brain imaging has been used to explore regional brain function6,7,8,9. The brain is the main consumer of glucose-derived energy, with glucose metabolism providing approximately 95% of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) required for the brain to function10. The uptake of [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) is a marker for the uptake of glucose by brain tissue. [18F]FDG-PET/CT can detect [18F]FDG uptake and is, therefore, a useful tool for examining brain function11. In general, [18F]FDG image analysis is divided into two categories: ROI analysis and voxel-based analysis (VBA)12. Previous reports show that ROI analysis is preferred for studying specific regions of traumatic injury. This is because VBA (such as statistical parametric mapping [SPM]) requires coregistration and normalization to a standard brain, which does not work well in cases of TBI due to brain tissue deformation such as brain atrophy, swelling, enlargement, and shrinking of ventricular space7,12. Although various algorithms and software have been developed for analyzing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, metals used in neurosurgical and orthopedic surgery generate noise artefacts7,12,13. Recently, the use of photomultipliers with PET/CT devices has improved the spatial resolution of PET/CT-derived brain images14. The current protocol focuses on semi-quantitatively measuring glucose uptake via ROI analysis in [18F]FDG-PET/CT using self-produced [18F]FDG tracers in patients with sTBI.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
This study was performed in compliance with the institutional review board (approval No. 07-01) and adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent for medical record and brain image use was obtained from the patients’ legal representatives. The study was conducted after approval by the institutional ethics committee (2017-14). This protocol was made following the guidelines of the Japanese Society of Nuclear Medicine and European Association of Nuclear Medicine as a reference15,16.
1. Screening of the Participants
- Obtain informed consent to use the medical records and brain images of the patients from the patients’ legal representatives. A Glasgow Coma Scale score ≤ 8 at the time of accident must have been recorded in each patient’s medical record17,18,19.
- Hold neurology, psychology, and multi-disciplinary staff conferences every six months to assess clinical manifestations.
Note: Conference members should include medical staff such as medical doctors, nurses, physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, nutritionists, and medical social workers. Be sure to constantly check whether patients can communicate (verbally or nonverbally) and make decisions for themselves because arousal state and neurological status are typically unstable. - Conduct clinical assessments of the auditory function, visual function, motor function, oromotor/verbal function, communication function, arousal state, facial expression, and other relevant functions, using standard assessment batteries such as the Coma Recovery Scale-Revised (CRS-R), the Nociception Coma Scale, and the Wessex Head Injury Matrix20,21,22.
- Schedule [18F]FDG-PET/CT scans for the patients who are medically stable and can safely participate in examinations. Only schedule those who have provided informed consent or whose legal representatives have provided informed consent, as stated in the informed consent form. Schedule [18F]FDG-PET/CT image acquisition near the day of clinical assessment.
2. Preparation of the [18F]FDG Tracer in the Hot Lab
- In the hot lab, begin to manufacture reagent kits for the automated production of FDG tailored to the FDG synthesizer (see Table of Materials). Be sure to use the automatic program to check the mobility of the pumping system in the FDG synthesizer and to ensure that air does not leak from the reagent kit. Sterilize the contact area of the machine (this is the start time).
Note: Be sure to check the radiation monitor in the hot lab and use the portable radiation dosimeters to check the radiation levels of each person before they enter the hot lab. - Check the volume of [16O]-water and [18O]-water and the volume of helium, hydrogen, and nitrogen in the gas tank. Check whether the tap water temperature for primary cooling is under 25 °C and that for secondary cooling is under 22 °C. Use all water in the closed system (30 min after the start) for production.
- Begin the preliminary irradiation of [16O]-water in the cyclotron (1 h after the start). Check the monitor to be sure that 2 - 3 mL of [16O]-water is irradiated in optimal conditions (e.g., 20 µA, 5 min) in the target area of the cyclotron. After irradiation, install the vial of [16O]-water into a radioisotope dose calibrator and measure the level of radioactivity (see Table of Materials).
Note: The radioactive decay should be calculated using the following formula.
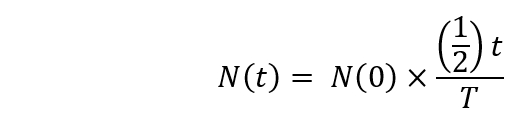
Here,
N(t) is the number radioactive nuclei at t = t seconds;
N(0) is the number radioactive nuclei at t = 0 seconds;
T = the half-life. - Begin the irradiation of [18O]-water in the cyclotron (1 h 30 min after the start). Set the bombardment time for up to 20 min and the energy of the impinging protons to 16.5 MeV.
- Start the FDG synthesizer according to the operator manual22 (2 h after the start). A modified procedure is given below.
- After the irradiation, use helium gas to transfer 2 - 3 mL of the [18O]-water from the cyclotron to the polypropylene receiver of the FDG synthesizer.
- Hook syringes onto the corresponding syringe drivers, pressurize reagent vials, dissolve the 1,3,4,6-Tetra-O-acetyl-2-O-trifluoromethanesulfonyl-β-D-mannopyranose in one vial (7 ± 0.2 mL) of acetonitrile (purity ≥ 99.5%), and rinse the cassette with acetonitrile.
- After the bombardment, transfer the irradiated [16O]-water and [18O]-water to the FDG synthesizer.
Note: Once the synthesis has started, the irradiated [18O]-water moves through an anion exchange cartridge (see Table of Materials). Be sure to condition and convert the cartridge to the carbonate before the synthesis. - After transferring the eluent containing the [18F]activity without liquid into the reaction vessels, allow the solvents to evaporate until dry. During the drying process, add small amounts of acetonitrile to the reaction vessel 3x (each time, add 80 µL). Perform the evaporation at 95 °C under nitrogen flow and vacuum.
- Add the mannose triflate precursor (25 mg) to the dry residue after dissolving it in about 3.5 mL of acetonitrile (with a purity of ≥ 99.5%). A nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs at 85 °C in the FDG synthesizer.
- As a preliminary purification, mix the labeled solution with 26 mL of distilled water. Send about 4 mL of the diluted labeling solution back to the reaction vessel to recover the remaining activity. Pass the solution through the reverse-phase cartridge (see Table of Materials). Rinse the cartridge containing the trapped labeled precursor 4x using 10 mL, 10 mL, 13 mL, and 13 mL of distilled water on the successive washes.
- Convert the acetylated compound (labeled precursor) into FDG within the cartridge via alkaline hydrolysis, using 750 µL of 2 N NaOH for 2 min at room temperature.
- After hydrolysis, collect the alkaline FDG solution in 7 mL of water and mix it with the neutralization solution (5 mL of citrate buffer and 1 mL of 2 N HCl).
- Purify the resulting neutralized FDG solution.
- Pass the neutralized FDG solution through a second reverse-phase cartridge (see Table of Materials), retaining the partially hydrolyzed compounds and nonpolar by-products.
- Pass it through an Alumina N cartridge (see Table of Materials), retaining the last traces of unreacted [18F]fluoride ions. Then, pass it through a 0.22-µm filter.
- Rinse the cassette and cartridges, filter with 3 mL of water to recover the residual FDG that is left in the lines and, then, drain the FDG into the final vial, which contains 15 - 17 mL of liquid.
- Perform a qualitative analysis of the [18F]FDG tracer (2 h 30 min after the start).
- Visually observe the vial. Confirm that it is transparent and that it does not include any particles.
- Measure the amount of liquid using a Roberval’s balance (should be 15 - 17 mL).
- Measure the radioactivity and half-life using a radioisotope dose calibrator (the same as in step 2.3, see Table of Materials) (criterion: 105 - 115 min).
- Dispense 0.5 mL from the vial. Perform a radiochemical purity test via carbohydrate analysis. Use columns of 3.9 x 300 mm for high-performance liquid chromatography (see Table of Materials) to detect the peak radioactivity (over 95).
Note: A single peak means high purity. - Measure the pH (pH 5.0 - 8.0) by using pH test paper (see Table of Materials). Measure the residual 4,7,13,16,21,24-Hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane (see Table of Materials) (< 40 ppm) using test paper (see Table of Materials). Measure the endotoxins with the appropriate endotoxin-measuring device through absorbance measuring (see Table of Materials) (0.25 EU/mL). Do a test for sterility (finding no bacteria after 8 d at 37 °C).
- Fill the vial covered by lead and tungsten with the [18F]FDG tracer at a dosage of 5 MBq/kg body weight.
- Transfer the [18F]FDG tracer from the hot lab to the working room (3 h 25 min after the start).
3. Time Course for the Acquisition of the [18F]FDG-PET/CT Brain Images
- Schedule the patients. Be sure to inform the staff to stop nutrition and feeding via gastrostomy. Do not stop providing water. The patients should fast starting 7 h before the image acquisition.
- Prepare the intravenous route for [18F]FDG tracer administration. Secure a 22- to 24-G needle with 5 mL of heparin sodium (10 units/mL) on one of the lower limbs before entering the radiation-controlled area.
- Have the patients lie down on a light stretcher before entering the radiation-controlled area. Bring the patients to the radiation-controlled area and wait for 30 min, in silence, while medical staff are on stand by.
- Recheck the patency of the intravenous route by drawing blood with a 10-mL syringe. Measure the blood-glucose levels with a glucose meter.
- After transferring the [18F]FDG tracer from the hot lab to the working room, set it up in the auto-dispensing and injection system (see Table of Materials).
- Recheck the following information (via the medical staff): patient ID number, name, birthday, height, and body weight; the name of the tracer, the amount of tracer (water with 3.5 mL of [18F]FDG tracer + 12 mL of saline), the programmed radioactivity (5 MBq/kg), the time of injection, the [18F]FDG tracer-lot number, the injection speed (normally, 0.3 mL/s), and the level of radioactivity that was measured in the hot lab.
- Record the automatic measurement of preinjected radioactivity that appears on the display of the auto-dispensing and injection system.
- Inject the [18F]FDG tracer via the intravenous route prepared in step 3.2 (3 h 30 min after the start).
- Record the residual volume of the [18F]FDG tracer, which is shown automatically on the display of the auto-dispensing and injection system.
- Have the patients wait in the waiting room of the radiation-controlled area for 50 min.
- Transfer the patients from the waiting room to the PET/CT machine (see Table of Materials). Record the brain images for 10 min (4 h 30 min after the start).
Note: The imaging parameters for [18F]FDG-PET/CT images are 10 min list mode. Reconstruct the data from 10-min bins. The data under 3 min are not used because the low-intensity signals are not adequate. Set the image reconstruction parameters: a block sequential regularized expectation maximization reconstruction algorithm (see Table of Materials); the matrix size = 192; the field of view = 25 cm; β-value: 100 - 200; z-axis filter: none. - After taking the images, check the injection area for extravasation. Discard all urine if the patient has a urinal catheter with urine bag.
- Remove the patient from the radiation-controlled area (4 h 50 min after the start).
Note: See Figure 1 for a schematic of the time schedule of events (patient procedure and synthesis of the [18F]FDG tracer).
4. Analysis of the [18F]FDG-PET/CT Images
- Evaluate all image data for a standardized uptake value (SUV) measurement using the imaging software (see Table of Materials).
- Select the patients.
- Assign the data to the MM oncology workflow.
- Click the button for Functional browsers.
- Click the VOI (volume of interest) threshold button.
- Set the VOI sphere to the three-dimensional browser.
Note: The maximum SUV (SUVmax) and mean SUV (SUVmean) are automatically measured for the VOI according to the chosen SUVmax threshold. Be sure to draw a border around the targeted VOI on the browser using the three-dimensional sphere, excluding other targets, extraocular muscles, and the scalp because they tend to disturb the set SUV threshold. Check the target area on axial, coronal, and sagittal slices. - After selecting all the right settings, click the Edit the measure button.
- Change the threshold value (e.g., 50%) of the VOI and click OK.
- Record the SUVmax, SUVmean, target volume, and threshold of the target area, which are automatically measured.
- To sterically visualize the glucose metabolism of the whole-brain surface, use the software (see Table of Materials) to set a color map for the [18F]FDG-PET/CT images based on blood glucose.
- Finally, compare the clinical assessment with the [18F]FDG-PET/CT images.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
A 63-year-old man who had been run over by a car while cycling was brought to the emergency room via ambulance. The examination revealed a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 7 (eye opening = 1, best verbal response = 2, best motor response = 4), anisocoria (right: 2 mm, and left: 3 mm), and a negative corneal response17. A CT of the head showed subarachnoid and intracranial hemorrhage and a skull fracture of the left zygoma, temporal bones, and parietal bones. Th...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
This protocol provides the means to conduct a series of brain-glucose metabolic assessments with [18F]FDG-PET/CT using self-produced [18F]FDG tracer at a single institution.
The production of [18F]FDG tracer follows the procedure described in the FDG synthesizer operator manual; however, caution is necessary regarding three points. First, the bombardment time and energy (step 2.5) should be adjusted according to the number of patients. Second, attention should ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Uchino in Sousen hospital for all procedures. The authors also thank Adam Phillips from the Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 20ml syringe | Terumo | SS-20ESZ | |
| 10ml syringe | Terumo | SS-10ESZ | |
| 1ml syringe | Terumo | SS-01T | |
| Protective plug | Top | ML-KS | |
| Three-way cock L type 180° | Terumo | TS-TL2K | |
| Extension tube | Top | X1-50 | |
| Indwelling needle 22G or 24G | Terumo | SR-OT2225C | |
| Tegaderm transparent dressing | 3M | 1624W | |
| Hepaflash 10U/ml 10ml | Terumo | PF-10HF10UA | |
| Auto dispensing and injection system | Universal Giken Co., Ltd. | UG-01 | |
| Fluid for auto dispensing and injection system | Universal Giken Co., Ltd. | UG-01-001 | |
| Millex-GS Syringe Filter Unit | Millipore | SLGSV255F | |
| Air needle | Terumo | XX-MFA2038 | |
| Check valve | Hakko | 23310100 | |
| Saline 500ml | HIKARI pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 18610155-3 | |
| Yukiban 25x7mm | Nitto | 3252 | |
| Elascot No.3 | Alcare | 44903221 | |
| Presnet No.3 27x20mm | Alcare | 11674 | |
| Steri Cotto a 4x4cm | Kawamoto | 023-720220-00 | |
| StatstripXp3 | Nova Biomedical | 11-110 | |
| Statstrip Glucose strips | Nova Biomedical | 11-106 | |
| JMSsheet | JMS | JN-SW3X | |
| Injection pad | Nichiban | No.30-N | |
| Stepty | Nichiban | No.80 | |
| Advantage Workstation | GE Healthcare | Volume Share 7. version 4.7 | |
| Discovery MI PET/CT | GE Healthcare | ||
| EV Insite | PSP | ||
| GE TRACERlab MXFDG synthesizer reagent kit | ABX | K-105TM | |
| TRACERlab MXFDG cassette | GE Healthcare | P5150ME | |
| Extension tube | Universal Giken Co., Ltd | AT511-ST-001 | |
| TSK sterilized injection needle 18x100 | Tochigiseiko | AT511-ST-004 | |
| TSK sterilized injection needle 18x60 | Tochigiseiko | AT511-ST-002 | |
| TSK sterilized injection needle 21x65 | Tochigiseiko | AT511-ST-003 | |
| Seal sterile vial -N 5ml | Mita Rika Kogyo Co., Ltd. | SSVN5CBFA | |
| k222 TLC plate | Universal Giken Co., Ltd. | AT511-01-005 | |
| Anion-cation test paper | Toyo Roshi Kaisha | 7030010 | |
| Endospecy ES-24S set | Seikagaku corporation | 20170 | |
| Sterile evacuated vial | Gi phama | 10214 | |
| 5ml syringe | Terumo | SS-05SZ | |
| Extension tube | Top | X-120 | |
| Finefilter F | Forte grow medical Co.Ltd. | F162 | |
| Millex FG | Merck | SLFG I25 LS | |
| Vented Millex GS | Merck | SLGS V25 5F | |
| Injection needle 18x38 | Terumo | NN-1838R | |
| Injection needle 21x38 | Terumo | NN-2138R | |
| Water-18O | Taiyo Nippon Sanso | F03-0027 | |
| Distilled water | Otsuka phrmaceutical | ||
| Hydrogen gas G1 | Hosi Iryou Sanki | ||
| Helium gas G1 | Hosi Iryou Sanki | ||
| Nitrogen G1 | Hosi Iryou Sanki | ||
| TRACERlabMXFDG | GE Healthcare | ||
| Sep-Pak Light Accell Plus QMA | WATERS | ||
| Sep-Pak Plus tC18 | WATERS | ||
| Sep-Pak Plus Alumina N | WATERS | ||
| HPLC with 3.9 X 300 mm columns | WATERS | ||
| US-2000 | Universal Giken CO. Ltd. | ||
| Kryptofix222 | Merck | ||
| EG Reader SV-12 | Seikagaku Corporation | ||
| UG-01 | Universal Giken Co., Ltd. | ||
| syngo.via | Siemens Healthineers | ||
| Advantage Workstation Volume Share 7, version 4.7 | GE Healthcare | ||
| Q clear | GE Healthcare | ||
| CRC-15PET dose calibrator | CAPINTEC, INC. |
References
- Godbolt, A. K., et al. Disorders of consciousness after severe traumatic brain injury: a Swedish-Icelandic study of incidence, outcomes and implications for optimizing care pathways. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 45 (8), 741-748 (2013).
- Klingshirn, H., et al. Quality of evidence of rehabilitation interventions in long-term care for people with severe disorders of consciousness after brain injury: A systematic review. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 47 (7), 577-585 (2015).
- Fischer, D. B., Truog, R. D. What is a reflex? A guide for understanding disorders of consciousness. Neurology. 85 (6), 543-548 (2015).
- Klingshirn, H., et al. RECAPDOC - a questionnaire for the documentation of rehabilitation care utilization in individuals with disorders of consciousness in long-term care in Germany: development and pretesting. BMC Health Services Research. 18 (1), 329(2018).
- Stéfan, A., Mathé, J. F. SOFMER group. What are the disruptive symptoms of behavioral disorders after traumatic brain injury? A systematic review leading to recommendations for good practices. Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation. 59, 5-17 (2016).
- Liu, S., et al. Multimodal neuroimaging computing: a review of the applications in neuropsychiatric disorders. Brain Informatics. 2 (3), 167-180 (2015).
- Wong, K. P., et al. A semi-automated workflow solution for multimodal neuroimaging: application to patients with traumatic brain injury. Brain Informatics. 3 (1), 1-15 (2016).
- Chennu, S., et al. Brain networks predict metabolism, diagnosis and prognosis at the bedside in disorders of consciousness. Brain. 140 (8), 2120-2132 (2017).
- Di Perri, C., et al. Neural correlates of consciousnes s in patients who have emerged from a minimally conscious state: a cross-sectional multimodal imaging study. The Lancet Neurology. 15 (8), 830-842 (2016).
- Erecińska, M., Silver, I. A. ATP and brain function. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 9 (1), 2-19 (1989).
- Lundgaard, I., et al. Direct neuronal glucose uptake heralds activity-dependent increases in cerebral metabolism. Nature Communications. 6, 6807(2015).
- Byrnes, K. R., et al. FDG-PET imaging in mild traumatic brain injury: a critical review. Frontiers in Neuroenergetics. 5, 13(2014).
- Mortensen, K. N., et al. Impact of Global Mean Normalization on Regional. Glucose Metabolism in the Human Brain. Neural Plasticity. , 6120925(2018).
- Wagatsuma, K., et al. Comparison between new-generation SiPM-based and conventional PMT-based TOF-PET/CT. Physica Medica. 42, 203-210 (2017).
- Fukukita, H., et al. Japanese guideline for the oncology FDG-PET/CT data acquisition protocol: synopsis of Version 2.0. Annals of Nuclear Medicine. 28 (7), 693-705 (2014).
- Varrone, A., et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine Neuroimaging Committee. EANM procedure guidelines for PET brain imaging using [18F]FDG, version 2. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 36 (12), 2103-2110 (2009).
- Teasdale, G., Jennett, B. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. The Lancet. 2 (7872), 81-84 (1974).
- Valadka, A. B. Injury to the cranium. Trauma. Moore, E. J., Feliciano, D. V., Moore, E. E. , McGraw-Hill. New York, NY. 377-399 (2000).
- Carney, N., et al. Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Fourth Edition. Neurosurgery. 80 (1), 6-15 (2017).
- Giacino, J. T., Kalmar, K., Whyte, J. The JFK Coma Recovery Scale-Revised: measurement characteristics and diagnostic utility. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 85 (12), 2020-2029 (2004).
- Schnakers, C., et al. The Nociception Coma Scale: a new tool to assess nociception in disorders of consciousness. Pain. 148 (2), 215-219 (2010).
- Shiel, A., et al. The Wessex Head Injury Matrix (WHIM) main scale: a preliminary report on a scale to assess and monitor patient recovery after severe head injury. Clinical Rehabilitation. 14 (4), 408-416 (2000).
- GE Healthcare. TRACERlabMXFDG operator manual, Version 1. , (2003).
- Yamaki, T., et al. Association between uncooperativeness and the glucose metabolism of patients with chronic behavioral disorders after severe traumatic brain injury: a cross-sectional retrospective study. BioPsychoSocial Medicine. 12, 6(2018).
- Schwaiger, M., Wester, H. J. How many PET tracers do we need? Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 52, Suppl 2, 36S-41S (2011).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved