A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Microplot Design and Plant and Soil Sample Preparation for 15Nitrogen Analysis
In This Article
Summary
A microplot design for 15N tracer research is described to accommodate multiple in-season plant and soil sampling events. Soil and plant sample collection and processing procedures, including grinding and weighing protocols, for 15N analysis are put forth.
Abstract
Many nitrogen fertilizer studies evaluate the overall effect of a treatment on end-of-season measurements such as grain yield or cumulative N losses. A stable isotope approach is necessary to follow and quantify the fate of fertilizer derived N (FDN) through the soil-crop system. The purpose of this paper is to describe a small-plot research design utilizing non-confined 15N enriched microplots for multiple soil and plant sampling events over two growing seasons and provide sample collection, handling, and processing protocols for total 15N analysis. The methods were demonstrated using a replicated study from south-central Minnesota planted to corn (Zea mays L.). Each treatment consisted of six corn rows (76 cm row-spacing) 15.2 m long with a microplot (2.4 m by 3.8 m) embedded at one end. Fertilizer-grade urea was applied at 135 kg N∙ha-1 at planting, while the microplot received urea enriched to 5 atom % 15N. Soil and plant samples were taken several times throughout the growing season, taking care to minimize cross-contamination by using separate tools and physically separating unenriched and enriched samples during all procedures. Soil and plant samples were dried, ground to pass through a 2 mm screen, and then ground to a flour-like consistency using a roller jar mill. Tracer studies require additional planning, sample processing time and manual labor, and incur higher costs for 15N enriched materials and sample analysis than traditional N studies. However, using the mass balance approach, tracer studies with multiple in-season sampling events allow the researcher to estimate FDN distribution through the soil-crop system and estimate unaccounted-for FDN from the system.
Introduction
Fertilizer nitrogen (N) use is essential in agriculture to meet the food, fiber, feed, and fuel demands of a growing global population, but N losses from agricultural fields can negatively impact environmental quality. Because N undergoes many transformations in the soil-crop system, a better understanding of N cycling, crop utilization, and the overall fate of fertilizer N are necessary to improve management practices that promote N use efficiency and minimize environmental losses. Traditional N fertilizer studies primarily focus on the effect of a treatment on end-of-season measurements such as crop yield, crop N uptake relative to the N rate applied (apparent fertilizer use efficiency), and residual soil N. While these studies quantify the overall system N inputs, outputs, and efficiencies, they cannot identify nor quantify N in the soil-crop system derived from fertilizer sources or the soil. A different approach using stable isotopes must be used to track and quantify the fate of fertilizer derived N (FDN) in the soil-crop system.
Nitrogen has two stable isotopes, 14N and 15N, that occur in nature at a relatively constant ratio of 272:1 for 14N/15N1 (concentration of 0.366 atom % 15N or 3600 ppm 15N2,3). The addition of 15N enriched fertilizer increases the total 15N content of the soil system. As 15N enriched fertilizer mixes with unenriched soil N, the measured change of 14N/15N ratio allows researchers to trace FDN in the soil profile and into the crop3,4. A mass balance can be calculated by measuring the total amount of 15N tracer in the system and each of its parts2. Because 15N enriched fertilizers are significantly more expensive than conventional fertilizers, 15N enriched microplots are often embedded within the treatment plots. The purpose of this methods paper is to describe a small-plot research design utilizing microplots for multiple in-season soil and plant sampling events for corn (Zea mays L.) and to present protocols for preparing plant and soil samples for total 15N analysis. These results can then be used to estimate N fertilizer use efficiency and create a partial N budget accounting for FDN in the bulk soil and the crop.
Protocol
1. Field site description
NOTE: When performing 15N tracer field trials, selected sites should minimize variation due to soil, topography, and physical features5. Cross-contamination may occur following lateral soil movement due to slope, wind or water translocation, or tillage while the vertical distribution of soil N may be impacted by subsurface water flow and tile-drainage6.
- Describe the experimental field site including past management (e.g., previous crops and tillage), latitude and longitude, soil physical and chemical properties (e.g., soil textural analysis, initial fertility conditions, pH, and soil bulk density).
- Record GPS coordinates for the research site and the field corners.
- Describe growing season management including pest and disease management (herbicide, insecticide, or fungicide use), soil fertility management (including rate, source, placement, and application timing), tillage, irrigation events and amounts, and residue management.
- As crop growth and microbe mediated N transformations are affected by soil moisture, soil temperature, and air temperature, record climate information including daily high and low temperatures, daily precipitation, and soil moisture and temperatures at several depths that reflect the soil sampling depths.
2. Plot design
- Plant six corn rows (~86,000 plants ha-1) on 76 cm spacing with a final plot dimension of 15.2 m by 4.6 m.
- Establish border areas 1.5 m from each end of the lengthwise dimension (0-1.5 m, 13.7-15.2 m) and an additional border area 1.5 m long (9.8-11.3 m) adjoining the sampling and harvest areas (Figure 1).
- Designate rows 2 and 3 as the in-season plant and soil sampling area (1.5-9.8 m) and rows 4 and 5 as the harvest area (1.5-9.8 m) for corn grain yield.
- Establish a microplot area (11.3-13.7 m) with dimensions of 2.4 m by 3.8 m centered on the width dimension. Collect all 15N enriched plant and soil samples from this area, leaving 0.38 m of unsampled border on the length and width dimensions to minimize edge effects (Figure 2).
- Delineate the treatment plot and microplot corners with different colored flags.
3. Soil and plant sample precautions
- Use dedicated equipment and processing areas for unenriched and enriched materials. Contamination of unenriched materials (fertilizer, soil, or plant) by enriched materials and vice versa can drastically affect results.
- Collect and process 15N enriched soil and plant samples in order of lowest to highest 15N expected enrichment to minimize cross-contamination. Ensure that work surfaces, gloves, utensils, and machinery are thoroughly cleaned between each sample to minimize cross-contamination from sample carryover.
- Minimize foot traffic in microplots to prevent contamination of unenriched sampling areas. Wear protective shoe coverings when accessing microplots and remove them when exiting the microplot area.
4. 15N enriched fertilizer preparation and application
- Following guidelines put forth by Ref. 2 for fertilizer 15N use efficiency (F15NUE) studies, dilute 10 atom % 15N enriched urea to 5 atom % 15N enriched urea and dissolve in 2 L of deionized water to ensure uniform enrichment of urea fertilizer.
NOTE: The required concentration of 15N enriched fertilizer is dependent on the goals of the agronomic study. If the concentration of stock 15N enriched fertilizer exceeds the researcher's requirements, the stock fertilizer concentration may be diluted with similar conventional fertilizer using the following formula3.
X2 = [(C1/C2) - 1] × X1
X2 is the mass of the conventional unenriched fertilizer, X1 is the mass of the tracer fertilizer, C1 is the isotopic concentration [expressed as atom % excess (measured atom % enrichment minus the natural background concentration assumed to be 0.3663 atom %)] of the original tracer fertilizer, and C2 is the isotopic concentration of the final mixture. As an example, given 100 g of 10 atom % enriched urea, 92.7 g of conventional unenriched fertilizer would be required for a final isotopic concentration of 5 atom %;
X2 = {[(10-0.3663)/5] - 1} × 100. - Analyze the solution for 15N concentration to verify enrichment. The authors utilized the analytical services provided by UC Davis Stable Isotope Facility.
NOTE: Reactions of the soil-plant-microbe regime to fertilizer additions may be affected by the physical form of fertilizer. Depending on the goals of the study, the urea solution may be applied as a liquid or dehydrated to reform crystals. The crystals may be compacted into a cake using a Carver press at 10,000 psi, followed by crushing the cake and screening the particles to the desired size3. - Evenly apply the 15N enriched urea solutions to the microplots using a calibrated backpack CO2 sprayer (Figure 3A). If multiple N rates or enrichment levels are used, consider using designated CO2 sprayers for each enrichment level or use a single sprayer and apply solutions from the lowest to the highest enrichment to minimize treatment cross-contamination.
- Incorporate urea-containing fertilizers with light tillage, hand rakes, or at least 0.6 cm of irrigation within 24 h of application to minimize volatilization loss potential.
- No additional 15N enriched urea fertilizer is applied to the microplot during the second growing season. Apply conventional unenriched urea to the entire treatment to avoid a differential response in corn growth due to nitrogen.
5. Field sample processing: aboveground corn biomass
- At each sampling stage, collect a six-aboveground corn plant composite sample from within the sampling area (15N unenriched) and a six-aboveground corn plant composite sample from the 15N enriched microplot. At least two plants should separate each sampled plant to avoid significantly altering plant growth dynamics. The authors collected plant samples at the V8 and R1 corn physiological development stages11 and at physiological maturity (Figure 2).
- Following the principles described in steps 3.1 and 3.2, chop V8 and R1 aboveground biomass (≤5 cm by ≤5 cm); a yard waste chipper is a satisfactory option. Place chopped biomass in labeled fabric or paper bags and dry in a forced-air oven at 60 °C until constant mass. Record the biomass dry weight (Figure 3B).
- Partition physiologically mature corn plants into stover (all vegetative tissues including leaves, husks, and stalks), grain, and cob fractions. Chop and dry in a forced-air oven at 60 °C until constant mass. Record the biomass dry weight.
- Within the microplot, cut all corn stalks at the soil surface, tie into a bundle, label according to plot, and remove from the field (Figure 3C). Adjust microplot corner flags to be nearly flush with the soil surface to minimize the risk of removal by the combine during harvest or tillage post-harvest.
- Harvest grain from the harvest area and report yield at 15.5% moisture content12. Harvest remaining research areas with a plot combine.
- Rake unenriched biomass from off the microplot area. Chop and reapply microplot aboveground biomass to the correct plot (Figure 3D).
- Incorporate residue into the soil surface with tillage taking care to minimize soil and corn residue transport into or out of the microplot area. Replace any microplot corner flags removed due to tillage.
- Plant second-year corn on the same rows as the first-year corn.
- Collect second-year aboveground corn biomass only at physiological maturity and process like first-year corn samples as described in step 5.3. Collect microplot samples from the center of the microplot area (1.52 m by 0.76 m) to avoid any potential signal dilution following tillage (Figure 2). Harvest grain from the harvest area and report yield at 15.5% moisture content.
- Following the principles of steps 3.1 and 3.2, thoroughly mix and grind 100 to 200 g of dried plant material to pass through a 2 mm sieve. Thoroughly mix the ground material and store a subsample in a labeled coin envelope for further processing.
NOTE: A Thomas Wiley mill is a satisfactory option for plant tissue grinding while a Perten Laboratory Mill 3610 is a satisfactory option for grinding grain.
CAUTION: People grinding plant samples should wear ear protection and be protected from inhaling dust by wearing a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health approved N95 Particulate Filtering Facepiece Respirator.
6. Field sample processing: soil
- Collect first-year soil samples 8 days after 15N enriched fertilizer application, V8, R1, and post-harvest before tillage. Collect second-year soil samples at pre-plant and post-harvest. Due to logistical sampling constraints, the authors collected in-season soil samples at 0- to 15-, 15- to 30-, and 30- to 60-cm depths, post-harvest soil samples at 0- to 15-, 15- to 30-, 30- to 60-, and 60- to 90-cm depths, and second-year pre-plant soil samples at 0- to 30-, 30- to 60-, 60- to 120- cm depths.
NOTE: If a soil probe is unable to collect a soil core to the deepest desired depth as a single core, collect deeper depth cores from the same boreholes as the upper depths discarding the top 1-cm of soil to avoid contamination from soil falling from upper depths.- Collect a four-core (1.8-cm diameter) composite soil sample from the unenriched sampling area at V8 and R1 using a hand probe. Collect one core in the corn row and three cores between the corn rows.
- Collect a two-core (5-cm diameter) composite soil sample from the unenriched sampling area at pre-plant and post-harvest using a hydraulic probe.
- Collect a 15-core (1.8-cm diameter) composite soil sample from the microplot area 8 days after 15N enriched fertilizer application, V8, and R1 using a hand probe. Collect three to four cores in the corn row and 11 to 12 cores between the corn rows.
NOTE: Soils are extremely heterogeneous. The greater number of cores collected from within the enriched microplot provides a better estimate of the true 15N enrichment of soil N13. - Collect a three-core (5-cm diameter) composite soil sample from the microplot area at pre-plant and post-harvest using a hydraulic probe.
- Homogenize each composite soil sample in a bucket and place it in a pre-labeled paper bag.
- Dry soil samples at 35 °C in a forced-air oven until constant mass. Grind each sample to pass through a 2 mm sieve. A mechanical soil grinder is satisfactory if it can be thoroughly cleaned between each sample.
NOTE: Soil samples may be air-dried by spreading samples on trays in a thin layer. Trays should be in an area free from contamination by outside N sources. Unenriched and enriched samples should be physically separated to prevent cross-contamination.
CAUTION: People grinding soil samples should wear ear protection and be protected from inhaling dust by wearing a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health approved N95 Particulate Filtering Facepiece Respirator.
7. Lab sample processing: grind soil and plant samples
- Dry ground plant samples (2 mm) overnight in an oven at 60 °C.
- Following the principles described in step 3, grind dried plant samples or soil material to a fine, flour-like consistency. A roller jar mill is a satisfactory option.
NOTE: The authors' jar mill is a custom-built conveyor belt system that can process 54 roller jars at a time.- Fill each roller jar (250 mL borosilicate glass jar with a screw-top lid) with 10 to 20 g of ground plant or soil sample and seven stainless steel rods (8.5 cm long, 0.7 cm diameter).
- Roll roller jars at 0.4 x g for 6-24 h or until samples have a fine, flour-like consistency.
- Transfer the finely ground material into a clean, labeled 20 mL scintillation vial.
- Between each sample, wash roller jars, stainless steel rods, and lids with soap and water to remove any residue.
- Immerse roller jars and lids in a 5% HCl acid bath (prepared from 36-38% concentrated stock) overnight14.
CAUTION: Hydrochloric acid is corrosive. It can cause severe skin burns, eye damage, and is harmful if inhaled. Always wear protective clothing, gloves, and eye and face protection. Flush contacted tissue thoroughly with water. Always use a secondary container when transporting acids. Always add acid to water as this reaction is exothermic. Immediately neutralize acid spills with baking soda.
NOTE: A large acid bath may be prepared as 100 L of 5% HCl in a 208 L plastic container. Prepare several smaller volumes in a fume hood and then transfer the solutions to the plastic container. Replace the solution every three months. - Triple rinse roller jars and lids with deionized water and air dry.
- Immerse stainless steel rods in a 0.05 M NaOH bath (prepared by dissolving 2 g of NaOH in 1 L of deionized water) overnight14. Prepare a new 0.05 M NaOH bath each day.
CAUTION: Sodium hydroxide can cause severe skin burns and eye damage. Always wear protective clothing and eye protection. Immediately remove contaminated clothing and rinse skin or eyes with water for several minutes. - Rinse the rods under running hot tap water for 5 minutes. Decant and triple rinse the rods with deionized water. Allow the rods to air dry on a paper towel-lined tray.
- Immerse roller jars and lids in a 5% HCl acid bath (prepared from 36-38% concentrated stock) overnight14.
8. Weigh ground plant and soil samples for total N and 15N analysis
- Analyze a few representative plant and soil samples for total N content (e.g., combustion analysis15). Calculate the sample mass that provides adequate N content for 15N analysis according to the analyzer specifications.
NOTE: The authors utilized the analytical services provided by UC Davis Stable Isotope Facility. Enriched sample weights were optimized for 20 µg of N with a maximum of 100 µg of N. - Organize like-samples from lowest to highest expected 15N enrichment. Duplicate every eighth to twelfth sample in each run to check sample precision. Include at least one check sample per run16.
- Label a clean 96-well plate and fitted lid with individual well evaporation rings. Cut a clean index card to fit just inside the lid to prevent sample movement between wells during transport.
- Wearing nitrile gloves, clean the microscale, work surfaces, spatula, and forceps with laboratory wipes and ethanol. Place cleaned utensils on a Kimwipe on the lab bench.
NOTE: Unenriched and enriched samples should be processed using separate scales and utensils to prevent cross-contamination. - Use forceps to place a pre-formed 5 mm x 9 mm tin capsule on a clean work surface, such as a stainless steel block with 5 mm x 8 mm well. Gently tap the capsule into the well to reform the cylindrical shape and flatten the bottom of the capsule if needed.
NOTE: Because sample masses will be very small, the risk of sample contamination is high. Never touch the capsules with gloves. Discard the capsule if it touches any surface other than the forceps, clean work surface, scale weigh pan, or 96-well plate. - Use forceps to gently flare out the top 1 mm of the capsule to facilitate manipulation. To avoid scale damage when taring the weight of the capsule, hover and release the capsule 1 to 2 mm above the microscale weigh pan. Tare the capsule. Use forceps to return the capsule to the clean work surface.
- Use a spatula to carefully add the required mass of finely ground sample material to the capsule. Avoid spilling sample material on the outside surface of the capsule or the work surfaces.
- Using forceps, slowly crimp the top third of the capsule and fold over to seal. Using forceps, continue to fold and compress the capsule into a spherical shape taking care not to puncture or tear the tin.
NOTE: Samples with low N content may require sample volumes that exceed the capacity of the 5x9 mm capsule. Larger capsules (e.g., 9 mm x 10 mm) may be used in these instances. - Use forceps to drop the wrapped capsule several times from a height of 1 cm onto a clean, dark surface or mirror to check for leaks. If no dust appears, weigh the sample using the same technique as described in step 8.6. Record the sample weight. Place the capsule in a 96-well plate and record the well placement.
- If dust appears on the dark surface, record the sample weight. Wrap the sample in a second tin capsule, recheck for leaks, and place it in a clean 96-well plate.
NOTE: If the wrapped capsule is too large to fit in a 96-well plate, use a 24- or 48-well plate.
- If dust appears on the dark surface, record the sample weight. Wrap the sample in a second tin capsule, recheck for leaks, and place it in a clean 96-well plate.
- Between samples, clean each of the utensils and surfaces with ethanol and laboratory wipes paying especial attention to the spatula and forceps edges.
- Secure the lid to the 96-well plate using tape and store in a desiccator.
9. Calculations
- Calculate the mass of N (kg∙ha-1) contained in the plant or soil samples using the following equations.
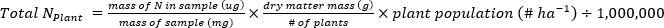
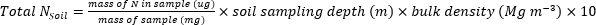
- Calculate the fertilizer N fraction (Nf), fertilizer derived N (FDN), and soil derived N (SDN) for plant and soil samples17.
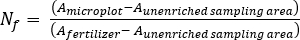
where A is the atom % 15N enrichment. 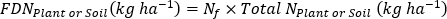
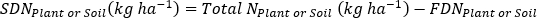
- Calculate fertilizer 15N use efficiency17.

Results
The results presented in this paper come from a field site established in 2015 at the University of Minnesota Southern Outreach and Research Center located near Waseca, MN. The site was managed as a corn-soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr] rotation prior to 2015 but was managed as a corn-corn rotation during the 2015 and 2016 growing seasons. The soil was a Nicollet clay loam (fine-loamy, mixed, superactive, mesic Aquic Hapludolls)-Webster clay loam (fine-loamy, mixed, superactive, m...
Discussion
Stable isotope research is a useful tool for tracking and quantifying FDN through the soil-crop system. However, there are three main assumptions associated with N tracer studies that if violated may invalidate conclusions drawn from using this methodology. They are 1) the tracer is uniformly distributed throughout the system, 2) processes under the study occur at the same rates, and 3) N leaving the 15N enriched pool does not return3. Because this study is interested in the distributio...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of the Minnesota Corn Research & Promotion Council, the Hueg-Harrison Fellowship, and the Minnesota's Discovery, Research and InnoVation Economy (MnDRIVE) Fellowship.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 20 mL scintillation vial | ANY; Fisher Scientific is one example | 0334172C | |
| 250 mL borosilicate glass bottle | QORPAK | 264047 | |
| 48-well plate | EA Consumables | E2063 | |
| 96-well plate | EA Consumables | E2079 | |
| Cloth parts bag (30x50 cm) | ANY | NA | For corn ears |
| CO2 Backpack Sprayer | ANY; Bellspray Inc is one example | Model T | |
| Coin envelop (6.4x10.8 cm) | ANY; ULINE is one example | S-6285 | For 2-mm ground plant samples |
| Corn chipper | ANY; DR Chipper Shredder is one example | SKU:CS23030BMN0 | For chipping corn biomass |
| Corn seed | ANY | NA | Hybrid appropriate to the region |
| Disposable shoe cover | ANY; Boardwalk is one example | BWK00031L | |
| Ethanol 200 Proof | ANY; Decon Laboratories Inc. is one example | 2701TP | |
| Fabric bags with drawstring (90x60 cm) | ANY | NA | For plant sample collection |
| Fertilizer Urea (46-0-0) | ANY | NA | ~0.366 atom % 15N |
| Hand rake | ANY; Fastenal Company is one example | 5098-63-107 | |
| Hand sickle | ANY; Home Depot is one example | NJP150 | For plant sample collection |
| Hand-held soil probe | ANY; AMS is one example | 401.01 | |
| Hydraulic soil probe | ANY; Giddings is one example | GSPS | |
| Hydrochloric acid, 12N | Ricca Chemical | R37800001A | |
| Jar mill | ANY; Cole-Parmer is one example | SI-04172-50 | |
| Laboratory Mill | Perten | 3610 | For grinding grain |
| Microbalance accurate to four decimal places | ANY; Mettler Toledo is one example | XPR2 | |
| N95 Particulate Filtering Facepiece Respirator | ANY, ULINE is one example | S-9632 | |
| Neoprene or butyl rubber gloves | ANY | NA | For working in HCl acid bath |
| Paper hardware bags (13.3x8.7x27.8 cm) | ANY; ULINE is one example | S-8530 | For soil samples and corn grain |
| Plant grinder | ANY; Thomas Wiley Model 4 Mill is one example | 1188Y47-TS | For grinding chipped corn biomass to 2-mm particles |
| Plastic tags | ULINE | S-5544Y-PW | For labeling fabric bags and microplot stalk bundles |
| Sodium hydroxide pellets, ACS | Spectrum Chemical | SPCM-S1295-07 | |
| Soil grinder | ANY; AGVISE stainless steel grinder with motor is one example | NA | For grinding soil to pass through a 2-mm sieve |
| Tin capsule 5x9 mm | Costech Analytical Technologies Inc. | 041061 | |
| Tin capsule 9x10 mm | Costech Analytical Technologies Inc. | 041073 | |
| Urea (46-0-0) | MilliporeSigma | 490970 | 10 atom % 15N |
References
- Sharp, Z. . Principles of Stable Isotope Geochemistry. , (2017).
- Van Cleemput, O., Zapata, F., Vanlauwe, B. Guidelines on Nitrogen Management in Agricultural Systems. Guidelines on Nitrogen Management in Agricultural Systems. 29 (29), 19 (2008).
- Hauck, R. D., Meisinger, J. J., Mulvaney, R. L. Practical considerations in the use of nitrogen tracers in agricultural and environmental research. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2-Microbiological and Biochemical Properties. , 907-950 (1994).
- Bedard-Haughn, A., Van Groenigen, J. W., Van Kessel, C. Tracing 15N through landscapes: Potential uses and precautions. Journal of Hydrology. 272 (1-4), 175-190 (2003).
- Peterson, R. G. . Agricultural Field Experiments: Design and Analysis. , (1994).
- Follett, R. F. Innovative 15N microplot research techniques to study nitrogen use efficiency under different ecosystems. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis. 32 (7/8), 951-979 (2001).
- Russelle, M. P., Deibert, E. J., Hauck, R. D., Stevanovic, M., Olson, R. A. Effects of water and nitrogen management on yield and 15N-depleted fertilizer use efficiency of irrigated corn. Soil Science Society of America Journal. 45 (3), 553-558 (1981).
- Schindler, F. V., Knighton, R. E. Fate of Fertilizer Nitrogen Applied to Corn as Estimated by the Isotopic and Difference Methods. Soil Science Society of America Journal. 63, 1734 (1999).
- Stevens, W. B., Hoeft, R. G., Mulvaney, R. L. Fate of Nitrogen-15 in a Long-Term Nitrogen Rate Study. Agronomy Journal. 97 (4), 1037 (2005).
- Recous, S., Fresneau, C., Faurie, G., Mary, B. The fate of labelled 15N urea and ammonium nitrate applied to a winter wheat crop. Plant and Soil. 112 (2), 205-214 (1988).
- Abendroth, L. J., Elmore, R. W., Boyer, M. J., Marlay, S. K. . Corn Growth and Development. , (2011).
- Gomez, K. A., Gomez, A. A. . Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research. , (1984).
- Khan, S. A., Mulvaney, R. L., Brooks, P. D. Diffusion Methods for Automated Nitrogen-15 Analysis using Acidified Disks. Soil Science Society of America Journal. 62 (2), 406 (1998).
- Horneck, D. A., Miller, R. O. Determination of Total Nitrogen in Plant Tissue. Handbook of Reference Methods for Plant Analysis. , 75-84 (1998).
- . Carbon (13C) and Nitrogen (15N) Analysis of Solids by EA-IRMS Available from: https://stableisotopefacility.ucdavis.edu/13cand15n.html (2019)
- Stevens, W. B., Hoeft, R. G., Mulvaney, R. L. Fate of Nitrogen-15 in a Long-Term Nitrogen Rate Study: II. Nitrogen Uptake Efficiency. Agronomy Journal. 97 (4), 1046 (2005).
- . Fertilizing Corn in Minnesota Available from: https://extension.umn.edu/crop-specific-needs/fertilizing-corn-minnesota (2018)
- Blake, G. R., Hartge, K. H. Bulk Density. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Methods. , 363-375 (1986).
- Jokela, W. E., Randall, G. W. Fate of Fertilizer Nitrogen as Affected by Time and Rate of Application on Corn. Soil Science Society of America Journal. 61 (6), 1695 (2010).
- Hart, S. C., Stark, J. M., Davidson, E. A., Firestone, M. K. Nitrogen Mineralization, Immobilization, and Nitrification. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Microbiological and Biochemical Properties. (5), 985-1018 (1994).
- Olson, R. V. Fate of tagged nitrogen fertilizer applied to irrigated corn. Soil Science Society of America Journal. 44 (3), 514-517 (1980).
- Follett, R. F., Porter, L. K., Halvorson, A. D. Border Effects on Nitrogen-15 Fertilized Winter Wheat Microplots Grown in the Great Plains. Agronomy Journal. 83 (3), 608-612 (1991).
- Balabane, M., Balesdent, J. Input of fertilizer-derived labelled n to soil organic matter during a growing season of maize in the field. Soil Biology and Biochemistry. 24 (2), 89-96 (1992).
- Recous, S., Machet, J. M., Mary, B. The partitioning of fertilizer-N between soil and crop: Comparison of ammonium and nitrate applications. Plant and Soil. 144 (1), 101-111 (1992).
- Bigeriego, M., Hauck, R. D., Olson, R. A. Uptake, Translocation and Utilization of 15N-Depleted Fertilizer in Irrigated Corn. Soil Science Society of America Journal. 43 (3), 528 (1979).
- Glendining, M. J., Poulton, P. R., Powlson, D. S., Jenkinson, D. S. Fate of15N-labelled fertilizer applied to spring barley grown on soils of contrasting nutrient status. Plant and Soil. 195 (1), 83-98 (1997).
- Khanif, Y. M., Cleemput, O., Baert, L. Field study of the fate of labelled fertilizer nitrate applied to barley and maize in sandy soils. Fertilizer Research. 5 (3), 289-294 (1984).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved