A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Determination of Tripartite Interaction between Two Monomers of a MADS-box Transcription Factor and a Calcium Sensor Protein by BiFC-FRET-FLIM Assay
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
Here we present, a method to visualize ternary complex formation between three protein partners using fluorescent-tagged proteins by BiFC based FRET-FLIM assay. This method is valuable for studying protein-protein interaction complexes in vivo.
Abstract
Protein-protein interactions are an integral part of all biological processes in the cells as they play a crucial role in regulating, maintaining, and amending cellular functions. These interactions are involved in a wide range of phenomena such as signal transduction, pathogen response, cell-cell interactions, metabolic and developmental processes. In the case of transcription factors, these interactions may lead to oligomerization of subunits, sequestering in specific subcellular contexts such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, etc., which, in turn, might have a more profound effect on the expression of the downstream genes. Here, we demonstrate a methodology to visualize in vivo tripartite interaction using Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) based Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) involving Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (FLIM). Two of the proteins selected for this demonstration interact as BiFC partners, and their reconstituted fluorescence activity is used to assay FRET-FLIM with the third partner. Four to five-week-old growth-chamber-grown Nicotiana benthamiana plants have been used as the model plant system for this demonstration.
Introduction
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) form the basis of the proper functioning of the eukaryotic cells by regulating various metabolic and developmental processes. Some PPIs are stable, while others are transient in nature. The interactions may be categorized based on the number and type of members in the interaction such as dimeric, trimeric, tetrameric homomeric, and heteromeric1. The identification and characterization of protein interactions may lead to a better understanding of protein functions and regulatory networks.
Transcription factors are proteins that are involved in regulatory functions. They regulate the rate of transcription of their downstream genes by binding to the DNA. Sometimes oligomerization or formation of higher-order complexes by proteins is a prerequisite for carrying out their functions2. Plant MADS-box transcription factors are homeotic genes that regulate various processes such as floral transition, floral organ development, fertilization, seed development, senescence, and vegetative development. They are known to form higher-order complexes which bind to the DNA3,4. Studying PPI networks among transcription factors and their interactors provides insights into the complexity underlying transcriptional regulation.
Transient protein expression in Nicotiana benthamiana has been a popular approach to study protein localization or protein-protein interactions in vivo5. BiFC and FRET are methods for studying protein-protein interactions in vivo using fluorescent reporter systems6. A combination of these two techniques has been shown to reveal the interaction between three proteins7. FRET is measured using acceptor photobleaching, sensitized emission, and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (FLIM) technique. FLIM-based FRET assay has emerged as a tool that provides accurate quantification and spatiotemporal specificity to energy transfer measurements between two molecules based on their fluorescence lifetimes8. FLIM measures the time a fluorophore stays in an excited state before emitting a photon and is better than techniques that use intensity measurements alone9,10. Besides heterologous systems such as Nicotiana benthamiana and onion epidermal peels, more recent reports have demonstrated the use of Arabidopsis roots and young rice seedlings, etc., for in vivo analysis of protein-protein interactions under native conditions11,12.
Other than a suitable expression system, the selection of interacting partners for BiFC and FRET assays is also crucial for the success of this experiment. The PPI among partners used in BiFC configuration should be validated using appropriate controls prior to their use as a conjugated partner in the FRET experiment13. BiFC utilizes the structural complementation of N- and C-terminal parts of the fluorescent protein. A common limitation in most if not all fluorescent proteins used in BiFC assays has been the self-assembly between the two derivative nonfluorescent fragments, contributing to false-positive fluorescence and decreases the signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio14. Recent developments, including point mutations or position of splitting the fluorescent protein, have given rise to BiFC pairs with increased intensity, higher specificity, high S/N ratio15,16. These fluorescent proteins can also be used for carrying out BiFC depending on the suitability of the experiment.
Traditionally, CFP and YFP have been used as the donor and acceptor pair in FRET experiments17. However, YFP or m-Citrine were found to be better FRET donors (when used with RFP as the acceptor) because of the high quantum yield (QY) during the native expression of target proteins in the Arabidopsis root system. The selection of promoters (constitutive versus native/endogenous) and fluorophore also play a crucial role in designing a successful BiFC-FRET-FLIM experiment. It is essential to note that the efficiency of FRET donors and suitability of FRET pairs tend to change with the change in the promoter and the biological system being used for expression. The QY of the fluorophore, which relates to its brightness, depends on the pH, temperature, and the biological system in use. We suggest that these criteria be thoroughly considered before choosing the fluorophore pair for the FRET experiment. The biological system, promoters, and the proteins used for this protocol worked well with CFP-YFP fluorophores for the BiFC FRET-FLIM experiment.
In the present study, we incorporate the feature of FLIM to visualize the interaction between three protein molecules using BiFC based FRET. In this technique, two proteins are tagged with split YFP protein and the third protein with CFP. Since we were interested in studying the interaction of a MADS-box protein (M) homodimer with a Calcium sensor protein (C), these proteins were tagged with fluorescent proteins in pSITE-1CA and pSITE-3CA vectors18. Two of the interacting partners, in this assay, were tagged with N- and C-terminal parts of the YFP in pSPYNE-35S and pSPYCE-35S vectors19, and their interaction results in the reconstitution of the functional YFP that acts as a FRET acceptor to the third interacting partner, which is tagged with CFP (acting as FRET donor) (Figure 1). In this particular case, the PPI between two M monomers and between M and C has been validated by performing BiFC in three different systems along with the yeast-two-hybrid system. These vectors were mobilized into Agrobacterium tumifaciens GV3101 strain by electroporation. The GV3101 strain has a disarmed Ti plasmid pMP90 (pTiC58DT-DNA) with gentamicin resistance20. A p19 Agrobacterium strain was added along with all infiltrations to prevent transgene silencing21. We recommend that the three proteins should also be used in opposite conformations to validate the tripartite interactions.
In this technique, we have employed FLIM, where first, the fluorescence lifetime of the donor (unquenched donor lifetime) is measured in the absence of an acceptor. After that, its lifetime is measured in the presence of the acceptor (quenched donor lifetime). This difference in donor fluorescence lifetimes is used to calculate FRET efficiency, which depends on the number of photons exhibiting a reduction in fluorescence lifetime. Mentioned below is a detailed protocol to determine the formation of a ternary complex between any three proteins by transiently expressing the fluorescent-tagged proteins in Nicotiana benthamiana and assaying their interaction by BiFC-FRET-FLIM.
Protocol
1. Cloning of genes in entry and destination vectors (Figure 2)
- Amplify the coding sequence (CDS) of the genes of interest (M and C genes in our case) by PCR and clone them in appropriate entry vectors (e.g., pENTR/D-TOPO vector; see Table 1 for vectors used in this experiment).
- Grow the clones on plates containing antibiotics. Validate clones that are selected on the antibiotics by restriction digestion and DNA sequencing22,23.
- Mobilize the reconstituted CDSs from entry clones to the destination vectors (pSPYNE-35S, pSPYCE-35S, pSITE-1CA and pSITE-3CA) and confirm the transfer of sequences from the entry to the destination vectors by restriction enzyme digestion.
NOTE: All vectors used in this experiment are listed in Table 1. - Finally, transform Agrobacterium GV3101 (pMP90 (GentR)) cells with the destination vectors by electroporation (Figure 3)24.
2. Growth conditions for Nicotiana benthamiana plants
NOTE: Grow Nicotiana plants till 4-6 leaf stage in control conditions.
- To grow Nicotiana plants, prepare the soil mix by mixing commercially available soil mixes with cocopeat and compost in a ratio of 2:1:1.
- Spread a 1-inch-thick layer of this soil mixture in a plastic tray to make the soil bed and saturate it with deionized water. Sprinkle about 200 seeds in this soil bed.
- Transfer it to a bigger tray containing 1 cm of standing water. Cover this tray with plastic wrap to create a moisture chamber.
- Transfer this set up to a growth chamber set at 23 °C with 16 h light and 8 h dark cycle with 150-170 µmol/m2s light intensity.
- After two weeks, transfer young seedlings to small, 3-4-inch pots containing water-saturated soil mix.
- Place these pots in plastic trays and transfer them to the growth chamber for four more weeks.
3. Prepare bacterial strains for agro-infiltration
NOTE: For agro-infiltration, bacterial strains need to be freshly subcultured and mixed along with p19 strain of Agrobacterium in appropriate ratios.
- Prepare 2xYT agar plates containing rifampicin (100 µg/mL), gentamicin (25 µg/mL) and kanamycin (50 µg/mL) for Agrobacterium harboring pSPYNE-35S and pSPYCE-35S vector. For pSITE vector containing strain, use rifampicin (100 µg/mL), gentamicin (25 µg/mL) and spectinomycin (50 µg/mL).
- Streak the Agrobacterium strains containing the plasmids on these plates using sterile inoculation loops in a laminar flow hood.
- Incubate these at 28 °C for 48 h in the dark.
- Start this procedure by inoculating Agrobacterium GV3101 strain harboring BiFC and FRET constructs (prepared in pSPYNE-35S, pSPYCE-35S and pSITE vectors) from streaked plates in 10 mL of 2xYT broth containing appropriate antibiotics (Rifampicin (100 µg/mL), gentamicin (25 µg/mL), kanamycin (50 µg/mL) or spectinomycin (50 µg/mL)).
- Additionally, initiate a culture of p19 strain of Agrobacteria by inoculating 10 mL of 2xYT broth containing rifampicin (100 µg/mL) and kanamycin (50 µg/mL).
NOTE: p19 strain is added to prevent transgene silencing. - Cover the flask with an aluminum foil and keep them in the incubator shaker set at 28 °C and 170 rpm for 16 h in the dark.
- After the overnight growth, transfer 1 mL of this culture to a disposable cuvette to measure the optical density (O.D.) of the cultures at 600 nm using a spectrophotometer.
- Mix the cultures of appropriate BiFC and FRET partner containing strains so that the final O.D. of each culture is 0.5 and that of p19 is 0.3 in a total volume of 2 mL.
- To achieve these ratios, use the formula mentioned below:
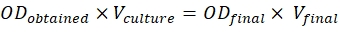
ODobtained = O.D. of the culture measured at 600 nm
Vculture = Volume of the culture required
ODfinal = 0.5 for constructs and 0.3 for p19
Vfinal = Final volume for the infiltration, which is 2 mL
NOTE: The construct combinations used in this study are specified in Table 2. - Centrifuge the mixed Agrobacterium cultures at 3,000 x g for 5 min at room temperature and carefully discard the supernatant. Resuspend the pellet in 2 mL of freshly prepared infiltration buffer (10 mM MES, 100 µM of Acetosyringone, and 10 mM MgCl2). Use a vortex mixer to make a homogenous cell suspension.
- Incubate the tubes containing resuspended cells in the dark at room temperature for 3 h.
- Meanwhile, label each plant pot with the construct mixture it is going to be infiltrated with. Use two plants for each infiltration mixture.
- Fill a 1 mL needleless syringe with the agrobacterial mix. Gently but firmly press the syringe onto the abaxial side of the fully expanded leaf while supporting the leaf from the other side. Gently push the plunger till the solutions fill up in the leaf area equivalent to 2-3 times the syringe tip.
- Infiltrate up to four spots on a leaf and 3-4 leaves per plant, as shown in Figure 4.
NOTE: Change gloves or wipe gloves with 70% alcohol between samples to prevent cross-contamination. - Transfer all the pots to a tray and incubate in a growth chamber under the same conditions as mentioned in step 2.
- Check a small part of the agroinfiltrated leaf at different time points using a fluorescence microscope. When the fluorescence from both YFP and CFP are detectable in cells, proceed to the confocal microscope for BiFC-FRET FLIM assay. In this experiment, the analysis was carried out 3 days after agro-infiltration.
NOTE: Set the post-agroinfiltration period of incubation individually for every promoter and gene combination to avoid overexpression of chimeric proteins used in the BiFC-FRET FLIM assay. The overexpression of the partner proteins may lead to false-positive interactions.
4. Prepare slides for fluorescence visualization
- When plants are ready for visualization, cut square leaf samples, 5-8 mm away from the infiltration wound, and mount them in distilled water on clean slides.
NOTE: To minimize background fluorescence, clean the slides with 80% ethanol followed by distilled water 3-4 times, air dry them, and keep them on an absorbent sheet. - Cover the leaf sample with a clean coverslip and seal using a nail enamel.
- Visualize these samples under a confocal laser scanning microscope.
5. FRET-FLIM analysis using a confocal laser scanning microscope
NOTE: In this procedure, the basis of determining and quantifying interaction between two proteins is the reduction in fluorescence lifetime of the FRET-donor partner upon its interaction with the acceptor, which is used to calculate the efficiency of FRET. The complexity in the case of tripartite interaction increases further because the FRET-acceptor, in this case, is not a single molecule but a split YFP-BiFC pair, which should first get reconstituted in vivo to become a functional FRET-acceptor fluorophore. To carry out FRET-FLIM, one needs to determine the donor molecule's fluorescence lifetime-first alone and then in the presence of a FRET partner.
- Open the FLIM application in the confocal laser scanning microscope, start the console and use pattern-recognition photon-counting to measure fluorescence lifetime. Select the standard 'All photon counting' measurement mode.
- Analyze samples from two types of agro-infiltrated plants: one with the donor only (C-CFP) and the other with the donor and the acceptor (C-CFP, along with M-YFP) both.
NOTE: Because the interaction of M protein has already been validated with C protein using BiFC and Y2H, good FRET efficiency is expected with this interacting pair. - Next, scan the C-CFP agro-infiltrated leaf and focus on a cell showing good CFP fluorescence. Initiate the laser scanning mode and set the system for CFP visualization and FLIM measurements (λex 440 nm pulse laser, λem 480-520 nm by hybrid detectors, Scan speed 512 x 512 pixels at 400 Hz).
- Adjust the focus, zoom, and smart gain to focus on the area that needs to be captured.
- Illuminate the sample at sufficient laser power to achieve the capture of approximately 0.1 photons per pulse. For samples with variable fluorescence intensity, capture 50 frames to collect adequate photons required for the lifetime measurement. CFP exhibits two fluorescence lifetimes due to its conformational adaptation; therefore, fit the data using the n-exponential reconvolution model while keeping the value of n equal to 2.
- At these settings, the CFP shows two lifetimes of 1.0 and 3.2 ns. Here the higher, 3.2 ns, lifetime is used for all subsequent calculations25,26.
- To calculate FRET efficiency using FLIM, which is the measure of the degree of interaction between two proteins, take a leaf sample that has been co-infiltrated with C-CFP and M-YFP. Look for a cell that expresses both C-CFP and M-YFP and confirm their respective emission patterns by exciting them using λex 440 nm pulse laser, λem 480-520 nm and λex 514 nm white light laser with λem 526-550 nm. Sequentially scan and identify a cell that shows both CFP and YFP fluorescence.
- After confirming the fluorescence from both the proteins, switch to the FLIM console to measure the lifetime of CFP using the same settings that we used earlier for measuring the lifetime of C-CFP (step 5.5).
NOTE: This cell is also expressing M-YFP that can potentially interact with C-CFP and cause a reduction in the lifetime of C-CFP. - Fit the graph obtained using the n-exponential reconvolution model, with n = 2. A decrease in the CFP lifetime from 3.2 to 2.6 ns was observed, indicating Förster resonance energy transfer between CFP and YFP (Figure 5A).
- Now start the FRET console in the software and calculate the FRET efficiency by manually entering unquenched donor lifetime in the equation provided in the software. And the observed FRET efficiency is: 56%.
- Tripartite interaction
- Finally, to visualize the interactions between three partners, take the leaf sample from a plant that was co-infiltrated with C-CFP, M-YFPn, and M-YFPc.
- Scan the leaf explant for a cell that shows both CFP and reconstituted YFP fluorescence emanating from BiFC interaction between two M proteins. Use the same laser and emission wavelengths as used earlier.
- Subsequently, switch off the 514 nm laser and move to the FLIM console.
NOTE: If the M-YFP dimer interacts with C-CFP, one should see a reduction in the lifetime of C-CFP as observed during its interaction with M-YFP. However, if the C-CFP fails to interact with the M-YFP dimer, its fluorescence lifetime should stay at 3.2 ns. - Using similar settings as mentioned above, measure the CFP lifetime in the presence of reconstituted YFP. Fit the graph obtained using the n-exponential reconvolution model, with n = 2, and move to the FRET console.
NOTE: There is a decline in the CFP lifetime from 3.2 to 2.3 ns. Calculate the FRET efficiency as described above. The calculated FRET efficiency is 55%. The reduction in donor lifetime and good FRET efficiency of 55% confirms tripartite interaction between two M proteins and the C protein in vivo (see Figure 5B).
Results
This protocol represents an optimized method to study in vivo tripartite protein-protein interactions in plants. The basic principle of the protocol is to combine two fluorescence-tagged protein-interaction techniques, i.e., BiFC and FRET, to create an assay to measure ternary complex formation between three protein partners. Here, we have used FLIM to measure the fluorescence lifetime of the FRET donor partner in the presence and absence of the FRET acceptor. A reduction in the fluorescence lifetime of the dono...
Discussion
The present protocol demonstrates the use of BiFC-based FRET-FLIM assay to ascertain the formation of a ternary complex between two monomers of a MADS-box protein and a calcium sensor protein. The protocol is adapted from a report by Y. John Shyu et al. where they have developed a BiFC-based FRET method to visualize ternary complex formed between Fos-Jun heterodimers and NFAT or p65 using the sensitized emission method7. Earlier, a three-fluorophore FRET system was developed by Galperin and co-wor...
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
NB, GG, SB, KC sincerely thank the University Grants Commission (UGC), UGC-BSR, DBT-INSPIRE, and Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for their research fellowships. We thankfully acknowledge the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India, the Department of Science and Technology (DST-FIST), Government of India for financial support.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1 ml Syringes without needles | Dispovan | - | |
| Acetosyringone | Sigma-Aldrich | D134406 | |
| Gateway LR Clonase II Enzyme mix | Thermo Fischer Scientific | 11791020 | The vectors used in the study are Gateway based |
| Gentamycin Sulphate | Himedia | CMS461 | |
| Kanamycin Sulphate | Himedia | MB105 | |
| MES hydrate | Sigma-Aldrich | M2933 | |
| MgCl2 | Sigma-Aldrich | M2670 | |
| pENTR/D-TOPO Cloning Kit | Thermo Fischer Scientific | K240020 | The vectors used in the study are Gateway based |
| Phusion high fidelity Taq DNA polymerase | Thermo Fischer Scientific | F530-S | Any High fidelity Polymerase can work |
| Rifampicin | Himedia | CMS1889 | |
| SP8 FALCON Confocal laser scanning microscope | Leica | SP8 FALCON | Any CLSM with FLIM capabilities can be used for this analysis |
| Spectinomycin dihydrochloride pentahydrate | Himedia | TC034 |
References
- Grove, C. A., Walhout, A. J. M. Transcription factor functionality and transcription regulatory networks. Molecular Biosystem. (4), 309-314 (2008).
- Amoutzias, G. D., Robertson, D. L., Van de Peer, Y., Oliver, S. G. Choose your partners: dimerization in eukaryotic transcription factors. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 33 (5), 220-229 (2008).
- Arora, R., et al. MADS-box gene family in rice: genome-wide identification, organization and expression profiling during reproductive development and stress. BMC Genomics. 8 (242), (2007).
- Theißen, G., Gramzow, L. Structure and evolution of plant MADS domain transcription factors. Plant Transcription Factors: Evolutionary, Structural and Functional Aspects. , 127-138 (2016).
- Schweiger, R., Schwenkert, S. Protein-protein interactions visualized by bimolecular fluorescence complementation in tobacco protoplasts and leaves. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (85), (2014).
- Bracha-Drori, K., et al. Detection of protein-protein interactions in plants using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Plant Journal. 40 (3), 419-427 (2004).
- Shyu, Y. J., Suarez, C. D., Hu, C. Visualization of ternary complexes in living cells by using a BiFC-based FRET assay. Nature Protocols. 3 (11), 1693-1702 (2008).
- Kwaaitaal, M., Keinath, N. F., Pajonk, S., Biskup, C., Panstruga, R. Combined bimolecular fluorescence complementation and förster resonance energy transfer reveals ternary SNARE complex formation in living plant cells. Plant Physiology. 152 (3), 1135-1147 (2010).
- Margineanu, A., et al. Screening for protein-protein interactions using Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM). Scientific Reports. 6, (2016).
- Datta, R., Heaster, T. M., Sharick, J. T., Gillette, A. A., Skala, M. C. Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy: fundamentals and advances in instrumentation, analysis, and applications. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 25 (07), 1 (2020).
- Long, Y., et al. Optimizing FRET-FLIM labeling conditions to detect nuclear protein interactions at native expression levels in living Arabidopsis roots. Frontiers in Plant Science. 9, 1-13 (2018).
- Burman, N., Chandran, D., Khurana, J. P. A Rapid and highly efficient method for transient gene expression in rice plants. Frontiers in Plant Science. , 11 (2020).
- Kudla, J., Bock, R. Lighting the way to protein-protein interactions: Recommendations on best practices for bimolecular fluorescence complementation analyses. Plant Cell. 28 (5), 1002-1008 (2016).
- Shyu, Y. J., Hu, C. D. Fluorescence complementation: an emerging tool for biological research. Trends in Biotechnology. 26 (11), 622-630 (2008).
- Kodama, Y., Hu, C. D. An improved bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay with a high signal-to-noise ratio. BioTechniques. 49 (5), 793-803 (2010).
- Kodama, Y., Hu, C. D. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC): A 5-year update and future perspectives. BioTechniques. 53 (5), 285-298 (2012).
- Piston, D. W., Kremers, G. J. Fluorescent protein FRET: the good, the bad and the ugly. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 32 (9), 407-414 (2007).
- Chakrabarty, R., et al. pSITE vectors for stable integration or transient expression of autofluorescent protein fusions in plants: Probing Nicotiana benthamiana- Virus Interactions. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions. 20 (7), 740-750 (2007).
- Walter, M., et al. Visualization of protein interactions in living plant cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Plant Journal. 40 (3), 428-438 (2004).
- Hellens, R., Mullineaux, P., Klee, H. A guide to Agrobacterium binary Ti vectors. Trends in Plant Science. 5 (10), 446-451 (2000).
- Van Der Hoorn, R. A. L., Rivas, S., Wulff, B. B. H., Jones, J. D. G., Joosten, M. H. A. J. Rapid migration in gel filtration of the Cf-4 and Cf-9 resistance proteins is an intrinsic property of Cf proteins and not because of their association with high-molecular-weight proteins. Plant Journal. 35 (3), 305-315 (2003).
- Xie, X., et al. Engineering SARS-CoV-2 using a reverse genetic system. Nature Protocols. 16, (2021).
- Xu, J., et al. Optimized plasmid construction strategy for Cas9. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 48, 131-137 (2018).
- Mattanovich, D., et al. Efficient transformation of Agrobacterium spp. by electroporation. Nucleic Acids Research. 17 (16), 6747 (1989).
- Rizzo, M. A., Springer, G. H., Granada, B., Piston, D. W. An improved cyan fluorescent protein variant useful for FRET. Nature Biotechnology. 22 (4), 445-449 (2004).
- Tramier, M., et al. Picosecond-hetero-FRET microscopy to probe protein-protein interactions in live cells. Biophysical Journal. 83 (6), 3570-3577 (2002).
- Alvarez, L. A. J., et al. SP8 FALCON: a novel concept in fluorescence lifetime imaging enabling video-rate confocal FLIM. Nature Methods. 20, 2-4 (2019).
- Postma, M., Goedhart, J. Plotsofdata-a web app for visualizing data together with their summaries. PLoS Biology. 17 (3), 1-8 (2019).
- Galperin, E., Verkhusha, V. V., Sorkin, A. Three-chromophore fret microscopy to analyze multiprotein interactions in living cells. Nature Methods. 1 (3), 209-217 (2004).
- Waadt, R., Kudla, J. In plant visualization of protein interactions using bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC). Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 3 (4), (2008).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved