A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Systematic Scoring Analysis for Intestinal Inflammation in a Murine Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis Model
In This Article
Summary
Systematic scoring of intestinal inflammation using a free computer-assisted system is a powerful tool to quantitatively compare histopathological changes in colitis models characterized by the presence of ulcers and inflammatory changes. Histological colitis score evaluation strengthens clinical observations and facilitates data interpretation.
Abstract
Murine colitis models are tools that are extensively employed in studies focused on understanding the pathobiology of inflammatory intestinal disorders. However, robust standards for objective and reproducible quantification of disease severity remain to be defined. Most colitis analysis methods rely on limited histological scoring of small segments of intestine, leading to partial or biased analyses. Here, we combine high-resolution image acquisition and longitudinal analysis of the entire colon to quantify intestinal injury and ulceration in the dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) induced model of murine colitis. This protocol allows for the generation of objective and reproducible results without extensive user training. Here, we provide comprehensive details on sample preparation and image analysis using examples of data from DSS induced colitis. This method can be easily adapted to other models of murine colitis that have significant inflammation associated with mucosal injury. We demonstrate that the fraction of inflamed/injured and eroded/ulcerated mucosa relative to the complete length of the colon closely parallels clinical findings such as weight loss amid DSS-induced disease progression. This histological protocol provides a reliable time and cost-effective aid to standardize analyses of disease activity in an unbiased way in DSS colitis experiments.
Introduction
The gastrointestinal epithelial barrier plays a pivotal role in separating luminal antigens and pathogens from underlying tissue compartments1. Epithelial injury and mucosal wounds seen in pathologic conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), ischemia, or surgical injury are associated with clinical symptoms that include diarrhea, weight loss, blood in stool, and abdominal pain. In response to injury, epithelial cells migrate and proliferate to re-epithelialize and repair mucosal barrier defects. Resolution of inflammation and restitution of mucosal integrity are crucial to re-establishing intestinal mucosal homeostasis and function2,3,4.
Various animal models have been employed to study the underlying molecular mechanisms that are associated with the damage to the intestinal epithelial barrier. Well-established and easily applicable models of chemically induced colitis are widely used, particularly in studies related to inflammatory injury such as IBD. A common, reproducible, and reliable murine colitis model employs dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) mediated colonic injury and inflammation. The severity of disease varies depending upon mouse strain, dose of DSS, length of DSS administration, and molecular weight of DSS5,6,7.
Intestinal mucosal damage during DSS colitis is usually evaluated using the Disease Activity Index (DAI), a composite score determined by weight loss, fecal blood content, and stool consistency. The fecal blood content can be microscopic (detected using a stool guaiac acid test) or macroscopic; fecal consistency is classified as hard, soft, or liquid (i.e., diarrhea)5,8. Scoring of these clinical parameters can be subjective and may vary depending on the user's experience and bias, although overall, the data provides reliable information and is thus widely used by IBD researchers. In contrast, there is no generally accepted method for histological evaluation of mucosal damage. Most commonly, selected areas of the colon are inspected by a trained pathologist and scored based on several parameters that usually include crypt injury and leukocyte infiltration9,10,11. However, because the number of investigated parameters and the amount of tissue analyzed varies considerably between individual reports, comparability of many published studies is limited. To reduce observer bias and enhance inter-study concordance, an ideal histological scoring protocol should: 1) include the entire length of the colon, as intestinal mucosal inflammation is most often variable and skip lesions are common, 2) limit analysis to specific key and easily interpretable parameters to reduce subjectivity, 3) facilitate fast, consistent processing of large numbers of samples, and 4) use widely available and affordable tools for data acquisition, analysis and presentation.
Here we describe a technique to process the entire colon or long segments of the small intestine in a "Swiss roll" configuration along with the use of a free computer-assisted scoring system to analyze intestinal mucosal inflammation and damage because of DSS-induced colitis.
Protocol
All animal experiments described were approved by the University of Michigan's Committee on the Use and Care of Animals.
1. Tissue harvest
- Euthanize mice humanely using isoflurane anesthesia followed by cervical dislocation, in accordance with approved protocols. For all animal experiments, approval was obtained by a certified review board in accordance with the National and Institutional guidelines for animal handling.
- Place the mouse on a dissecting pad in a supine position. Immobilize mouse extremities using 20 G x 1 1/2-inch G needles.
- Using forceps and scissors, make a small incision on the abdominal skin and pull it to the side to expose the peritoneum.
- Open the abdominal cavity with a midline incision in the peritoneum from the pubic bone to the sides of the abdomen.
- Carefully remove tissues and organs until large intestine is visualized. Cut the pelvic bone on both sides of the colon to fully visualize the organ, extending from the anus towards the cecum.
- Gently remove fat, small veins and arteries attached to the colon, while carefully dissecting the organ, cutting just proximal to the anus and just distal to the cecum.
NOTE: The dissected colon should remain at room temperature while completing the Swiss roll procedure. - Carefully flush the colon with 1x PBS, using a flexible plastic gavage needle inserted through the anus to remove fecal contents.
- Position the colon in a straight line, and open longitudinally along the mesenteric artery. Bisect the colon longitudinally from the distal to the proximal end (Figure 1A). One half of the tissue can be used for histological analysis while the other can be processed for western blot, PCR or rolled into a second Swiss roll for fresh frozen immunofluorescence microscopy12.
2. Preparation of swiss rolls
- Trim extra tissue from the proximal colon using a razor blade until approximately the same width along the length of the whole colon is obtained.
- Align the colon to expose the lumen facing-up, and flatten the tissue completely using a flexible gavage needle. Add more PBS, if needed, to keep the tissue moist throughout the procedure.
- Remove the excess of PBS using a paper wipe. With a syringe and gavage needle, add 10% neutral buffered formalin solution over the tissue for 2-3 min to fix and flatten the tissue.
- Use straight forceps to grab the end of the distal colon and twist the colon into concentric circles from the distal to proximal end (Figure 1B).
NOTE: It is possible to push back the inside of the Swiss roll while rolling using the forefinger to ensure the tissue is inside the roll. - Insert a 27 G needle to pin the colon in the middle to hold its Swiss roll shape (Figure 1C).
- Place the Swiss roll with the needle into an embedding cassette inside a histologic specimen container.
NOTE: Tissue must be oriented in parallel with respect to the cassette before fixation (Figure 1D). - Fix the tissue in 10% neutral buffered formalin solution overnight at 4 °C13.
- After overnight fixation, wash the tissue 3x with PBS.
- Add 70% ethanol to the tissue prior to the paraffin embedding process. Remove the needle from the Swiss roll before proceeding. Tissue can be stored in ethanol at room temperature until paraffin embedment13.
- Place samples into the tissue processor, embed in paraffin, and prepare 4 µm sections, mounted on positively charged microscopy slides (Figure 1E). This can be an optional stop point.
NOTE: Proper tissue orientation is critical to achieve sections suitable for image analysis. Parallel Swiss roll embedding in the paraffin cassette will result in full sections appropriated for image analysis (Figure 1F-1H). Oblique sections must be avoided to prevent incomplete sections (Figure 1I-1K). For more details, see the Discussion section. - Stain sections with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)13.
3. Digital scanning and analysis
NOTE: For accurate evaluation of mucosal changes, select only sections that include at least 90% of the total colon length.
- Scan stained sections using a slide scanner or imager (see Table of Materials). Images produced need a resolution of 0.25 microns per pixel with 40x objective and 40x magnification.
- Install and download an appropriate software for digital analysis of scanned slides (see Table of Materials).
- Open scanned images in the image processing software (Figure 2A). Verify that the entire colon is visible and that there are no missing areas of the sample.
- Activate the label imager and scale bar tools to properly identify scanned slides by clicking Label imager (Figure 2A).
- Open the annotations tool by clicking Annotations, (Figure 2A) and create 3 different layers by clicking New layer (Figure 2B) to quantify the total length the Swiss roll, inflammation/injury, and erosion/ulceration. Choose a different color for each layer by clicking Layer color (Figure 2B).
- Measure the length of each layer/category by clicking the Pen tool (Figure 2A), using the muscularis mucosa as a reference:
- View the image at 400 µm zoom (or more) to facilitate adequate visualization of the muscularis mucosa.
NOTE: Magnification is easily controlled using the mouse scroll wheel and will need to be adjusted as necessary while moving across the section to draw all the lines. - Click on the Pen tool to draw a line following the muscularis mucosa (Figure 2A). Move the pointer as needed to visualize the adjacent area for analysis.
NOTE: Each time that the pen is stopped, a small new layer region will be generated. It can be visualized and edited with the Layer regions tab (select desired segment and click Delete Layer in case of mistakes or corrections, Figure 2B).
- View the image at 400 µm zoom (or more) to facilitate adequate visualization of the muscularis mucosa.
- Once all layers (Figure 2C) are defined, export the data using the Export Grid to Text File button inside the layer regions options (Figure 2B).
NOTE: Save files often while creating the layers to ensure data is properly stored. - Open the text files and copy the data with a spreadsheet software. Total all the segments from each region and calculate percentage of injury and ulceration with respect to total length.
- To calculate the Histological Colitis Score (HCS) and to evaluate the severity of disease, consider three main characteristics as detailed below.
- Check for healthy intestinal mucosa which is characterized by organized epithelial cells in the crypt-luminal axis, lamina propria with few immune cells, and subjacent muscularis mucosa that interfaces the mucosa and submucosa (Figure 3A).
- Check for inflammation/injury which is characterized by epithelial crypts that are attenuated or partially missing epithelial cells and mucosal inflammation with neutrophil infiltration into crypts (Figure 3B).
- Check for the presence of erosion/ulceration which is characterized by areas devoid of surface epithelium or areas completely lacking epithelial crypts with or without associated leukocytes (Figure 3C).
- Calculate HCS of injured and ulcerated regions expressed as a percentage of the total length in the following formula:
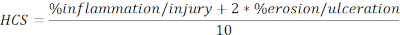
NOTE: HCS combines the percentage of inflammation/injury and erosion/ulceration adding a factor of two to the latter, based on a reasonable assumption that complete loss of the epithelium results in maximum loss of barrier integrity and hence worse disease. HCS consistently represents the morphological changes caused by DSS induced experimental colitis. Interestingly, we have not seen a clear correlation between the numbers of colonic lymphoid aggregates or follicles and clinical disease severity in DSS colitis and, therefore, we did not include the quantification in this analysis. - Take a snapshot of the representative images (click Snapshot, Figure 2A), and save. Include scale bars if needed by clicking on Show/Hide Scale Bar (Figure 2A).
Results
To illustrate the reliability of this Histological Colitis Score Analysis in the context of mucosal damage after DSS challenge and subsequent recovery from colitis, we administered 2.5% DSS in the drinking water of eight 10 weeks old male C57BL6 wild type mice for 5 days followed by a recovery period with regular water for 5 days. There was no change in body weight during the acute administration of DSS, from day 0 to 5 (Figure 4A). Body weight dramatically d...
Discussion
Our Histological Colitis Score system constitutes a reliable tool to quantify tissue inflammation and damage in the intestine. This approach provides an improved understanding of the histopathological state of the whole organ without the bias of selecting small areas or incomplete sections. Among the critical steps to successfully execute this protocol are proper preparation of Swiss rolls that allow for analysis of at least 90% of the length of the colon; parallel orientation during paraffin embedding and sectioning to ...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge support from NIH funding DK055679, DK089763, DK079392, DK061739, DK072564 and the University of Michigan Pathology Slide Scanning Services.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Aperio AT2 – High Volume, Digital Whole Slide Scanning | Leica Biosystems | Aperio AT2 | |
| Absorbent Underpads with waterproof moisture barrier | VWR International | 56616-032 | |
| American Line 66-0089 Single Edge Blade, 100 per pkg | GT Midwest | TL5837 | |
| BD Luer-Lok Disposable Syringes without Needles | Fisher scientific | 14-823-2A | |
| Bonn Strabismus Scissors - ToughCut | Fine Science tools | 11103-09 | |
| Bonn Strabismus Scissors - ToughCut | Fine Science tools | 14084-09 | |
| Dumont #5 Forceps | Fine Science tools | 11251-20 | |
| Formalin solution, neutral buffered, 10% | Sigma | HT501640-19L | |
| HistoPrep 70% Ea | Fisherbran | 70% denatured ethyl alcohol | |
| ImageScope | Aperio | Version 12.3.3.5039 | http://www.leicabiosystems.com/pathology-imaging/aperio-epathology/integrate/imagescope/ |
| LeakBuster Specimen Containers: Sterile | Starplex Scientific | B120210 | |
| Phosphate-Buffere Saline, without calcium & magnesium | Corning | 21-040-CV | |
| Plastic Feeding tubes, 20 GA x 30 mm | Instech | FTP2030 | |
| PrecisionGlide Needle, Size: 20 G x 1 1/2 in | BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company) | 305176 | |
| PrecisionGlide Needle, Size: 27 G x 1/2 in | BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company) | 305109 | |
| Syringe, 10 ml | BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company) | 302995 | |
| Unisette Tissue Cassettes | Simport | M505-2 |
References
- Kagnoff, M. F. The intestinal epithelium is an integral component of a communications network. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 124 (7), 2841-2843 (2014).
- Laukoetter, M. G., Nava, P., Nusrat, A. Role of the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 14 (3), 401-407 (2008).
- Baumgart, D. C., Sandborn, W. J. Crohn's disease. Lancet. 380 (9853), 1590-1605 (2012).
- Ordas, I., Eckmann, L., Talamini, M., Baumgart, D. C., Sandborn, W. J. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 380 (9853), 1606-1619 (2012).
- Vowinkel, T., Kalogeris, T. J., Mori, M., Krieglstein, C. F., Granger, D. N. Impact of dextran sulfate sodium load on the severity of inflammation in experimental colitis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 49 (4), 556-564 (2004).
- Kitajima, S., Takuma, S., Morimoto, M. Histological analysis of murine colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium of different molecular weights. Experimental Animals. 49 (1), 9-15 (2000).
- Mahler, M., et al. Differential susceptibility of inbred mouse strains to dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. American Journal of Physiology. 274 (3), 544-551 (1998).
- Wirtz, S., Neufert, C., Weigmann, B., Neurath, M. F. Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nature Protocols. 2 (3), 541-546 (2007).
- Kozlowski, C., et al. An entirely automated method to score DSS-induced colitis in mice by digital image analysis of pathology slides. Disease Models & Mechanisms. 6 (3), 855-865 (2013).
- Perse, M., Cerar, A. Dextran sodium sulphate colitis mouse model: traps and tricks. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology. 2012, 718617 (2012).
- Mizoguchi, A. Animal models of inflammatory bowel disease. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science. 105, 263-320 (2012).
- Flemming, S., et al. Desmocollin-2 promotes intestinal mucosal repair by controlling integrin-dependent cell adhesion and migration. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 31 (6), 407-418 (2020).
- Luna, L. G. . Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (U.S) & Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (U.S.). Manual of Histologic Staining Methods of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. 3d edn. , (1968).
- Kelm, M., et al. Targeting epithelium-expressed sialyl Lewis glycans improves colonic mucosal wound healing and protects against colitis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation Insight. 5 (12), (2020).
- Reed, M., et al. Epithelial CD47 is critical for mucosal repair in the murine intestine in vivo. Nature Communications. 10 (1), 5004 (2019).
- Laukoetter, M. G., et al. JAM-A regulates permeability and inflammation in the intestine in vivo. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 204 (13), 3067-3076 (2007).
- Khounlotham, M., et al. Compromised intestinal epithelial barrier induces adaptive immune compensation that protects from colitis. Immunity. 37 (3), 563-573 (2012).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved